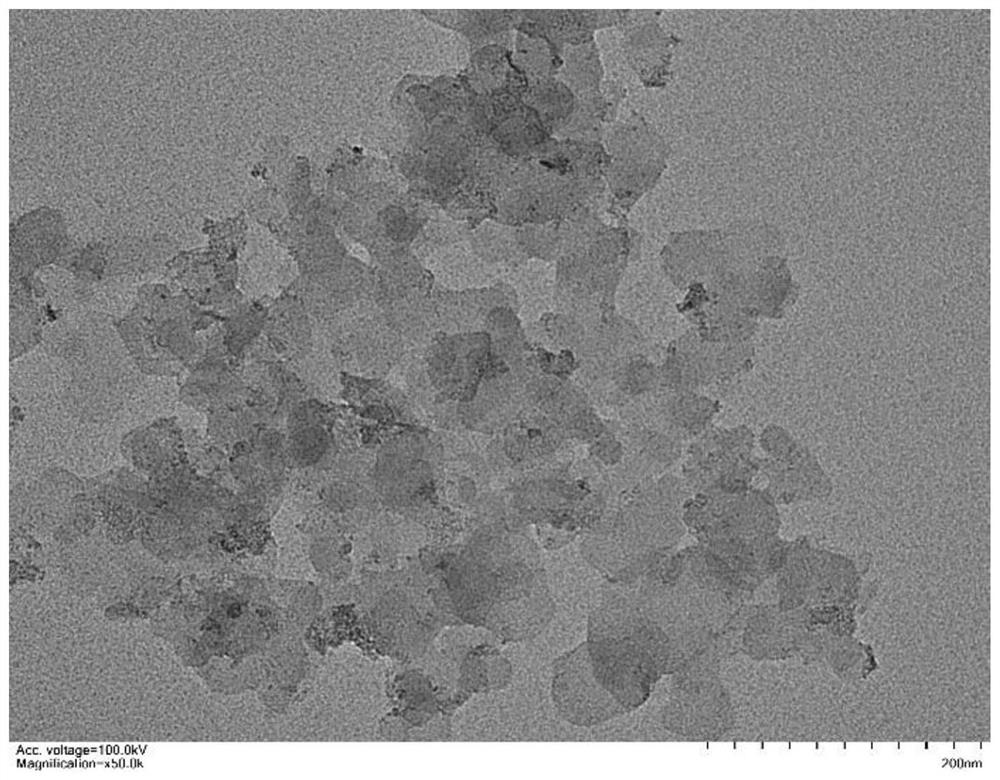
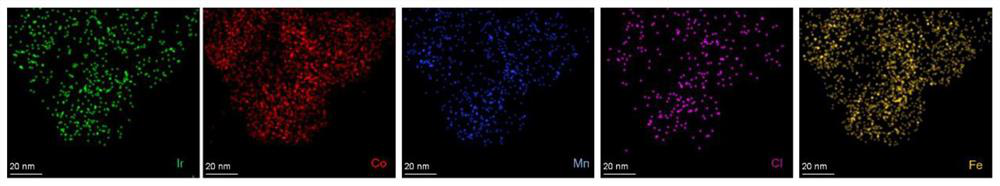
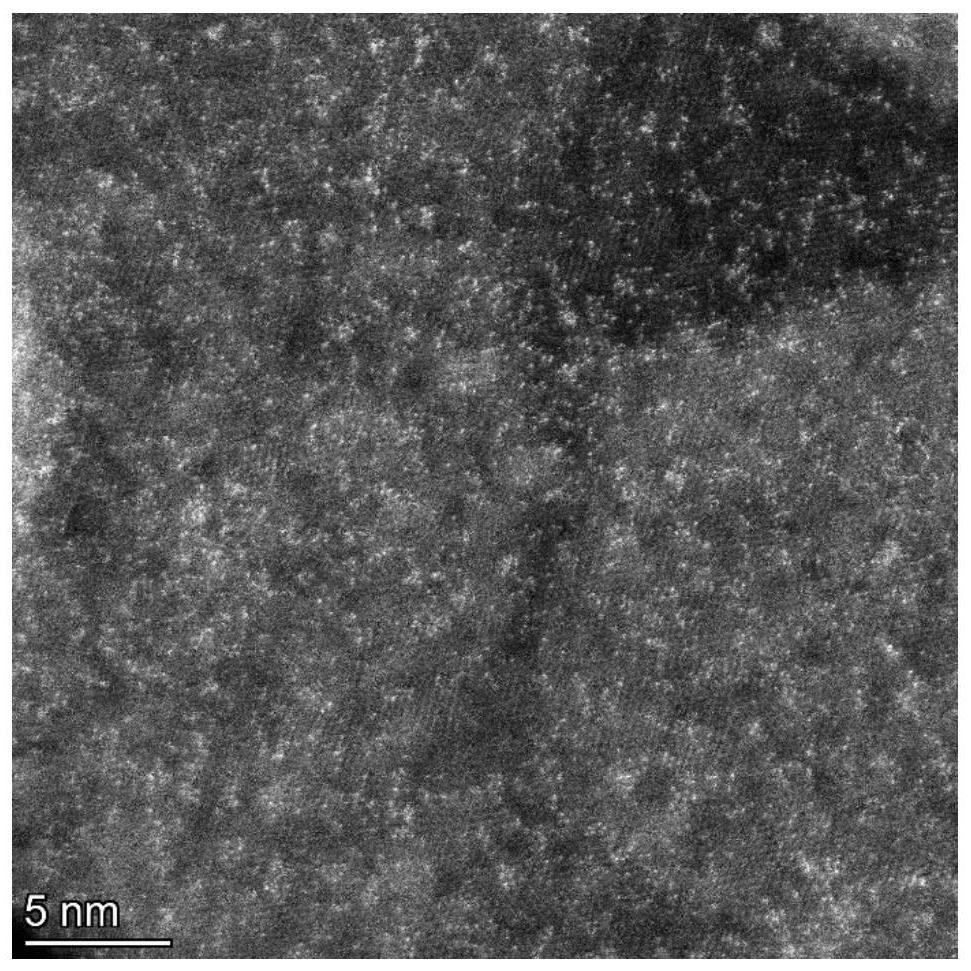
Nanometer material with precious metal particles dispersed on surface of non-precious metal substrate and preparation method and application of nanometer material
A non-precious metal and nano-material technology, applied in the field of inorganic advanced nano-materials, can solve the problems such as the easy dissolution of noble metal catalysts, achieve the effects of not easy to fall off stability, improve reactivity, and reduce costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] Example 1 - Chemical Deposition
[0084] The preparation method of the nanomaterial (iridium / cobalt manganese iron hydroxide) in which the precious metal particles are dispersed on the surface of the non-precious metal substrate, adopts the chemical deposition method described in the second aspect of the present invention, and is specifically as follows:
[0085] Step (1) Preparation of non-precious metal substrate-cobalt manganese iron hydroxide nanosheets
[0086] Prepare 40 milliliters of lye A: prepare 40 milliliters of lye A with 0.48 grams of sodium hydroxide and 0.106 grams of sodium carbonate and an appropriate amount of deionized water;
[0087]To prepare 40 ml of salt solution B: 0.291 g of cobalt nitrate, 0.05 g of manganese nitrate and 0.202 g of ferric nitrate and an appropriate amount of deionized water were prepared into 40 ml of salt solution B.
[0088] Solution A and solution B were dropped into 40 ml of high-speed stirring water at the same time, and...
Embodiment 2
[0104] Example 2 - Chemical Deposition
