Patents
Literature
120 results about "Active cable" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
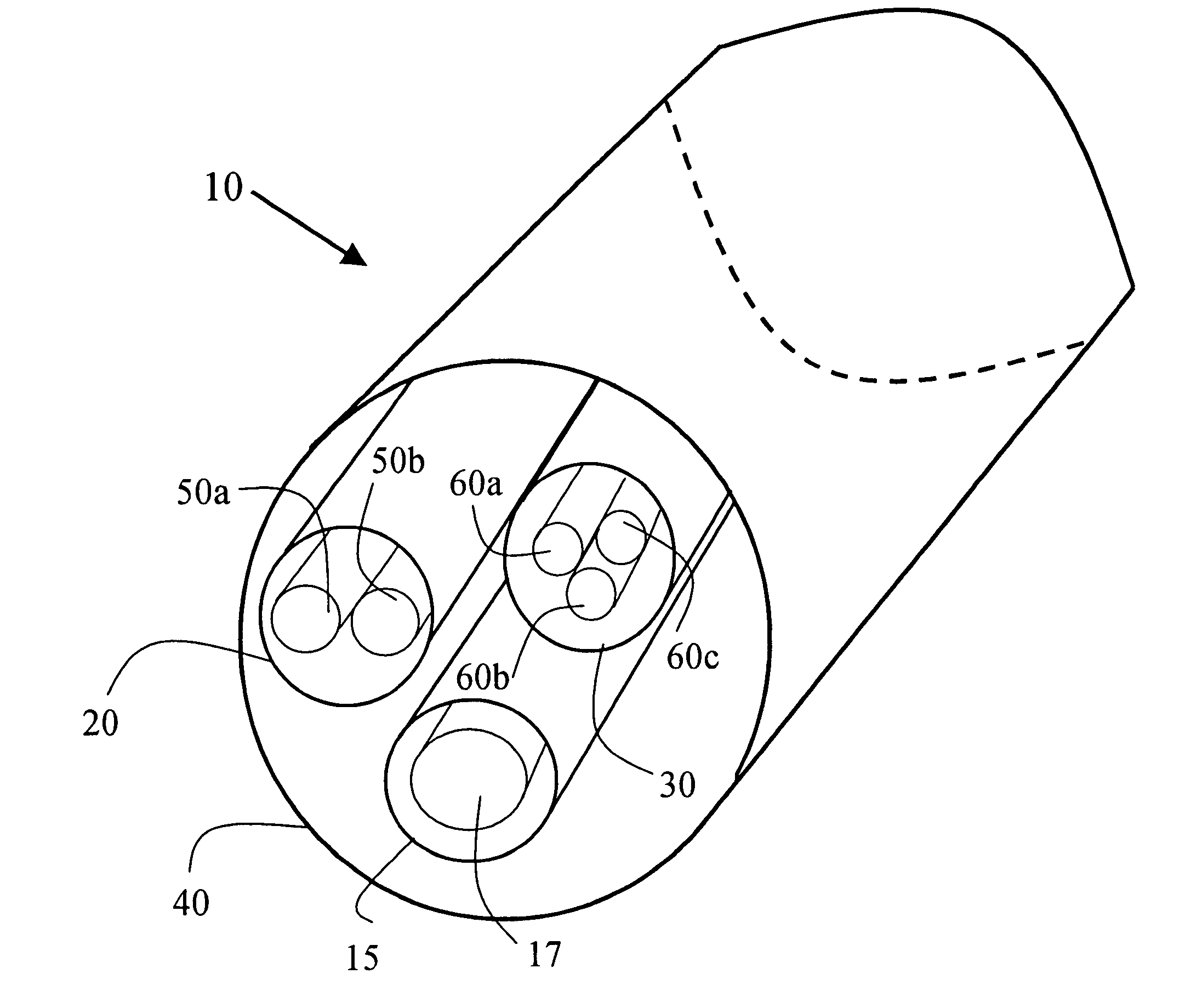
Active cables are copper cables for data transmission that use an electronic circuit to boost the performance of the cable. Without an electronic circuit a cable is considered a 'passive' cable. Passive cables are liable to degrade the data they carry, due to "channel impairments" including attenuation, crosstalk and group velocity distortion. In active cables, a circuit using one or several integrated circuits is embedded in the cable to compensate for some or all of these impairments. This active boosting allows cables to be more compact, thinner, longer and transmit data faster than their passive equivalents.
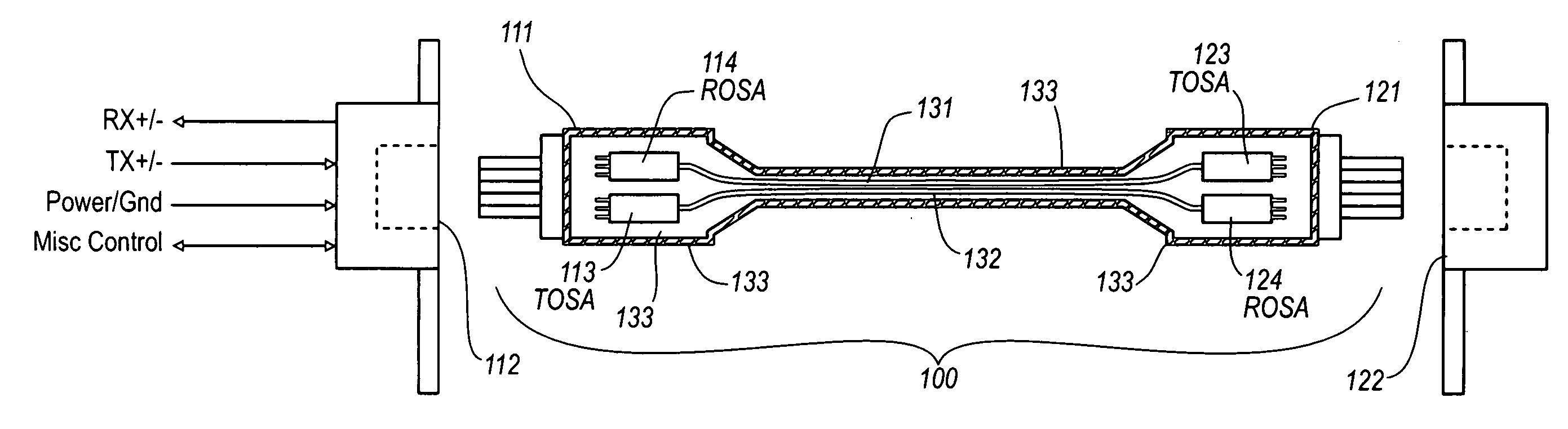
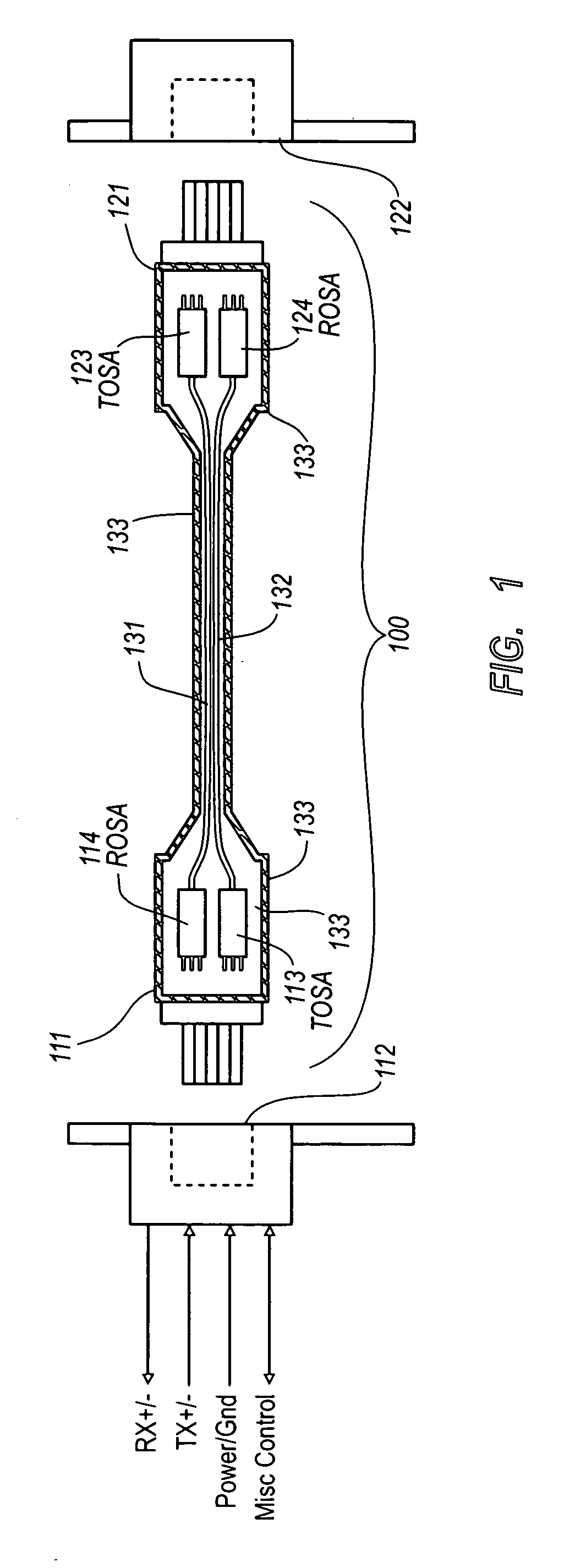
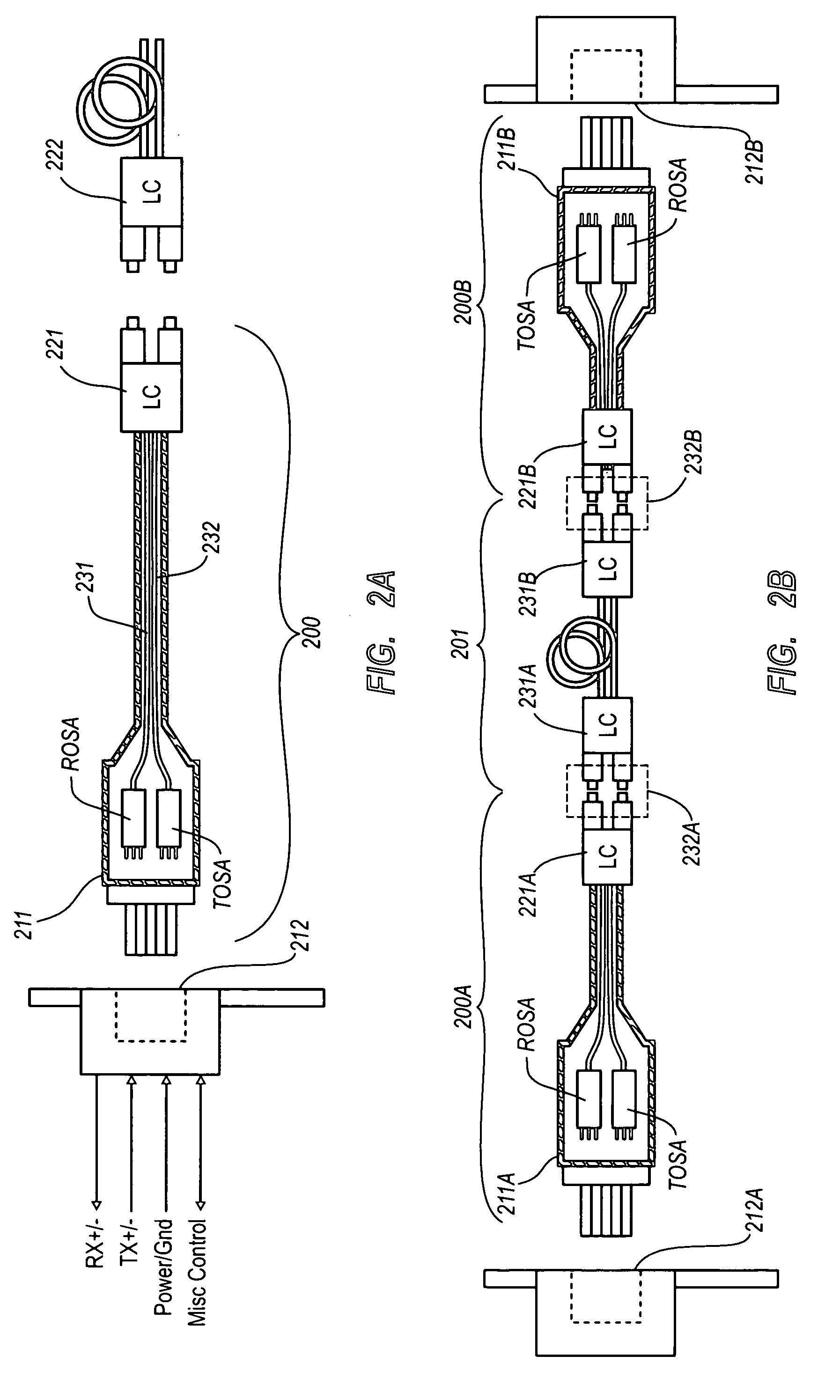
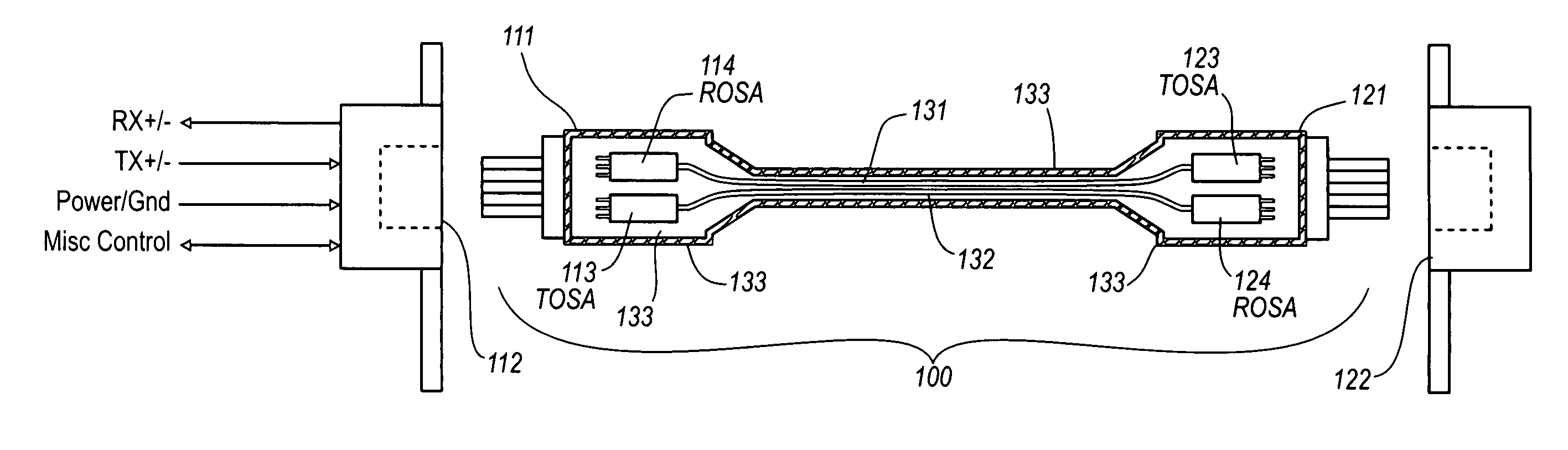
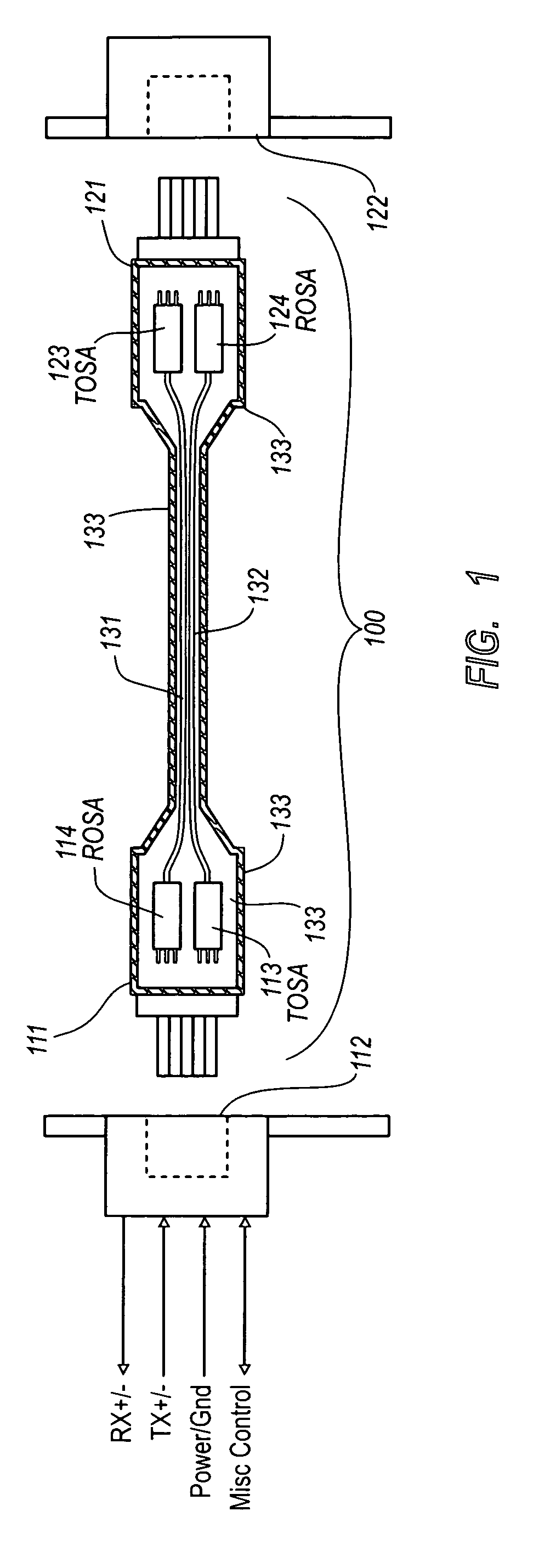
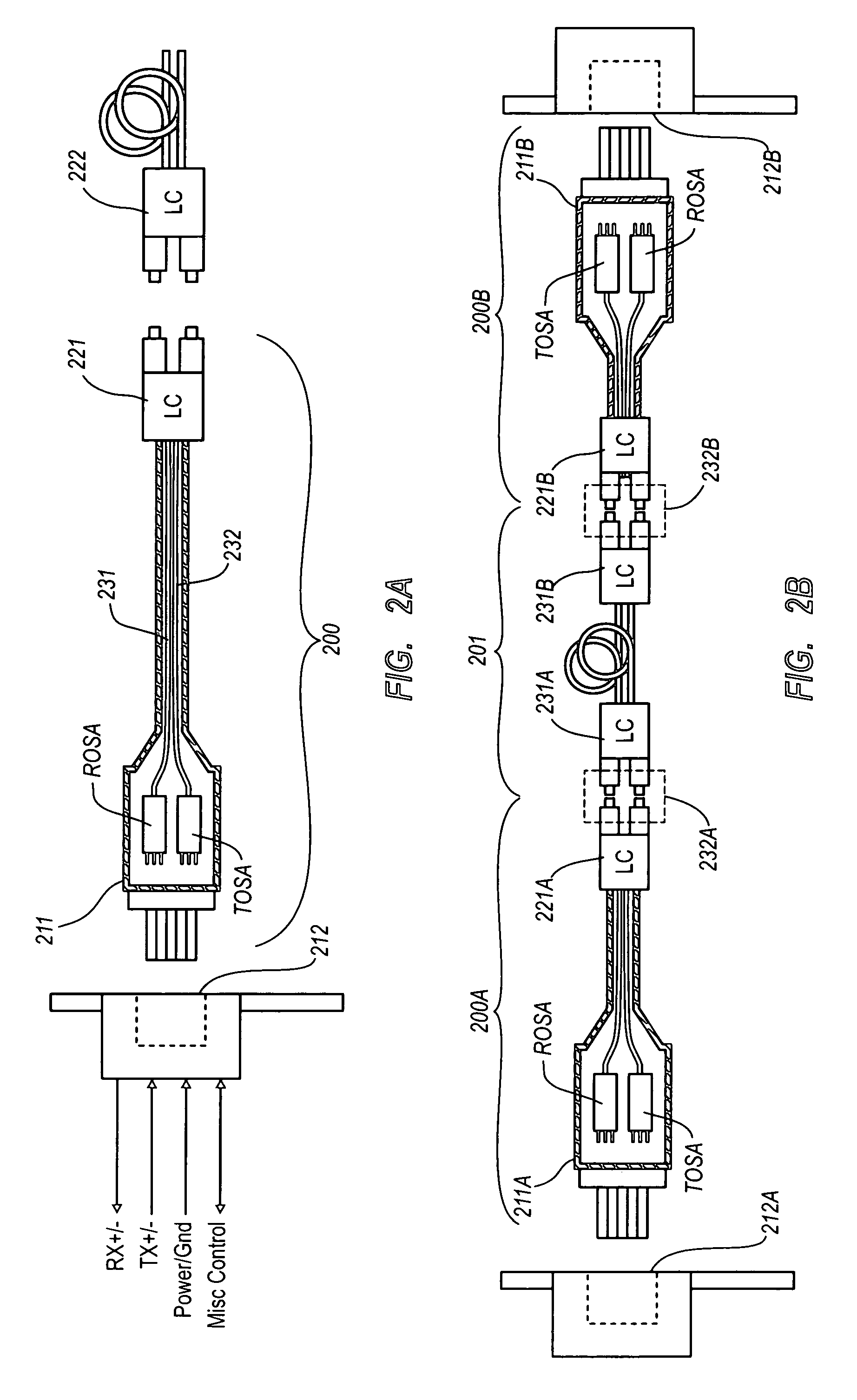
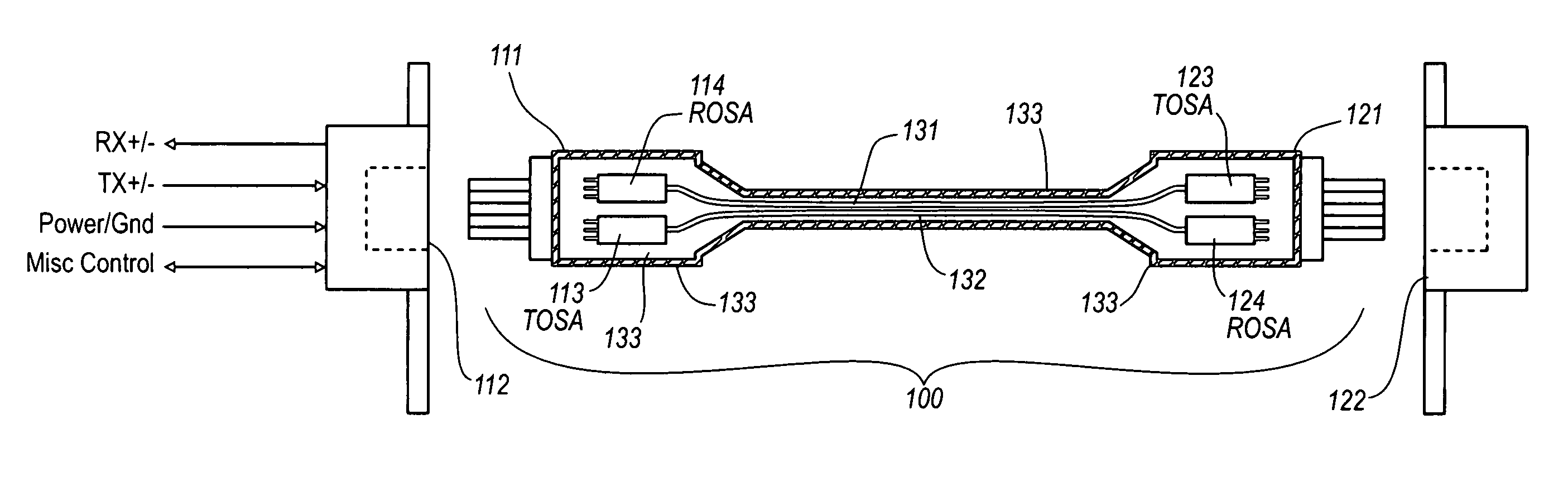
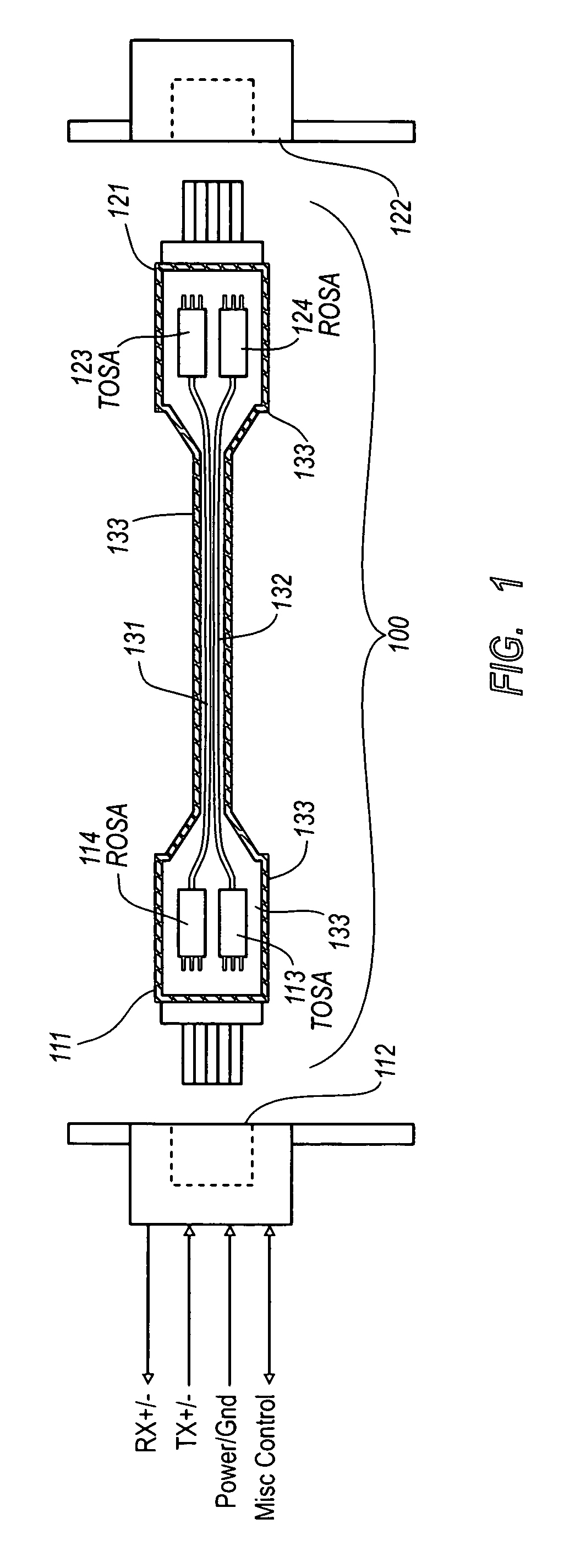
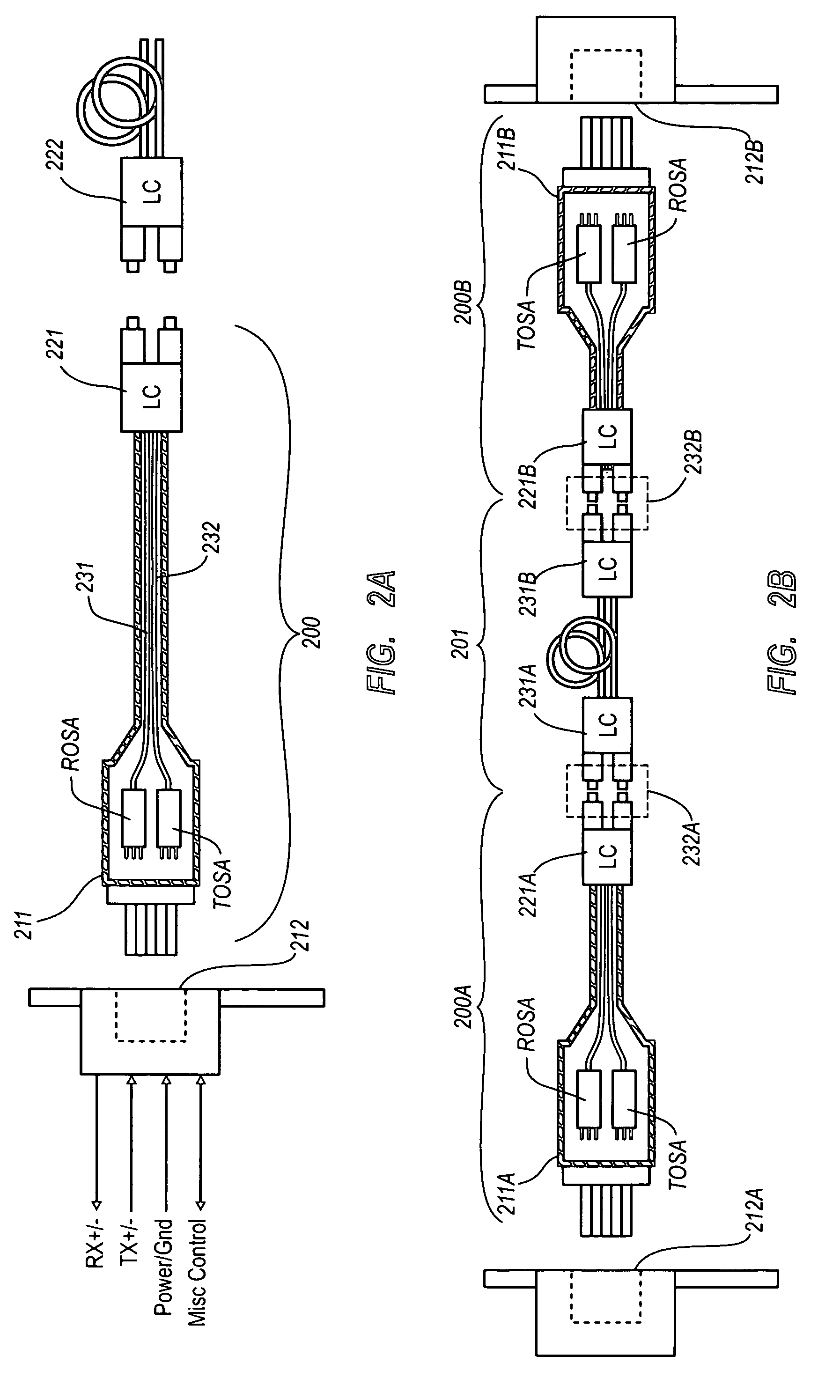
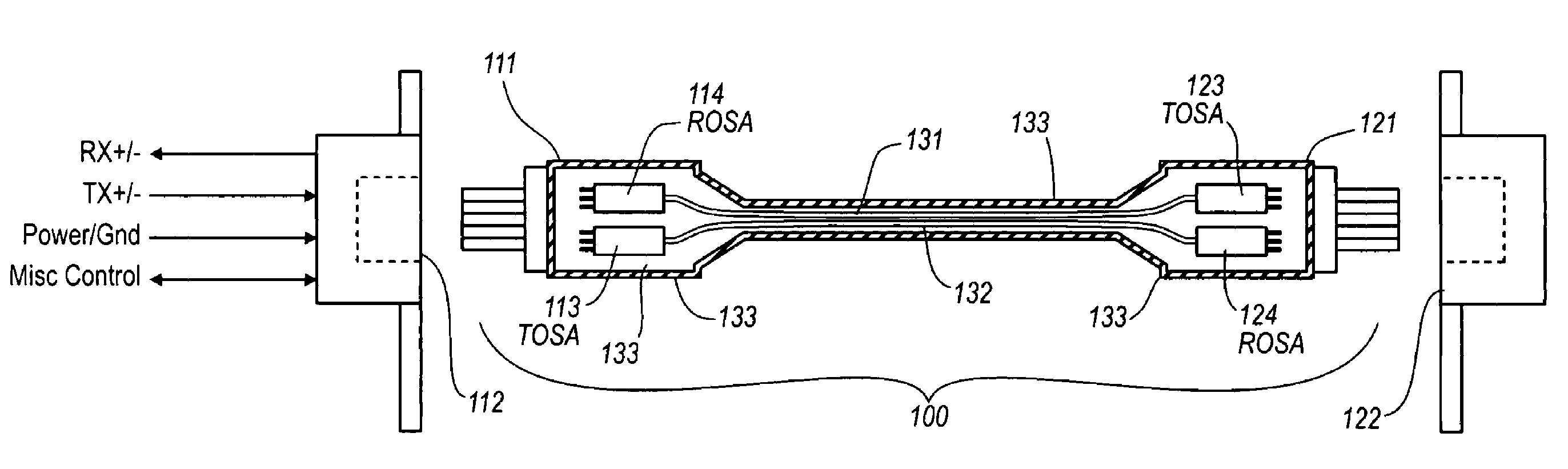
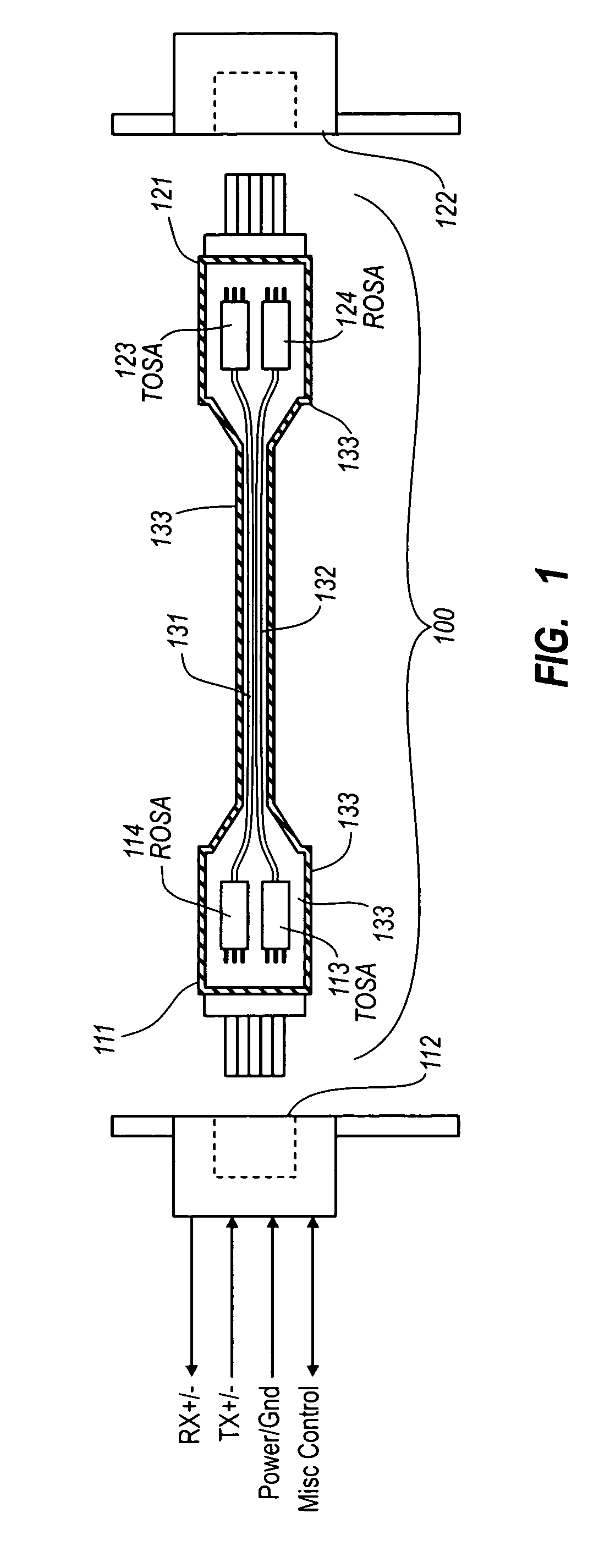
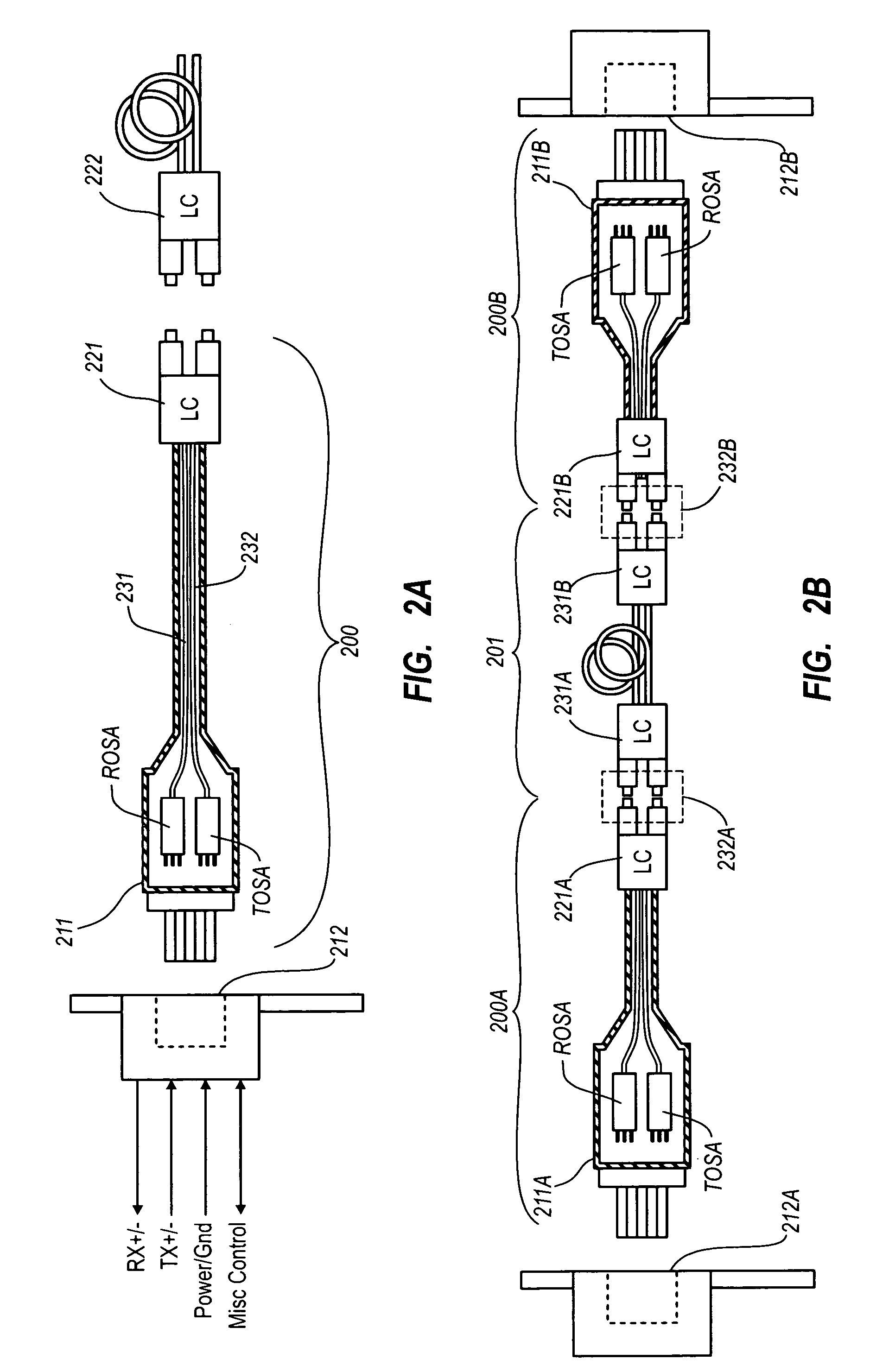
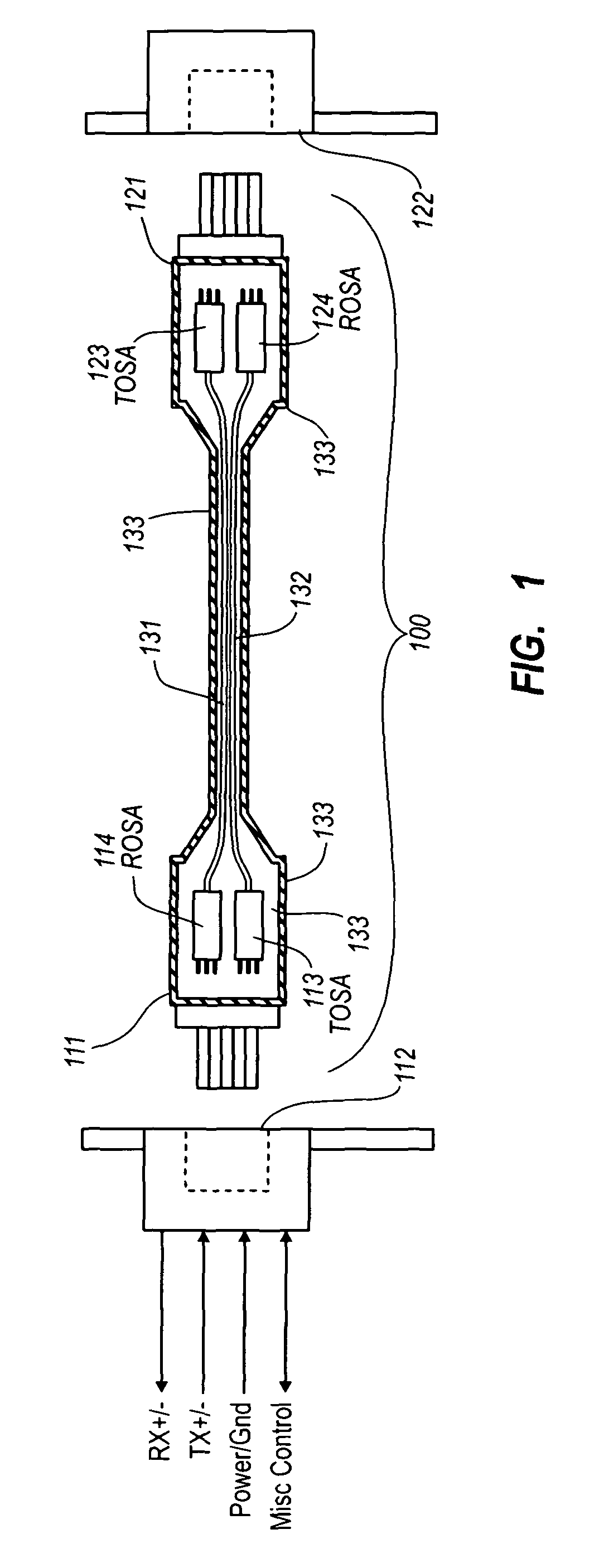
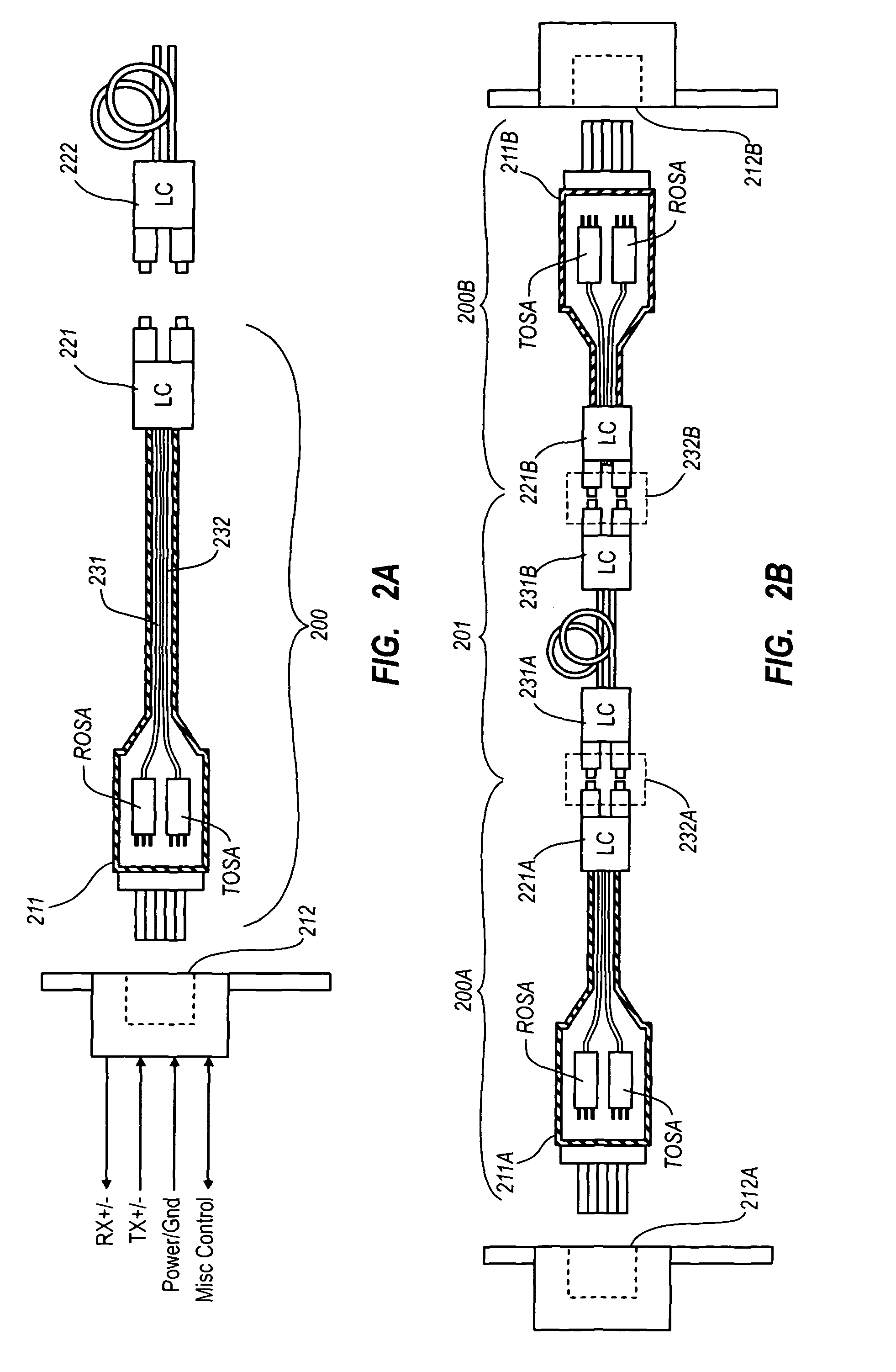
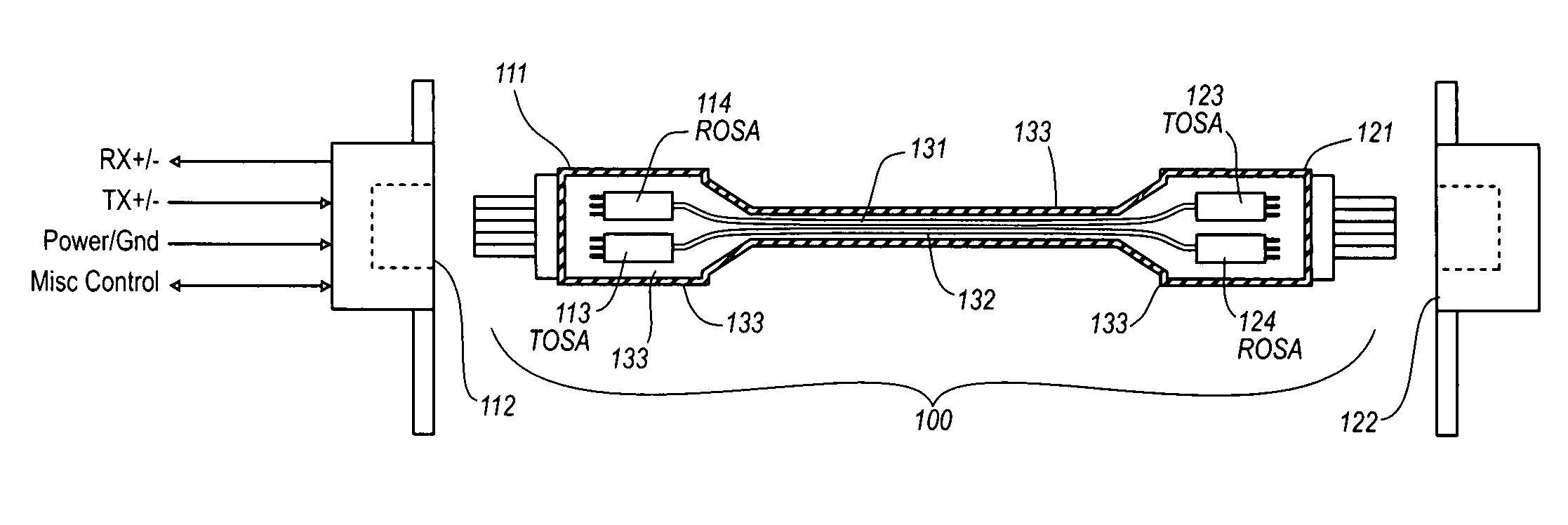
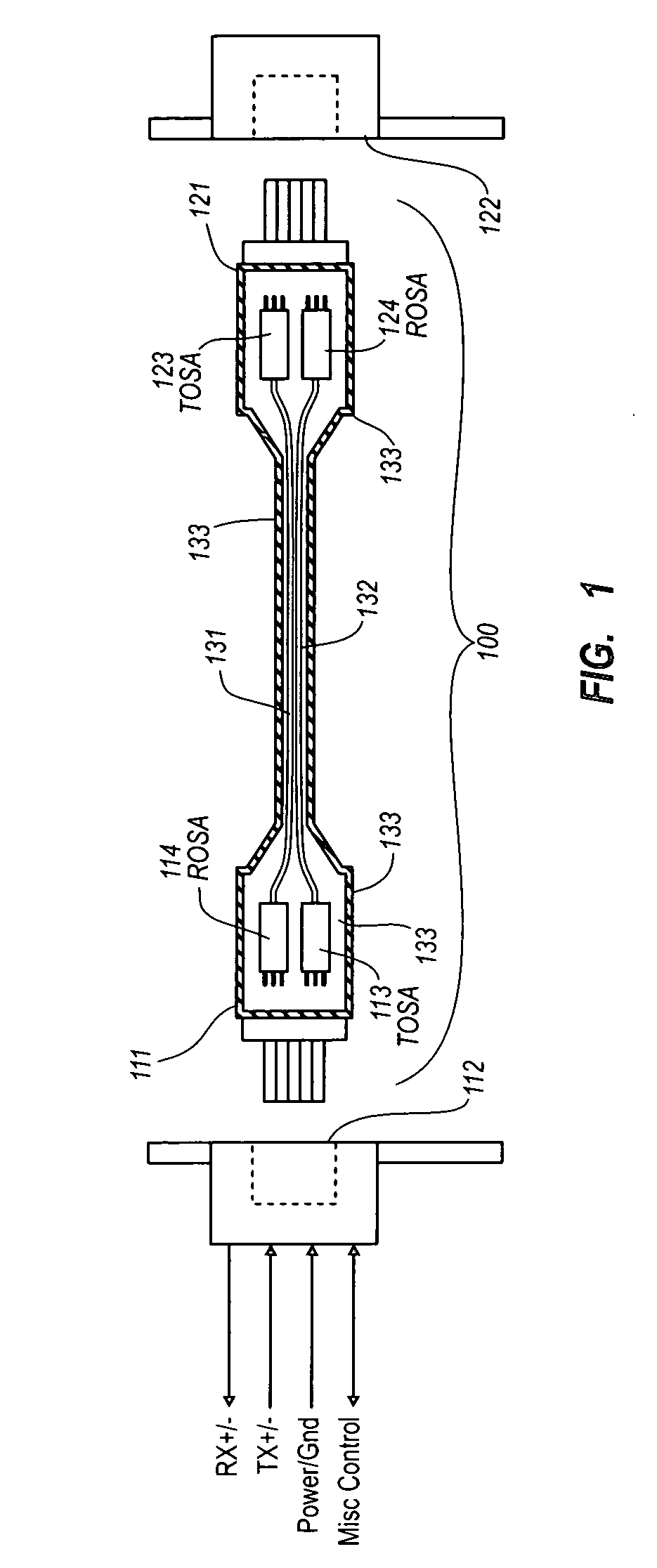
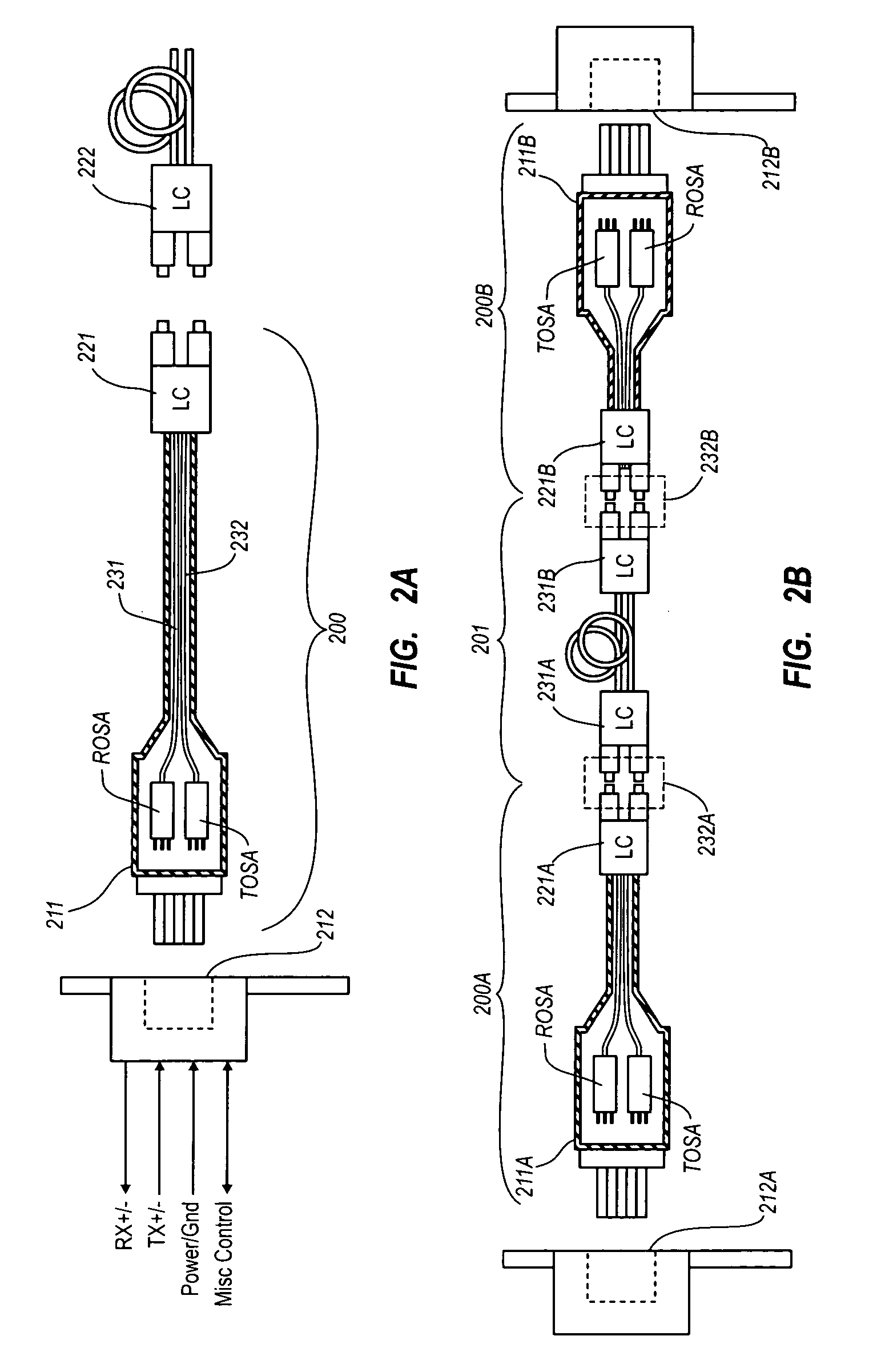
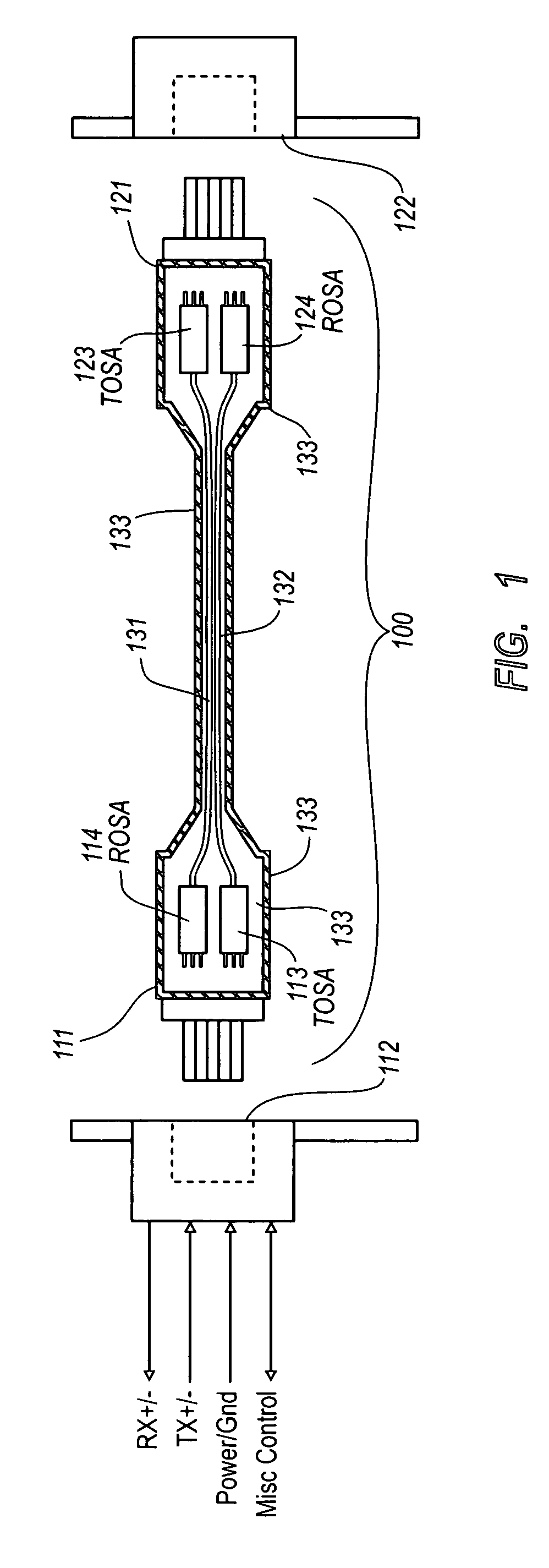
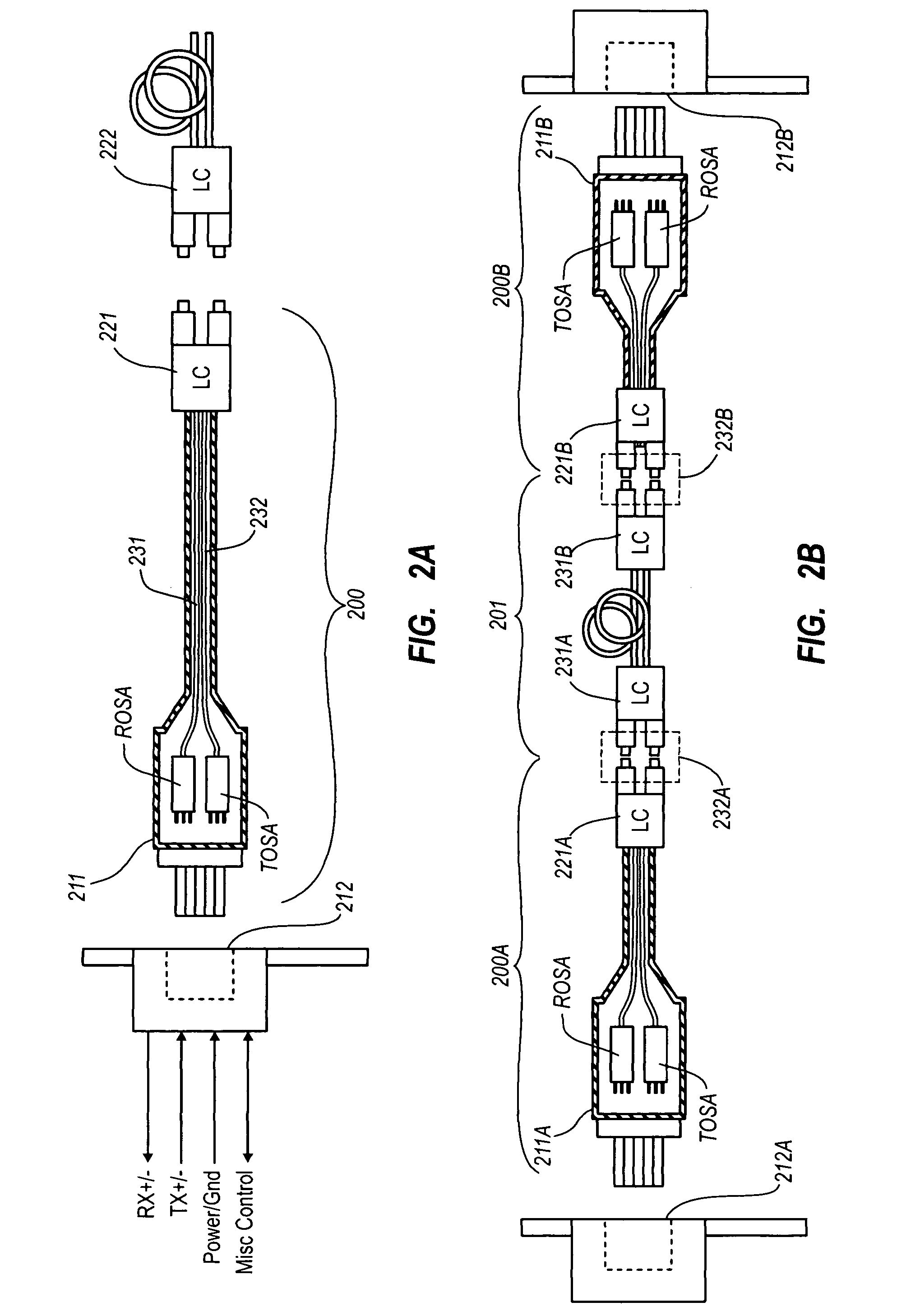
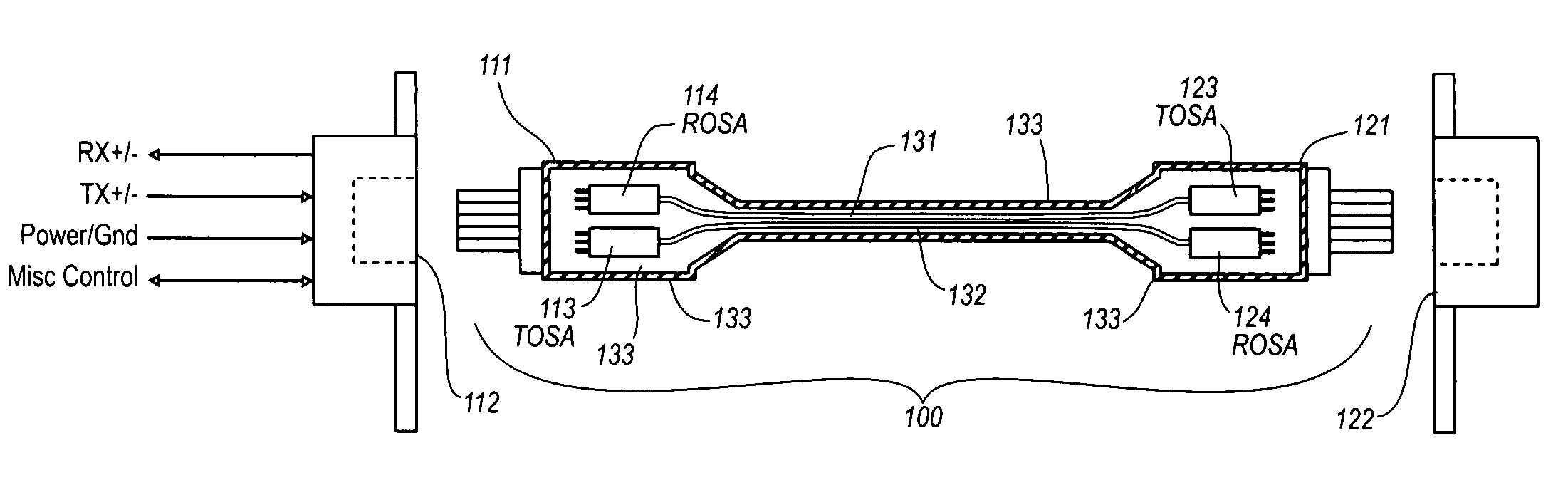
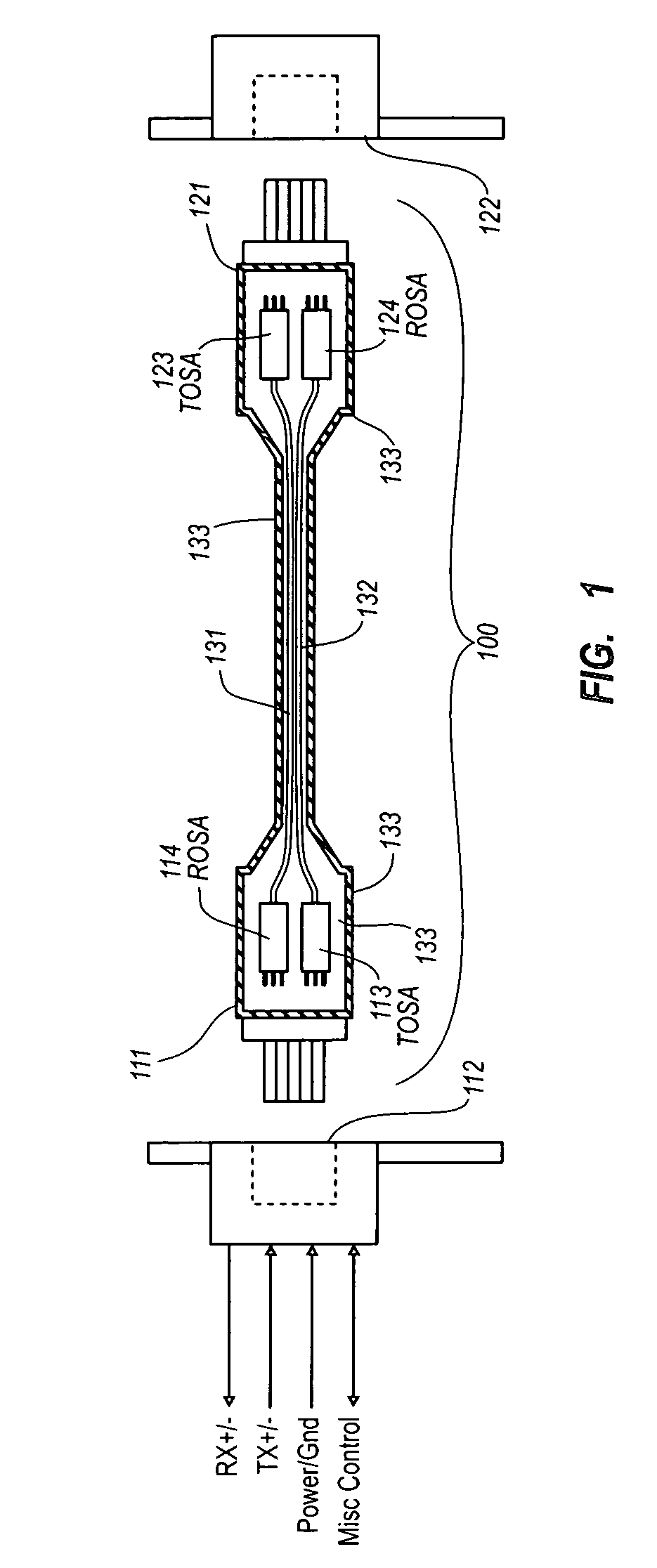
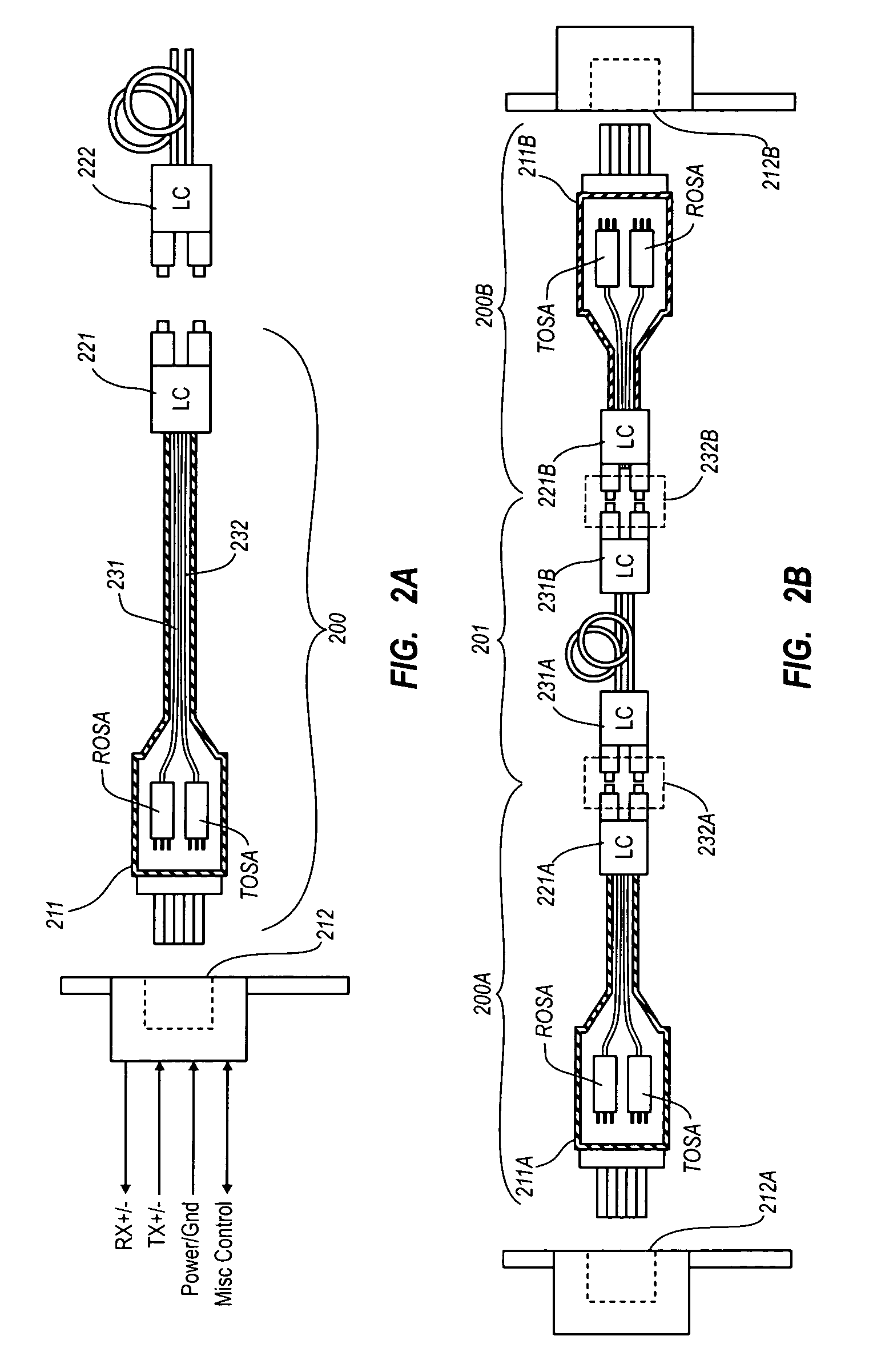
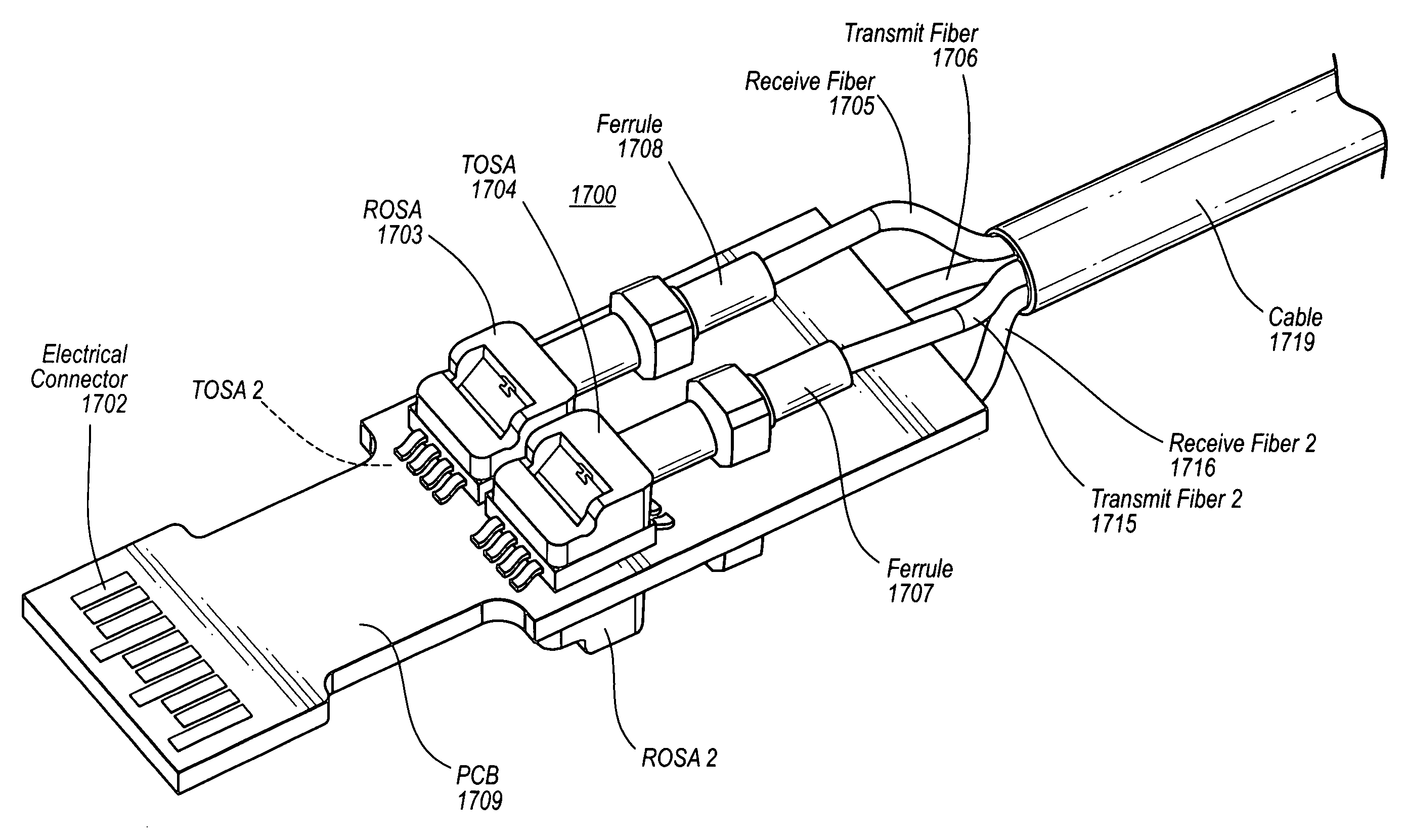
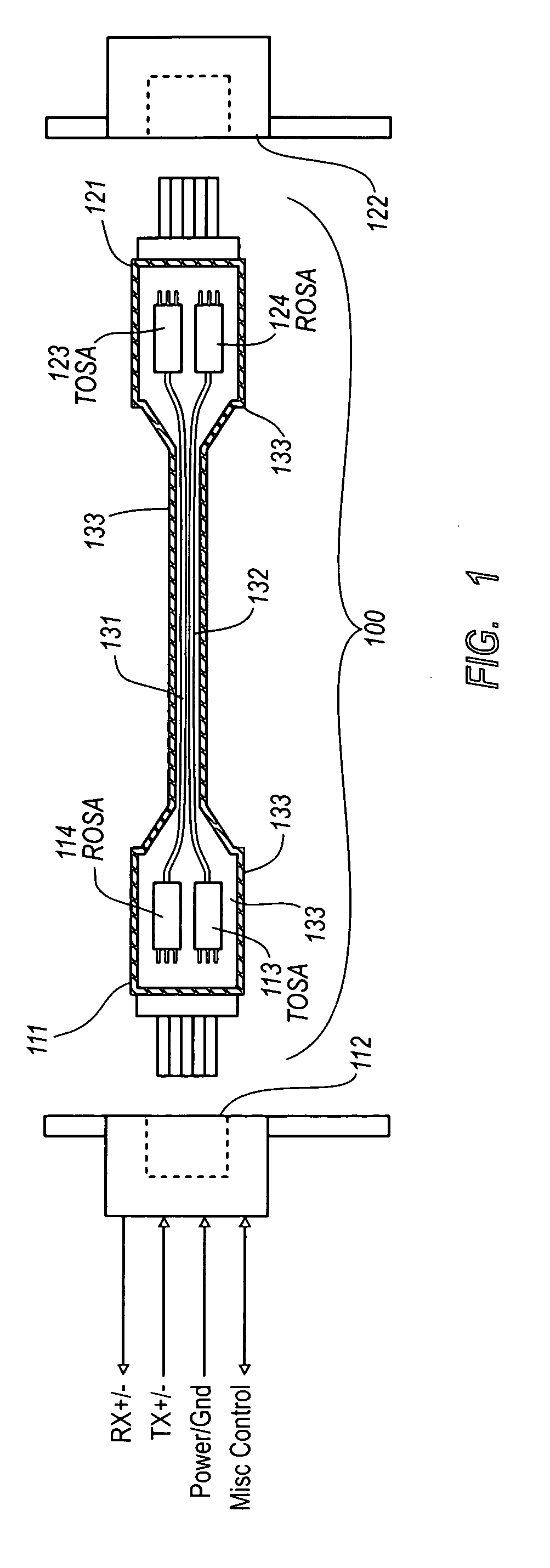
