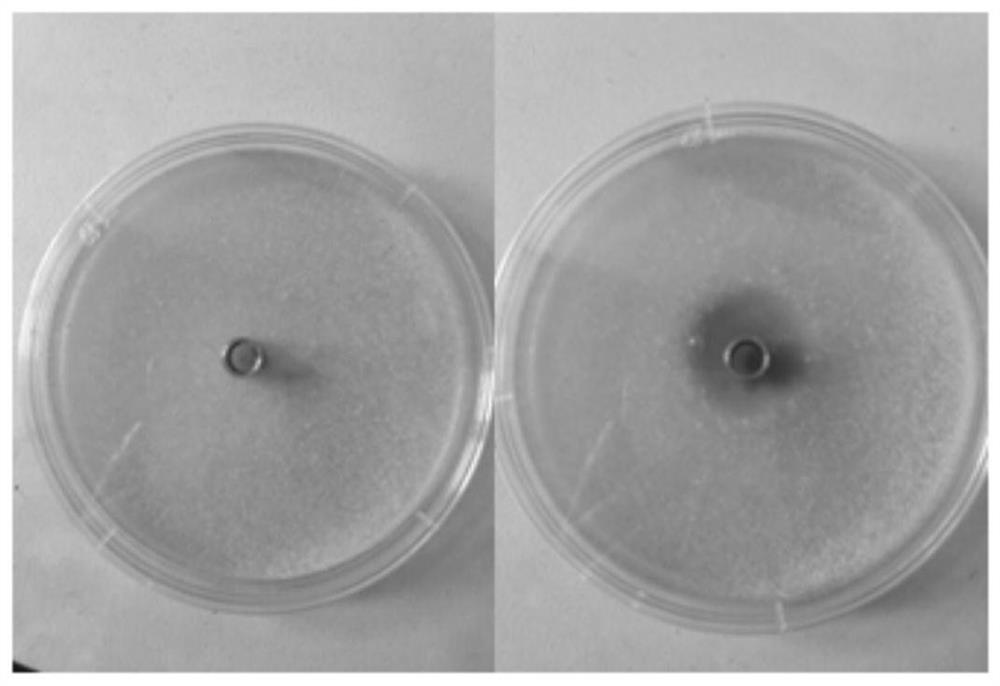
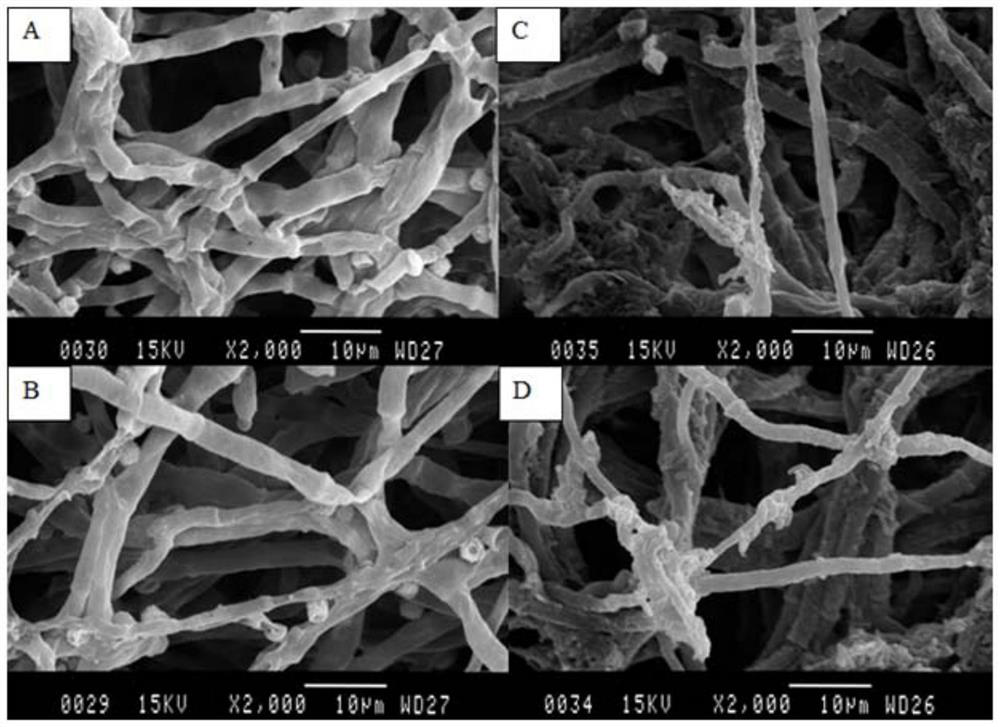
Application of antibacterial lipopeptide fengycin in inhibiting the growth and toxin synthesis of Aspergillus flavus
An antimicrobial lipopeptide and Aspergillus flavus technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problem that there are no marine microorganisms to inhibit Aspergillus flavus, and achieve the effect of inhibiting the biosynthesis of aflatoxin and inhibiting spore germination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Isolation of marine microorganisms
[0031] The retrieved marine samples were treated as follows: seaweed, seaweed and other marine organisms were fully washed with sterile normal saline, then cut into pieces with sterile equipment and then diluted; marine fish were first fully washed with sterile normal saline, and then washed with sterile Dissect the sterilized utensils, take their intestinal tract and body surface respectively, add 50mL of sterile seawater to each, vortex shaker for 1min, let it stand until clarified, take 3mL of the supernatant and dilute it in 30mL of sterile normal saline ; Sediment was diluted with sterile normal saline at a ratio of 1:10 (V / V) to make a suspension; seawater was directly diluted with sterile normal saline at a ratio of 1:10 (V / V). Pipette 100 μL of the diluted fish intestine, fish body, sediment, seawater, and seaweed 5 groups of sample solutions and spread them on Gaoshi No. 1, beef extract peptone, MRS, and PDA medium plates. ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Culture of marine Bacillus megaterium
[0047] Pick a ring from the fresh Bacillus megaterium slant and inoculate it into the seed medium (100mL / 250mL), culture it on a shaker at 160r / min at 36°C for 18-22h, and then insert the inoculation amount into the foundation Fermentation medium (100mL / 250mL) was shaken for 72 hours under the same culture conditions as above.
