Process for comprehensively recycling micro-etching waste liquid
A technology of micro-etching and waste liquid, which is applied to the improvement of process efficiency, copper sulfate, etc., can solve the problems of high processing cost, landfill, poor purity, etc., and achieve simple process operation, reduce the amount of sulfuric acid, and the scope of application wide effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
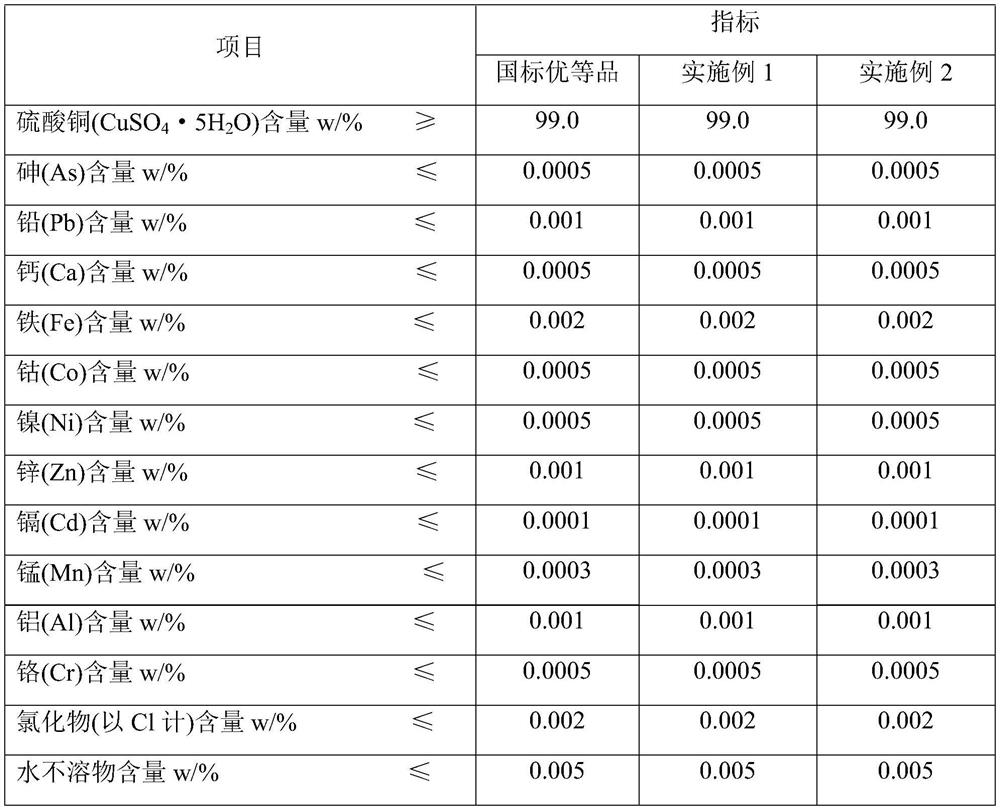
Embodiment 1
[0050] A process for comprehensively recycling micro-etching waste liquid, comprising the following steps:
[0051] (1) Add a slight excess of basic copper chloride Cu to the 5L micro-etching waste liquid 2 (OH) 3 450 g of Cl was stirred and dissolved for 4 h, the pH of the solution was adjusted to precipitate iron ions, and impurities were removed by filtration to obtain a pretreatment solution; after adding basic copper chloride in step (1), the reaction that occurred was as follows:
[0052] Cu 2 (OH) 3 Cl+2H 2 SO 4 =3H 2 O+2CuSO 4 +HCl (1)
[0053] 2Cu 2 (OH) 3 Cl+Fe 2 (SO4) 3 =2Fe(OH) 3 ↓+3CuSO 4 +CuCl 2 (2)
[0054] (2) 5L of pretreatment solution was added to the three-necked distillation flask of 5L, heated and evaporated under agitation, and distilled water was collected. When the amount of evaporation reached 4L, the heating was stopped to obtain concentrated micro-etching waste liquid; the pretreatment after concentration at this time The solution i...
Embodiment 2
[0060] A process for comprehensively recycling micro-etching waste liquid, comprising the following steps:
[0061] (1) Add a slight excess of basic copper chloride Cu to the 5L micro-etching waste liquid 2 (OH) 3 450 g of Cl was stirred and dissolved for 4 h, the pH of the solution was adjusted to precipitate iron ions, and impurities were removed by filtration to obtain a pretreatment solution; after adding basic copper chloride in step (1), the reaction that occurred was as follows:
[0062] Cu 2 (OH) 3 Cl+2H 2 SO 4 =3H 2 O+2CuSO 4 +HCl (1)
[0063] 2Cu 2 (OH) 3 Cl+Fe 2 (SO4) 3 =2Fe(OH) 3 ↓+3CuSO 4 +CuCl 2 (2)
[0064] (2) 5L of pretreatment solution was added to the three-necked distillation flask of 5L, heated and evaporated under agitation, and distilled water was collected. When the amount of evaporation reached 4L, the heating was stopped to obtain concentrated micro-etching waste liquid; the pretreatment after concentration at this time The solution i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com