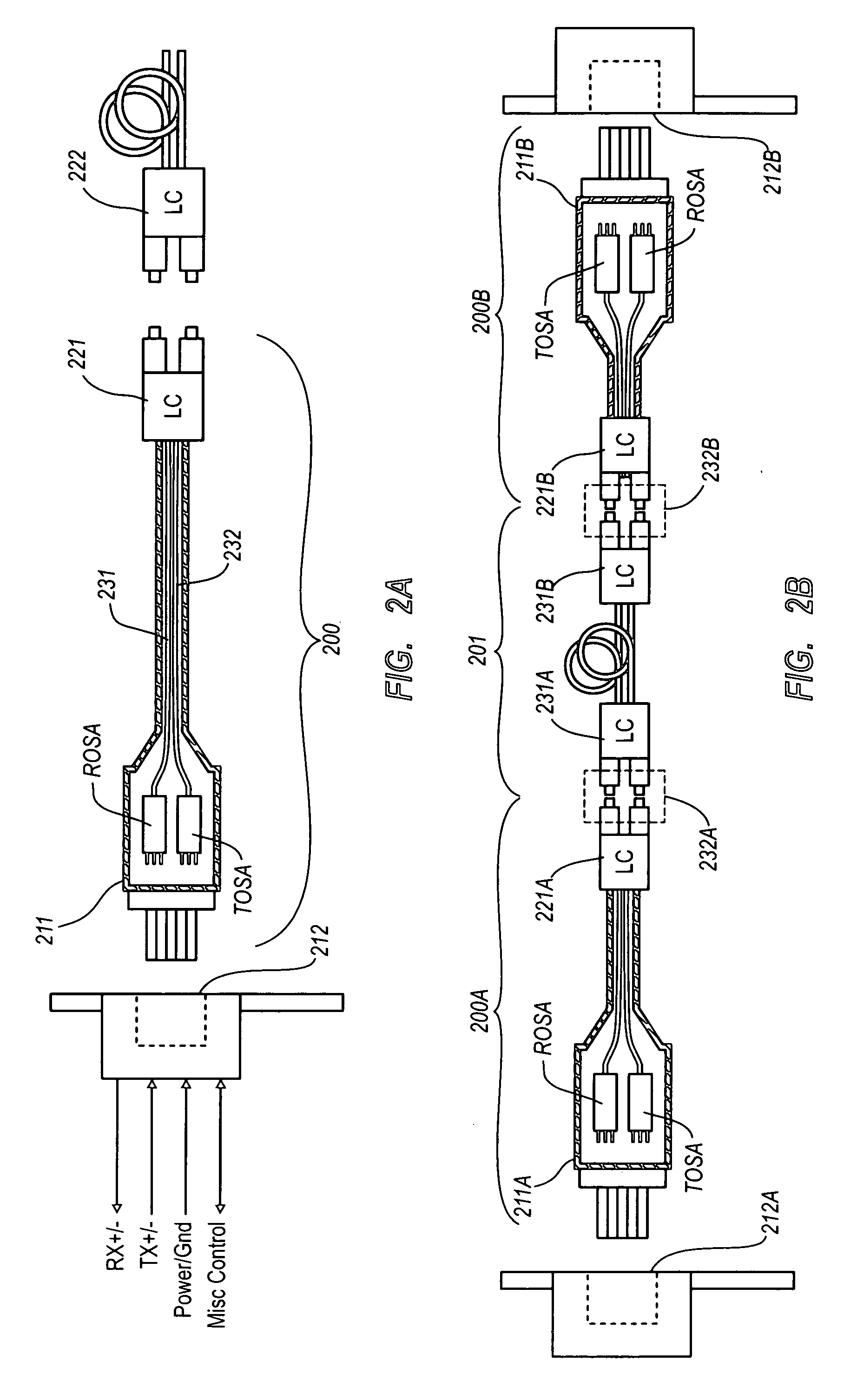
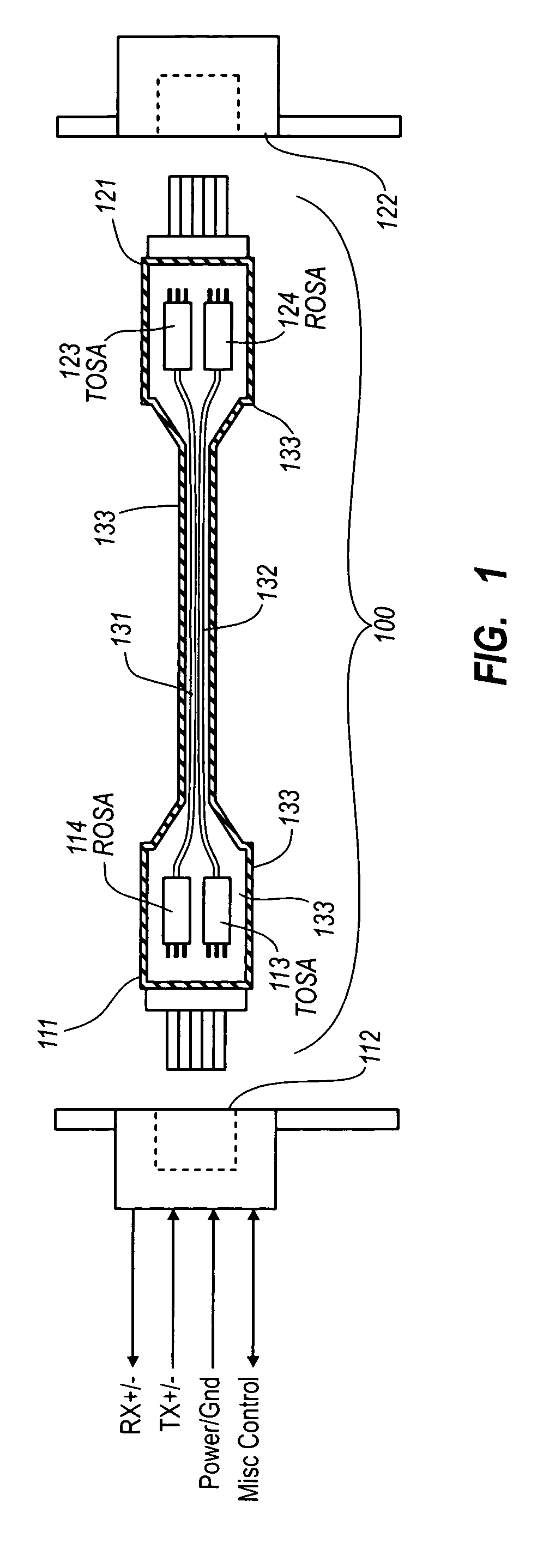
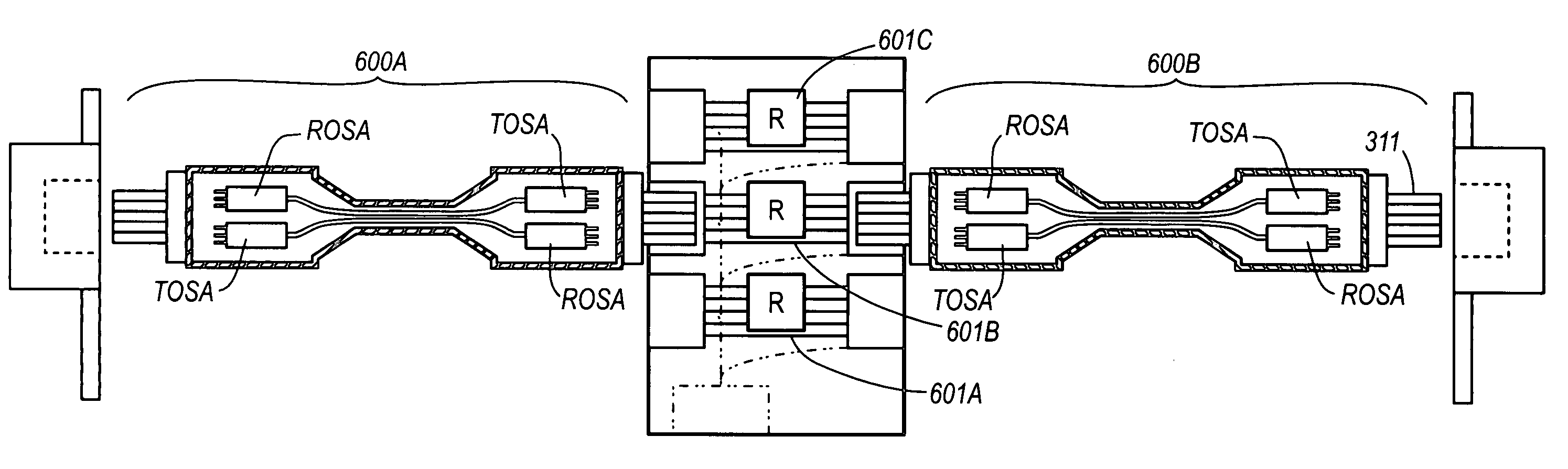
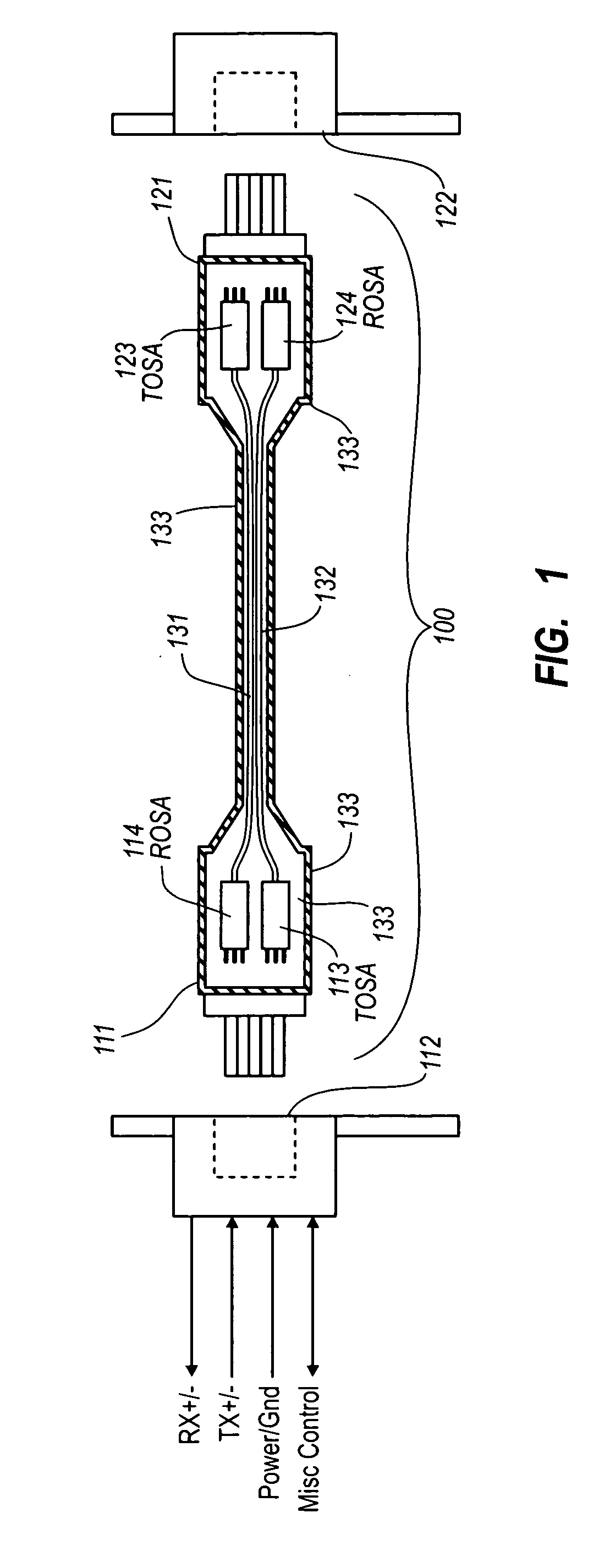
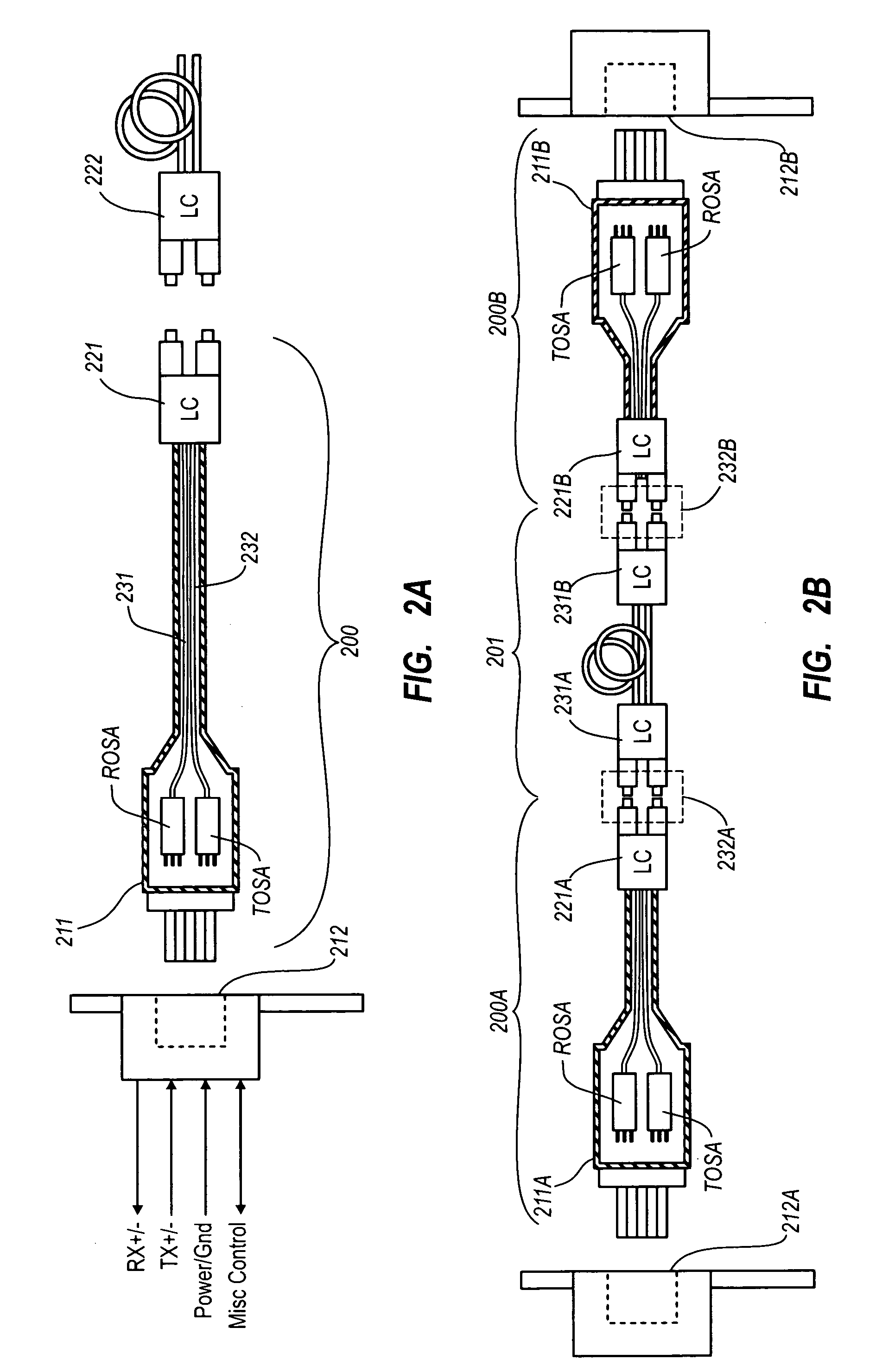
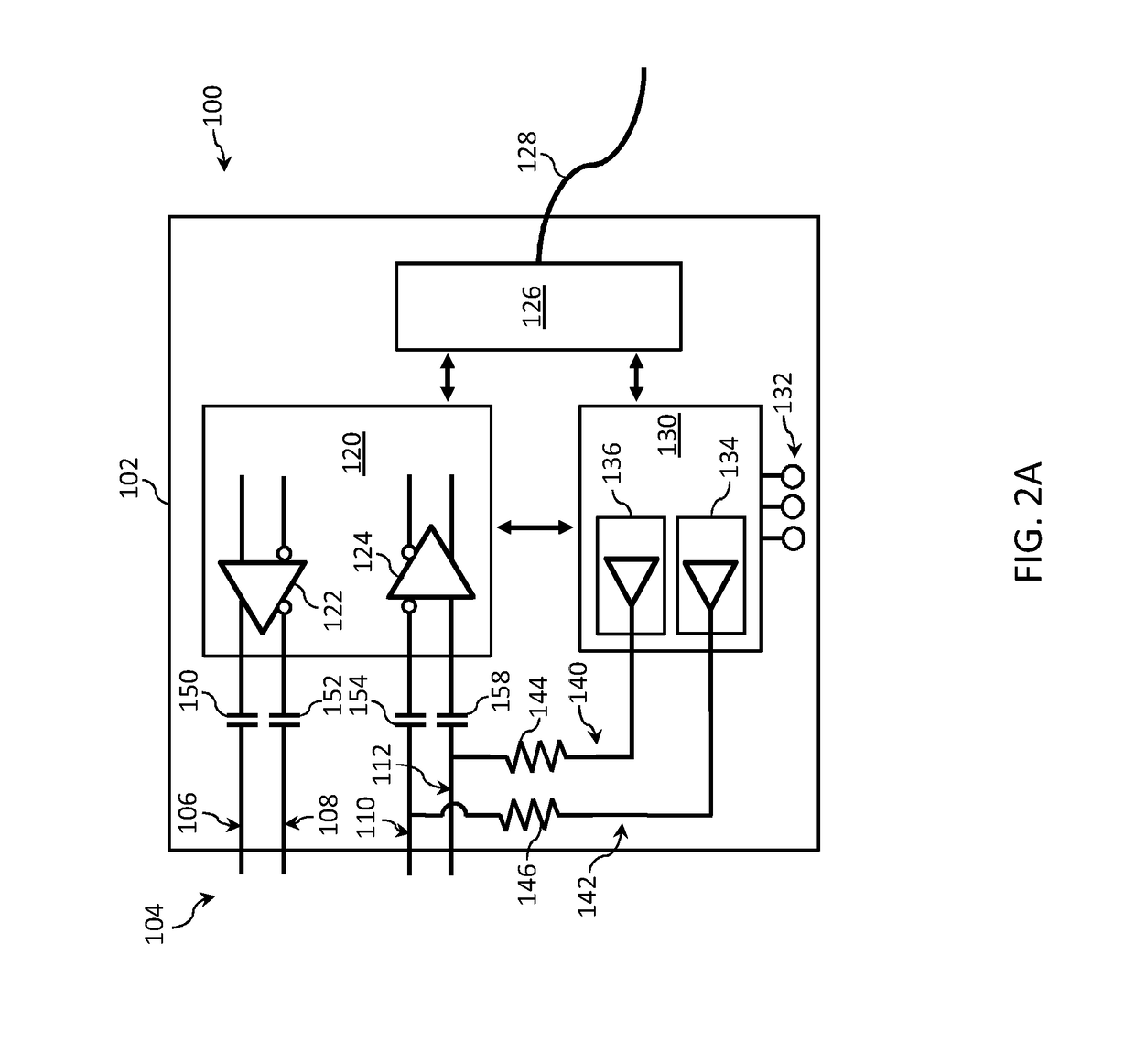
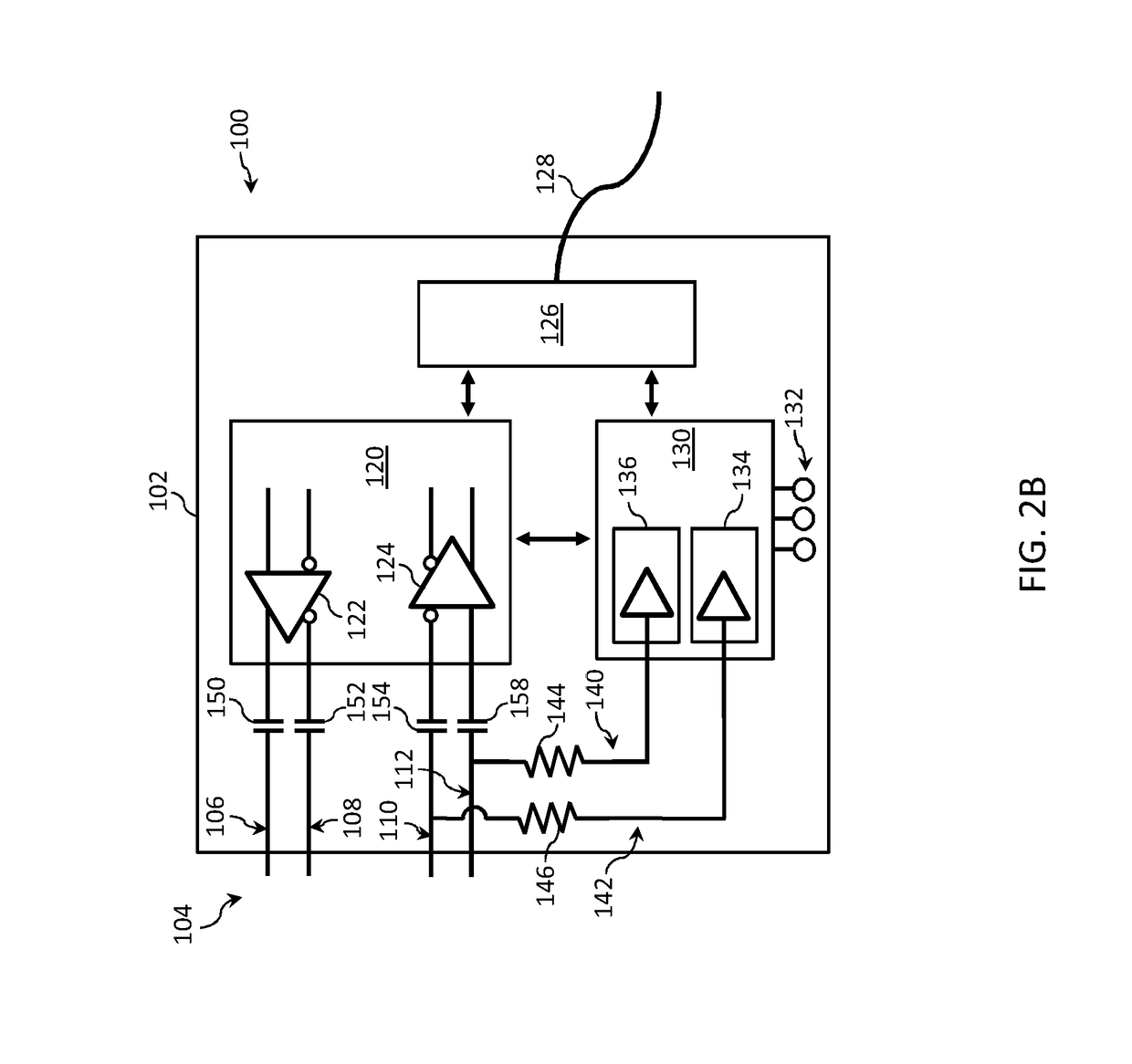
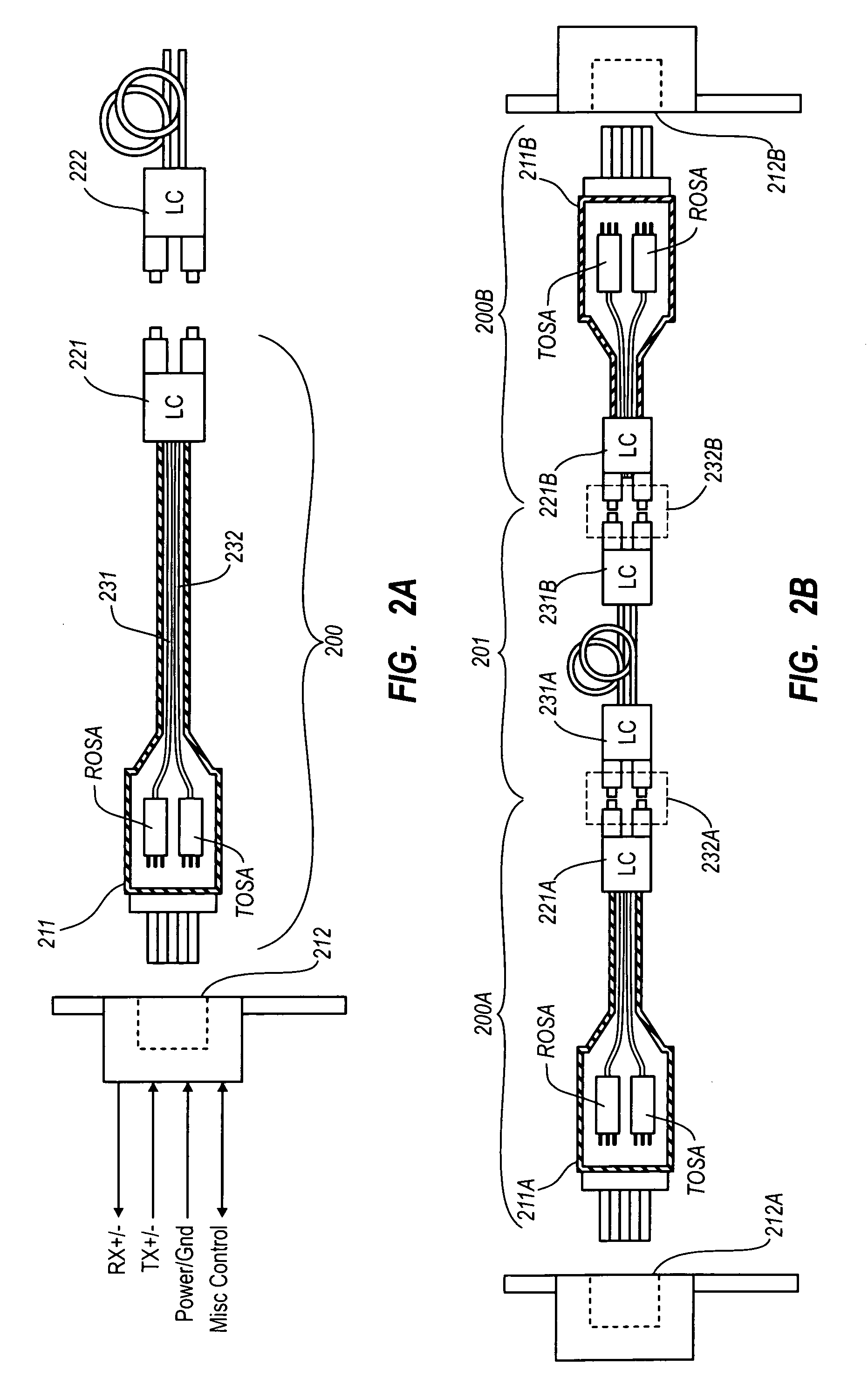
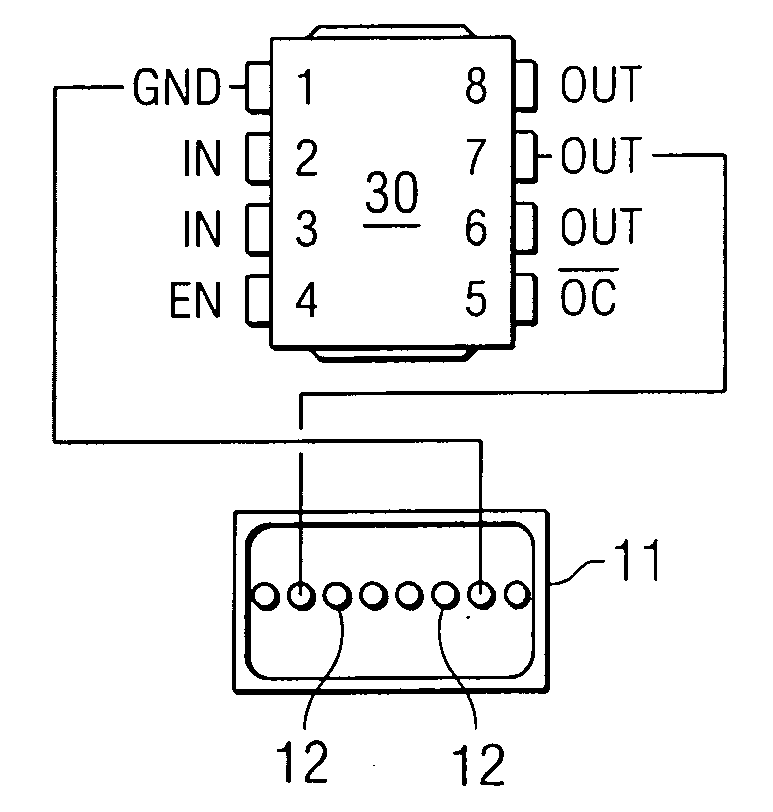
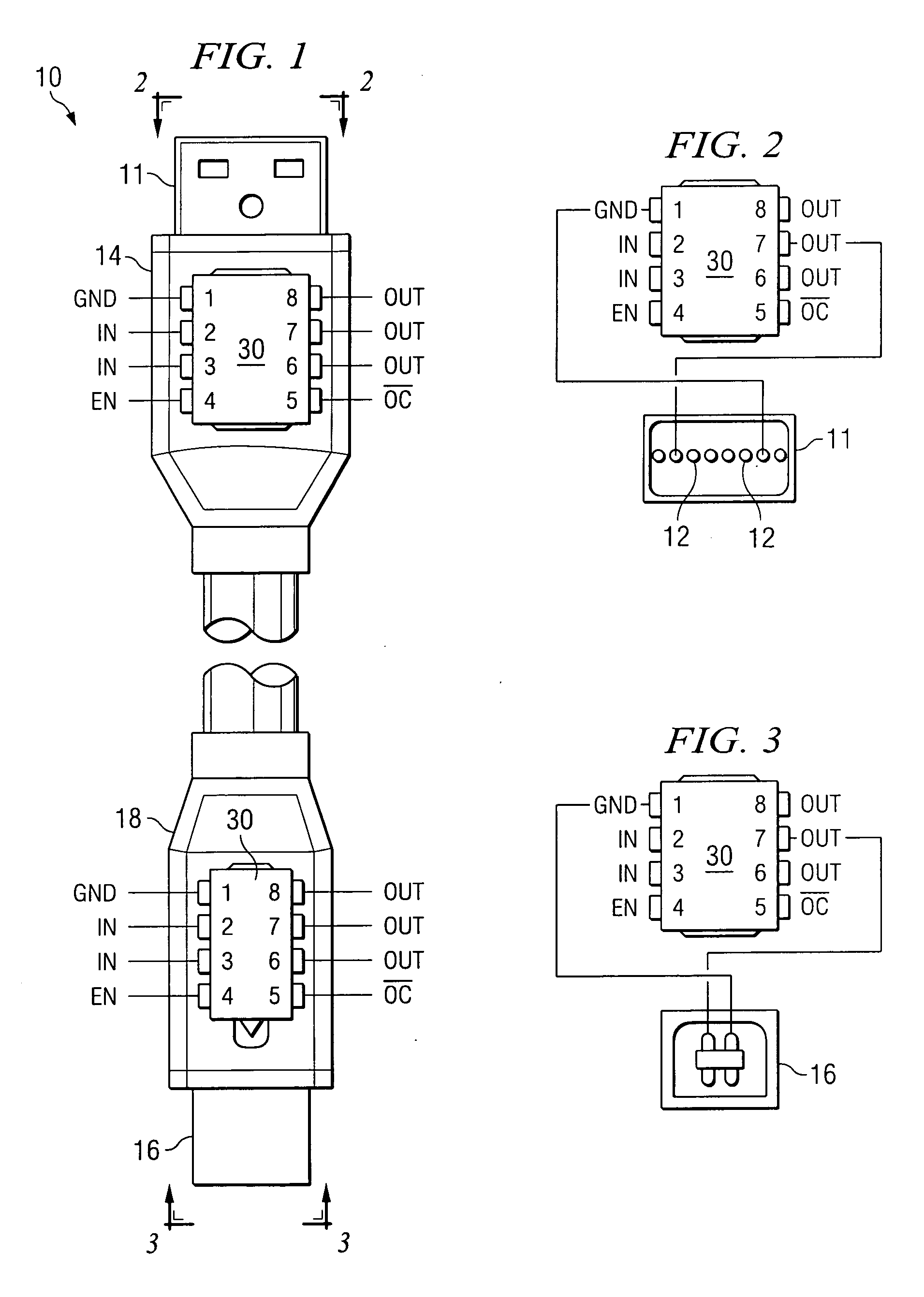
Active optical cable with electrical connector
ActiveUS20070237470A1Well formedAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsCoupling light guidesElectricityElectrical connector
An active cable that communicates over much of its length using one or more optical fibers, but which includes at integrated electrical connector at least one of its ends. The cable may be an electrical to optical cable, and electrical to electrical cable, or one of many other potential configurations.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
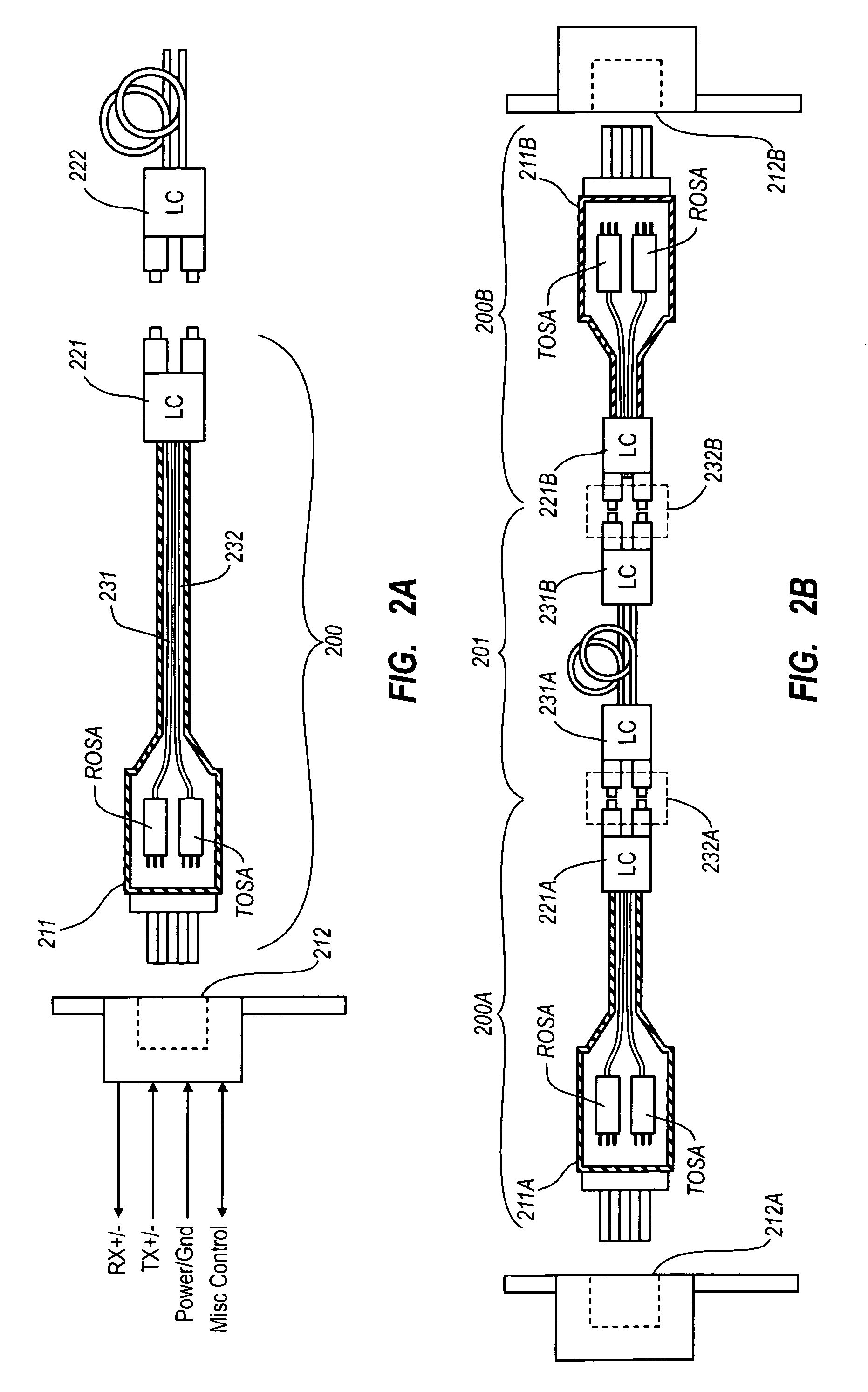
Electrical-optical active optical cable
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
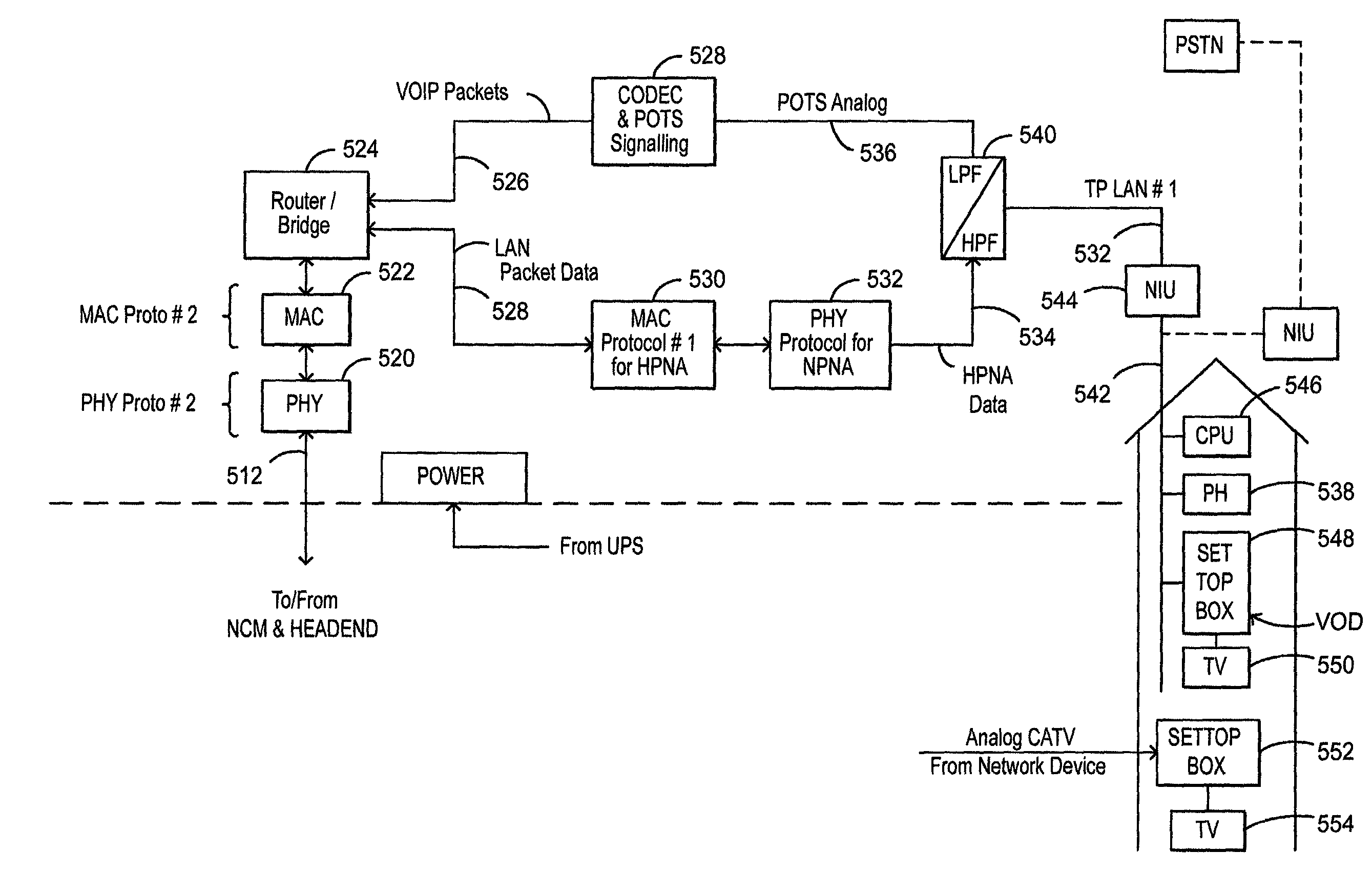
Active cable modem outside customer premises servicing multiple customer premises
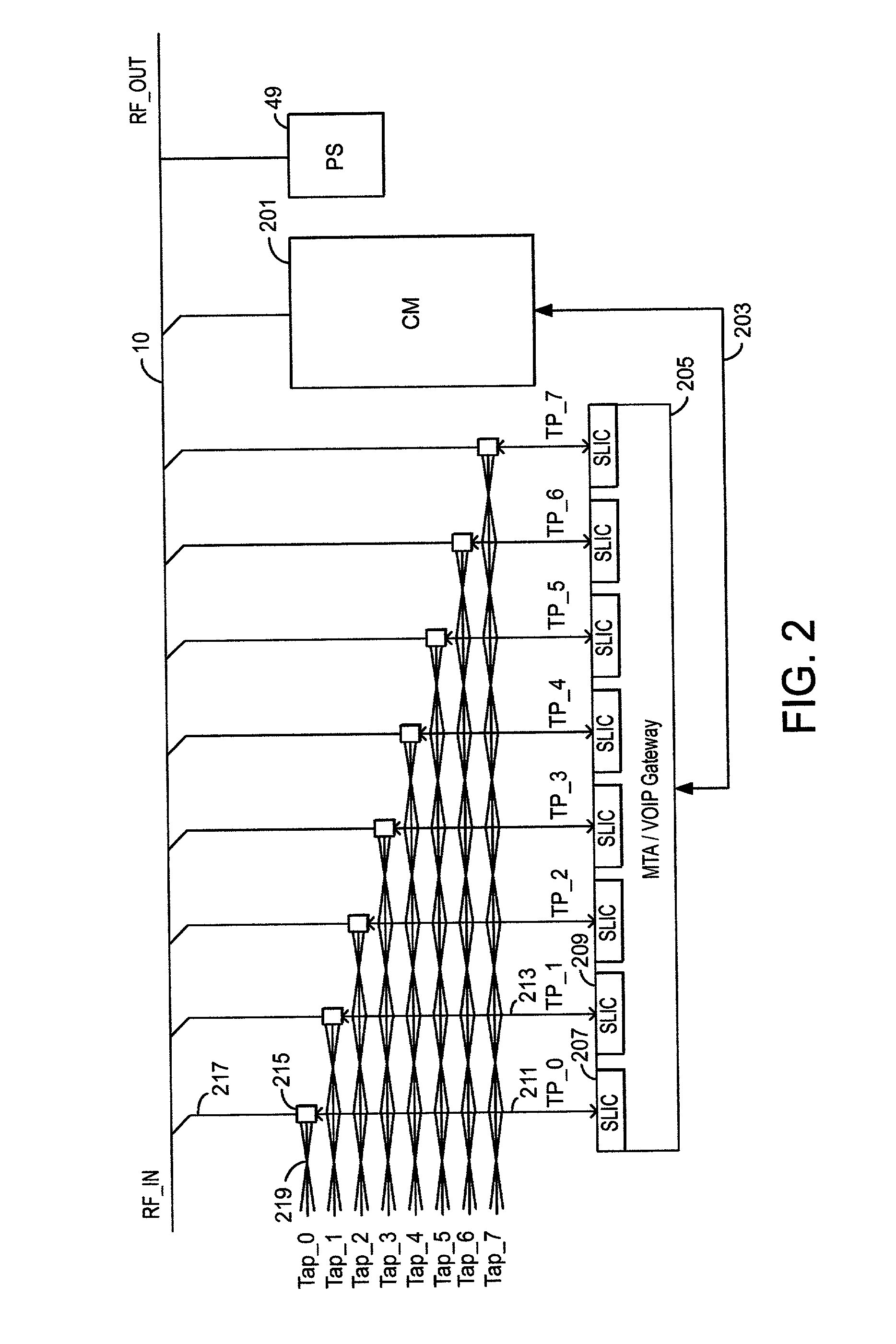
InactiveUS7007296B2Affect numberAvoiding inefficiency of collisionTwo-way working systemsElectrical cable transmission adaptationDigital dataModem device
A signal distribution system to save on the cost of cable modems for cable TV headend operators who wish to deliver broadband digital data services, DSL, video-on-demand or POTS service over their HFC CATV delivery networks. All species within the genus have a shared cable modem and a filtration and combining circuit comprised of a plurality