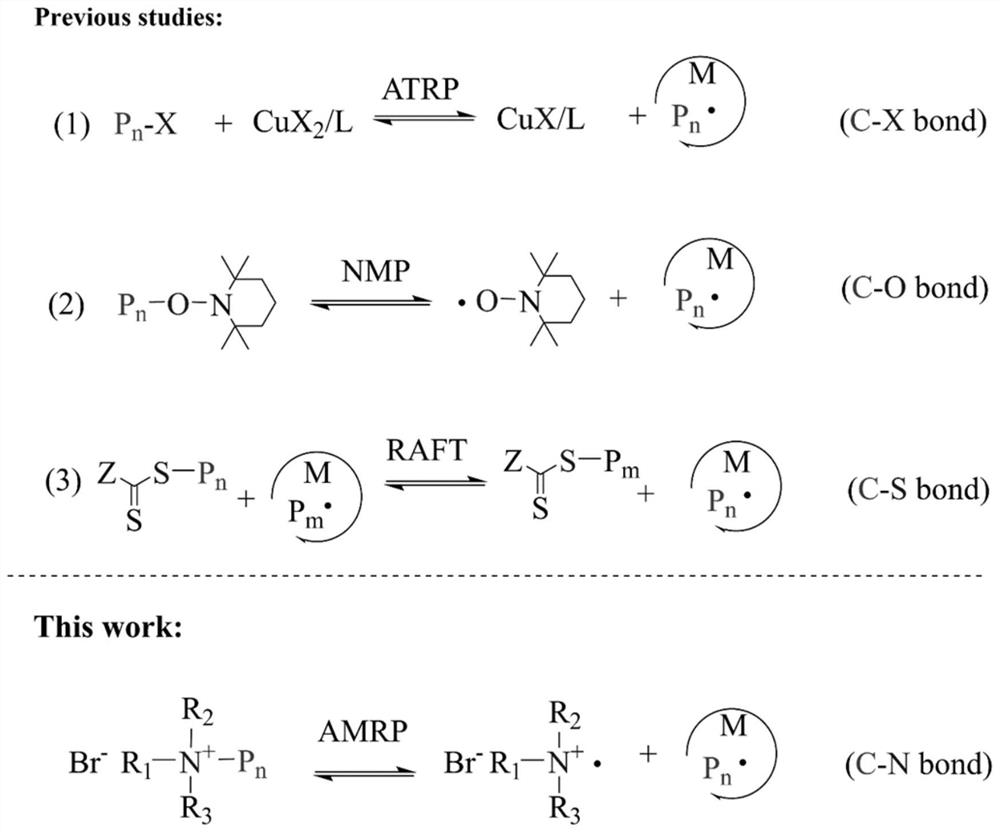
A Controlled Radical Polymerization Method Based on C-N Bond Breakage
A polymerization method and free radical technology, applied in the field of reversible deactivation free radical polymerization catalysis, to achieve the effect of simple and easy operation of equipment, low cost and mild catalytic conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1: synthetic quaternary ammonium salt catalyst
[0037] The present embodiment provides a kind of synthetic method of quaternary ammonium salt catalyst, specifically comprises the following steps:
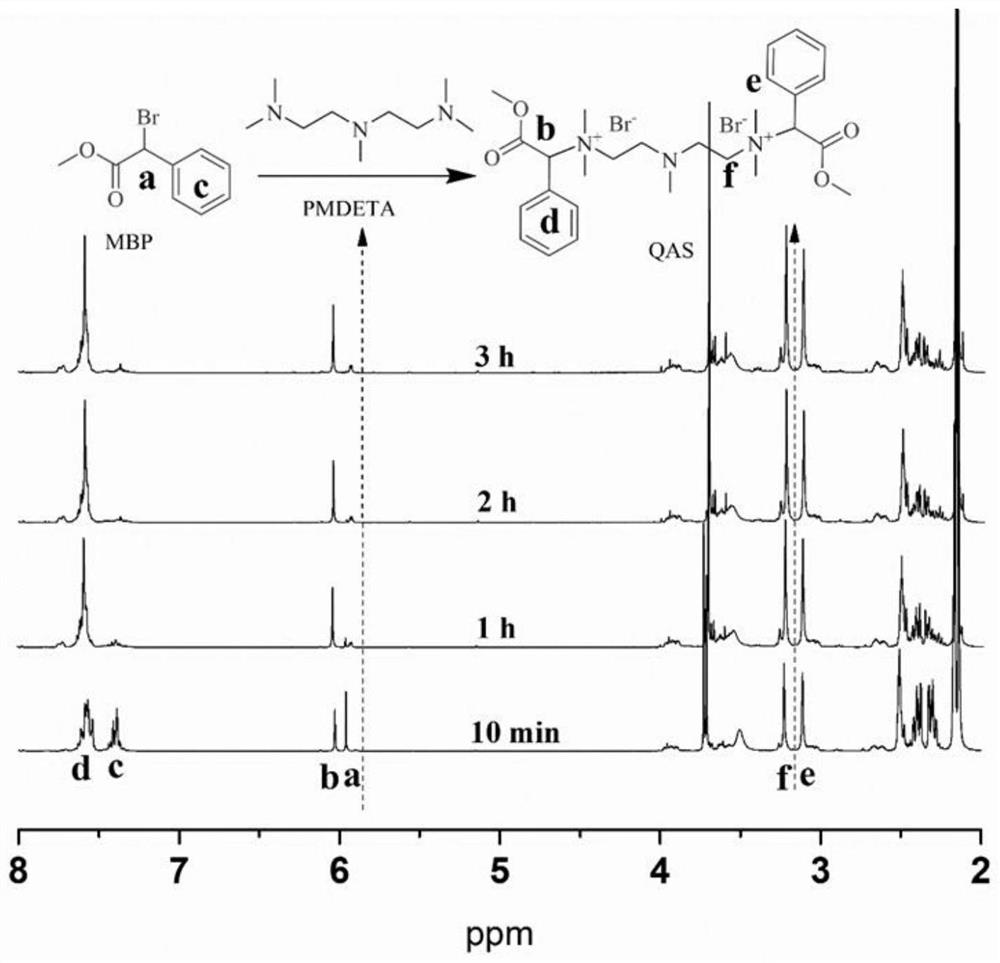
[0038] 1) Mix methyl α-bromophenylacetate (MBP) and pentamethyldiethylenetriamine (PMDETA) evenly at a molar ratio of 1:1, and react at room temperature to form a quaternary ammonium salt.
