Acyl CoA synthetase and application thereof
A technology of synthase and acyl group, which is applied in the field of acyl CoA synthase to achieve the effect of excellent catalytic performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0086] Example 1. Sequence analysis of UkaQ
[0087] (1) Sequence analysis of UkaQ
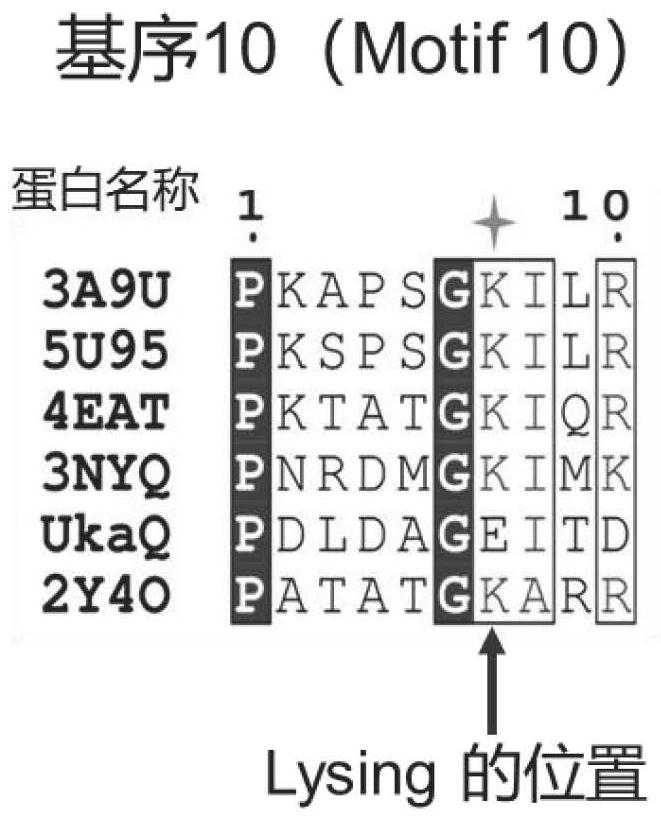
[0088] The amino acid sequences of UkaQ and the analyzed acyl-CoA synthase were compared using the multiple sequence alignment software ClustalW, and the conserved motifs MotifA1-MotifA10 of UkaQ were found by combining the features of the conserved motifs MotifA1-MotifA10 of this type of enzymes. The acyl-CoA synthase sequences used for comparison are 4-coumaric acid-CoA ligase 3A9U from Populus tomentosa, 4-coumaric acid-CoA ligase 5U95 from tobacco, benzene from Rhodopseudomonas swampis Formate-CoA ligase 4EAT, malonyl CoAA3NYQ from Streptomyces coelicolor, phenylacetic acid-CoA ligase 2Y4O from Burkholderia neocepacia. Multiple sequence alignment results are as figure 1 As shown, the marked "Lysing position" is a key site in the conserved motif of acyl-CoA synthase (MotifA10) responsible for catalyzing the adenylation reaction.
[0089] The sequence alignment results show that the chara...
Embodiment 2
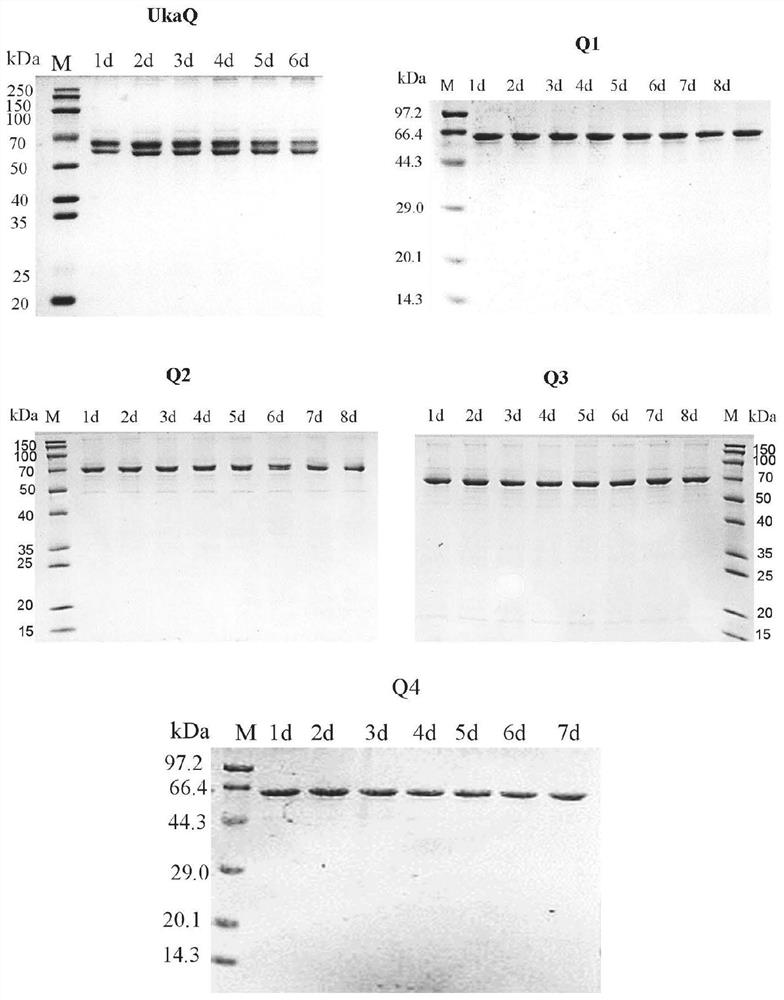
[0090] The expression vector construction and expression of embodiment 2.UkaQ
[0091](1) Use the following steps to obtain the gene encoding UkaQ
[0092] Using the amino acid sequence SEQ ID NO: 1 (GenBank: AQN08598.1) of UKaQ as a template, the nucleic acid sequence of the gene was converted into the gene through reverse translation, and the DNA of the UkaQ gene was fully synthesized and synthesized on the universal vector PUC57.