of diplexer filters or junction boxes or both which mix baseband packet data with analog CATV signals onto coax drop lines coupled to the various subscribers and connect POTS or DSL signals onto twisted pair portions of siamese cables. Various species have the cable modem feeding digital data or packets of DOCSIS or other data or digitized DSL signals sent over the HFC to the cable modem or digitized POTS signals send over the HFC to the cable modem to either a packet switch, a DSL concentrator, a voice-over-IP gateway or some combination of the above. This data is either delivered to each subscriber as LAN packets or analog POTS signals or DSL signals or some combination of the above using coaxial cable or siamese cable drop lines.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Active optical cable with electrical connector
An active cable that communicates over much of its length using one or more optical fibers, but which includes at integrated electrical connector at least one of its ends. The cable may be an electrical to optical cable, and electrical to electrical cable, or one of many other potential configurations.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Active optical cable with integrated eye safety
An active cable that is configured to communicate over much of its length using one or more optical fibers, and that includes an integrated electrical connector at at least one end. The active cable includes an integrated eye safety controls to thereby reduce the chance of injury should the active cable be severed, or otherwise unplugged at an optical end, if any. The cable may be an electrical to optical cable, and electrical to electrical cable, or one of many other potential configurations.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Active optical cable electrical adaptor
An adaptor that mechanically and / or electrically adapts to and / or from an electrical connector that is integrated with an active cable at one end of an active optical cable, wherein the optical cable is configured to communicate over much of its length using one or more optical fibers. The cable may be an electrical to optical cable, and electrical to electrical cable, or one of many other potential configurations.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Active optical cable electrical connector
ActiveUS20070237472A1Well formedCoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresElectricityElectrical connector
An electrical connector that is integrated within an active cable at one end of the active cable, wherein the active cable is configured to communicate over much of its length using one or more optical fibers. The cable may be an electrical to optical cable, and electrical to electrical cable, or one of many other potential configurations.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
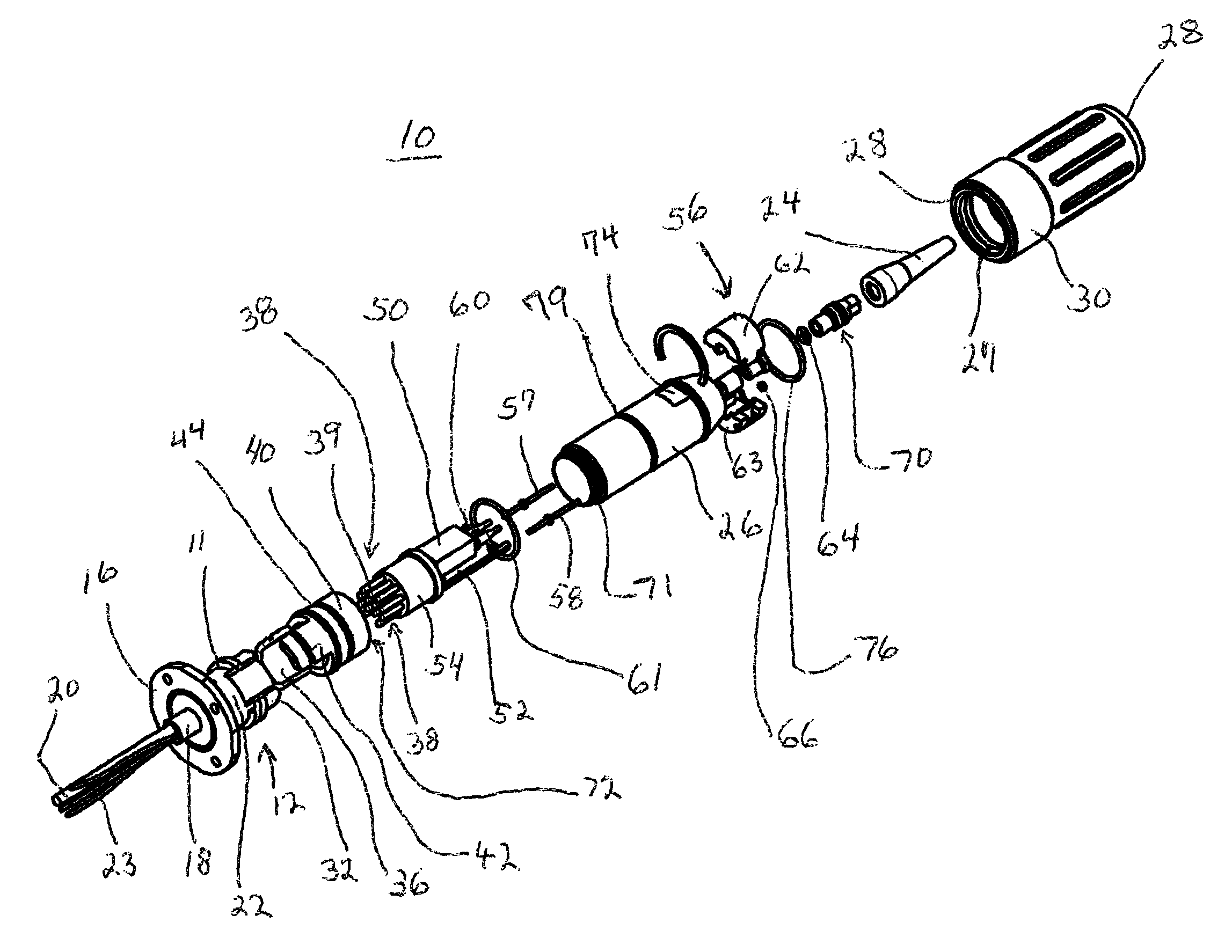
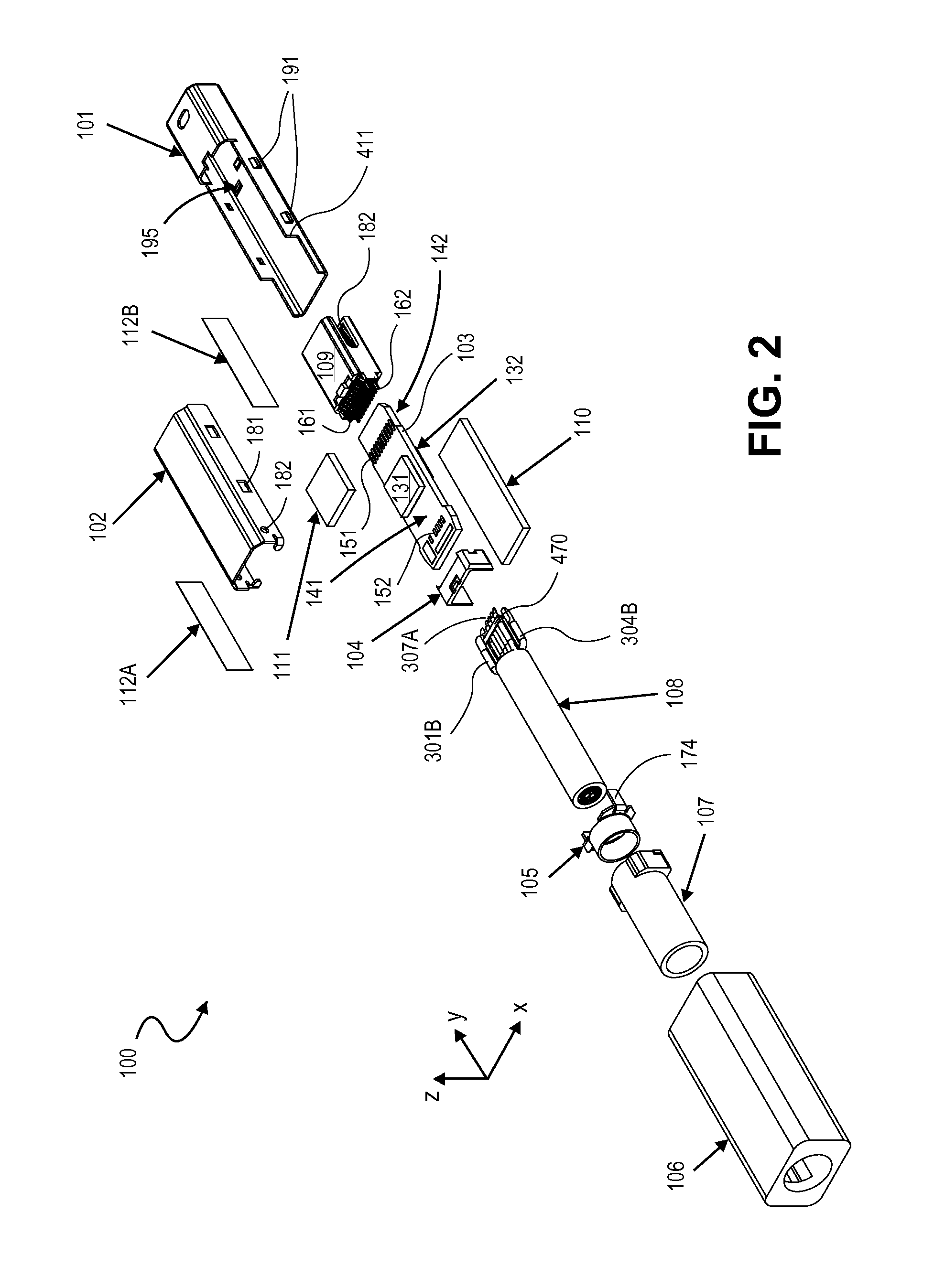
Gigabit wet mate active cable
InactiveUS8792759B2Convenient spacingMinimized in sizeCoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresElectricityTransceiver
A combination of a wet mate electrical connector and a gigabit miniature transceiver in a pressure resistant cable plug connector assembly. The cable plug connector assembly includes a wet mate connector, a miniature gigabit transceiver, and electrical and optical connections necessary to convert transmitted electrical data signals to optical data signals and vice versa.