[0039] 2) After all the liquids are converted into solids, wash the synthesized quaternary ammonium salt with n-hexane, centrifuge in a centrifuge, pour off the upper layer liquid, wash with n-hexane, wash and centrifuge repeatedly for three times, then dry in a vacuum oven to obtain the quaternary ammonium salt. salt solids.
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: verification of quaternary ammonium salt catalyst
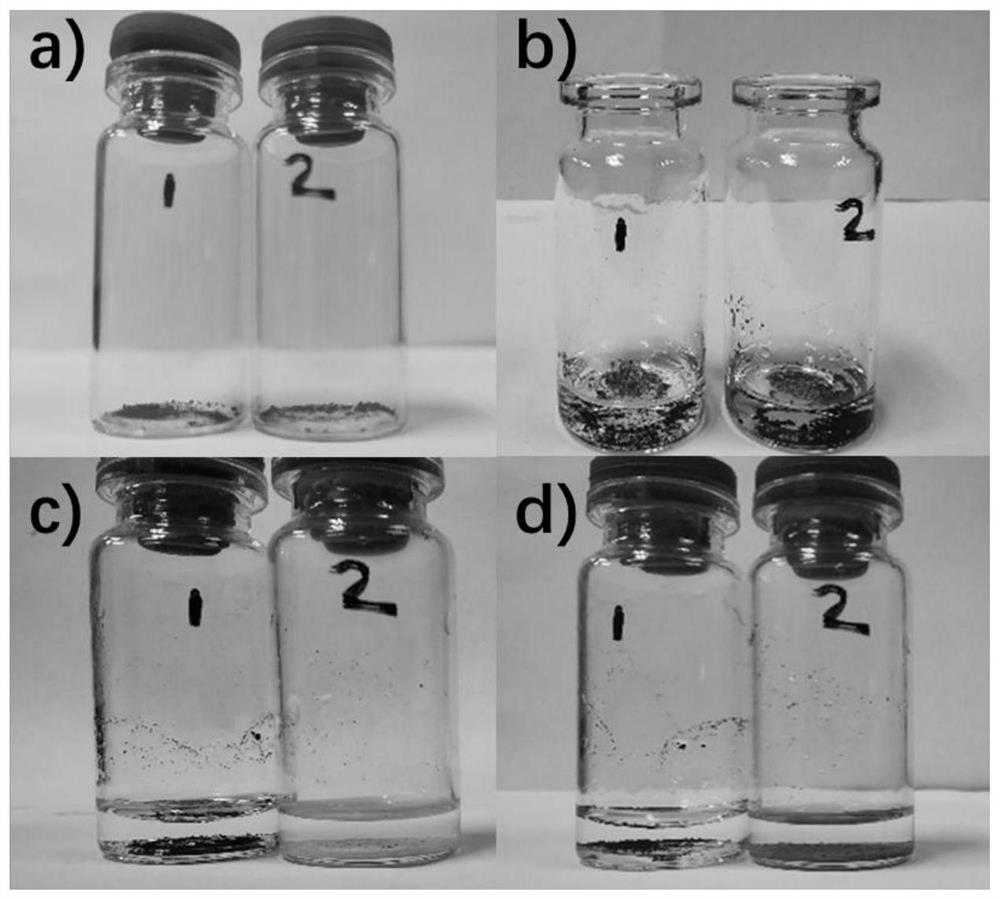
[0041] 1) Take appropriate amount of black silver oxide (Ag 2 O) The powder is placed in two identical vials 1 and 2, and 1 ml of deionized water is added to each of the vials 1 and 2.
[0042]2) Add an appropriate amount of the solid obtained in Example 1 to No. 2 vials, and after storing Vials 1 and 2 in the dark for a period of time, find the black Ag in No. 2 vials. 2 O turned into a light yellow substance, and No. 1 vial had no obvious change.
[0043] 3) Put the vials 1 and 2 under the light again, and after a period of time, it was found that the light yellow substance in the No. 2 bottle turned black while the No. 1 bottle had no obvious change.
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3: MMA active polymerization catalyzed by quaternary ammonium salt catalyst
[0045] This embodiment provides a controllable free radical polymerization quaternary ammonium salt catalyst based on C-N bond breaking to catalyze the active polymerization of methyl methacrylate (MMA), specifically comprising the following steps:
[0046] 1) Add MMA (0.472g, 4.71mmol), MBP (0.00108g, 0.00471mmol), Me6TREN (0.00109g, 0.00471mmol) into a 5ml ampoule, and then add 0.5ml DMSO as a reaction solvent.
[0047] 2) Pass the argon gas through the ampoule containing the solution for 15 minutes to remove oxygen, and then seal the tube.
[0048] 3) Put the sealed tube under LED lamp (14W) to react.
[0049] 4) After the reaction reaches the set time, open the tube, and add an appropriate amount of tetrahydrofuran (THF) to dilute the polymerization solution. The diluted polymer solution was dropped into 250ml of refrigerated anhydrous methanol, precipitated, and suction filte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com