Aqueous zinc ion battery positive electrode material, preparation method thereof and aqueous zinc ion battery
A technology of zinc ion battery and positive electrode material, applied in battery electrodes, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, positive electrode, etc. Battery system stability and other issues, to achieve the effect of increasing conductivity, less side reactions, and high specific capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0042] According to the method for preparing the positive electrode material of the aqueous zinc ion battery according to the embodiment of the present invention, firstly, the manganese carbonate and the carbon source solution are mixed and dried to obtain the mixed dry powder, and then the above-mentioned MnO with good stability and high specific capacity can be obtained by sintering Aqueous zinc ion cathode material with / C structure. The preparation method has low raw material cost and simple preparation process, and can be used for large-scale industrial production, and the prepared aqueous zinc ion battery has good electrochemical performance, high specific capacity and good cycle performance. It should be noted that the features and advantages described above for the positive electrode material of the aqueous zinc ion battery are also applicable to the method for preparing the positive electrode material of the aqueous zinc ion battery, and will not be repeated here.
[...
Embodiment 1
[0046] 1. Preparation of MnO / C
[0047] (1) Mix manganese sulfate and sodium carbonate solutions of the same concentration at a molar ratio of 1:1, stir magnetically for 2 hours, wash 5 times with deionized water, and dry at 80°C to obtain MnCO 3 Precursor, the secondary particle size is about 5 μm;
