Method for realizing pulmonary embolism modeling and non-invasive quantitative detection by labeling thrombus through near-infrared fluorescent probe
A fluorescent probe and near-infrared technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as embolism and different pathophysiological processes, and achieve the effect of simple method and simplified experimental operation process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
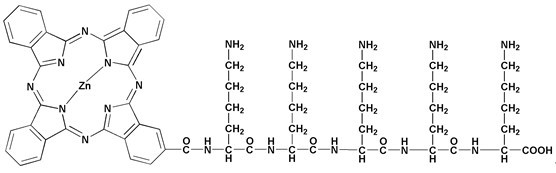
[0036] Example 1: ZnPc-(Lys) 5 Preparation and Characterization of Labeled Thromboembolic Microparticles
[0037] (1) ZnPc-(Lys) 5 Preparation of labeled thrombus microparticles: Blood was taken from the orbit of SD rats, anticoagulated with 3.2% sodium citrate (the volume ratio of anticoagulant to whole blood was 1:9), and the whole blood was separated by centrifugation at 1200 g for 10 min plasma. Take 500 μL plasma and add 2 μL ZnPc-(Lys) 5 (4.5 mM), 11.5 μL thrombin (10 U / mL) and 46.5 μL calcium chloride (240 mM), mix well and incubate in an oven at 37 °C for 2 h. ZnPc-(Lys) will be formed 5 The marked thrombus was placed in a mortar, cut into small pieces, resuspended in 1 mL Tyrodes-Hepes buffer (THB), and ground for 10 min to form thrombus particles.
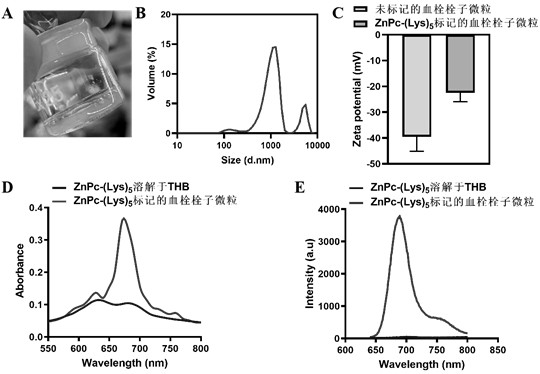
[0038] (2) ZnPc-(Lys) 5 Characterization of labeled thrombus microparticles: randomly sample 100 μL of the prepared fluorescently labeled thrombus microparticles into a 96-well plate, and put them into a Spectra Ma...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2: In vitro thrombolysis of unground thrombus and thrombus microparticles after grinding
[0041] (1) Thrombolysis of unground thrombus in vitro: blood was collected from the orbit of SD rats, anticoagulated with 3.2% sodium citrate (the volume ratio of anticoagulant to whole blood was 1:9), and 1200 g of whole blood Plasma was separated by centrifugation for 10 min. Add 30 μL of plasma to a 96-well plate, add 123.3 μL of Tris buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4) and 6.7 μL of calcium chloride (240 mM) in sequence, mix well and store in an oven at 37 °C Incubate for 2 h. After thrombus formation, different concentrations of r-tPA were added for thrombolysis, and the absorption at 405 nm was recorded in a Spectra Max i3x microplate reader.
[0042] (2) Thrombolysis of the ground thrombus in vitro: Take out the unground thrombus formed above with microscopic tweezers, place it in a mortar, cut it into small pieces and add 0.2 mL Tyrodes-Hepes buffer (THB...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3: Construction of mouse PE model and in vivo optical imaging
[0045] The prepared ZnPc-(Lys) 5 The labeled thrombus microparticles were injected into the ICR mice (200 μL / 20 g) through the tail vein. After the mice were anesthetized with isoflurane gas, the chest skin was depilated, and placed in a small animal in vivo imager (FMT2500 TM Real-time monitoring of mouse lung ZnPc-(Lys) in LX instrument, PerkinElmer) 5 fluorescent signal. The instrument uses a 680 nm laser diode to excite ZnPc-(Lys) 5 For molecules, mouse lungs were selected as Regions of interests (ROIs), and 50-60 source locations were scanned (the distance between adjacent scanning points was 3 mm). At the same time, the same concentration of free ZnPc-(Lys) 5 The solution was injected into mice as a control (free fluorescent probe set). For quantification of ZnPc-(Lys) 5 Concentration of 1 μM ZnPc-(Lys) 5 (dissolved in DMSO) was used as a standard to calibrate the FMT instrument. The ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com