Degradation of plastic micro-beads in wastewater by ultrasonic iron-nitrogen doped titanium dioxide
A technology of titanium dioxide and iron nitrogen, which is applied in the field of photocatalyst preparation and wastewater treatment, can solve the problems of low light source utilization rate, difficult recycling, high photocatalyst density, etc., to overcome low light source utilization rate, improve photocatalytic performance, improve photocatalytic The effect of catalytic performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0034] The invention provides a kind of preparation method of photocatalyst, comprises the steps:
[0035] S1, slowly drop tetrabutyl titanate into absolute ethanol, stir well to make it evenly mixed, then add a predetermined amount of acetic acid and stir to prepare a titanium dioxide precursor solution;
[0036] S2, add ferric nitrate and carbonamide into absolute ethanol according to a predetermined ratio, add a predetermined amount of water, stir until fully dissolved, and prepare an iron-nitrogen precursor solution;
[0037] S3, slowly drop the iron-nitrogen precursor solution prepared in step S2 into the titanium dioxide precursor solution prepared in step S1, adjust the pH value to 3-4, stir for 30-40min, prepare a mixed solution, and The mixed solution is transferred into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, a predetermined amount of water is added, supplemented by ultrasonic treatment, and the hydrothermal reaction is carried out at 150-170°C for 8-24 hours;
[0038] S4. Af...
Embodiment 1
[0051] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a kind of preparation method of photocatalyst, comprises the following steps:
[0052] S1, slowly drop 20mL of tetrabutyl titanate into 50mL of absolute ethanol, stir well to make it evenly mixed, then add 10mL of acetic acid and stir to prepare a titanium dioxide precursor solution;
[0053] S2, add ferric nitrate and carbonamide with a molar mass ratio of 1:1 to 30mL of absolute ethanol, add 10mL of water, stir until fully dissolved, and prepare an iron-nitrogen precursor solution; wherein, the molar mass of iron and nitrogen The ratio of the molar mass to the molar mass of titanium is 2: 4: 100;
[0054] S3, slowly drop the iron-nitrogen precursor solution prepared in step S2 into the titanium dioxide precursor solution prepared in step S1, adjust the pH value to 3-4, stir for 30-40min, prepare a mixed solution, and The mixed solution was transferred into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, 20mL of water was added, suppleme...
Embodiment 2-5
[0078] The difference from Example 1 lies in that the photocatalyst preparation process parameters are set differently, and the others are the same as in Example 1, which will not be repeated here.
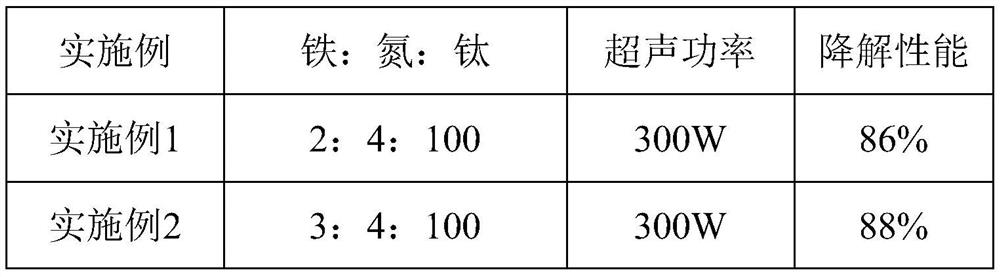
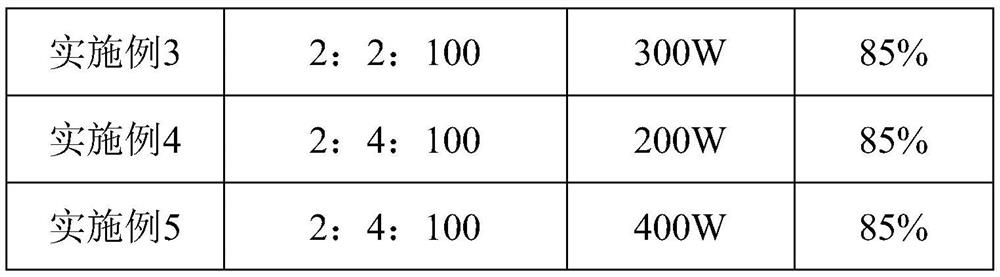
[0079] Table 2 is the process parameter setting and performance parameter thereof of embodiment 1-6
[0080]
[0081]
[0082] The examples 1-5 were analyzed in conjunction with Table 2: It can be seen from Table 2 that the doping amount of iron and nitrogen and the change of ultrasonic power have a certain influence on the degradation performance of the photocatalyst.
[0083] In the present invention, the molar mass ratio of iron, nitrogen and titanium is preferably 2:4:100; the ultrasonic power is preferably 300W.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com