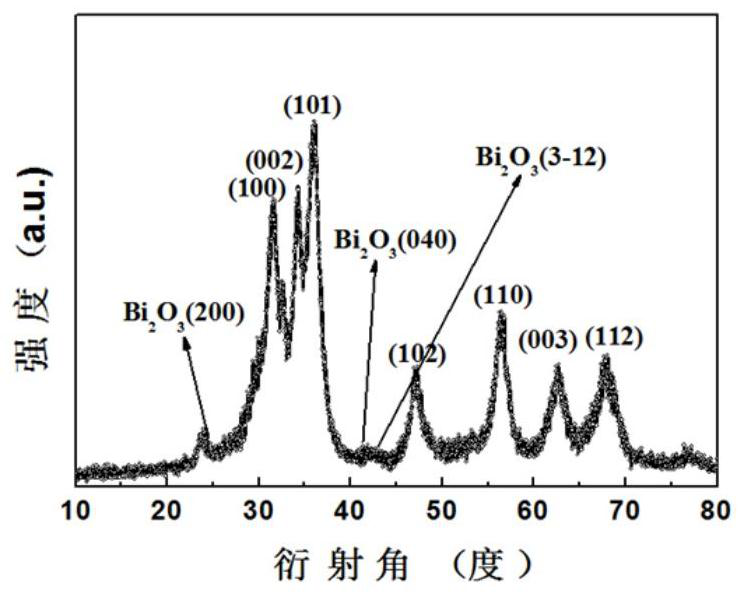
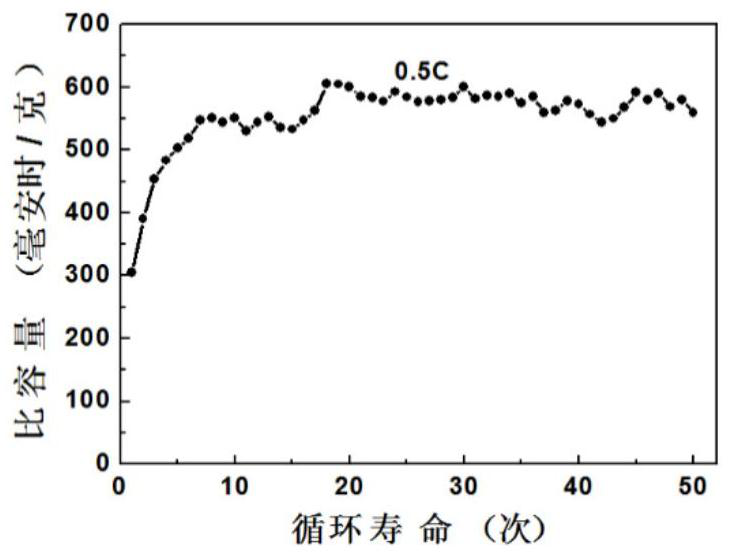
Bismuth trioxide modified indium-doped zinc oxide material and preparation and application thereof
A technology of bismuth trioxide and zinc oxide, which is applied in the direction of active material electrodes, nickel storage batteries, structural parts, etc., can solve the problems of reduced utilization of active materials, dendrite growth of zinc negative electrodes, battery capacity attenuation, etc., and the method is simple, Effect of high specific capacity and long cycle life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0035] The present invention is a preparation method of a negative electrode material of a zinc-nickel oxide secondary battery modified by dibismuth trioxide modified with indium, comprising the following steps:
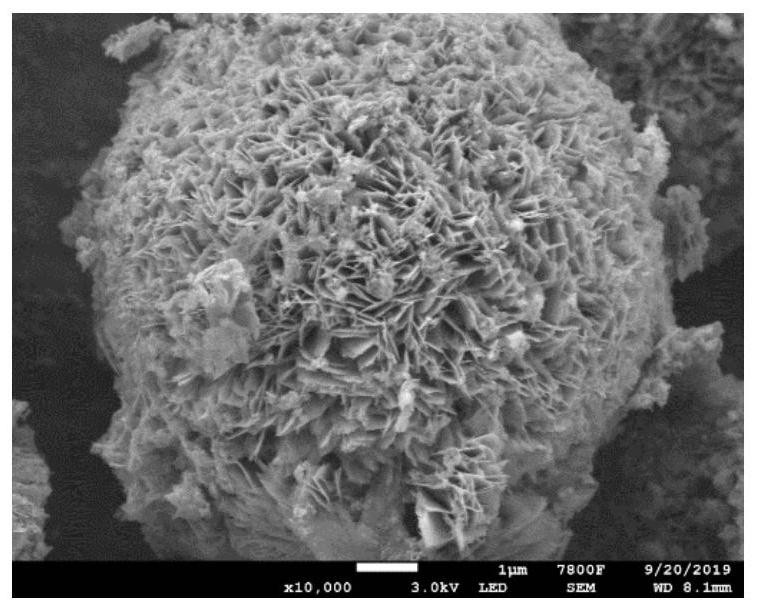
[0036] Step 1, preparation of bismuth trioxide modified indium-doped zinc oxide material
[0037]Zinc acetate and indium chloride are dissolved in water, urea and potassium citrate are added at the same time, and the reactant is subjected to ultrasonic treatment after stirring uniformly. Afterwards, the obtained mixture was transferred to a reactor and reacted at a certain temperature for a period of time. After the reaction kettle was cooled to room temperature, it was centrifuged and washed three times with deionized water, and then dried in a vacuum drying oven to obtain an indium-doped zinc oxide material.
[0038] The obtained indium-doped zinc oxide is dispersed in water and stirred, bismuth nitrate is added to continue stirring, and then the obtained mixture ...
Embodiment 1
[0045] Step 1, preparation of bismuth trioxide modified indium-doped zinc oxide material
[0046] Dissolve 1.3170g of zinc acetate and 0.0395g of indium chloride in 70mL of water, add 2.8818g of urea and 0.1838g of potassium citrate at the same time, stir for 5 minutes until uniform, and then ultrasonically treat the reactant for 10 minutes, then transfer the resulting solution to the reaction In the kettle, and reacted at 120 ° C for 12 h. After the reaction kettle was cooled to room temperature, it was centrifuged and washed three times with deionized water, and then dried in a vacuum drying oven at 60° C. for 10 h to obtain an indium-doped zinc oxide material.
[0047] Weigh 0.36 g of the obtained indium-doped zinc oxide material and disperse it in 70 mL of water, add 0.12 g of bismuth nitrate and stir until uniform for 5 minutes, transfer the obtained solution to a reaction kettle, and react at 120° C. for 12 h. When the reaction kettle was cooled to room temperature, it ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Step 1, preparation of bismuth trioxide modified indium-doped zinc oxide material
[0055] Dissolve 1.3170g of zinc acetate and 0.0790g of indium chloride in 70mL of water, add 2.8818g of urea and 0.1838g of potassium citrate at the same time, stir for 5 minutes until uniform, and then sonicate the reactant for 10 minutes, then transfer the resulting solution to the reaction In the kettle, and at a certain 120 ° C, the reaction was carried out for a period of 12 h. After the reaction kettle was cooled to room temperature, it was centrifuged and washed three times with deionized water, and then dried in a vacuum drying oven at 60° C. for 10 h to obtain an indium-doped zinc oxide material.
[0056] Weigh 0.36 g of the obtained indium-doped zinc oxide material and disperse it in 70 mL of water, add 0.12 g of bismuth nitrate and stir until uniform for 5 minutes, transfer the obtained solution to a reaction kettle, and react at 120° C. for 12 h. After the reaction kettle wa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com