Composite guided tissue regeneration membrane and preparation method thereof
A technology that guides tissue regeneration and magnesium alloys, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as increasing patient pain and cost, affecting bone tissue regeneration, and affecting mechanical properties, and achieves simple and easy preparation methods, promotion of growth and repair, and easy promotion and apply the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0051] The invention provides a method for preparing a composite guided tissue regeneration membrane, which comprises:
[0052] The upper matrix layer, the magnesium alloy film and the lower matrix layer are arranged sequentially from top to bottom, and then a composite guided tissue regeneration membrane is prepared by freeze-drying-vacuum lamination.
[0053] In a preferred embodiment of the application of the present invention, the vacuum degree is 0.05-0.5 Pa and the temperature is -40--10°C when the above-mentioned vacuum drying is carried out by the freeze-drying-vacuum lamination method. Optionally, the vacuum degree during vacuum drying is 0.1-0.5Pa, and the temperature is -30--20°C; optionally, the vacuum degree during vacuum drying is 0.1-0.2Pa, and the temperature is -20°C.
[0054] In one embodiment, the vacuum drying time is 20-50 hours. Optionally, the vacuum drying time is 24-48h.
[0055] In one embodiment, after vacuum drying, the dried film is vacuum compac...
Embodiment 1
[0080] This embodiment provides a composite guiding tissue regeneration membrane and a preparation method thereof. The composite guiding tissue regeneration membrane is composed of an upper matrix layer, a magnesium alloy membrane and a lower matrix layer arranged in sequence from top to bottom.
[0081] First, the acellular small intestinal submucosa matrix material is prepared, and in other embodiments, a commercially available acellular small intestinal submucosa matrix material can also be selected. The preparation method of the decellularized small intestine submucosa matrix material in this example comprises the following steps:
[0082] 1) Obtain fresh Changbai pig jejunum from the slaughterhouse, rinse out the contents, and freeze and preserve;
[0083] 2) Mechanically peel off the mucous membrane layer, muscular layer and serosa layer on the jejunum, and rinse it;
[0084] 3) Using 0.5% peracetic acid solution to sterilize the small intestine;
[0085] 4) Using eth...
experiment example 1
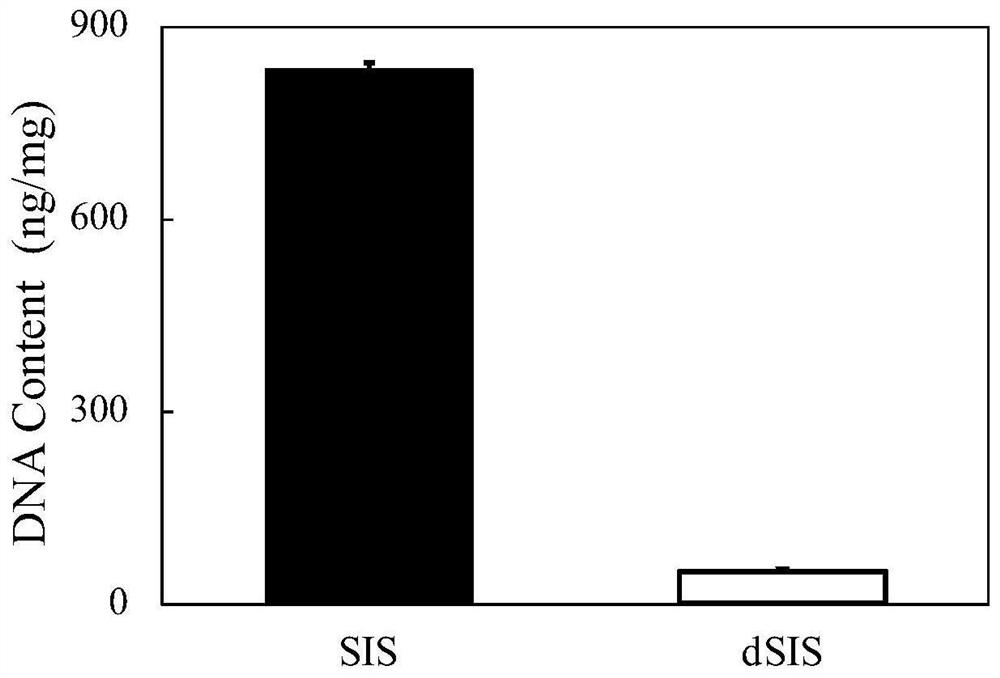
[0095] This experimental example refers to the standard of "YY / T 0606.25-2014 Tissue Engineering Medical Products Part 25 Determination of DNA Residues in Animal-derived Biomaterials: Fluorescent Staining Method". Quantitative detection was carried out, and the results were as follows figure 1 As shown, the DNA content in SIS before decellularization was 835.73±9.65ng / mg, and the DNA content after decellularization (dSIS) was 52.50±1.23ng / mg.
[0096] The results show that the decellularization process can obviously remove the immune antigenic substances in SIS, thereby improving the biosafety performance of SIS.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com