[0105] The preparation method of the nanomaterial (ruthenium / nickel-iron hydroxide) in which the precious metal is dispersed on the surface of the non-precious metal substrate, adopts the chemical deposition method described in the second aspect of the present invention, and is specifically as follows:
[0106] Referring to the method in Example 1, when 40 ml of salt solution B was prepared in step (1), the mass of nickel nitrate was changed to 0.436 g, the mass of ferric nitrate was 0.202 g, and the alkaline solution was changed to 0.14 g of sodium hydroxide and 0.053 g of sodium carbonate.
[0107] Change step (2) to prepare 2 ml of ruthenium chloride solution: 2.489 g of ruthenium chloride (6000 mmol / L), 480 mg of sodium hydroxide (6000 mmol / L).
[0108] Conditions were: 10°C, 120 hours.
Embodiment 3
[0117] Example 3 - Electrodeposition
[0118] The preparation method of the nanomaterial in which the precious metal particles are dispersed on the surface of the non-precious metal substrate adopts the electrodeposition method described in the third aspect of the present invention, and the details are as follows:
[0119] Step (1) prepare a conductive carrier loaded with a non-precious metal substrate - nickel foam loaded with nickel-iron hydroxide:
[0120] Mix 0.6 g of urea, 0.121 g of ferric nitrate, 0.174 g of nickel nitrate, 0.05 g of vanadium chloride, 0.037 g of ammonium fluoride and deionized water into a 36-ml solution, pour the solution into a 40-ml 3*4 cm 2 The foamed nickel is soaked in the solution, put into an oven, and the reaction temperature is 100 degrees Celsius, and the time is 12 hours, and hydrothermally, crystallization, washing, drying obtains the foamed nickel (nickel-iron-vanadium hydrogen) that is loaded with nickel-iron-vanadium hydroxide. oxide ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com