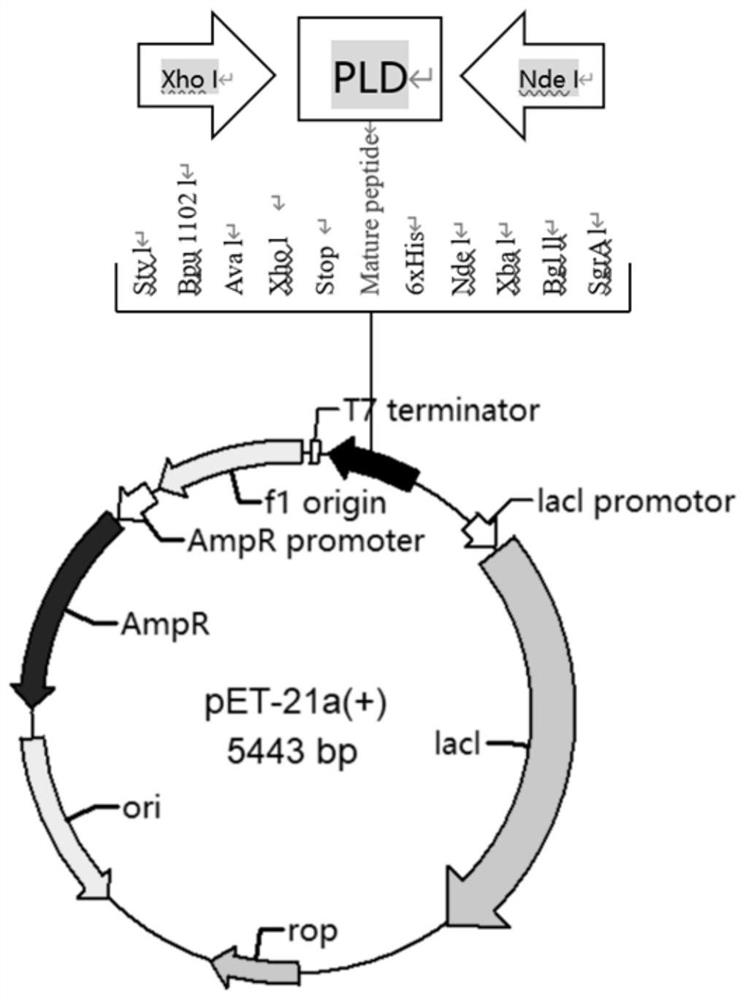
Low-temperature-resistant phospholipase D derived from Antarctic bacteria and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of Antarctic bacteria and phospholipase, which is applied in the field of enzyme genetic engineering, can solve the problems of limiting the large-scale preparation of phospholipase D, low enzyme activity, and high price, and achieve good enzyme activity, storage stability, and high expression. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
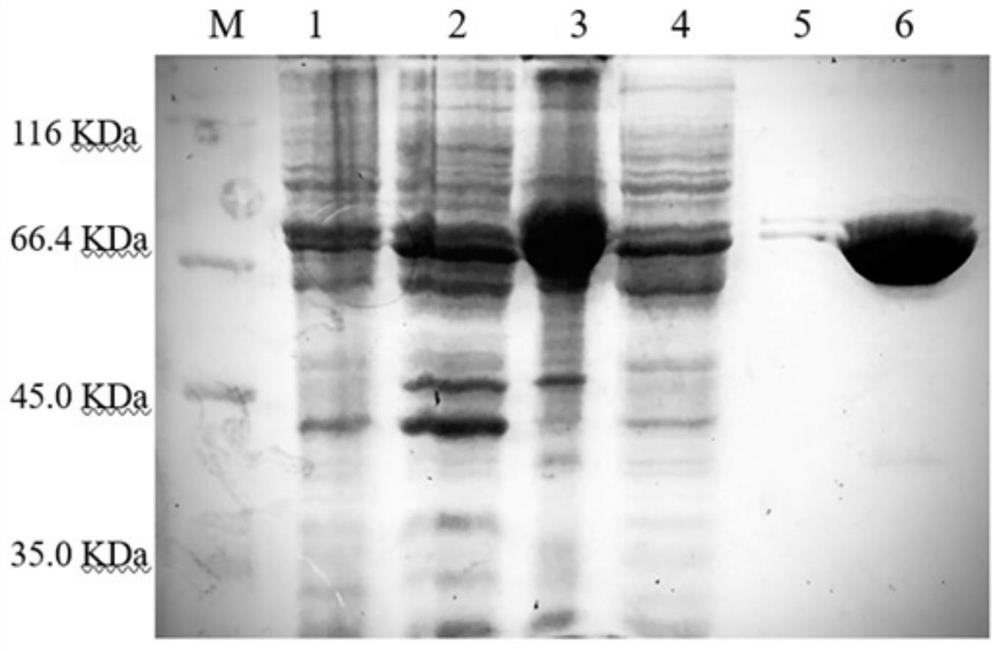
[0041] Recombinant expression and purification of MsPLD
[0042] Transform the constructed MsPLD recombinant expression plasmid into Escherichia coli SHuffle T7 competent cells by heat shock, smear the plate to obtain the recombinant, pick a single colony to culture and extract the plasmid, and send it to Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. for sequencing verification If the sequencing is correct, the MsPLD recombinant expression strain will be obtained. Inoculate the recombinant strain in LB (containing 100 μg / mL Amp) liquid medium, cultivate overnight at 37°C, expand to 100mL LB medium according to the inoculum size of 5%, when the culture solution OD 600nmWhen = 0.8, add isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) to a final concentration of 0.2mM, induce at 16-20°C for 20h, centrifuge at 10000rpm for 5min, and collect the bacteria. Cells were obtained and resuspended in buffer A (50 mM Tris-HCl, 500 mM NaCl, pH 8.0) and sonicated. After crushing, the lysate was c...
