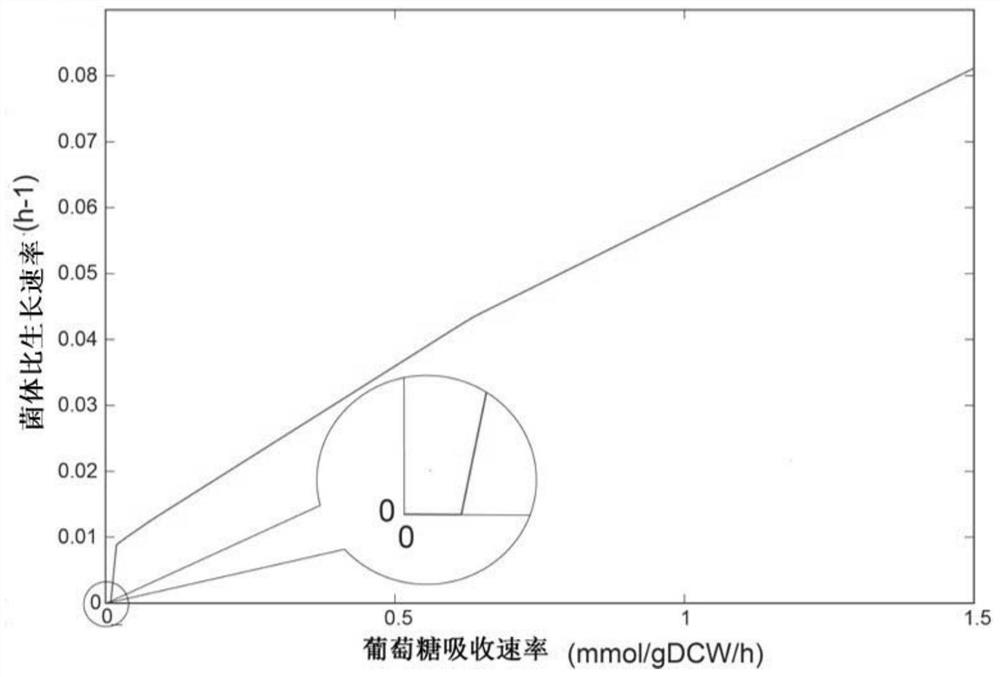
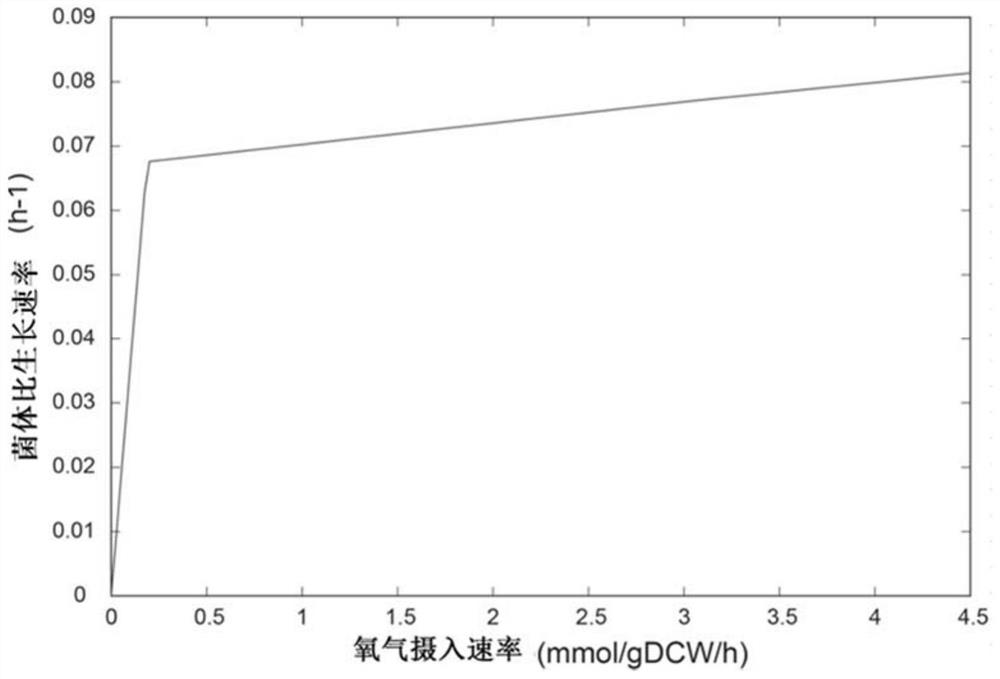
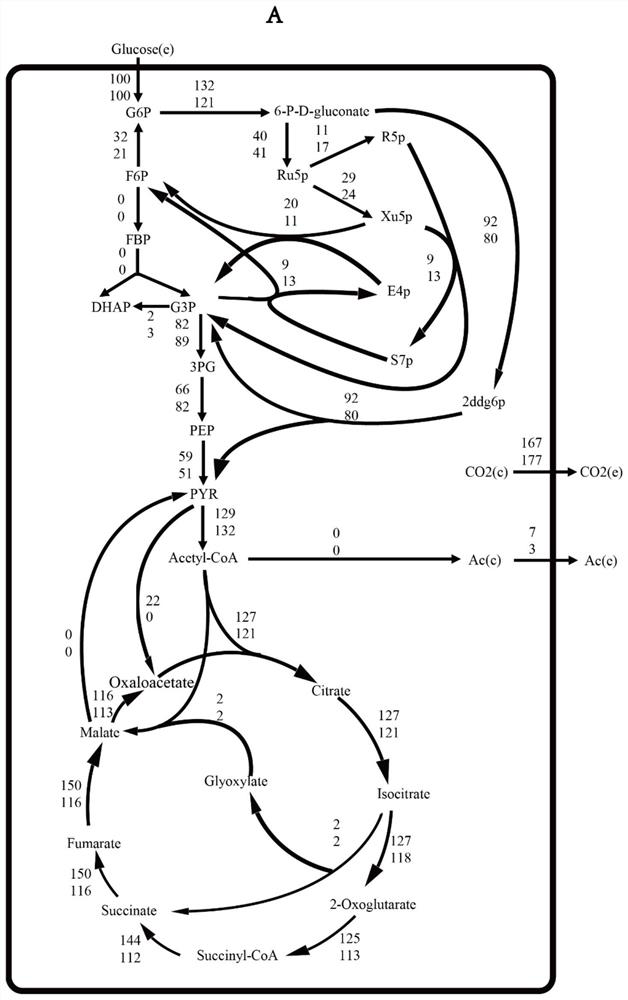
Method for improving erythromycin yield by guiding n-propyl alcohol feeding through genome model
A technology of n-propanol and erythromycin, which is applied in the field of systems biology, can solve the problems of low utilization rate of n-propanol, high medium requirements, low yield, etc., achieve good accuracy and prediction ability, increase yield, Yield improvement effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1. Construction of Genome-wide Metabolic Network Model
[0042] The construction of the genome-wide metabolic network model of Saccharopolyspora rubrum engineering bacteria includes genome-wide annotation, manual refinement of the draft metabolic network model, transformation of the metabolic network model into a mathematical model, and model verification and correction.
[0043] (1) Whole genome annotation
[0044] Annotate and check the genome sequence of Saccharopolyspora rubrum genetically engineered bacteria measured by Huada University. The annotation of genome function can be carried out through various databases (such as KEGG, NCBI, Enzyme, UniprotKB, SwissProt, IMG, and BioCyc, etc.). The database information used is shown in Table 1.
[0045] Table 1
[0046]
[0047]
[0048] (2) Manual refinement of the sketch of the metabolic network model
[0049] First, it is necessary to check the material and charge balance of reactions and metabolites ...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Example 2, Preparation of sucC Knockout Genetic Engineering Bacteria