[0048] (2) dissolving sucrose in a mixed solution containing ethanol and water at a volume ratio of 1:1, and configuring it as a 5wt% sucrose solution;
[0049] (3) MnCO 3 Stir and mix the precursor material and sucrose solution evenly, and put them in an oven at 80°C for drying;
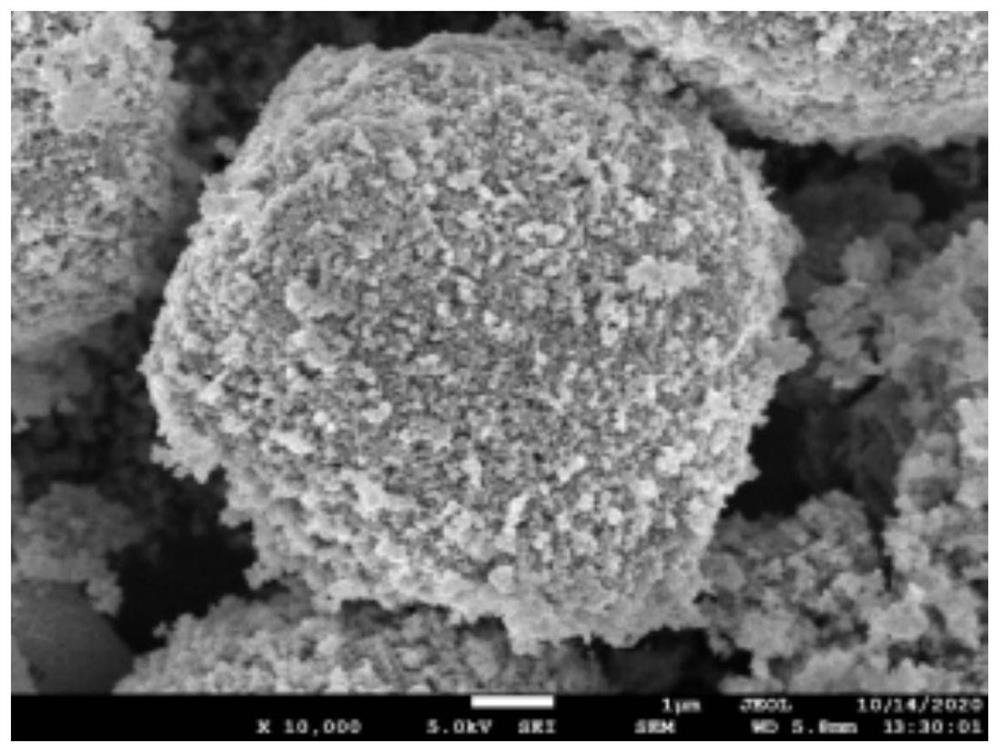
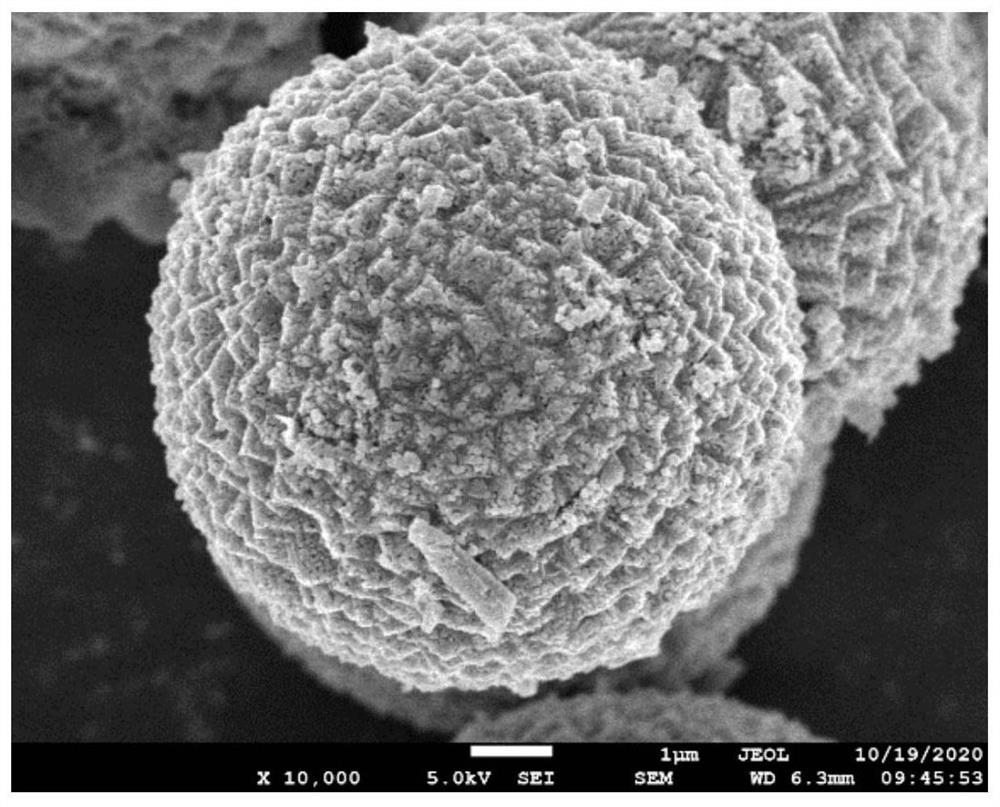
[0050] (4) Put the material in step (3) in a tube furnace, calcined in a nitrogen atmosphere, and calcined at 600°C for 1 hour to obtain MnO / C, whose scanning electron microscope shows figure 2 As shown, the core particle size of MnO / C is 6 μm, the thickness of the cladding layer is 20 nm, and the molar ratio of MnO to carbon is 100:2.
[0051] 2. Preparation of MnO / C-Zn aqueous battery
[0052] ...
Embodiment 2
[0059] 1. Preparation of MnO / C
[0060] The concentration of the sucrose solution was changed from 5wt% to 1wt%, the calcination temperature was changed from 600°C to 650°C, and the others were the same as in Example 1, the inner particle diameter of the obtained MnO / C was 6.5 μm, and the thickness of the coating layer was 2nm. And the molar ratio of MnO to carbon is 100:0.45.
[0061] 2. The method for preparing the MnO / C-Zn aqueous battery is the same as that in Example 1.
[0062] 3. Electrical performance test
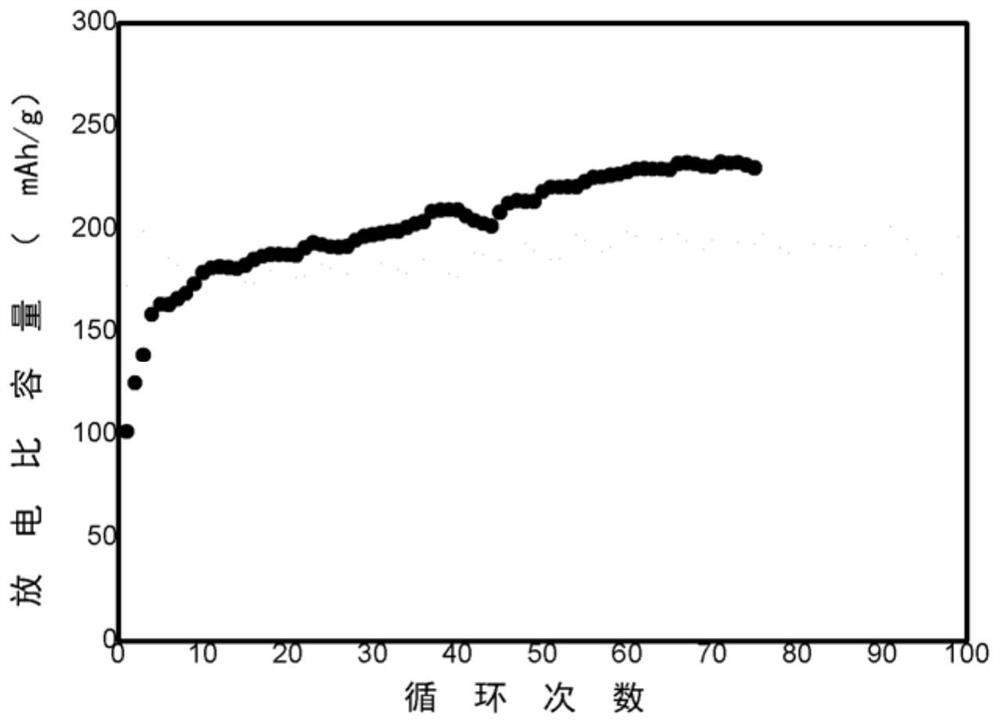
[0063] Electrical performance: The initial specific capacity is 162mAh / g. As the cycle progresses, the specific capacity continues to rise, and the capacity reaches the highest after 75 cycles, which is 192mAh / g.
[0064] Conclusion: The reduction of carbon source content leads to a thinner carbon-containing protective layer of MnO / C, therefore, the specific capacity decreases.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com