Embodiment 2
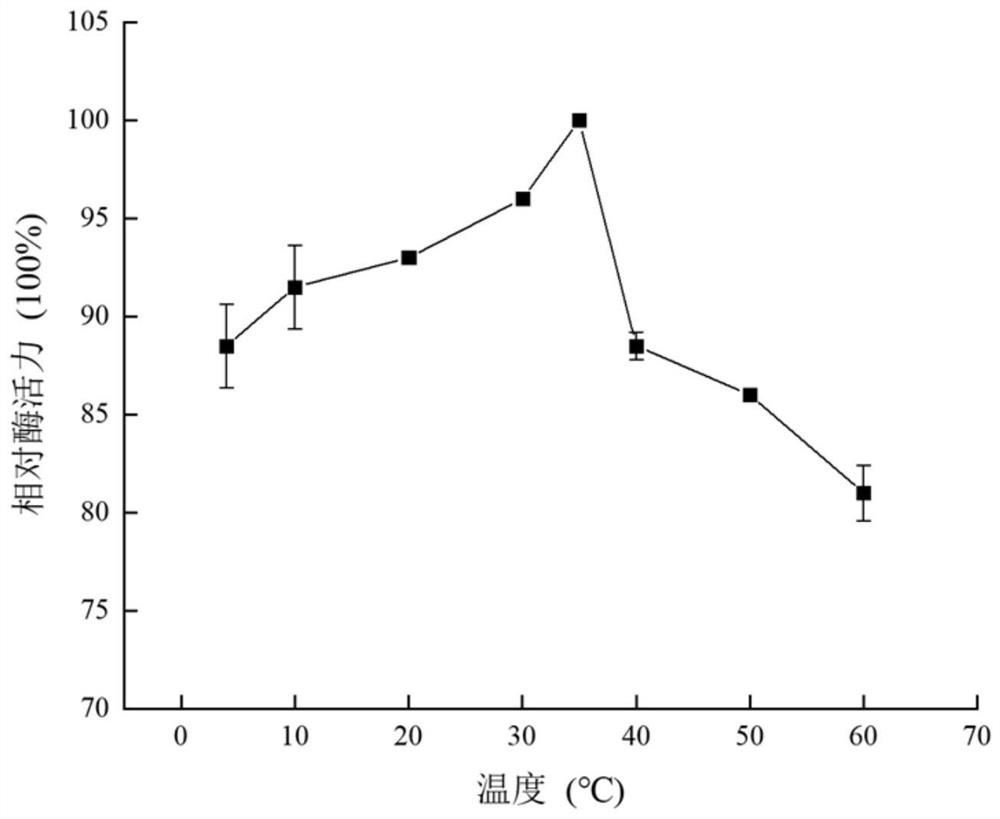
[0044] Optimum Reaction Temperature and Temperature Stability of Phospholipase D
[0045] In order to explore the effect of different temperature conditions on the activity of MsPLD enzyme, at different temperatures (4°C, 10°C, 20°C, 30°C, 35°C, 40°C, 50°C, 60°C), the enzyme-linked colorimetric assay its enzyme activity. The reaction system (100 μL) contains 0.1MTris-HCl (pH8.0), 5mM soyPC, 15mM SDS, 15mM Tritonx-100 and 10μL purified enzyme solution, react at each temperature for 5min, heat to terminate the reaction, after the solution is cooled, Add a chromogenic solution containing 10U / mL choline oxidase, 1U / mL peroxidase, 5mM 4-aminoantiline and 7mM phenol, incubate at 30°C for 30min, and finally add 1% TrionX-100 to terminate the color reaction. Absorbance was measured at 490 nm. The experiment was repeated three times, and the experimental results were expressed by relative enzyme activity, and the maximum enzyme activity measured was set as 100%. The results showed t...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Optimum pH and pH Stability
[0050] In order to explore the effect of pH on the enzyme activity of MsPLD, the enzyme activity of MsPLD was determined by enzyme-linked colorimetry under different pH conditions (pH4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0, 9.0, 10.0). Refer to Example 2 for the enzyme activity assay reaction system and reaction conditions. Buffers of various pHs used were: 50 mM citrate (pH 4.0-5.0), 50 mM sodium phosphate (pH 6.0-7.0), 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) and 50 mM glycine-NaOH (pH 9.0-10.0). The experiment was repeated three times, and the experimental results were expressed by relative enzyme activity, and the maximum enzyme activity measured was set as 100%. The results show that the optimum pH of MsPLD is 8.0 (see Figure 6 ).
[0051] In order to evaluate the pH stability of MsPLD, it was treated for 12 hours under the conditions of different pH values (pH4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0, 9.0, 10.0), and the residual enzyme activity of MsPLD was determined. The enzy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com