Multi-element environment-responsive polysaccharide microspheres as well as preparation and application methods thereof
An environmentally responsive and environmentally responsive technology, applied in the fields of polymer materials and biomedicine, can solve the problems of uncontrollable strict orthogonality of required enzymes, easy mutual interference, and reduced reaction efficiency, so as to avoid interference and cross-contamination, The effect of low cost and simple synthesis process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
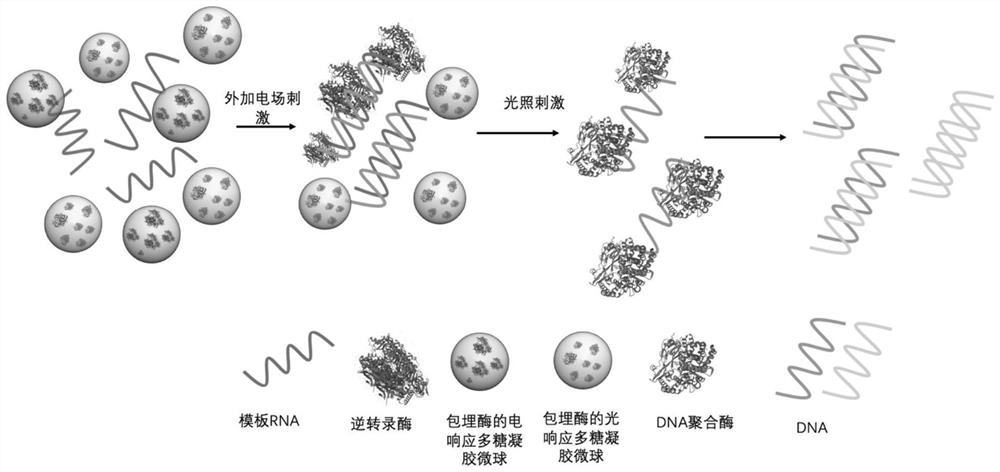
[0060] Example 1: Preparation of photoresponsive polysaccharide microspheres embedded with nucleic acid polymerase
[0061] (1) Dissolve the modified agarose grafted with melanin molecules (Tm=100°C) and high-temperature stable DNA polymerase in the buffer solution, and heat at 100°C to prepare the water phase W.
[0062] (2) Heating isooctyl alcohol to 100°C to obtain oil phase O.
[0063] (3) The water phase W was quickly transferred to the oil phase O, and vigorously shaken by hand for 30 seconds to obtain a water-in-oil emulsion.
[0064] (4) Quickly transfer the emulsion to an ice-water bath, and solidify at low temperature for 1 hour.
[0065] (5) Centrifuge the emulsion at a speed of 1500 rpm for 5 minutes, and wash with absolute ethanol, absolute ethanol and pure water in sequence to remove excess oil phase on the surface of the microspheres.
Embodiment 2
[0066] Example 2: Preparation of magnetic field-responsive polysaccharide microspheres embedded with endonucleases
[0067] (1) Dissolve modified hyaluronic acid (Tm=60° C.), iron ferric oxide particles, and endonuclease in a buffer solution, and heat at 60° C. to prepare a water phase W.
[0068] (2) Mix petroleum ether and liquid paraffin at a volume ratio of 1:1, and heat to 60°C to obtain oil phase O.
[0069] (3) Using a microfluidic device to inject the water phase into the oil phase to obtain a water-in-oil emulsion.
[0070] (4) Quickly transfer the emulsion to liquid nitrogen, and wait for the emulsion to return to room temperature after curing at low temperature for 20 seconds.
[0071] (5) Centrifuge the emulsion at a speed of 1000rpm for 3 minutes, wash with absolute ethanol, absolute ethanol and pure water in sequence to remove excess oil phase on the surface of the microspheres.
Embodiment 3
[0072] Example 3: Preparation of electric field-responsive polysaccharide microspheres for embedding nucleic acid molecules
[0073] (1) Dissolve the modified positively charged aminoalginic acid (Tm=50°C), negatively charged silicon carbide particles and guiding DNA molecules in buffer solution, and heat at 50°C to prepare the aqueous phase W.
[0074] (2) Heating soybean oil to 50° C. to obtain oil phase O.
[0075] (3) The water phase W was quickly transferred to the oil phase O, and stirred at a speed of 1000 rpm for 3 minutes to obtain a water-in-oil emulsion.
[0076] (4) Quickly transfer the emulsion to an ice-water bath, and solidify at low temperature for 3 hours.
[0077] (5) Centrifuge the emulsion at a speed of 1000 rpm for 5 minutes, and wash with absolute ethanol, absolute ethanol and pure water in sequence to remove excess oil phase on the surface of the microspheres.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com