[0073] The industrial strain S. erythraea E3 strain (obtained from Shanghai Guojia Biochemical Engineering Technology Research Center Co., Ltd.) was used as the starting strain to prepare the genetically engineered bacteria with succinyl-CoA synthetase gene (sucC) knockout. The sucC gene was knocked out by insertional inactivation, and primers were designed during the insertional inactivation process to amplify a fragment of 1021 bp in length from 196 bp to 1216 bp behind the start codon of the sucC gene. The primer sequences are as follows:
[0074] Upstream primers:
[0075] CCCAAGCTTGGGATGAGGCCAAGACGAA (SEQ ID NO: 1);
[0076] Downstream primers:
[0077] GAAGATCTTCGCCCTGGACGATGACCTTG (SEQ ID NO: 2).
[0078] The genome of the S. erythraea E3 strain was used as a template, and the above primers were used to amplify to obtain the target fragment, which was 1021 bp in length. The fragment was i...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Example 3. Basic culture of S.erythraea E3-△sucC strain
[0081] Plate Seed Medium:
[0082] Starch 10.0g / L, corn steep liquor 13.0g / L, sodium chloride 3.0g / L, ammonium sulfate 3.0g / L, agar 20.0g / L, calcium carbonate 3.0g / L.
[0083] Shake Flask Seed Medium:
[0084] Starch 40.0g / L, sodium chloride 4.0g / L, calcium carbonate 1.5g / L, peptone 20.0g / L, glucose 10.0g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.25g / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.2g / L.
[0085] Fermentation medium (using synthetic medium):
[0086] Glucose 22.0g / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 1.0g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.64g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 1.28g / L, alanine 0.86g / L, arginine 0.68g / L, semi Cystine 0.78g / L, Serine 0.73g / L, Trisodium Citrate 2.28g / L, Cobalt Chloride 0.009g / L, Sodium Borate 0.006g / L, Ferric Chloride 0.0068g / L, Copper Chloride 0.00027g / L, ammonium molybdate 0.00027g / L.
[0087]1. Plate seed culture
[0088] Prepare the flat seed medium according to the required amount, adjust...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com