Owner:ADVANCED FIBER PROD LLC
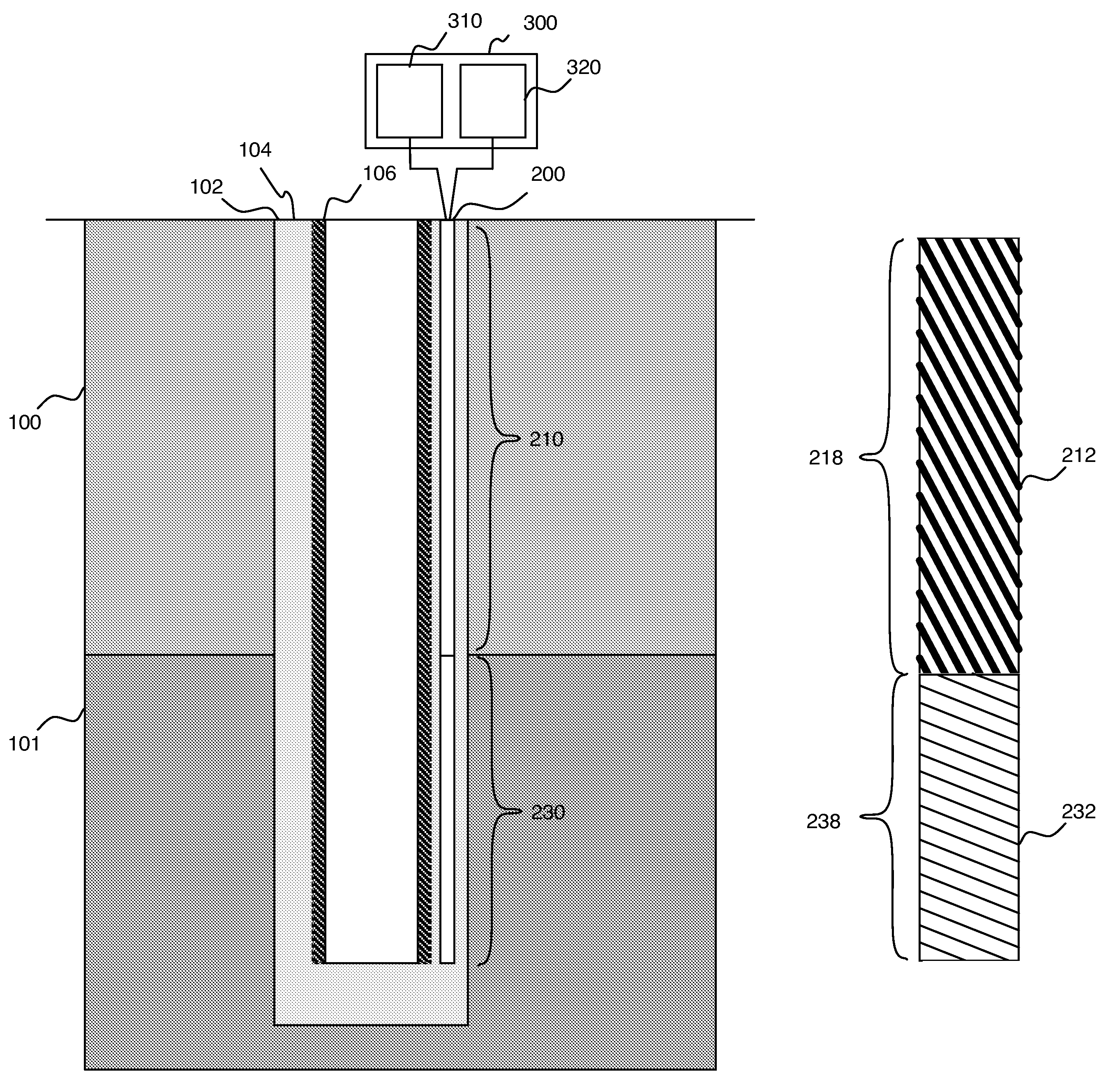
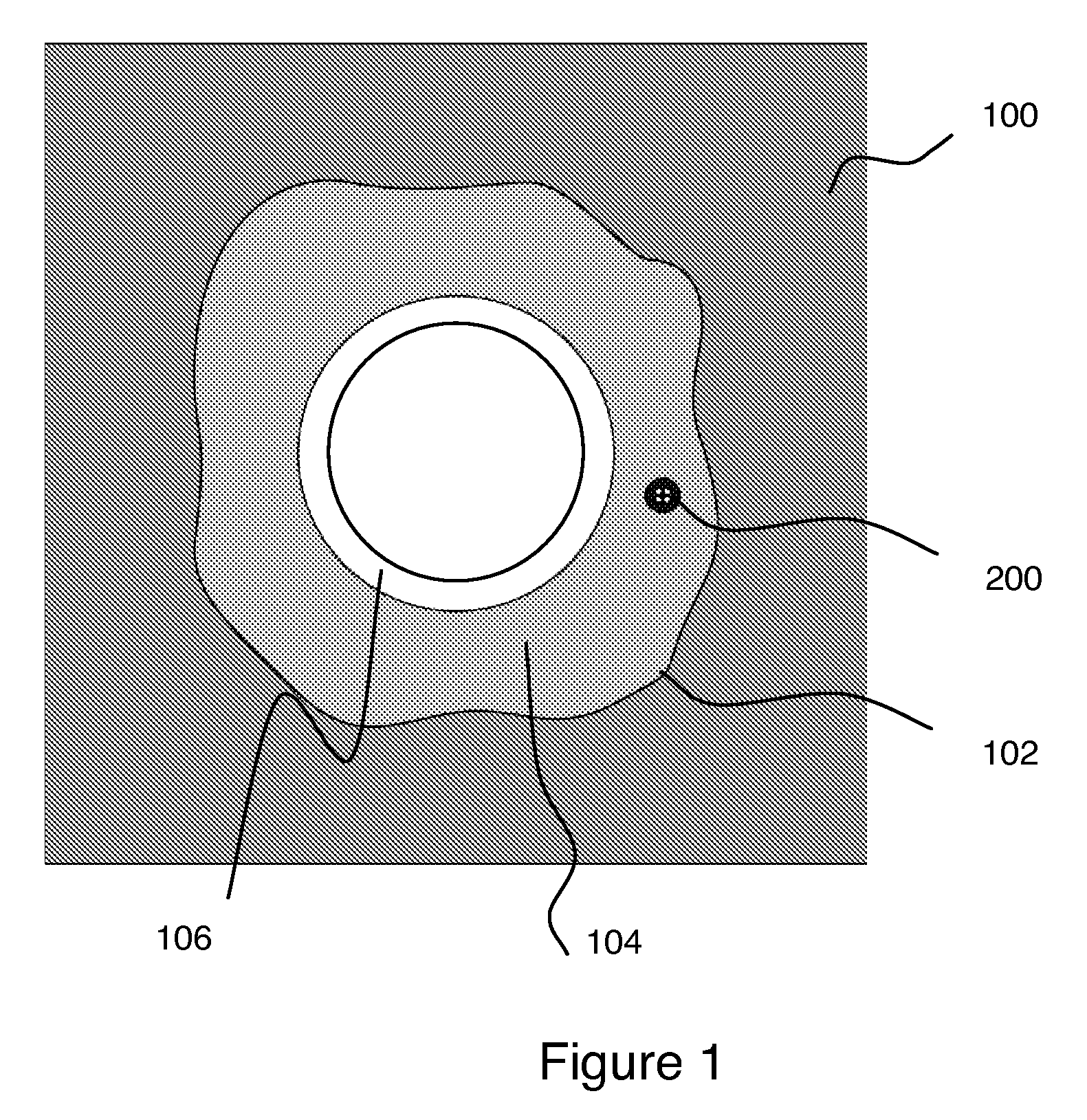
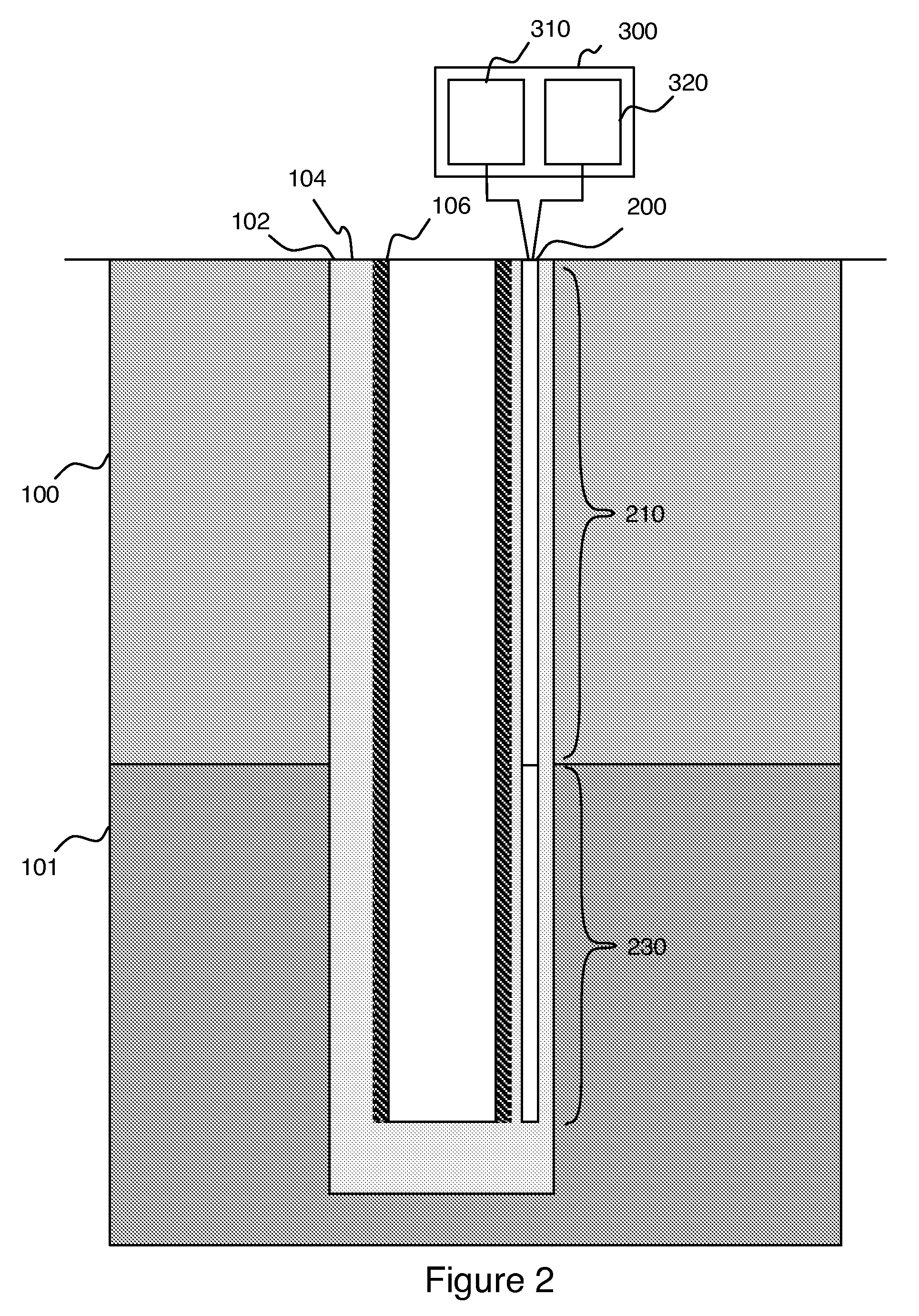
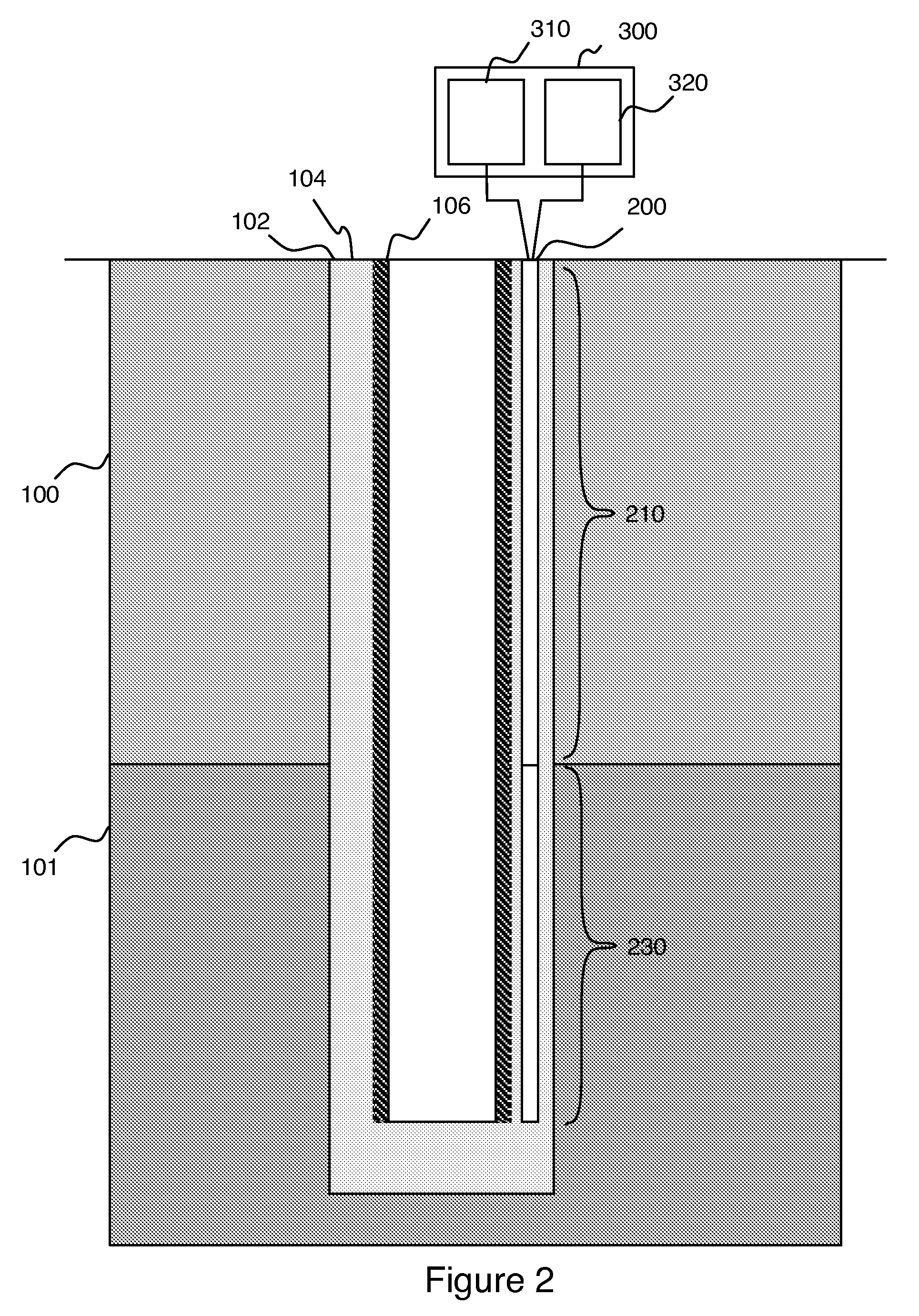
Active cable for wellbore heating and distributed temperature sensing
A heating and distributed-temperature-sensor cable permanently fixed in a wellbore that permits known amounts of heat to be introduced to subsurface formations and improved temperature measurement thereof. The heat is introduced into a target zone of the wellbore by forming the cable in two sections: an upper section that carries an electrical current without generating significant amounts of heat, and a lower section that generates heat from the electrical current. Continuous distributed-temperature-sensing is performed through measuring various scattering mechanism in optical fibers that run the length of the cable.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
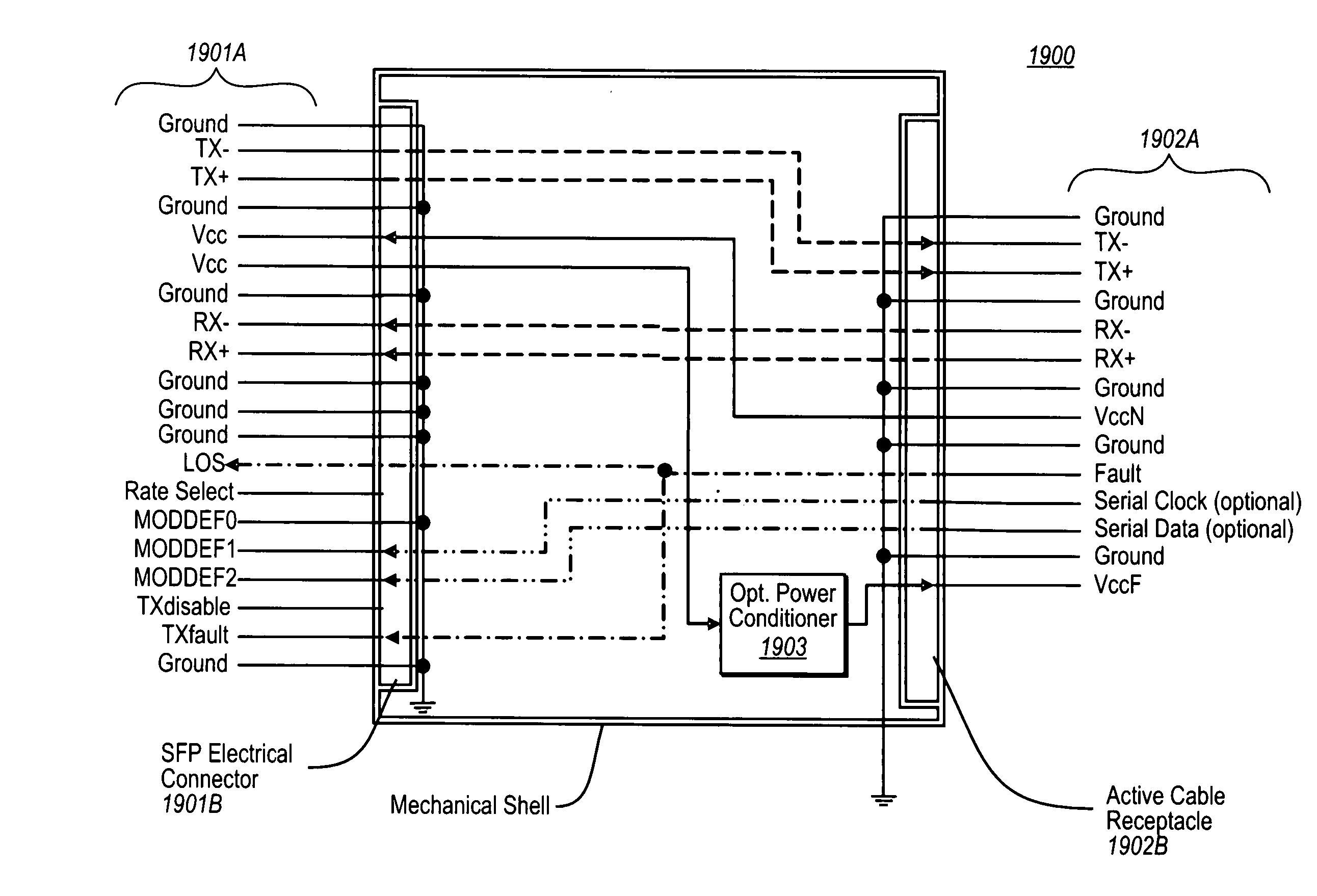
Active optical cable with integrated power
ActiveUS7876989B2Fibre mechanical structuresElectromagnetic transmissionElectricityElectrical connector
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Active optical cable electrical connector
An electrical connector that is integrated within an active cable at one end of the active cable, wherein the active cable is configured to communicate over much of its length using one or more optical fibers. The cable may be an electrical to optical cable, and electrical to electrical cable, or one of many other potential configurations.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Electrical-optical active optical cable
ActiveUS20070237464A1Facilitate optical communicationWell formedCoupling light guidesEngineeringOptical communication
An active cable that includes an integrated electrical connector at one end and an optical connector at the other end, and one or more optical fibers disposed therebetween to facilitate optical communication over much of the length of the active cable. The communication may be one direction or even duplex.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