[0093] (2) Construction of expression vector p-UkaQ and recombinant strain
[0094] The UkaQ gene DNA and pET28a plasmid were digested with NdeI / XhoI and recovered respectively. After enzymatic ligation, they were transformed into EcoliDH5α competent cells, and the correct recombinant bacteria were screened. After successful verification, the plasmid was extracted and named p-UkaQ.
[0095] (3) Use the following steps to express p-UkaQ in vitro
[0096] The recombinant plasmid p-UkaQ in Example 1 was transformed into E.coli BL21 (DE3) competent...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Example 3: Biochemical function identification of UkaQ
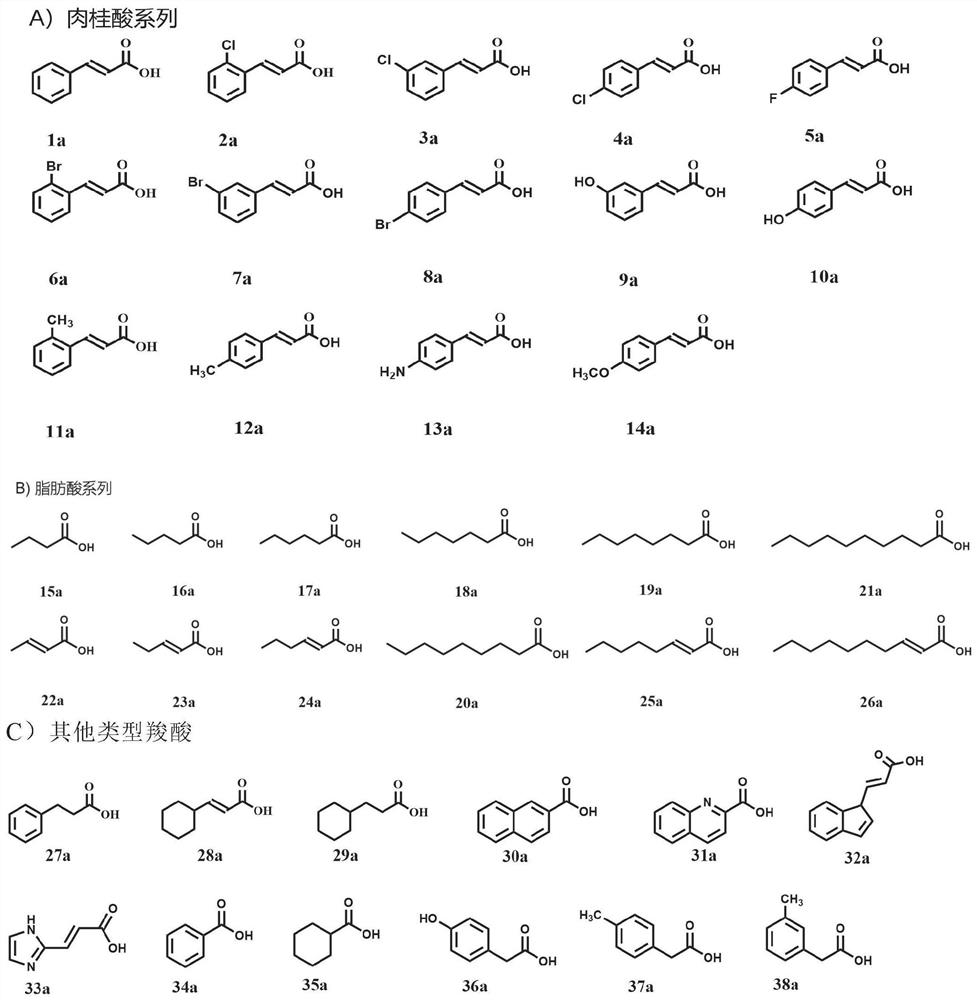
[0098] The composition of the in vitro activity assay system of UkaQ is as follows: 1.5mM carboxylic acid substrate, 2mM ATP, 1.5mM COA, 5mM Mg 2 + , 50 mM Hepes Buffer (pH 7.5) and 1 μM UkaQ, the total volume was 200 μl, the reaction was carried out in a 1.5 mL EP tube, and the reaction without UkaQ or its mutant protein was used as a control. The reaction was incubated at 25 °C for 1 h, quenched by adding an equal volume of methanol, centrifuged at 12,000 rmp for 20 min to remove proteins, and 1 μl of the sample supernatant was taken for UPLC analysis. UPLC analysis of all samples was performed on an Eclipse XDB-C18 analytical column with a flow rate of 0.2 mL min-1 and the analysis procedure was as follows: T=0 min, 5%B; T=3min, 5%B; T=10min, 65% B; T=12 min, 5% B; T=15 min, 5% B (solvent A: H2O with 10 mM CH3COONH4, solvent B: CH3CN). For LC-HRMS analysis, the conditions were the same as for UPLC analysis. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com