Method for measuring content of major elements in multi-component alloy by proportionality coefficient correction glow mass spectrometry
A multi-element alloy, proportional coefficient technology, applied in the field of analysis and testing, can solve the problems of polluting the environment, difficult to directly quantitatively analyze the content of major elements in the sample, and difficult to observe.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Embodiment 1 is illustrated with Ni-Cr alloy as example:
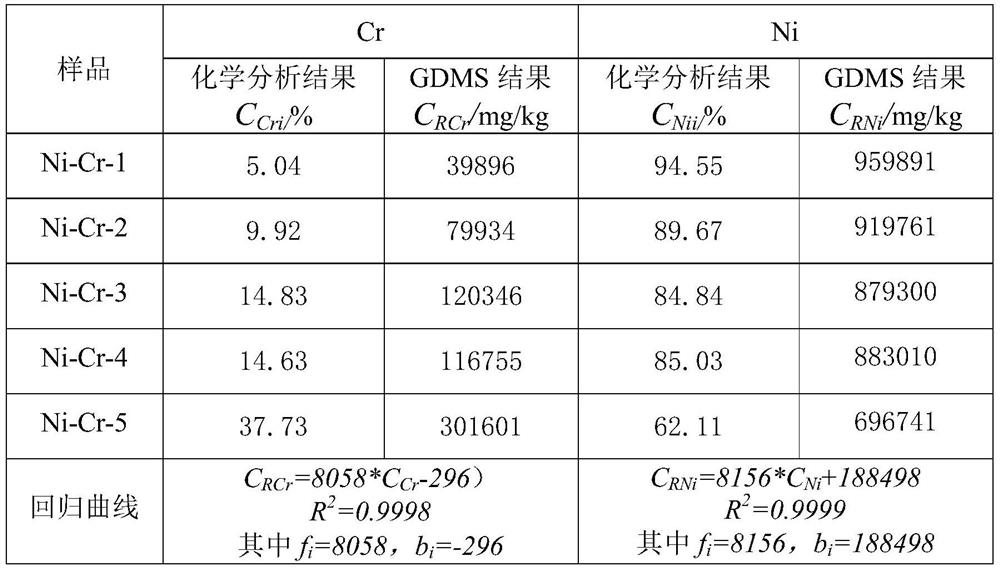
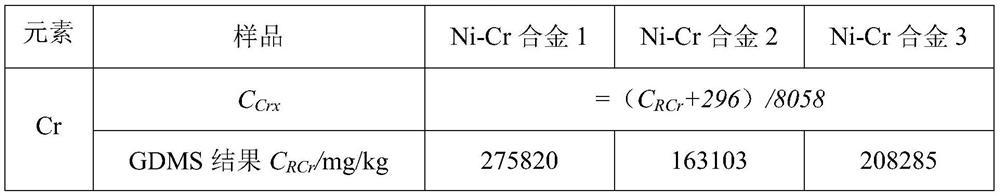
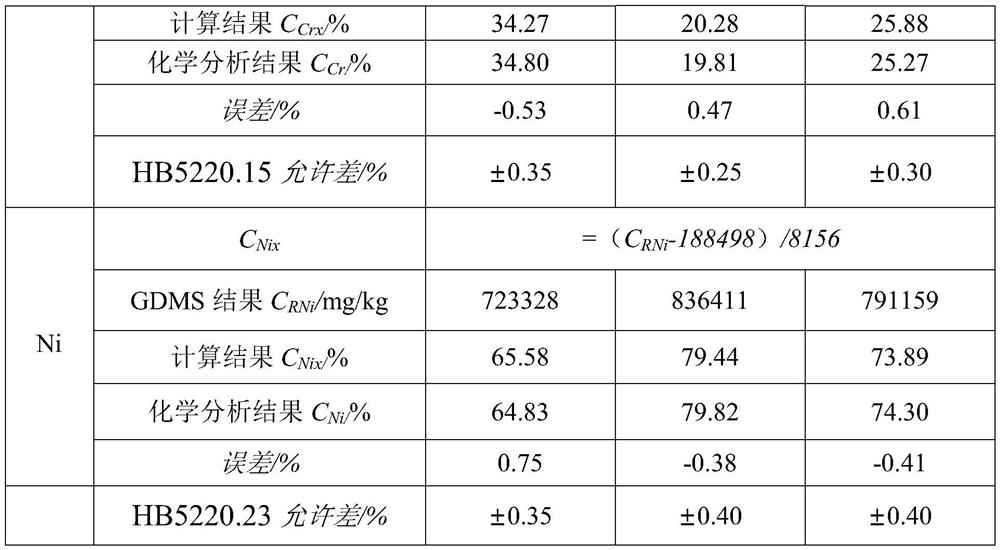
[0023] a. Determination of Cr in Ni-Cr alloy, reference standard HB5220.15-2008: put 5 Ni-Cr chip samples -1~5 with different Ni and Cr contents in a 500mL conical flask, add hydrochloric acid, Nitric acid, heating and dissolving is complete, then add sulfuric acid-phosphoric acid mixed acid. Add nitric acid dropwise for oxidation, add approximately water, add silver nitrate and ammonium persulfate solution and heat to oxidize to purple. Add sodium chloride for reduction. With N-phenyl anthranilic acid as indicator, titrate with ferrous ammonium sulfate standard solution to obtain the mass fraction C of each sample Cri , the results are shown in Table 1.
[0024] b. Determination of Ni in Ni-Cr alloy, reference standard HB5220.23-2008: put 5 Ni-Cr chip samples -1~5 with different Ni and Cr contents in a beaker, add hydrochloric acid and nitric acid, heat After the dissolution is completed, in the ammonium me...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2 is illustrated by taking the Mg-Al-V ternary alloy as an example:
[0034]a. Determination of Mg in Mg-Al-V ternary alloy, reference standard GB / T 20975.16-2008: Mg-Al-V ternary alloy chips are placed in a 500mL beaker, heated and dissolved with hydrochloric acid, and nitric acid is added After the dissolution is completed, filter the residue; after ashing, add sulfuric acid, hydrofluoric acid, nitric acid to dissolve, smoke sulfuric acid, add hydrochloric acid to dissolve, add hydrogen peroxide, potassium cyanide and a small amount of iron, and separate magnesium and a large amount of aluminum with NaOH precipitation. Separate iron, manganese, aluminum, etc. again, use methyl thymol blue as indicator, titrate magnesium with CyDTA standard solution, and calculate the mass fraction of magnesium C Mgi , the results are shown in Table 3.
[0035] b. Determination of Al in Mg-Al-V ternary alloy, reference standard YS / T 1075.8-2015: Mg-Al-V ternary alloy chips ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com