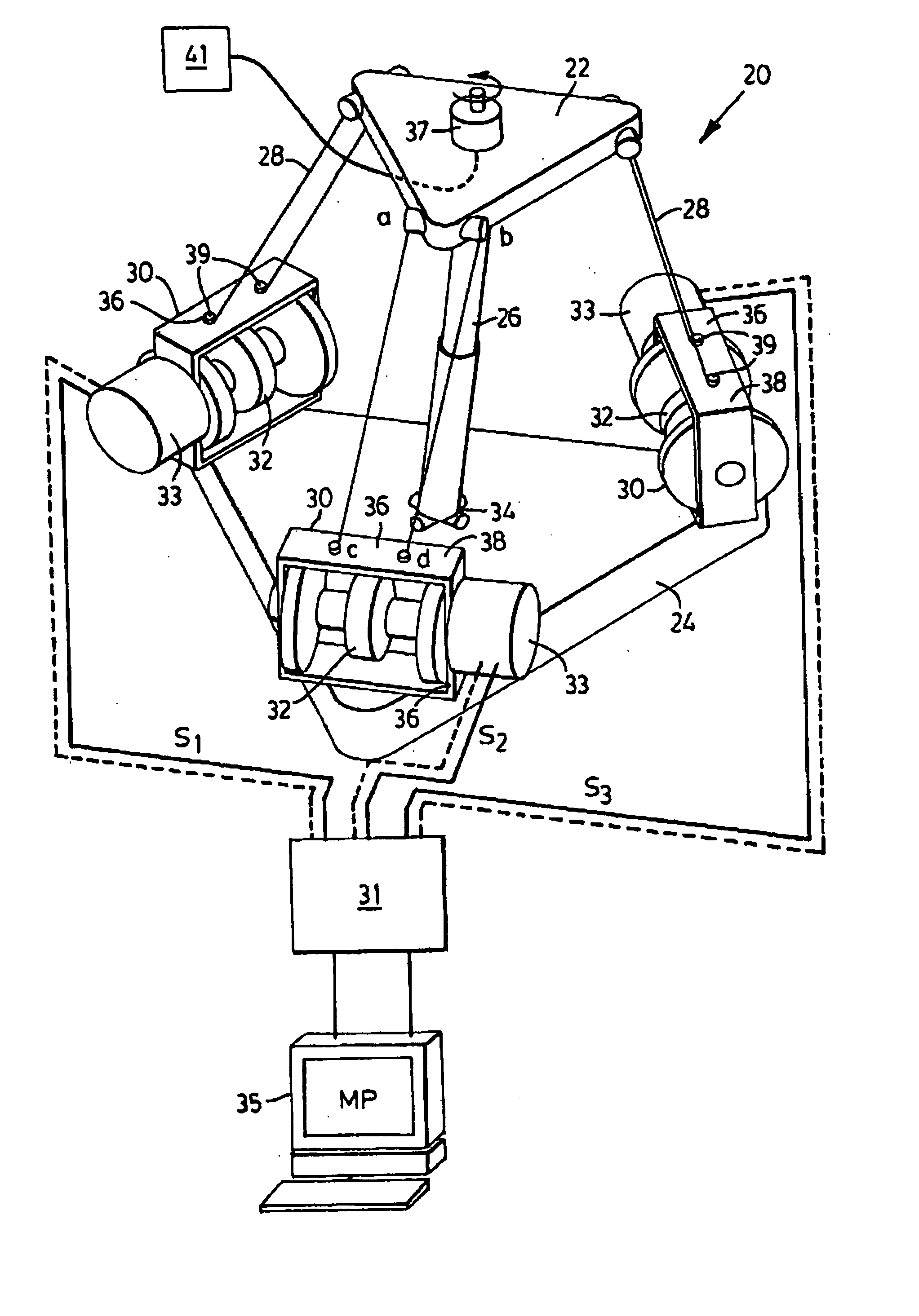
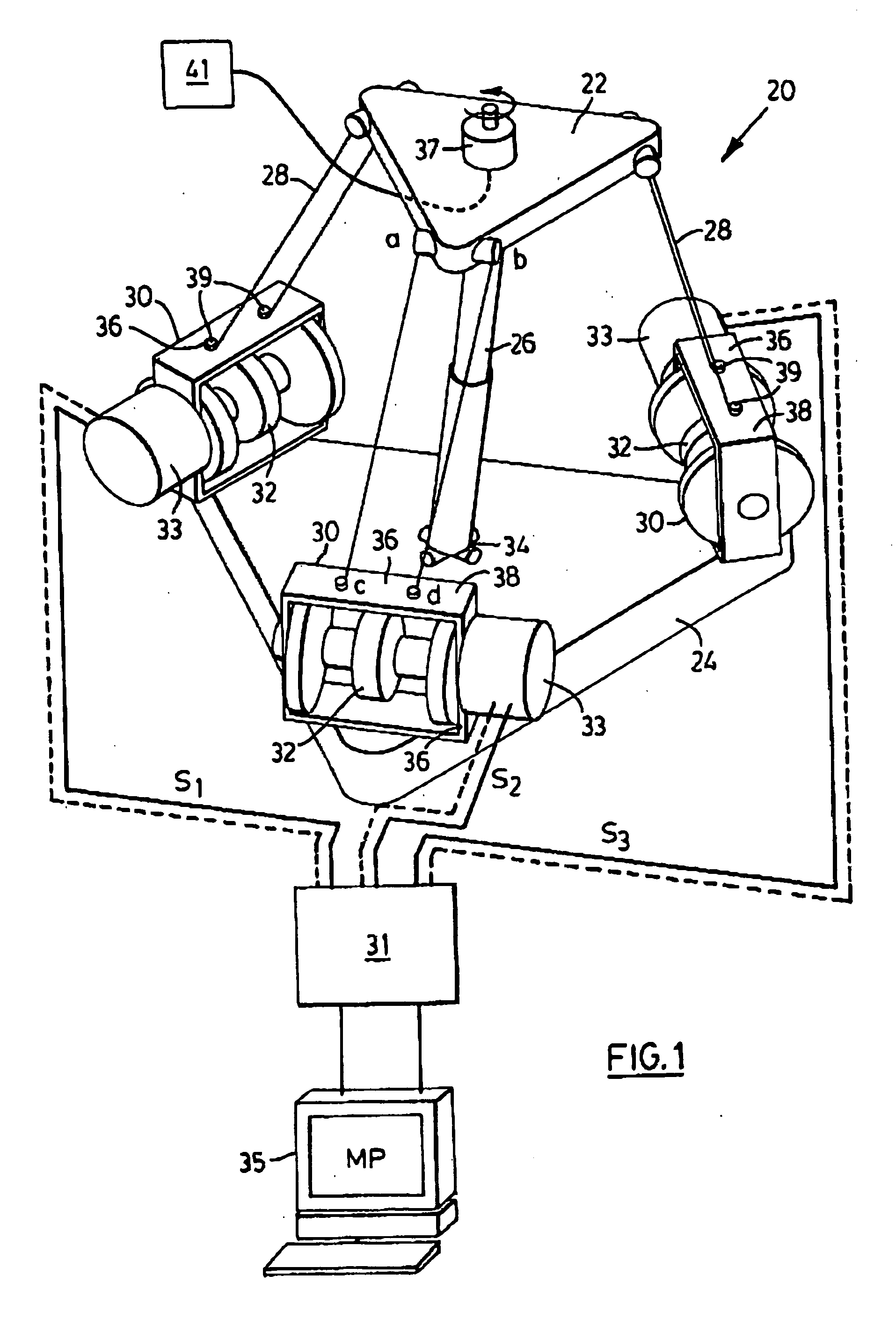
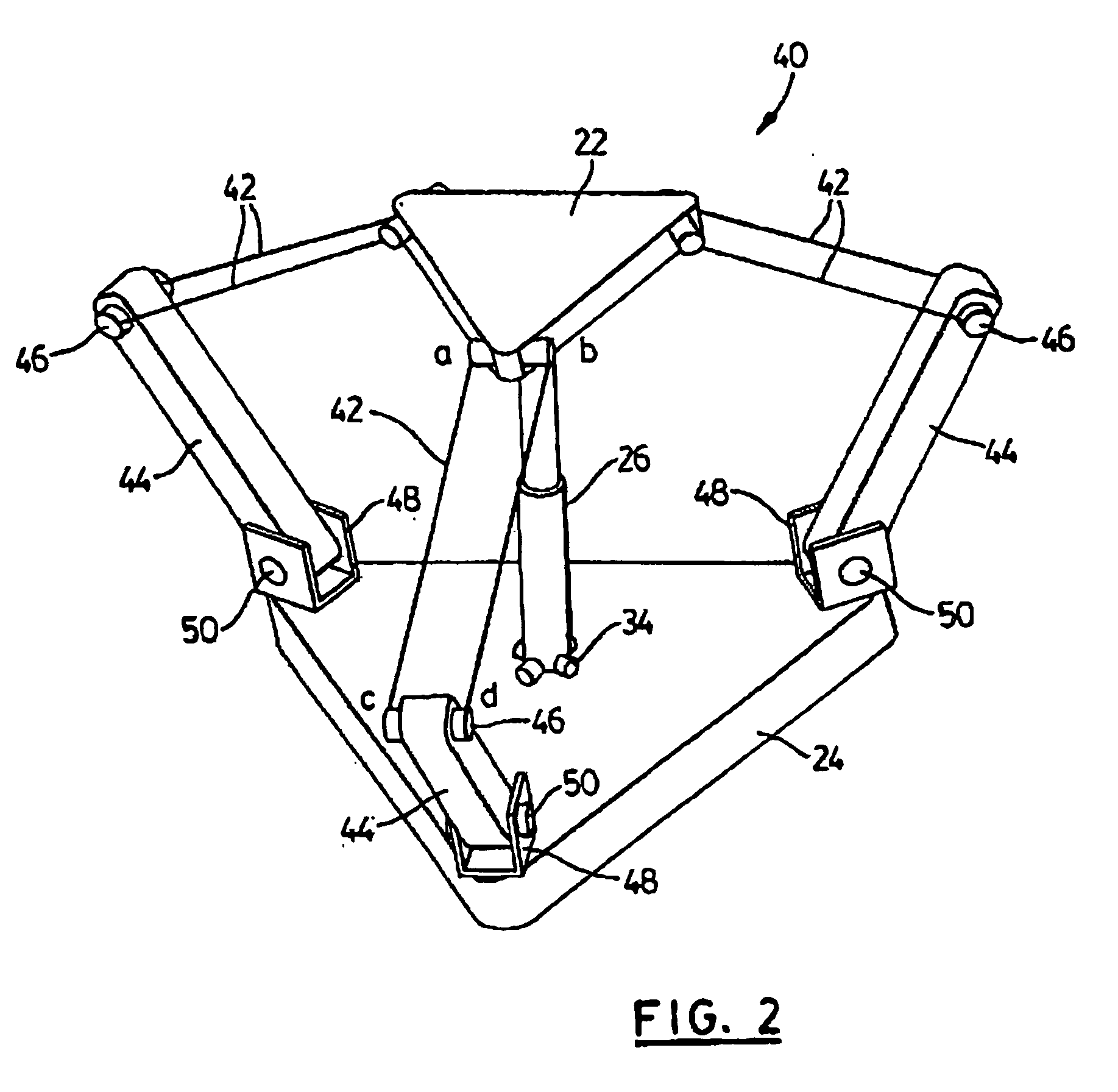
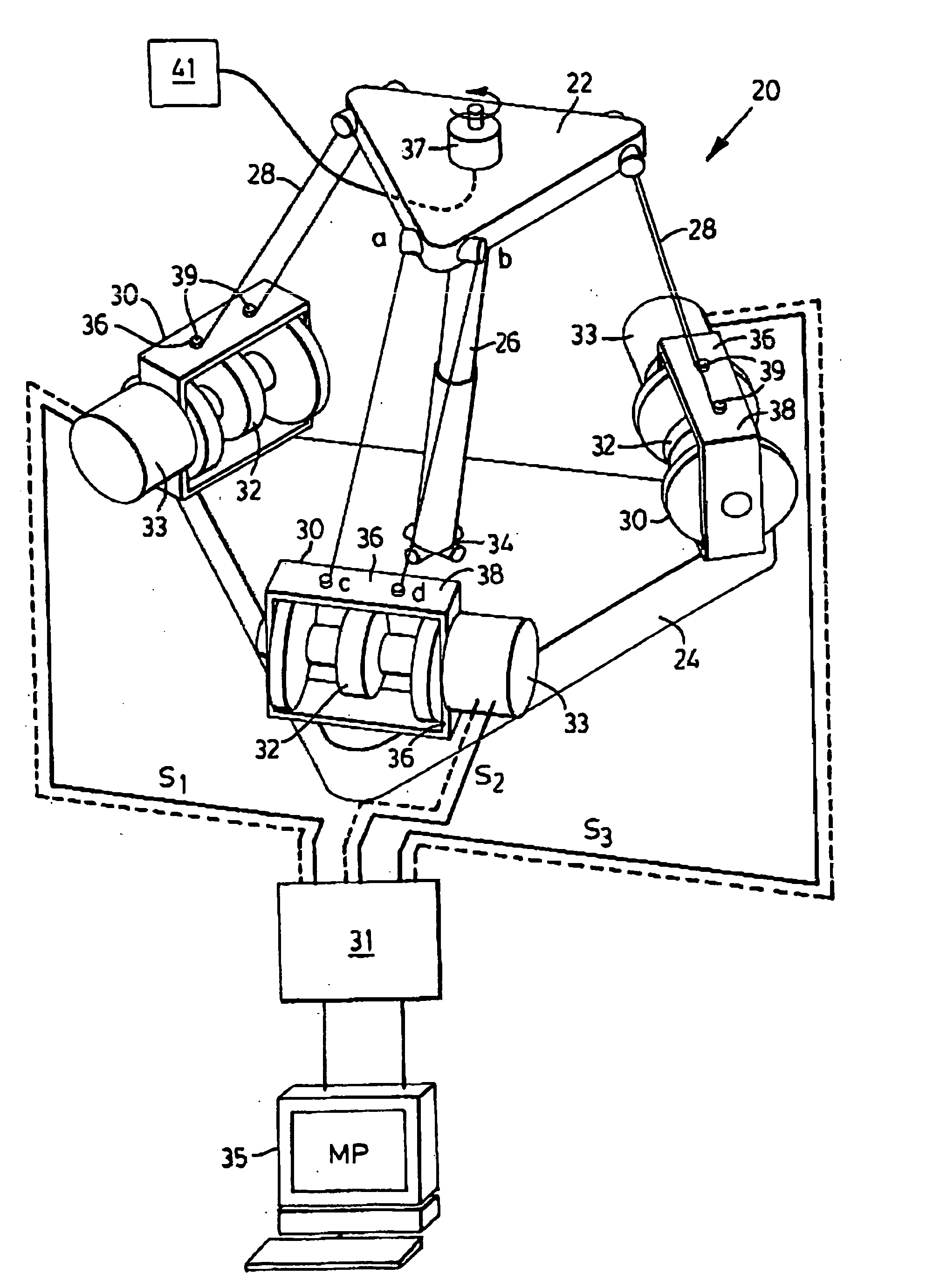
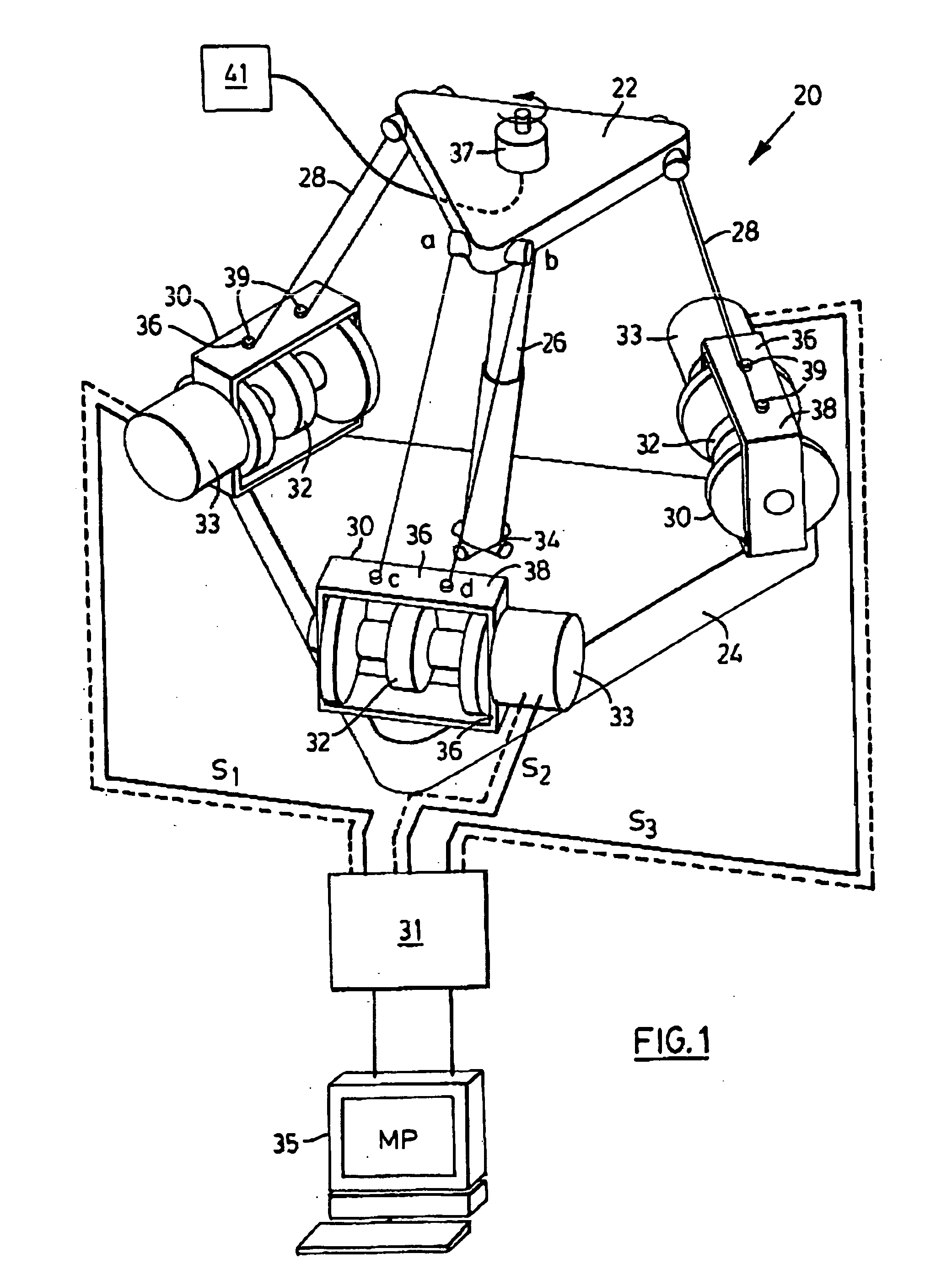
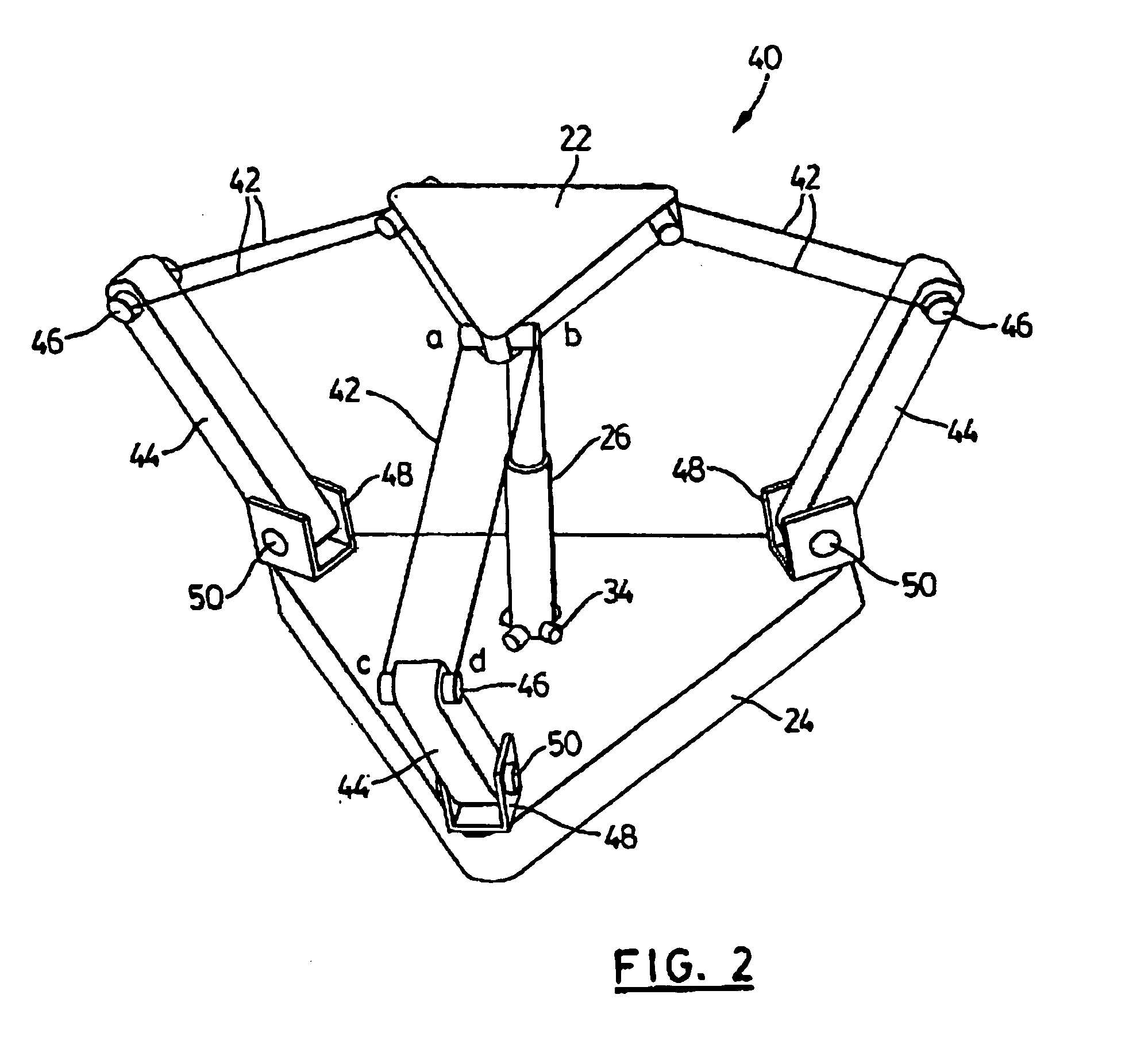
Light weight parallel manipulators using active/passive cables
ActiveUS7172385B2Simple processMaximize the benefitsProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusUltra high speedCost effectiveness
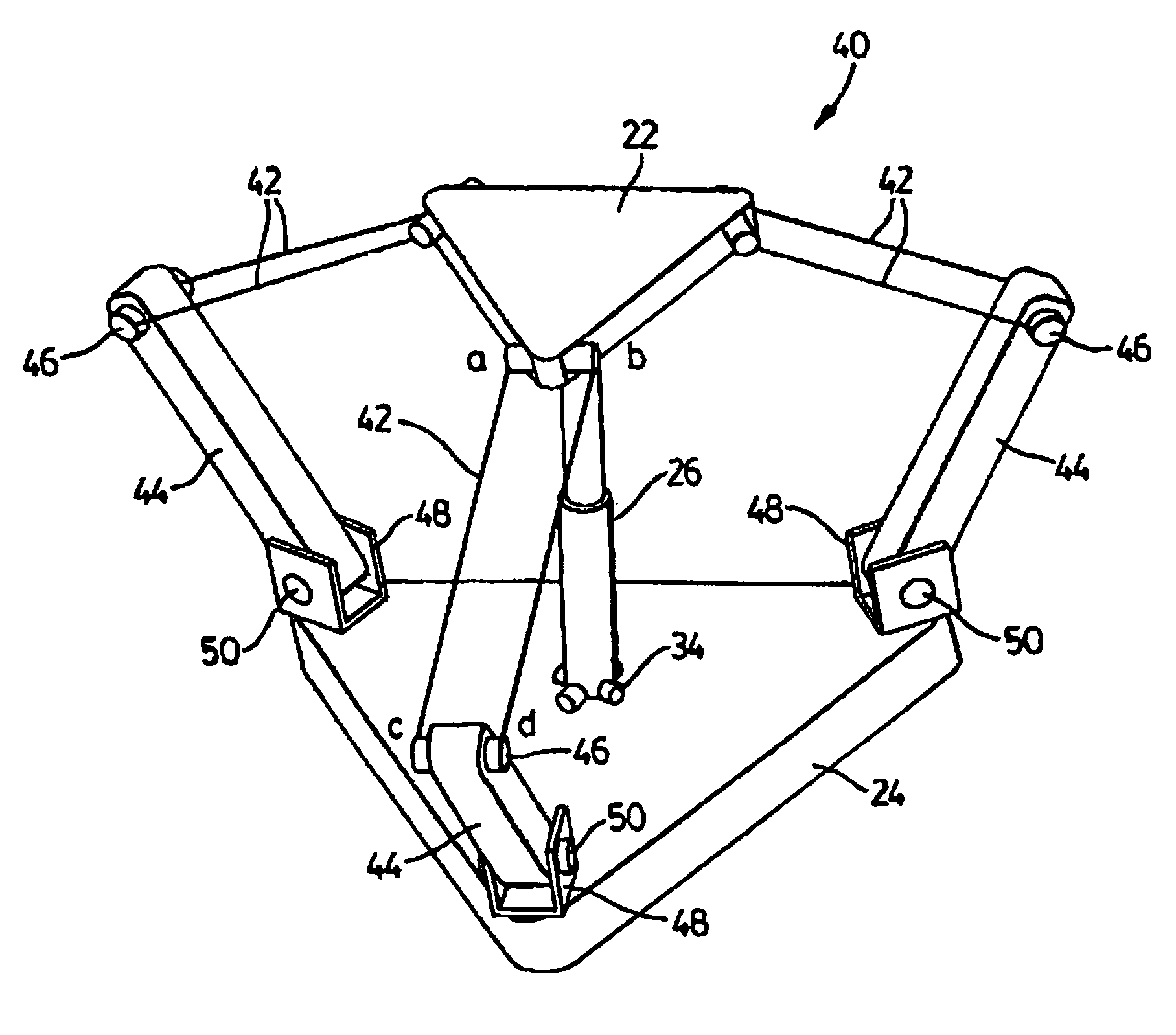
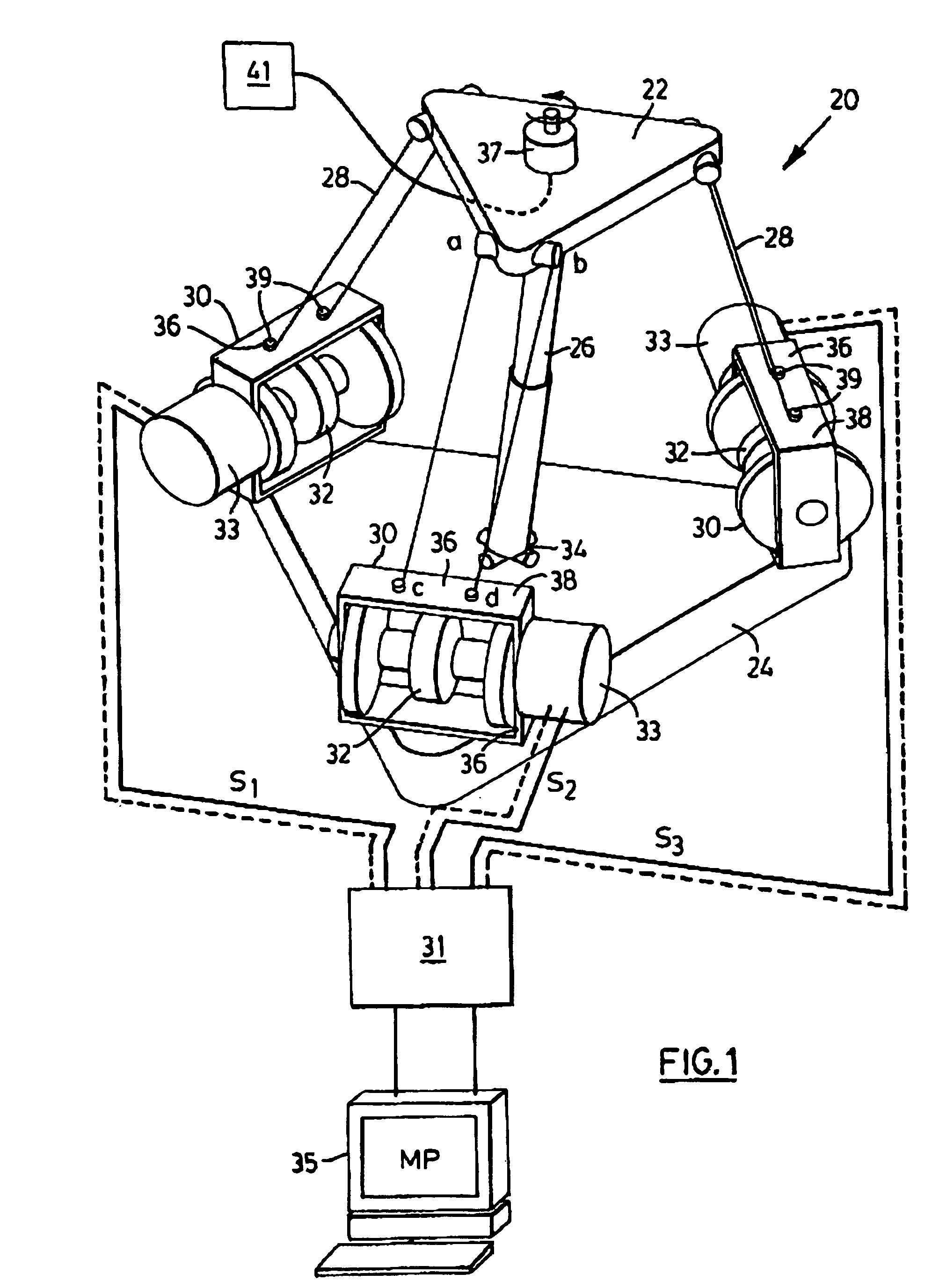
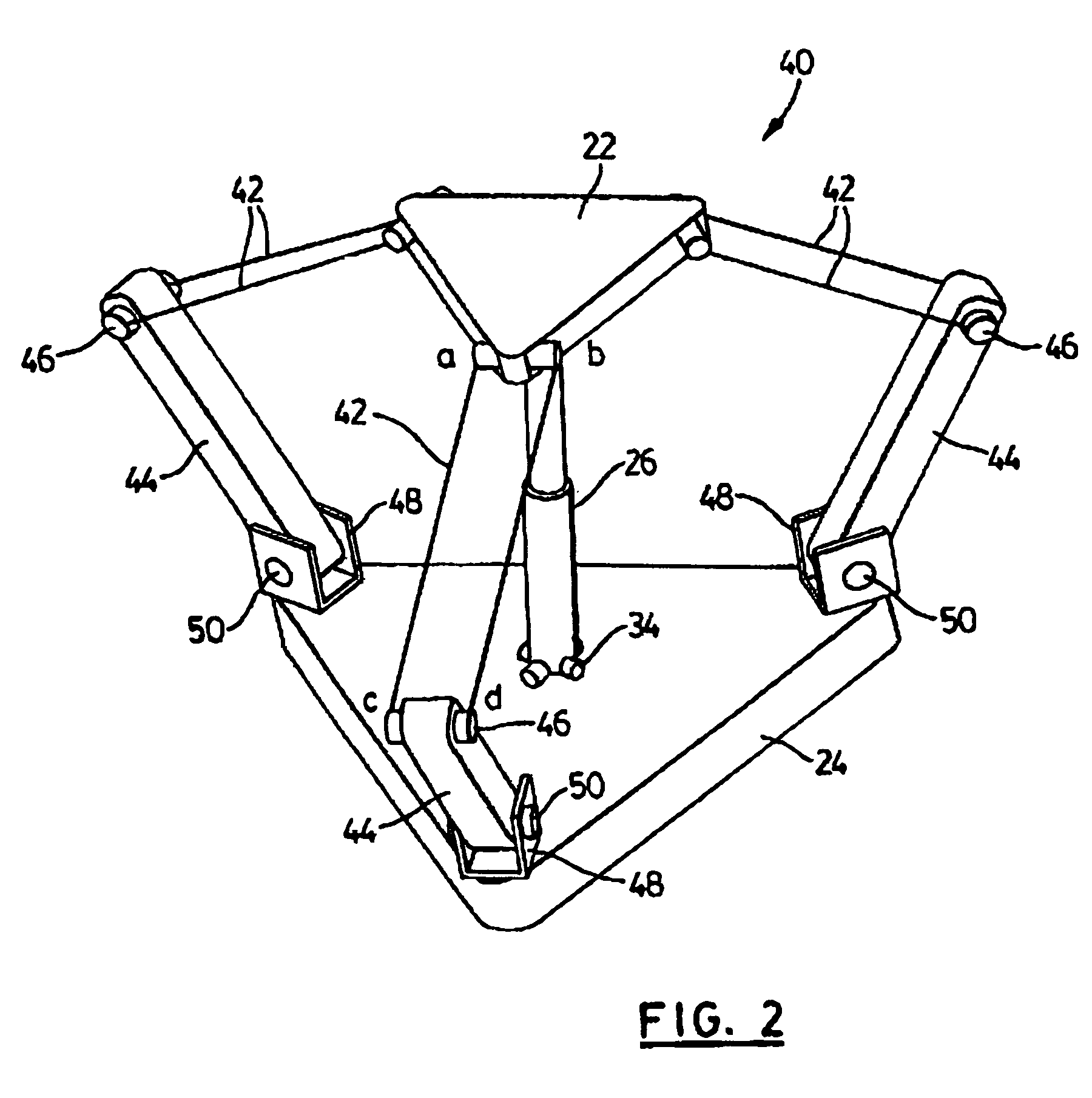
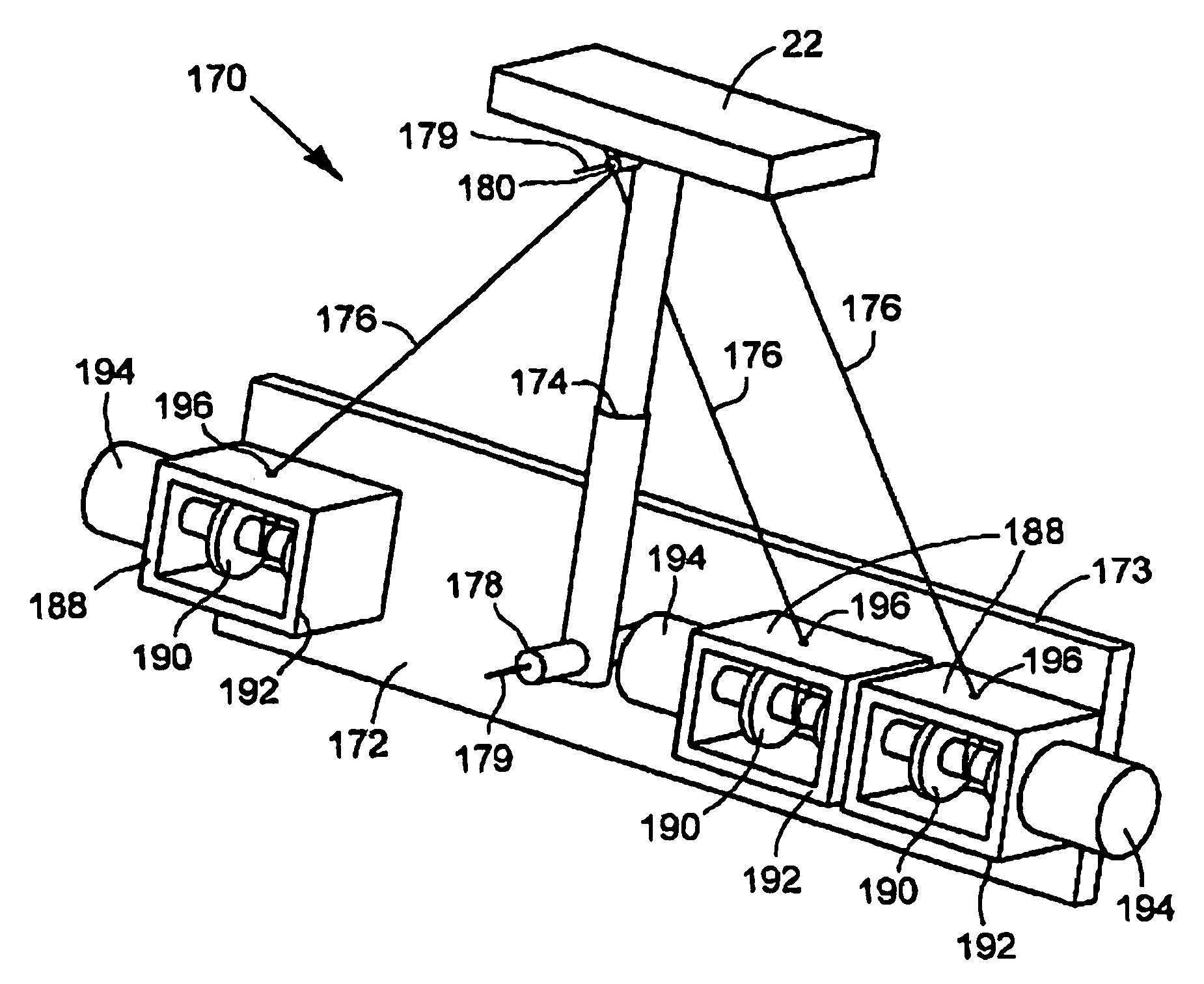
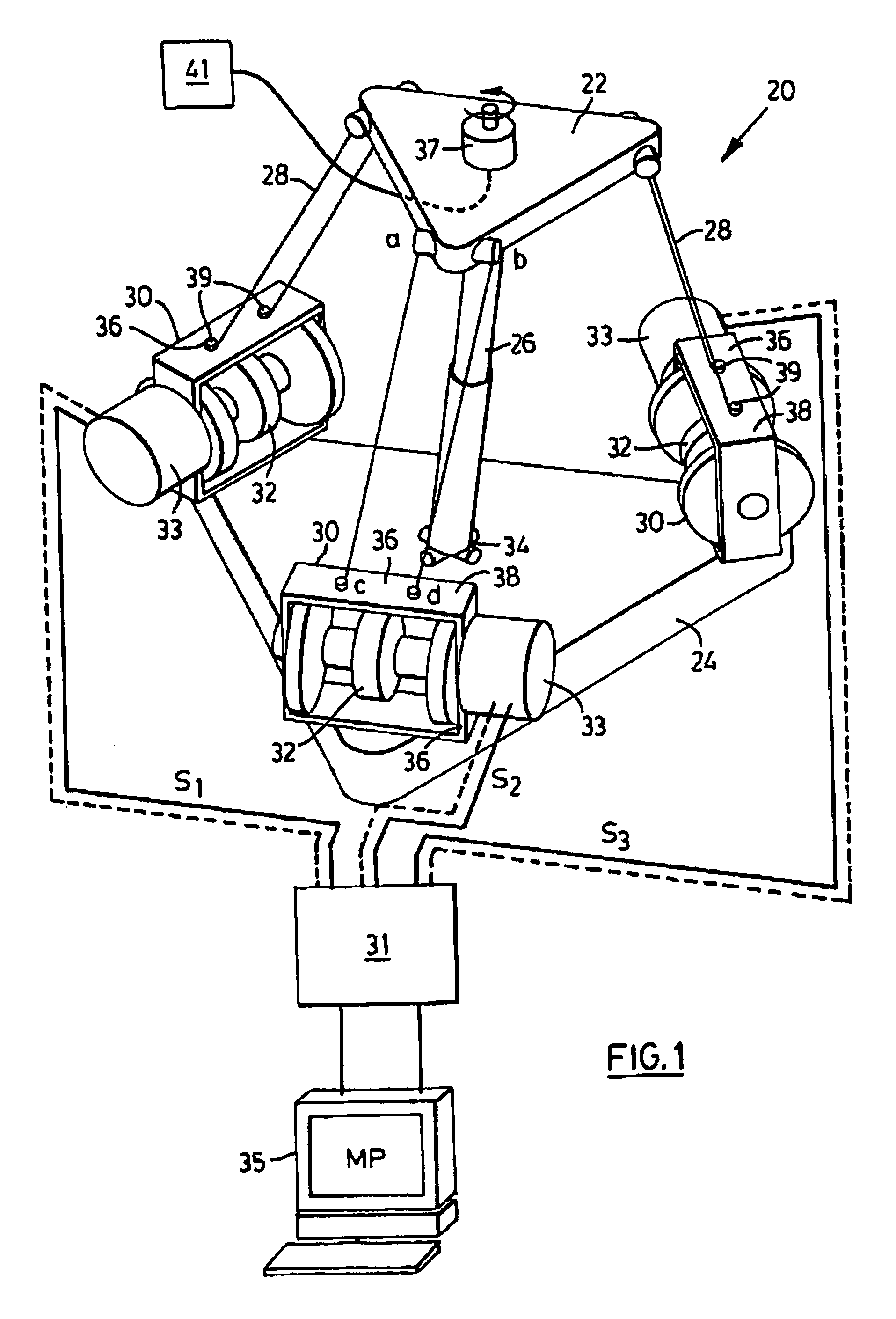
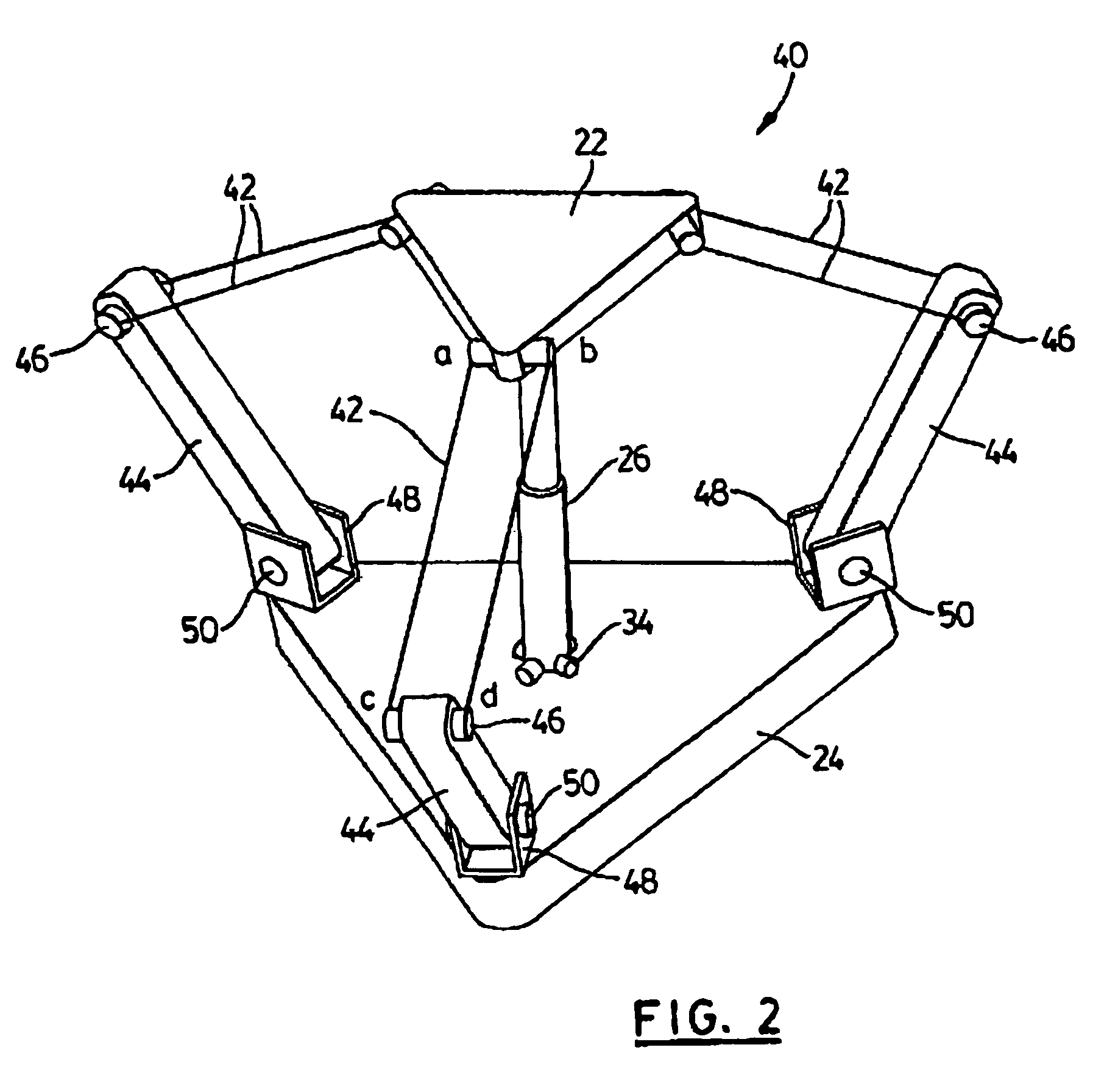
The present invention provides parallel, cable based robotic manipulators, for use in different applications such as ultra high-speed robots or positioning devices with between three to six degrees of freedom. The manipulators provide more options for the number of degrees of freedom and also more simplicity compared to the current cable-based robots. The general structure of these manipulators includes a base platform, a moving platform or end effector, an extensible or telescoping central post connecting the base to moving platform to apply a pushing force to the platforms. The central post can apply the force by an actuator (active), or spring or air pressure (passive) using telescoping cylinders. The robotic manipulators use a combination of active and passive tensile (cable) members, and collapsible and rigid links to maximize the benefits of both pure cable and conventional parallel mechanisms. Different embodiments of the robotic manipulators use either active cables only, passive cables only, or combinations of active and passive cables. An active cable is one whose length is varied by means of a winch. A passive cable is one whose length is constant and which is used to provide a mechanical constraint. These mechanisms reduce the moving inertia significantly to enhance the operational speed of the robots. They also provide a simpler, more cost effective way to manufacture parallel mechanisms for use in robotic applications.
