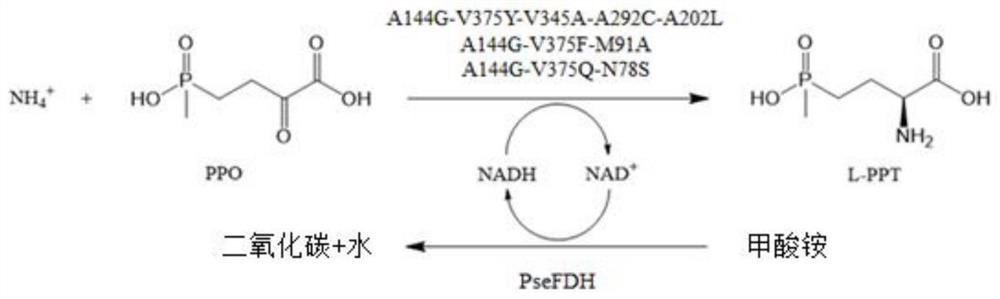
Glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant, engineering bacterium, immobilized cell and application
A technology of immobilized cells and glufosinate-ammonium, applied in applications, genetic engineering, immobilized on or in inorganic carriers, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, low reduction activity and low catalytic efficiency of L-glufosinate-ammonium , to achieve the effect of improving thermal stability and operational stability, realizing repeated use and high stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1: Construction and screening of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant library
[0038] 1. Parent engineering bacteria of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase
[0039] The nucleotide sequence of wild-type glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase KmGDH (NCBI accession number WP_010290083.1) from Kurthia massiliensis was codon-optimized and synthesized by Hangzhou Qingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. , the obtained KmGDH gene (the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1, the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein is shown in SEQ ID No.2), cloned on the NcoI of MCS1 (multiple cloning site 1) of the plasmid pETDuet , construct the recombinant expression vector pETDuet-KmGDH, retain the His-Tag gene of the plasmid itself, transform it into Escherichia coli E.coli BL21(DE3), and send it to Hangzhou Qingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. to synthesize the glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase female engineering bacterium E .coli BL21(DE3) / pETDuet-KmGDH.
[0040] SEQ ID NO.1
[0...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Embodiment 2: Induced expression of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant engineering bacteria
[0060] The parent engineering bacteria of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase in Example 1, the parent of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase set out to co-express strains and the co-expression of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutants with formate dehydrogenase The strains were inoculated into LB liquid medium containing a final concentration of 50 μg / mL ampicillin, cultured at 37°C for 8 hours, and inoculated into fresh LB liquid medium containing a final concentration of 50 μg / mL ampicillin at an inoculum volume concentration of 2%. In the culture medium, culture at 37°C and 180 rpm for 2 hours, then add 0.1mM IPTG to the culture medium at a final concentration of 0.1mM, cultivate at 18°C for 14 hours, centrifuge at 4°C and 8000 rpm for 10 minutes to obtain the corresponding wet bacteria. The composition of LB liquid medium: 10g / L pepton...
Embodiment 3
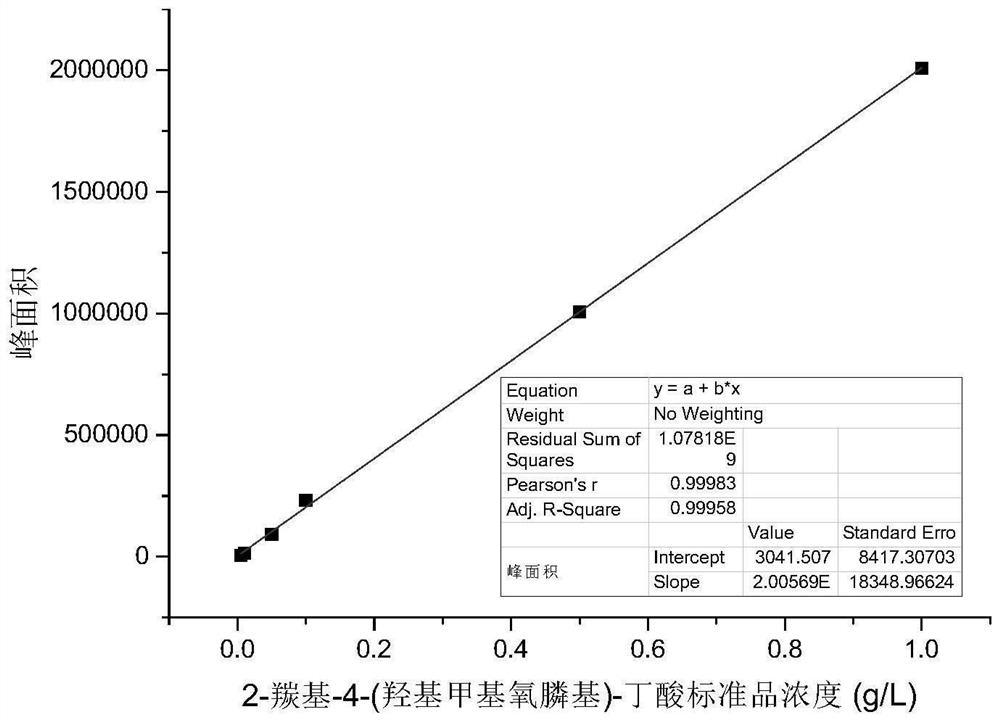
[0063] Example 3: Mutant library screening
[0064]The glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase parent engineering bacteria prepared by the method in Example 2, the glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase parent and formate dehydrogenase co-express wet bacteria or the glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant and formate dehydrogenation Enzyme co-expression wet bacteria as a catalyst, 2-carbonyl-4-(hydroxymethylphosphono)-butyric acid as a substrate, ammonium formate as a coenzyme regeneration substrate, and a small amount of NAD added exogenously + , with pH 7.4, 100mM phosphate buffer as the reaction medium to form a 1mL reaction system, the catalyst dosage is based on the weight of wet bacteria, the final concentration is 10g / L, the final substrate concentration is 100mM, the final concentration of ammonium formate is 125mM, NAD + The final concentration was 1 mM, and the reaction was carried out at 35°C and 600 rpm for 5 min. Take 50 μL of the reaction solution, add 5 μL hydrochlori...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| catalytic efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com