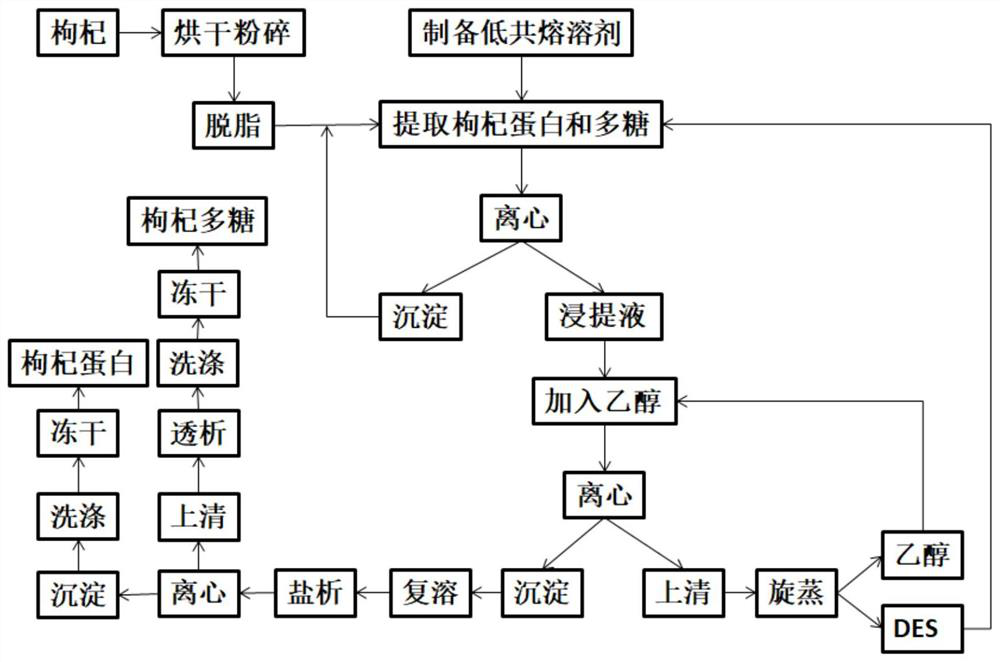
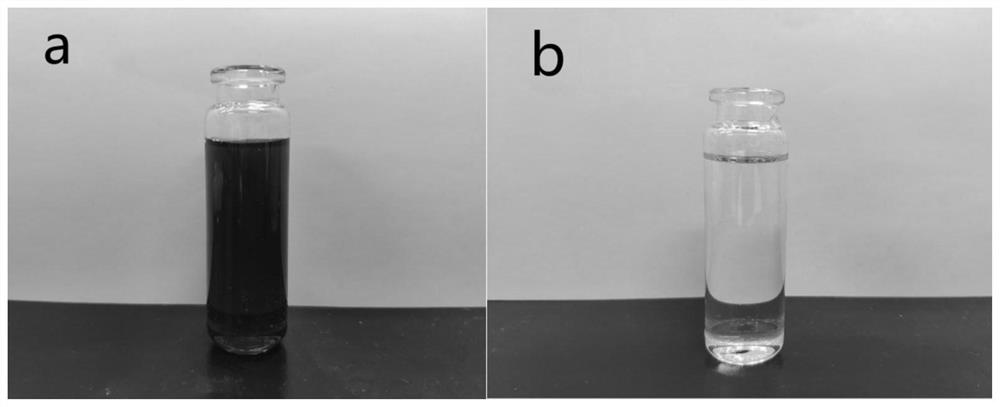
Method for synchronously extracting and separating lycium barbarum protein and polysaccharide
A technology for synchronous extraction of wolfberry protein, applied in peptide preparation methods, chemical instruments and methods, bulk chemical production, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable simultaneous extraction of wolfberry protein, extraction of polysaccharides and proteins, and destruction of wolfberry protein. Simple, high extraction rate, efficient extraction and separation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] Example 1 Extraction of Lycium barbarum protein and polysaccharide by deep eutectic solvent at different temperatures
[0084] Prepare defatted wolfberry powder as follows:
[0085] a) Place the wolfberry fruit in a cool, dry and ventilated place to air dry naturally, bake it in an oven at a temperature of 60°C until the water content of the wolfberry fruit is about 10%, then pulverize it with a pulverizer, and pass it through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain wolfberry powder;
[0086] b) Degreasing the wolfberry powder obtained in step a) with n-hexane, mixing the wolfberry powder and n-hexane according to a mass-volume ratio of 1 g: 2 mL, stirring intermittently at 55° C. for 4 h, cooling to room temperature, and centrifuging at 4000 rpm for 10 min. The sediment was dried in a fume hood, pulverized with a pulverizer, and passed through an 80-mesh sieve to obtain defatted wolfberry powder.
[0087] Prepare the deep eutectic solvent as follows:
Embodiment 2
[0099] Example 2 Extraction of Lycium barbarum protein and polysaccharide by deep eutectic solvent at different extraction times
[0100] The preparation method of defatted wolfberry powder and low eutectic solvent is the same as that in Example 1.
[0101] Simultaneously extract and separate Lycium barbarum protein and polysaccharide according to the following steps:
[0102] (1) Weigh 0.5000g of defatted Lycium barbarum powder into a conical flask, add 5mL of distilled water to dissolve, then add 15mL of deep eutectic solvent to it and mix evenly, and stir magnetically for 60min, 120min, 180min, and 240min in a water bath at 45°C, respectively. , 300min, centrifuged at 6000rpm for 10min to obtain Lycium barbarum extract;
[0103] Steps (2) to (4) are the same as in Example 1.
[0104] The protein extraction rates obtained under different extraction times in this example are shown in Table 2.
[0105] Table 2 Effect data under different extraction times
[0106] ...
Embodiment 3
[0108] Example 3 Extraction of Lycium barbarum protein and polysaccharide by deep eutectic solvent under different water additions
[0109] The preparation method of defatted wolfberry powder and low eutectic solvent is the same as that in Example 1.
[0110] Simultaneously extract and separate Lycium barbarum protein and polysaccharide according to the following steps:
[0111] (1) Weigh 0.5000g of defatted wolfberry powder and place it in a conical flask, add 1.5mL, 3mL, 4.5mL, 6mL, 7.5mL of distilled water to dissolve, then add deep eutectic solvent (distilled water and deep eutectic solvent together) 15mL) mixed uniformly, magnetically stirred for 180min under 45°C water bath conditions, and centrifuged at 6000rpm for 10min to obtain Lycium barbarum extract;
[0112] Steps (2) to (4) are the same as in Example 1.
[0113] The protein extraction rates obtained under different water addition amounts in this example are shown in Table 3.
[0114] Table 3 Effect data under ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com