Owner:KHAJEPOUR AMIR +3
Active optical cable with integrated retiming
An active cable that is configured to communicate over much of its length using one or more optical fibers, and that includes an integrated electrical connector at least one end. The active cable includes an integrated retiming mechanism. Thus, multiple links of cable may be used while reducing the chance that the jitter will exceed allowable limits. The cable may be an electrical to optical cable, and electrical to electrical cable, or one of many other potential configurations.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
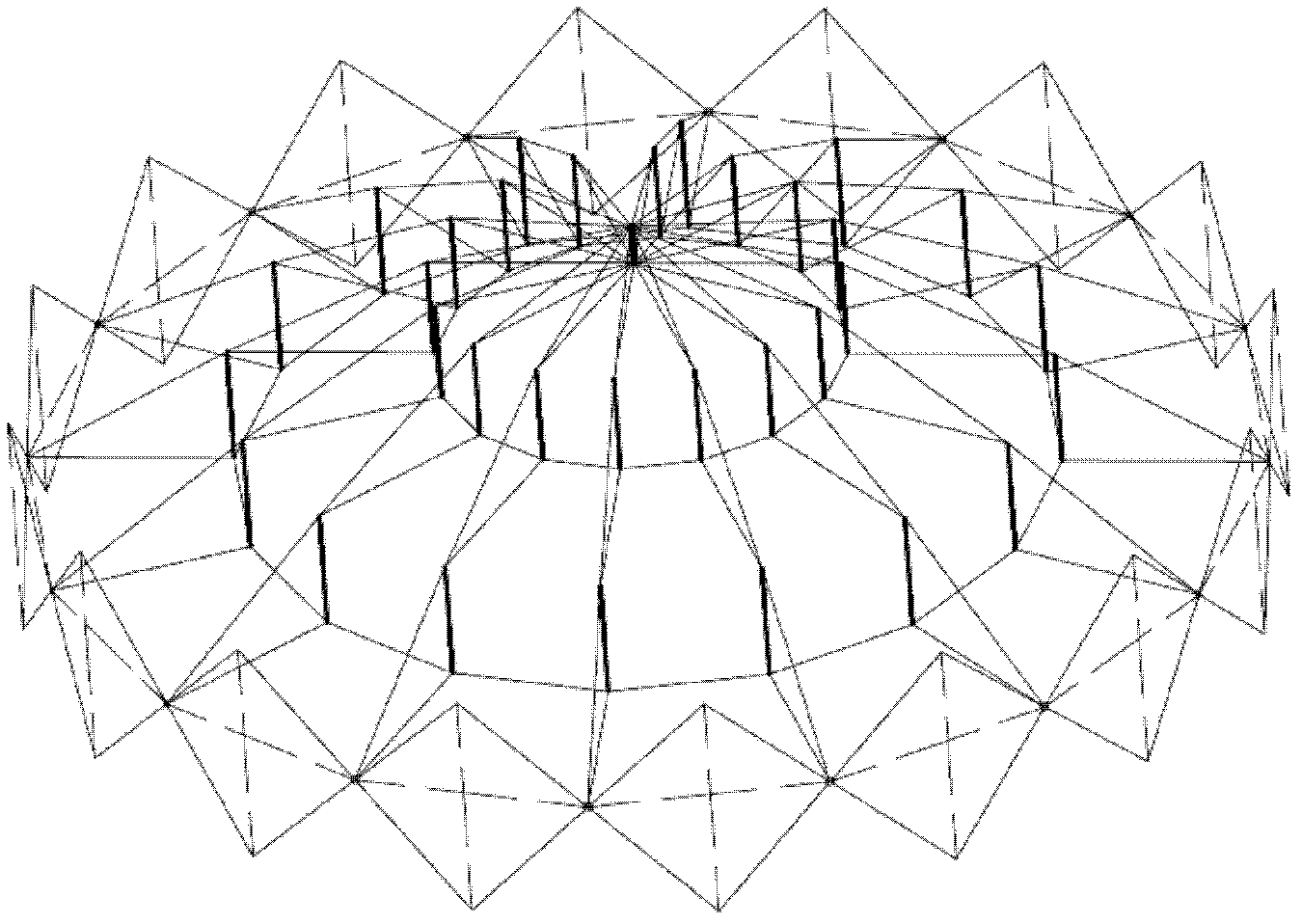
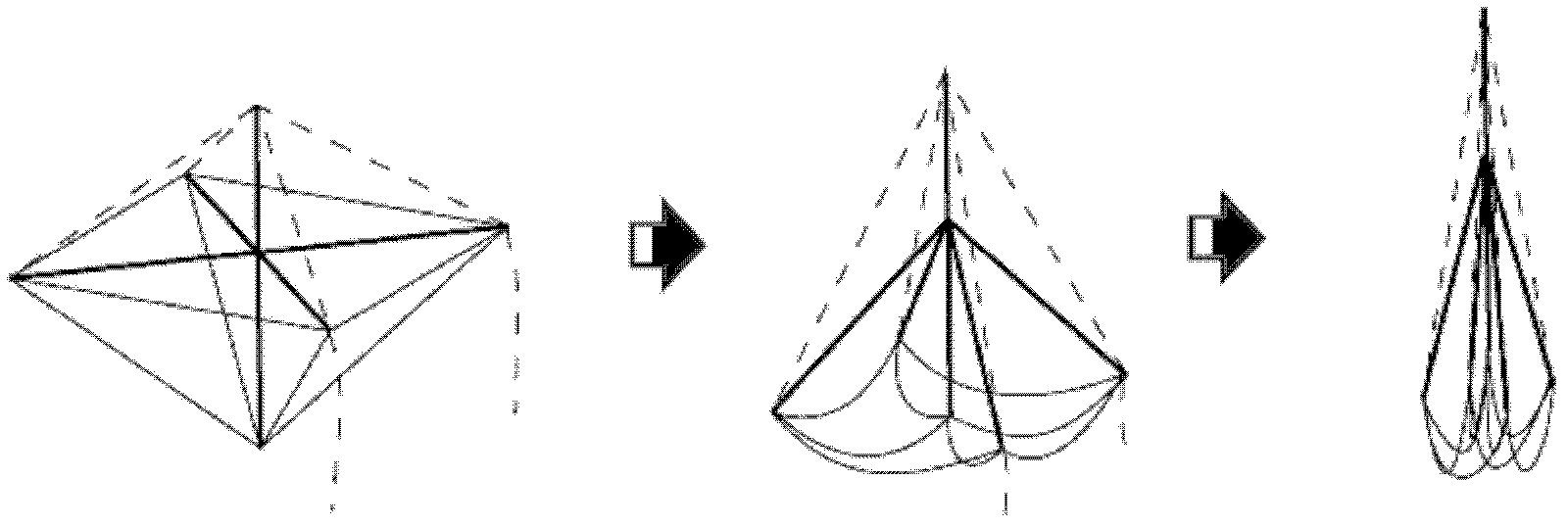
Deployable cable pole dome structure
InactiveCN102605861AIncrease stiffnessReduce in quantityArched structuresVaulted structuresActive cableFull extension
The invention discloses a deployable cable pole dome structure, comprising an inner cable pole body and an external single-freedom-degree annular connecting bar mechanism, wherein the single-free degree annular connecting bar mechanism comprises at least four shearing type units, a passive cable and an active cable. The invention uses the single-freedom-degree annular connecting bar mechanism to drive the dome structure to fold and unfold, thus number of driving devices is reduced; the active cable and the passive cable are arranged in the external annular connecting bar mechanism, and the prestressing force exists at a full extension state, so that the rigidity of the structure is increased and the material does is reduced; only the active cable needs to be fixed at a full extension state, and an additional locking device is not needed; a coverage range of the dome structure is provided by the inner cable pole body, thus, the external load of the structure is mainly born by the inner cable pole body; the inner cable pole body is composed of a high-strength inhaul cable and a pressure bar; the self weight is light; and the rigidity is mainly provided by the prestressing force, and the stress performance is excellent.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Active optical cable electrical adaptor
ActiveUS20070237468A1Well formedCoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresElectricityEngineering
An adaptor that mechanically and / or electrically adapts to and / or from an electrical connector that is integrated with an active cable at one end of an active optical cable, wherein the optical cable is configured to communicate over much of its length using one or more optical fibers. The cable may be an electrical to optical cable, and electrical to electrical cable, or one of many other potential configurations.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Active optical cable with integrated eye safety
An active cable that is configured to communicate over much of its length using one or more optical fibers, and that includes an integrated electrical connector at at least one end. The active cable includes an integrated eye safety controls to thereby reduce the chance of injury should the active cable be severed, or otherwise unplugged at an optical end, if any. The cable may be an electrical to optical cable, and electrical to electrical cable, or one of many other potential configurations.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Integrated sensor cable for ranging
An intrusion detection system provides the function of an “active” ranging sensor cable system utilized for identification of the location of the intruder, with that of a “passive” cable detection system, in an integrated cable configuration. This dual function is provided with a single conventional sensing cable optimized for both “active” and “passive” sensing, or in combination with other parallel sensing cables for a “passive” cable component. The “active” cable component includes a coaxial sensor cable having a loosely disposed conductor. A signal is injected into the sensor cable such that a reflection is altered when an intrusion disturbs the cable. Based on the timing of the reflection, a processor, or a reflectometer, identifies the location of the disturbance. The “passive” cable component can be sensitized to detect intrusion via some other sensing phenomenology, such as the triboelectric effect, for triboelectric effect sensing.
Owner:SENSTAR STELLAR CORP
Active Cable for Wellbore Heating and Distributed Temperature Sensing
A heating and distributed-temperature-sensor cable permanently fixed in a wellbore that permits known amounts of heat to be introduced to subsurface formations and improved temperature measurement thereof. The heat is introduced into a target zone of the wellbore by forming the cable in two sections: an upper section that carries an electrical current without generating significant amounts of heat, and a lower section that generates heat from the electrical current. Continuous distributed-temperature-sensing is performed through measuring various scattering mechanism in optical fibers that run the length of the cable.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Light weight parallel manipulators using active/passive cables
InactiveUS20070113699A1Maximize the benefitsImprove performance and simplicity and feasibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusActuatorWinch
The present invention provides parallel, cable based robotic manipulators, for use in different applications such as ultra high-speed robots or positioning devices with between three to six degrees of freedom. The manipulators provide more options for the number of degrees of freedom and also more simplicity compared to the current cable-based robots. The general structure of these manipulators includes a base platform, a moving platform or end effector, an extensible or telescoping central post connecting the base to moving platform to apply a pushing force to the platforms. The central post can apply the force by an actuator (active), or spring or air pressure (passive) using telescoping cylinders. The robotic manipulators use a combination of active and passive tensile (cable) members, and collapsible and rigid links to maximize the benefits of both pure cable and conventional parallel mechanisms. Different embodiments of the robotic manipulators use either active cables only, passive cables only, or combinations of active and passive cables. An active cable is one whose length is varied by means of a winch. A passive cable is one whose length is constant and which is used to provide a mechanical constraint. These mechanisms reduce the moving inertia significantly to enhance the operational speed of the robots. They also provide a simpler, more cost effective way to manufacture parallel mechanisms for use in robotic applications.