[0048] Among them, regarding the fermentation medium: the Plackett-Burman design method was used to screen the main influencing factors affecting the target product, and it was found that glucose (P=0.0004) had a positive effect on the production of antimicrobial lipopeptides, with a large degree of influence, and it was the most important factor in the fermentation medium. sole carbon source. However, due to the excessive addition of glucose, it is easy to cause the fermented product to be too viscous, which is not conducive to the separation and purification of bacterial cells and antibacterial substanc...
Embodiment 3
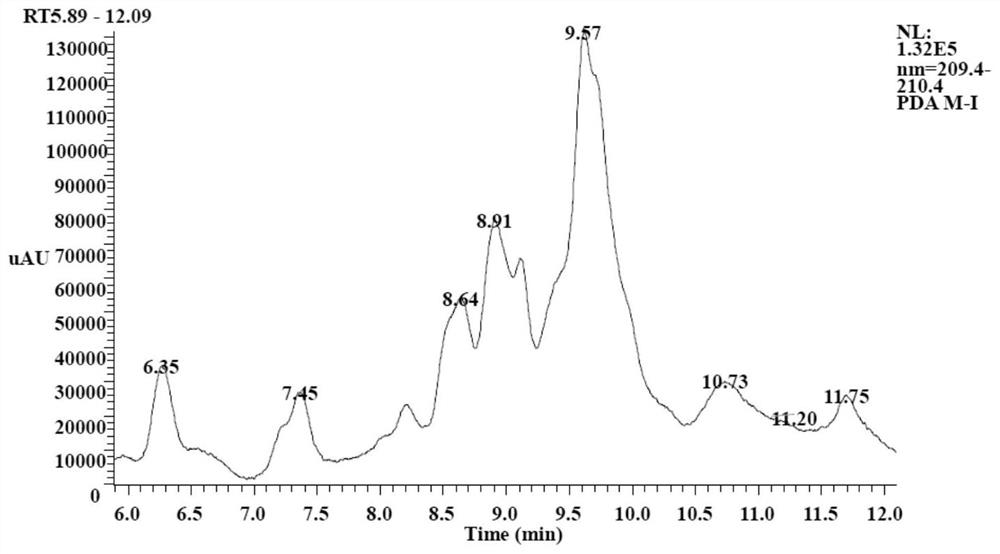
[0053] Purification of lipopeptides (two-step ultrafiltration method)
[0054] The lipopeptide aqueous solution was passed through a 0.22 μm cellulose acetate filter membrane (PALL Gelman Laboratory, New York, USA) to remove tiny impurities, and a polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane separation device with a molecular weight cut-off of 30 kDa was selected to preliminarily purify the lipopeptide by a two-step ultrafiltration method antibiotic. Specifically:
[0055] In the first step, the ultrafiltration membrane separation device is used to intercept macromolecular substances such as lipopeptide micelles and macromolecular miscellaneous proteins with a molecular weight exceeding 30 kDa and collect the intercepted products. Gently remove the retentate with a 200 μL pipette, dissolve it with Milli-Q water and add a certain amount of chromatographic grade methanol to disperse the lipopeptide micelles into monomers, adjust the pH of the solution to 7.0 with 1.0M NaOH and coo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com