Owner:KHAJEPOUR AMIR +3
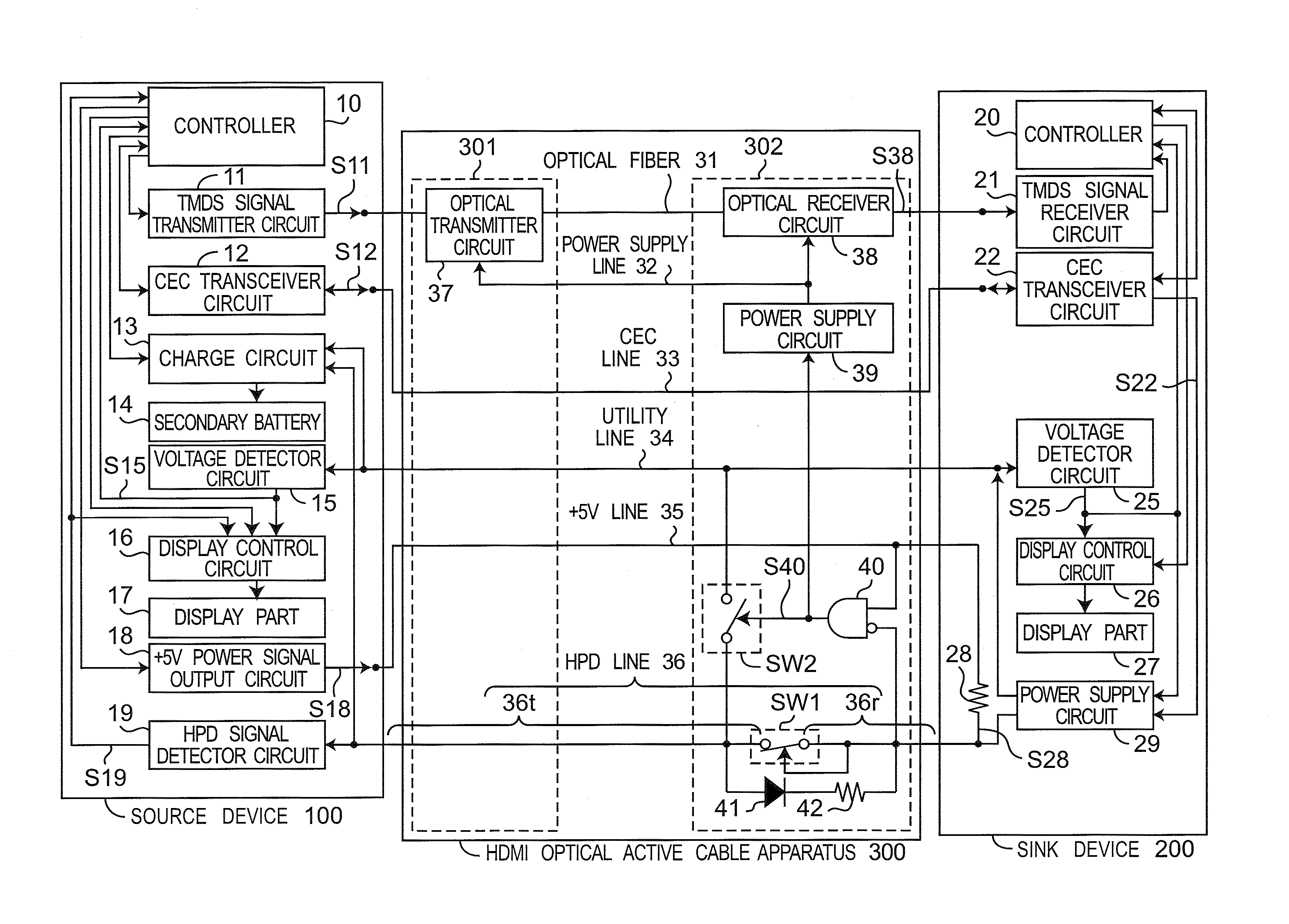
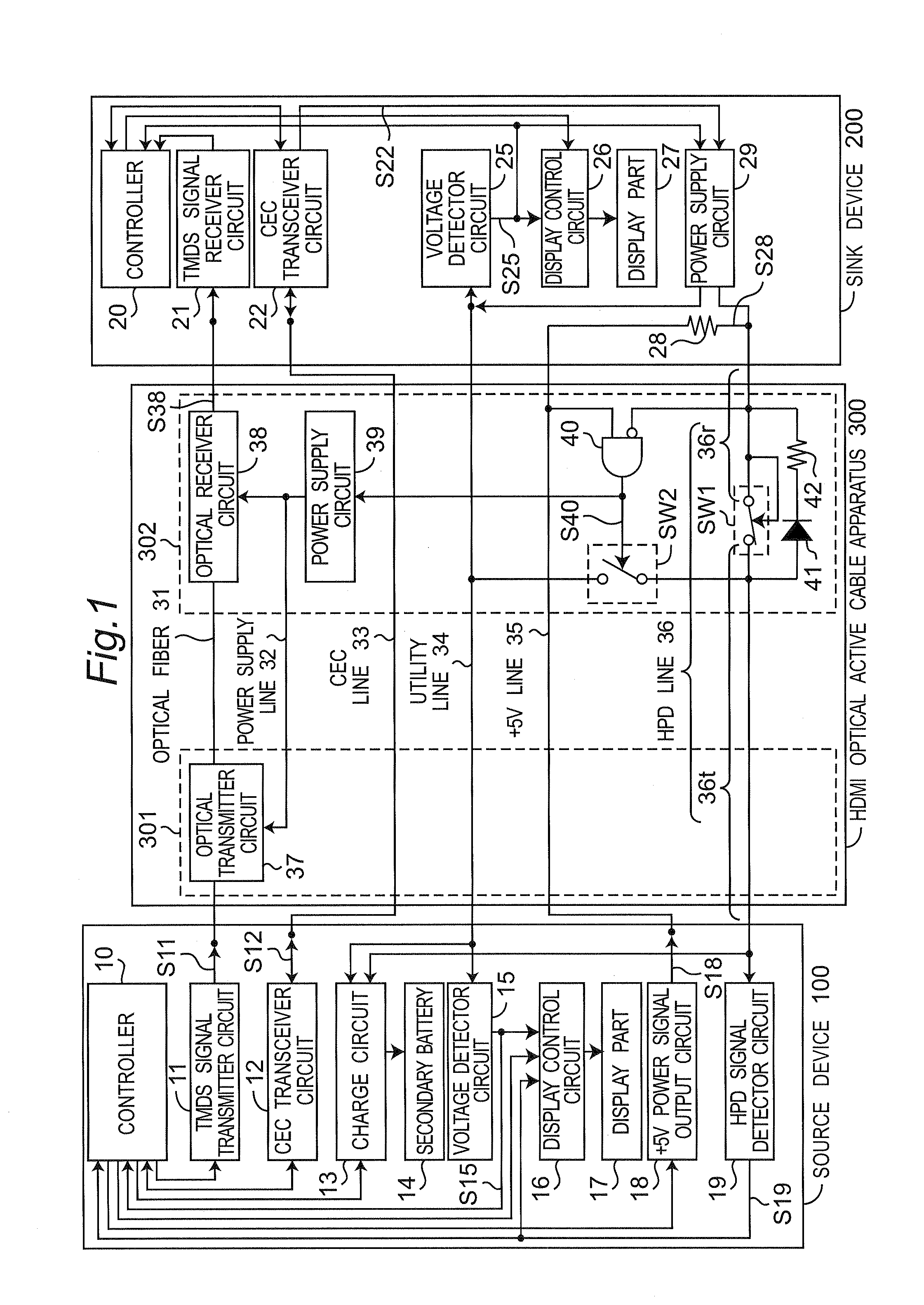
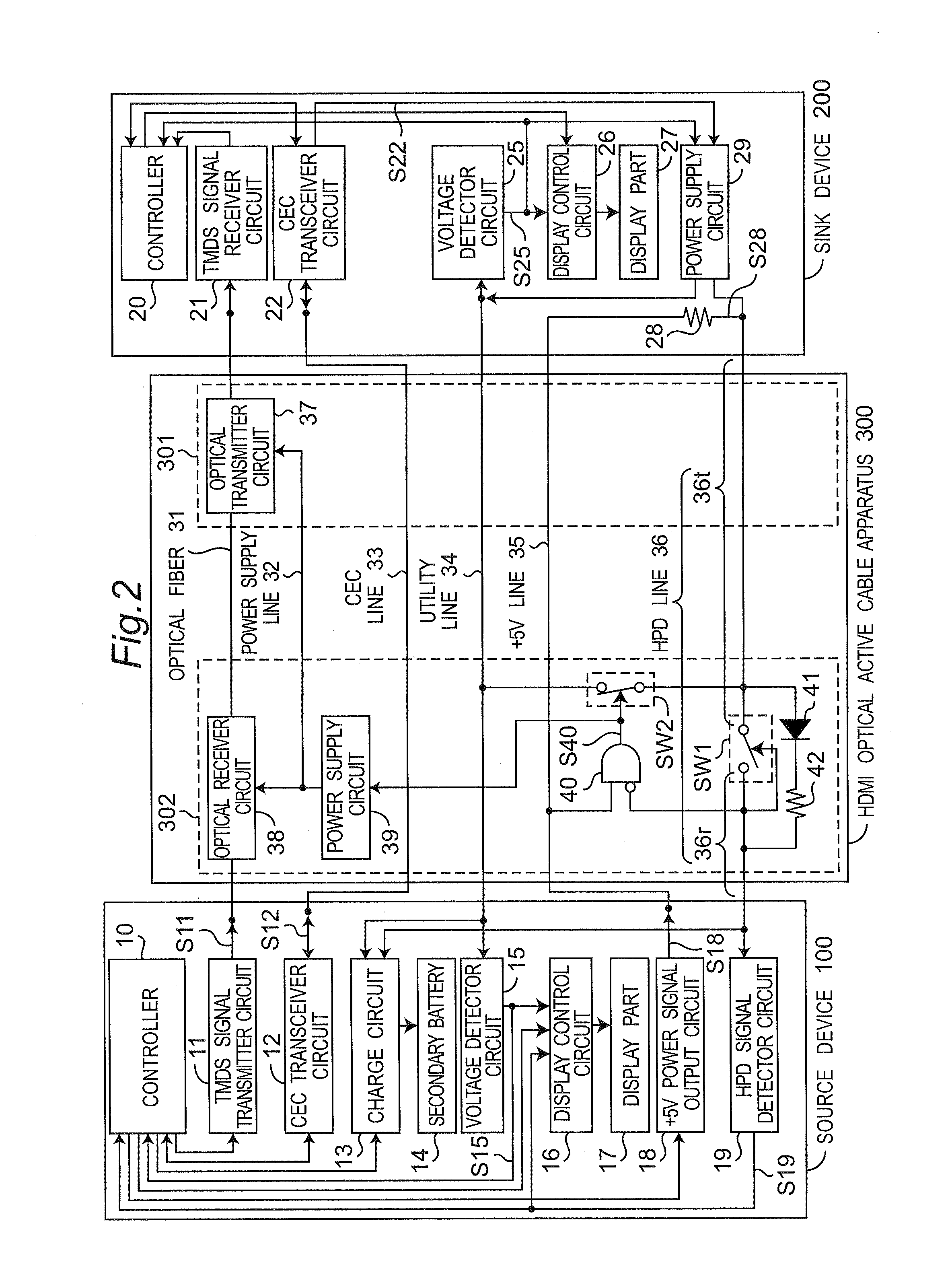
Communication cable apparatus including switch turned off in reverse connection state of communication cable apparatus
ActiveUS20130183045A1Avoid failureAvoid communicationCoupling light guidesFibre transmissionActive cableAND gate
A switch is inserted and connected between a first portion and a second portion of an HPD line. The switch connects the first portion to the second portion when an HPD signal is outputted to the second portion. The switch cuts off the connection between the first portion and the second portion when the HPD signal is not outputted to the second portion. An AND gate generates a connection state detection signal that represents the connection state of an HDMI optical active cable, and outputs the connection state detection signal to a switch.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
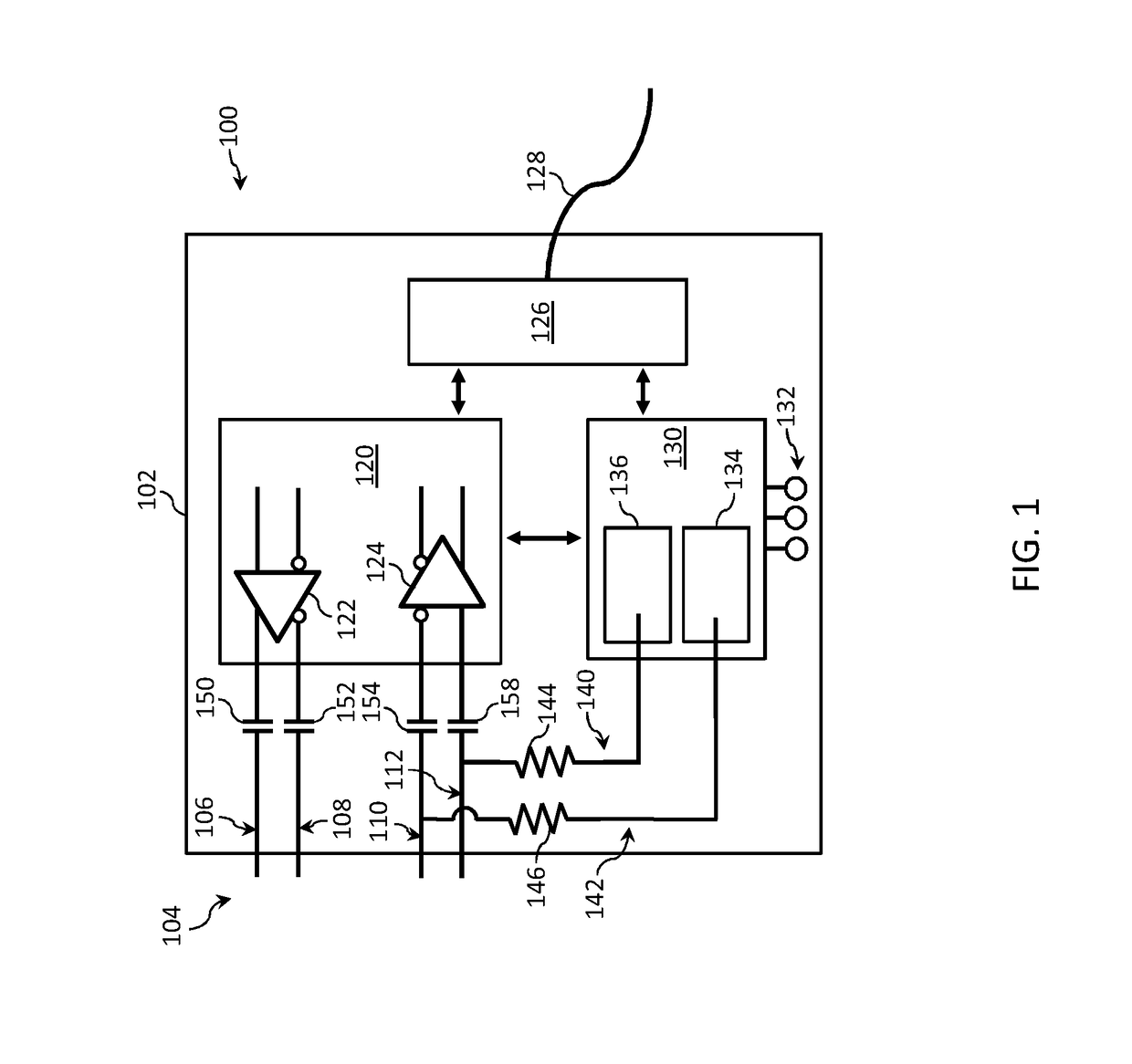
Boot loader for active cable assemblies
InactiveUS10235184B2Current interference reductionUnbalanced current interference reductionData signalControl theory
According to one embodiment, an active cable assembly may include a cable end, a data receiver, a controller characteristic circuit, and a controller. The data receiver, operable to receive a DC-balanced data signal, can be electrically coupled to a conductive input data line of the cable end. The controller characteristic circuit can be electrically coupled to the conductive input data line. The controller can be communicatively coupled to the data receiver. The controller may include a configurable communication port electrically coupled to the controller characteristic circuit, and memory for storing a boot loader. The controller can execute the boot loader to set the configurable communication port as an output for controller data signals and as an input for the controller data signals.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Active optical cable with integrated retiming
ActiveUS20070237471A1Reduce chanceWell formedCoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresElectrical connectorElectric cables
An active cable that is configured to communicate over much of its length using one or more optical fibers, and that includes an integrated electrical connector at at least one end. The active cable includes an integrated retiming mechanism. Thus, multiple links of cable may be used while reducing the chance that the jitter will exceed allowable limits. The cable may be an electrical to optical cable, and electrical to electrical cable, or one of many other potential configurations.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Light weight Parallel manipulators using active/passive cables
InactiveUS20070113700A1Maximize the benefitsImprove performance and simplicity and feasibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusEngineeringActuator
Owner:KHAJEPOUR AMIR +3
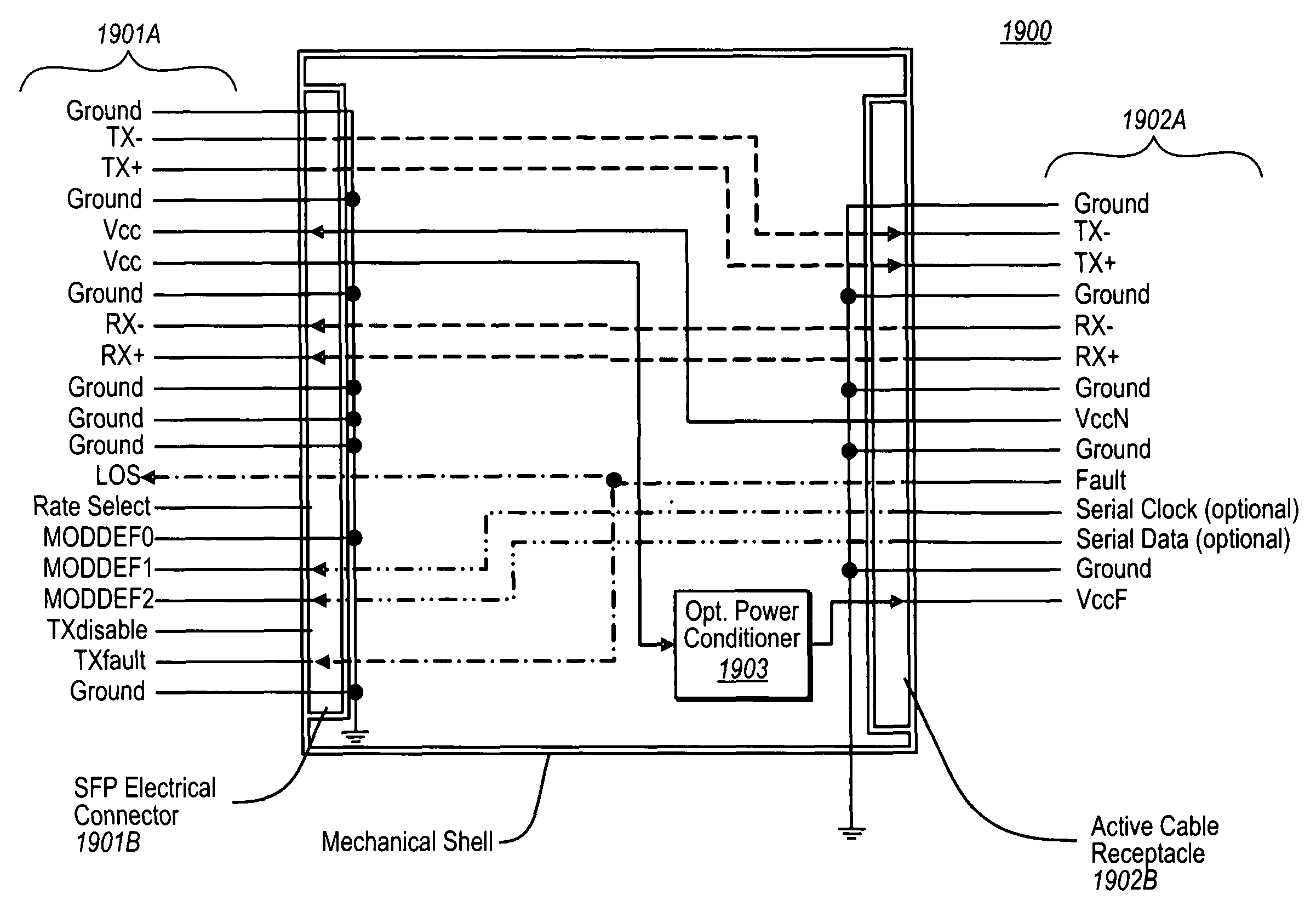
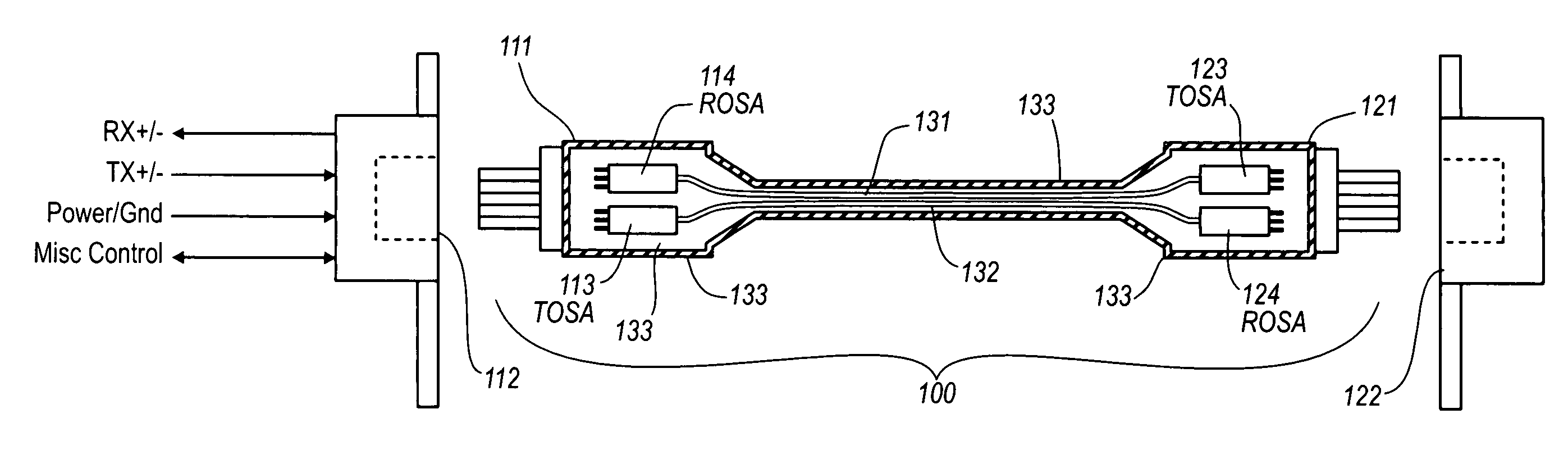
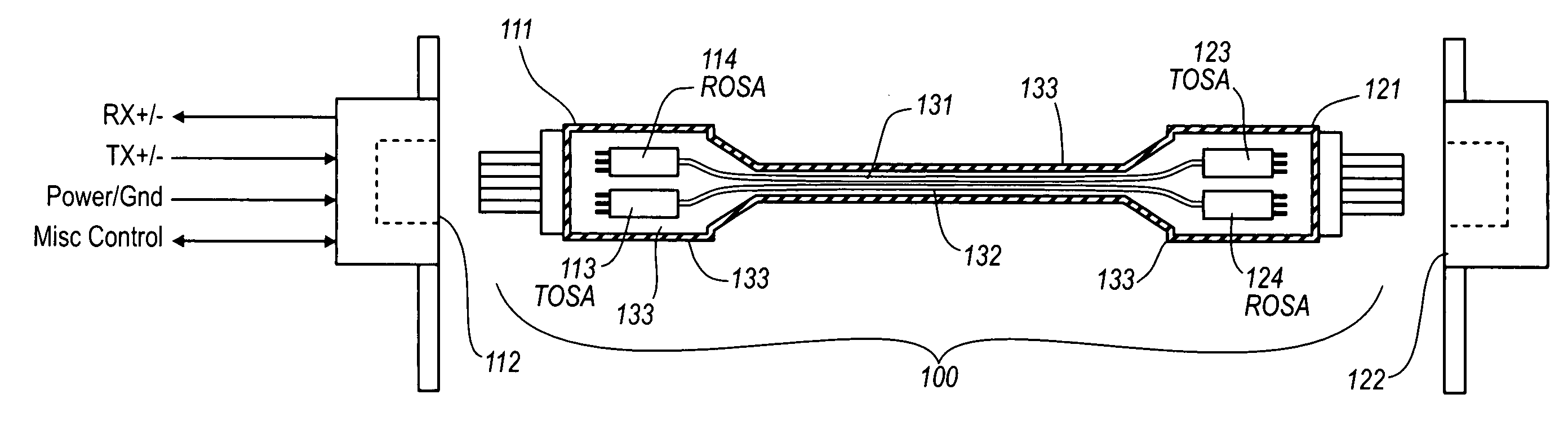
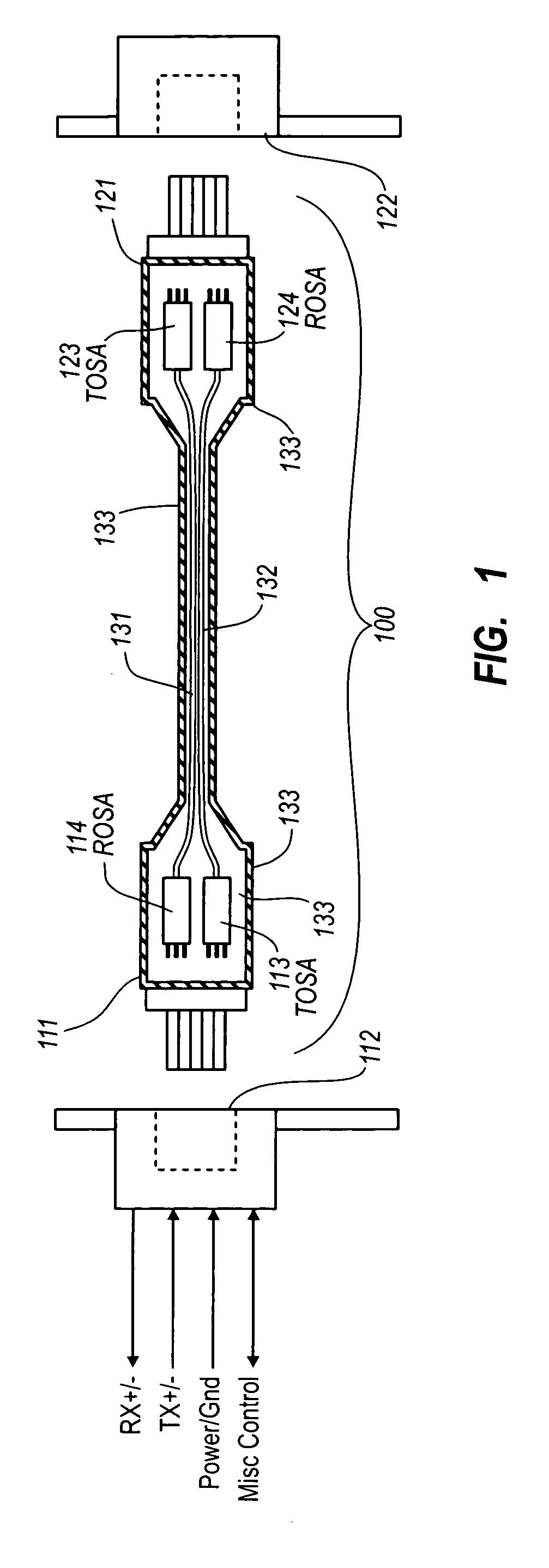
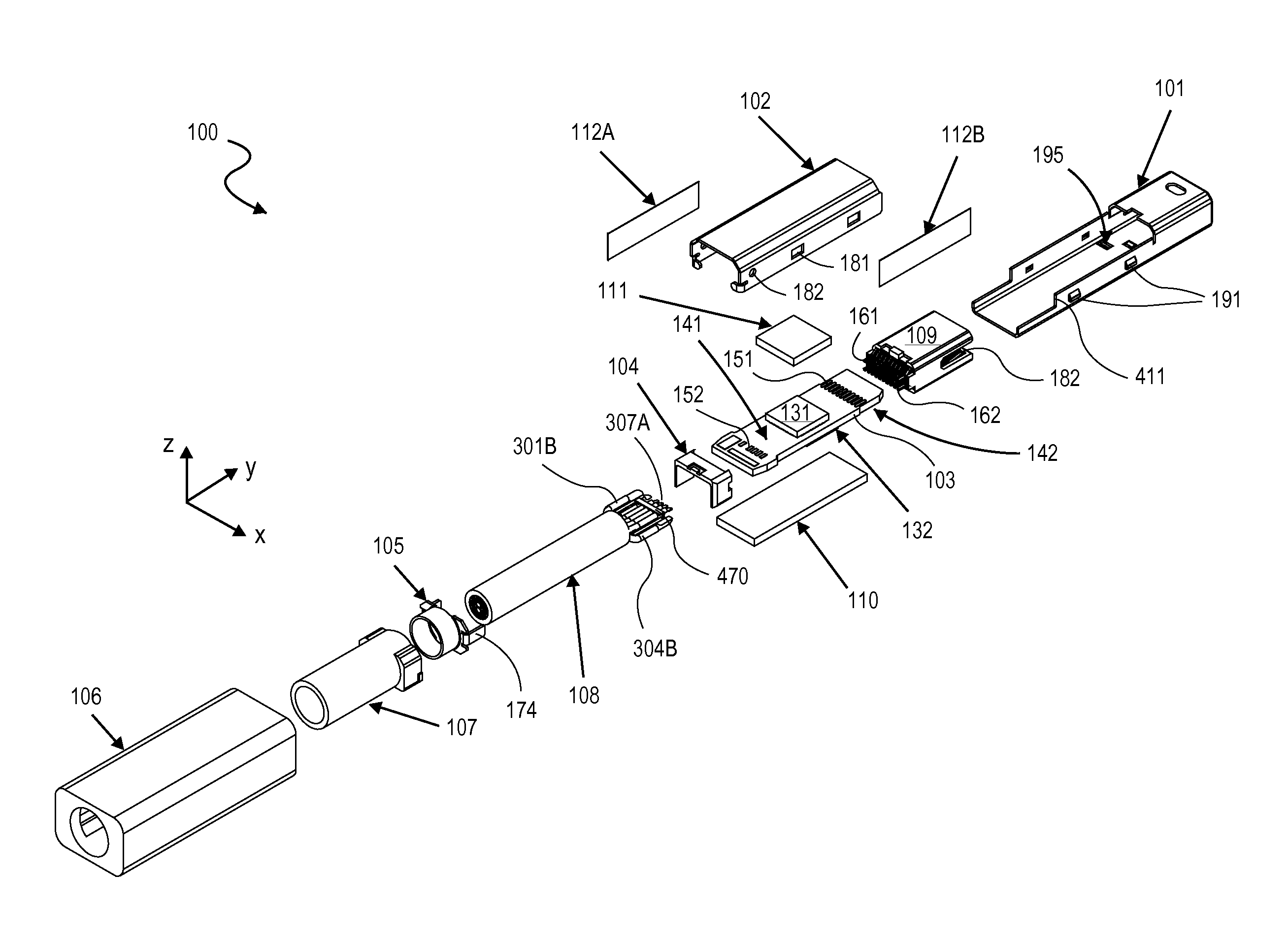
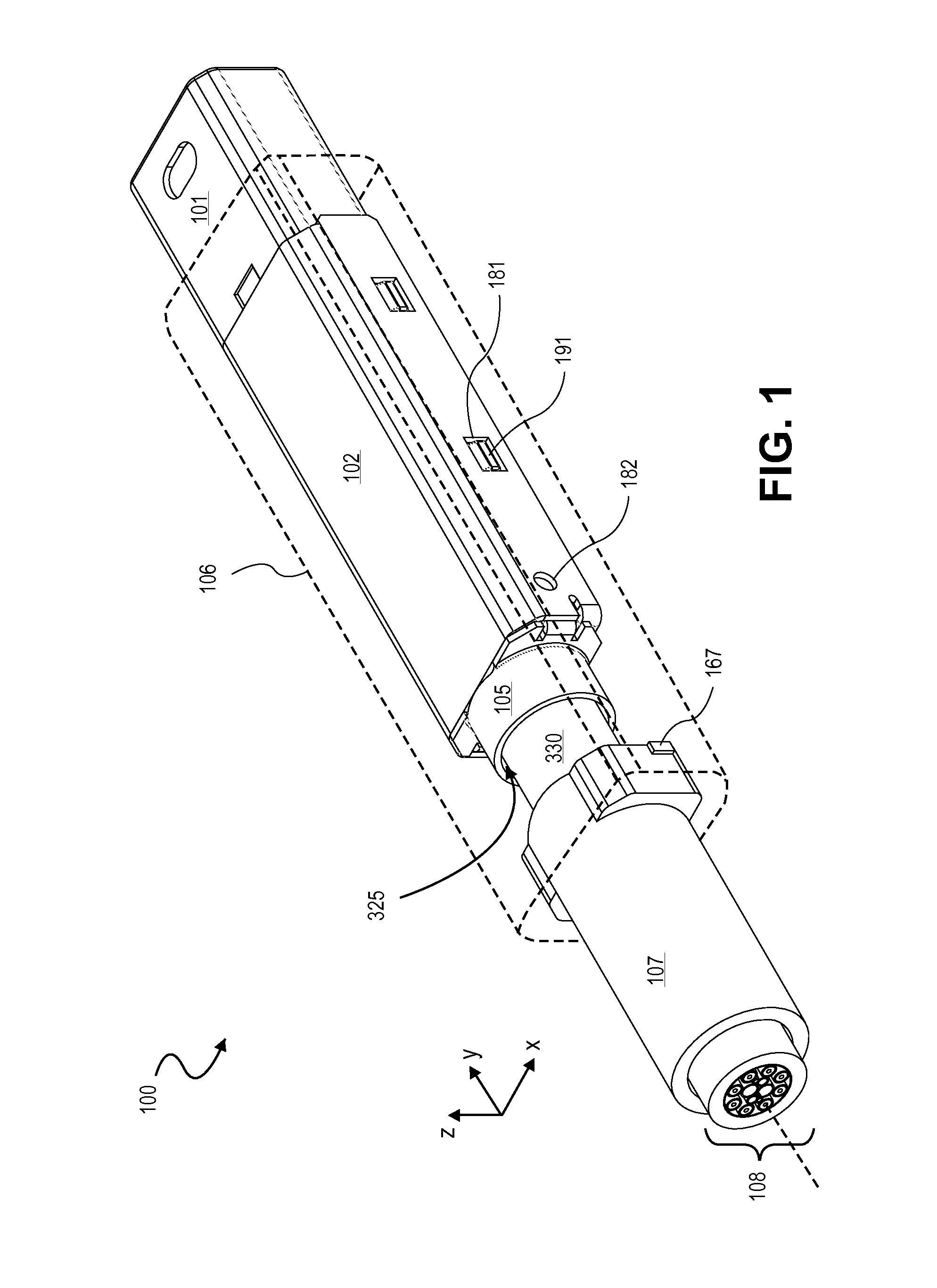
Active electrical communication cable assembly
An active electric cable assembly suitable for high speed communication (e.g., 10 Gbit / sec) between electronic devices, such as but not limited to a peripheral device (e.g., storage device, docking station, etc.) and a computing platform expansion bus. (e.g., supporting the standards and specifications associated with the trade name Thunderbolt®). In embodiments, through holes, embossments, mechanical stops, micro-coaxial single wires, thermal pads, and dielectric film sheets are utilized in a robust cable assembly.
Owner:INTEL CORP
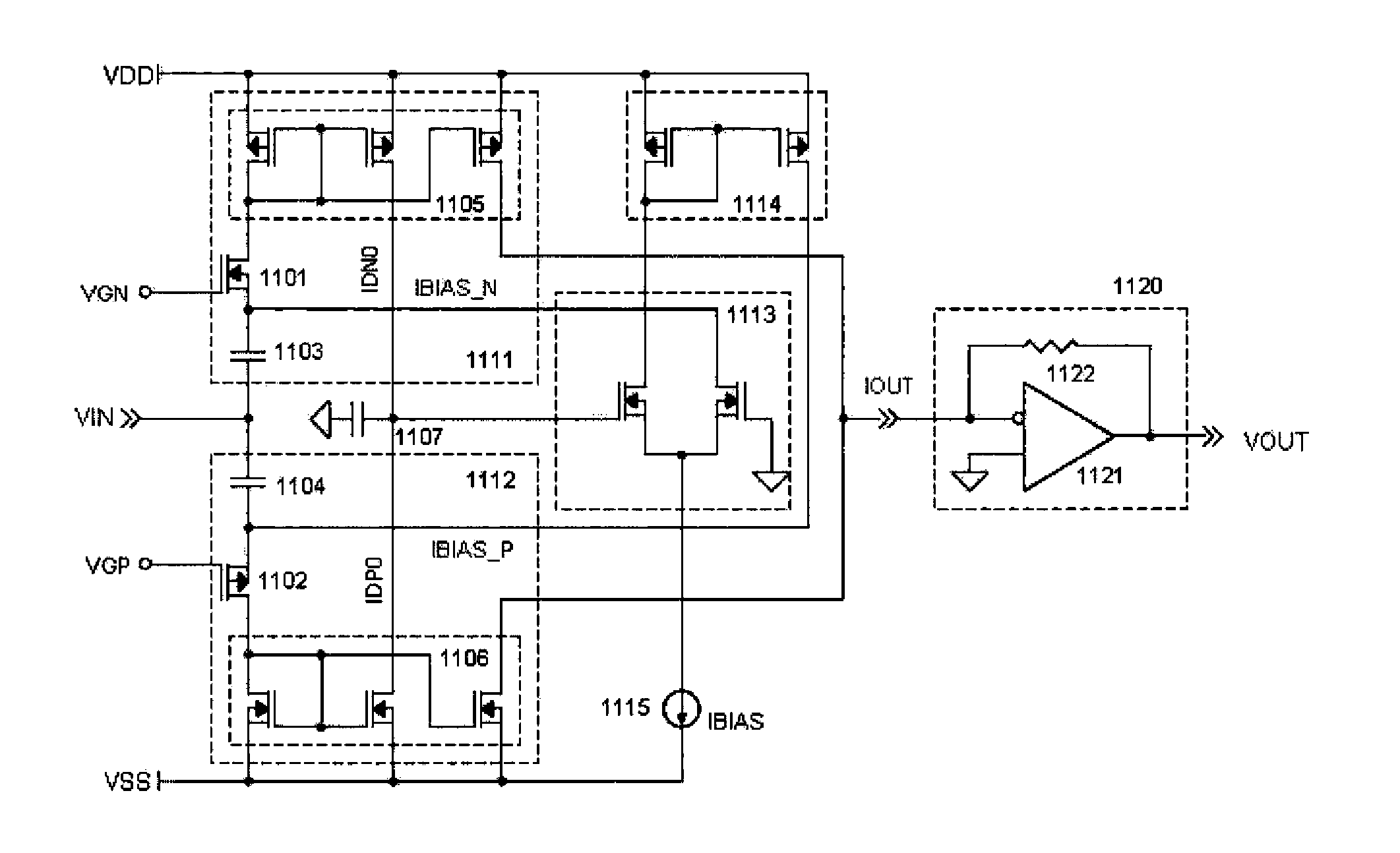
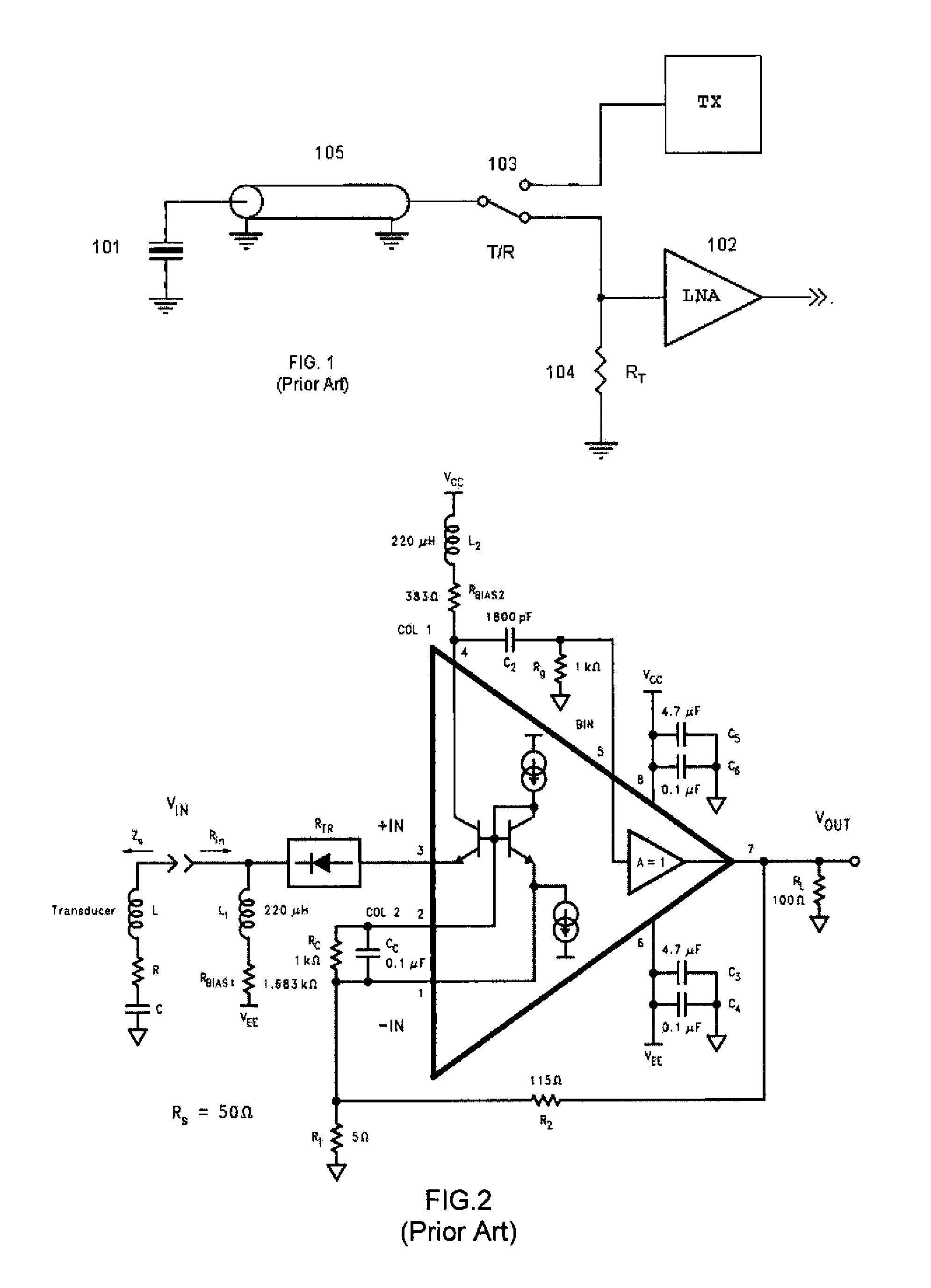
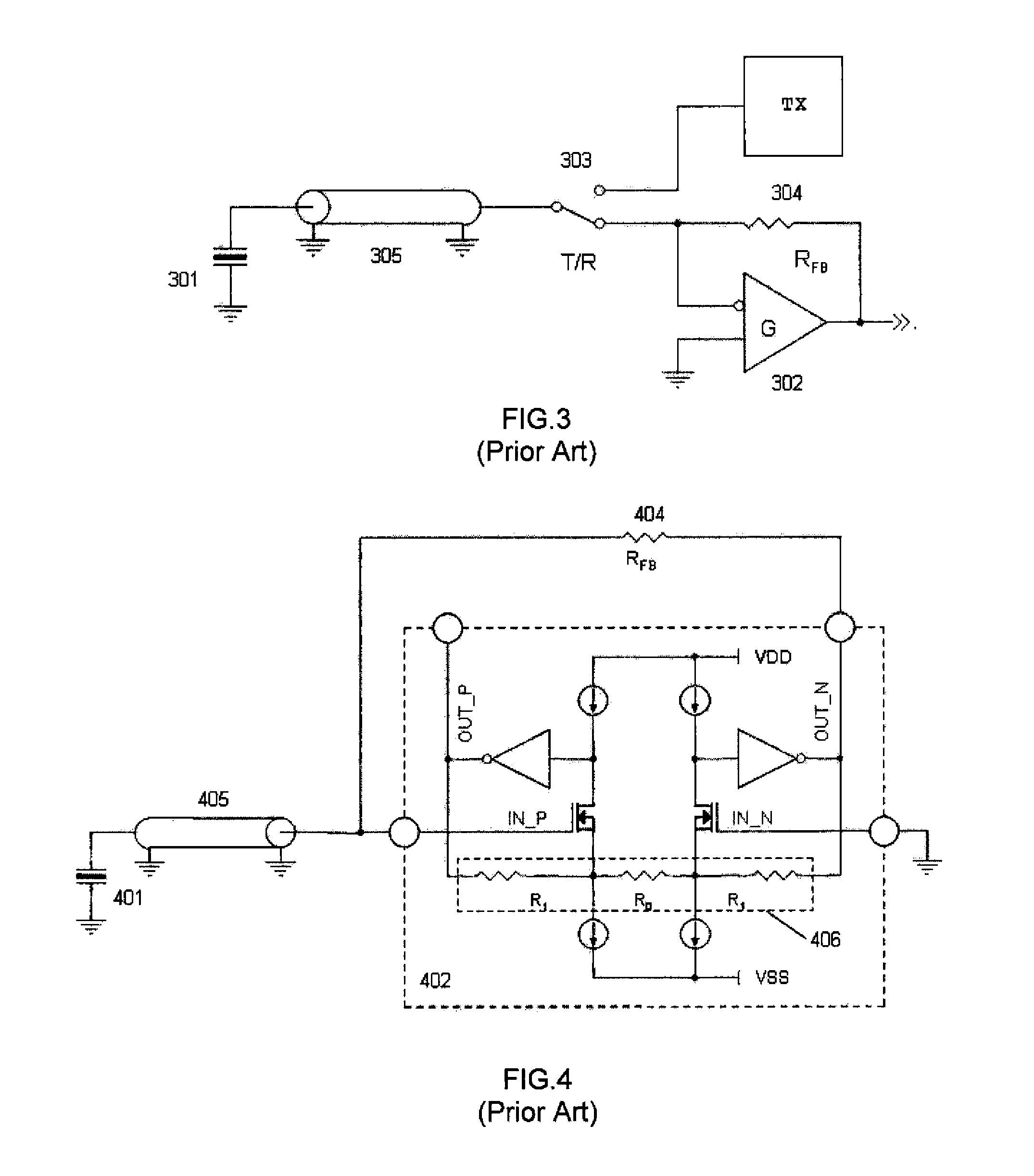
Current mode class ab low-noise amplifier and method of active cable termination
InactiveUS20150091646A1Minimize impactEasy to adjustPush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersUltrasound imagingDiagnostic Radiology Modality
This invention relates to medical ultrasonic imaging systems and, in particular, phased array imaging systems operating in different scan formats and imaging modalities. More specifically, the invention relates to the front-end processing of ultrasonic echoes.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Light weight parallel manipulators using active/passive cables
InactiveUS7367771B2Maximize the benefitsImprove performance and simplicity and feasibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusUltra high speedCost effectiveness
The present invention provides parallel, cable based robotic manipulators, for use in different applications such as ultra high-speed robots or positioning devices with between three to six degrees of freedom. The manipulators provide more options for the number of degrees of freedom and also more simplicity compared to the current cable-based robots. The general structure of these manipulators includes a base platform, a moving platform or end effector, an extensible or telescoping central post connecting the base to moving platform to apply a pushing force to the platforms. The central post can apply the force by an actuator (active), or spring or air pressure (passive) using telescoping cylinders. The robotic manipulators use a combination of active and passive tensile (cable) members, and collapsible and rigid links to maximize the benefits of both pure cable and conventional parallel mechanisms. Different embodiments of the robotic manipulators use either active cables only, passive cables only, or combinations of active and passive cables. An active cable is one whose length is varied by means of a winch. A passive cable is one whose length is constant and which is used to provide a mechanical constraint. These mechanisms reduce the moving inertia significantly to enhance the operational speed of the robots. They also provide a simpler, more cost effective way to manufacture parallel mechanisms for use in robotic applications.
Owner:KHAJEPOUR AMIR +3
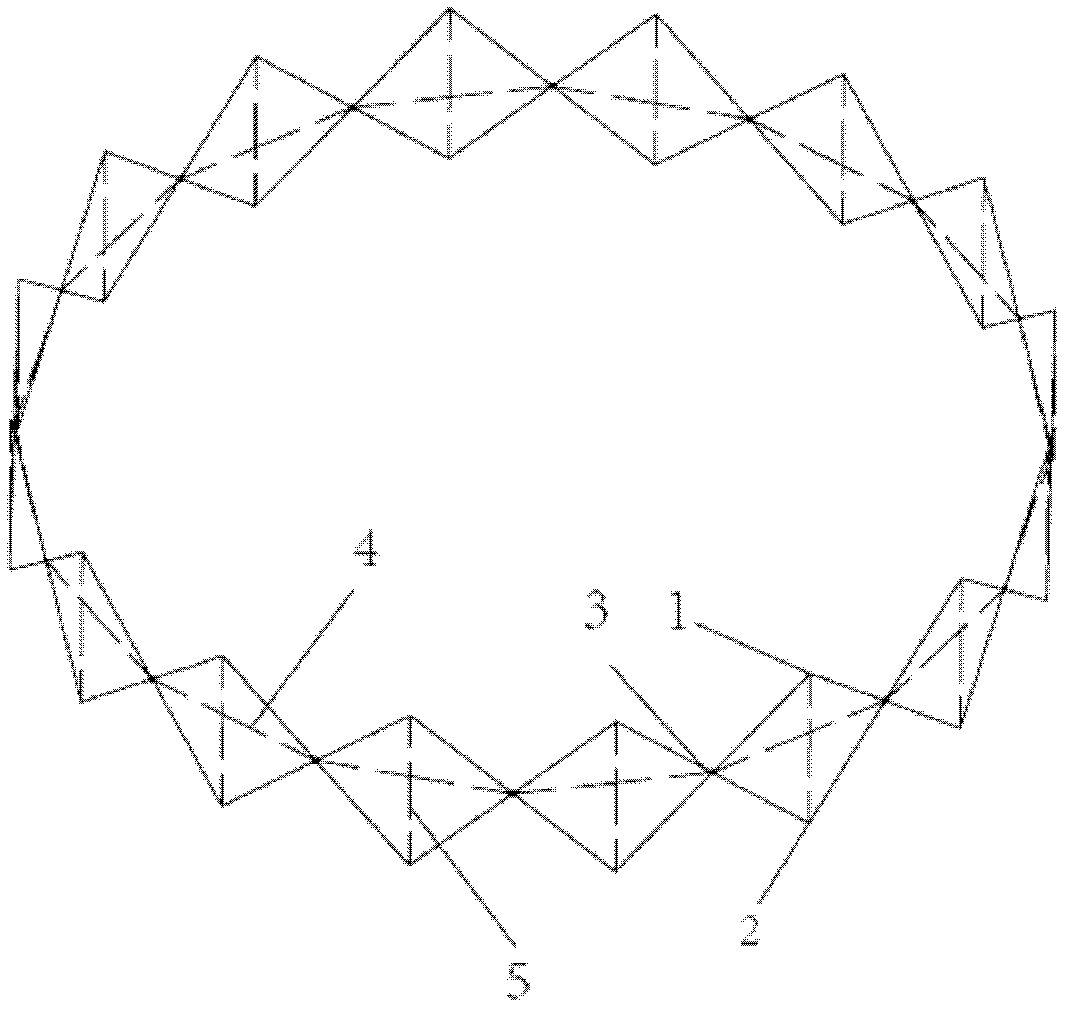
Cable-pole type deployable structure
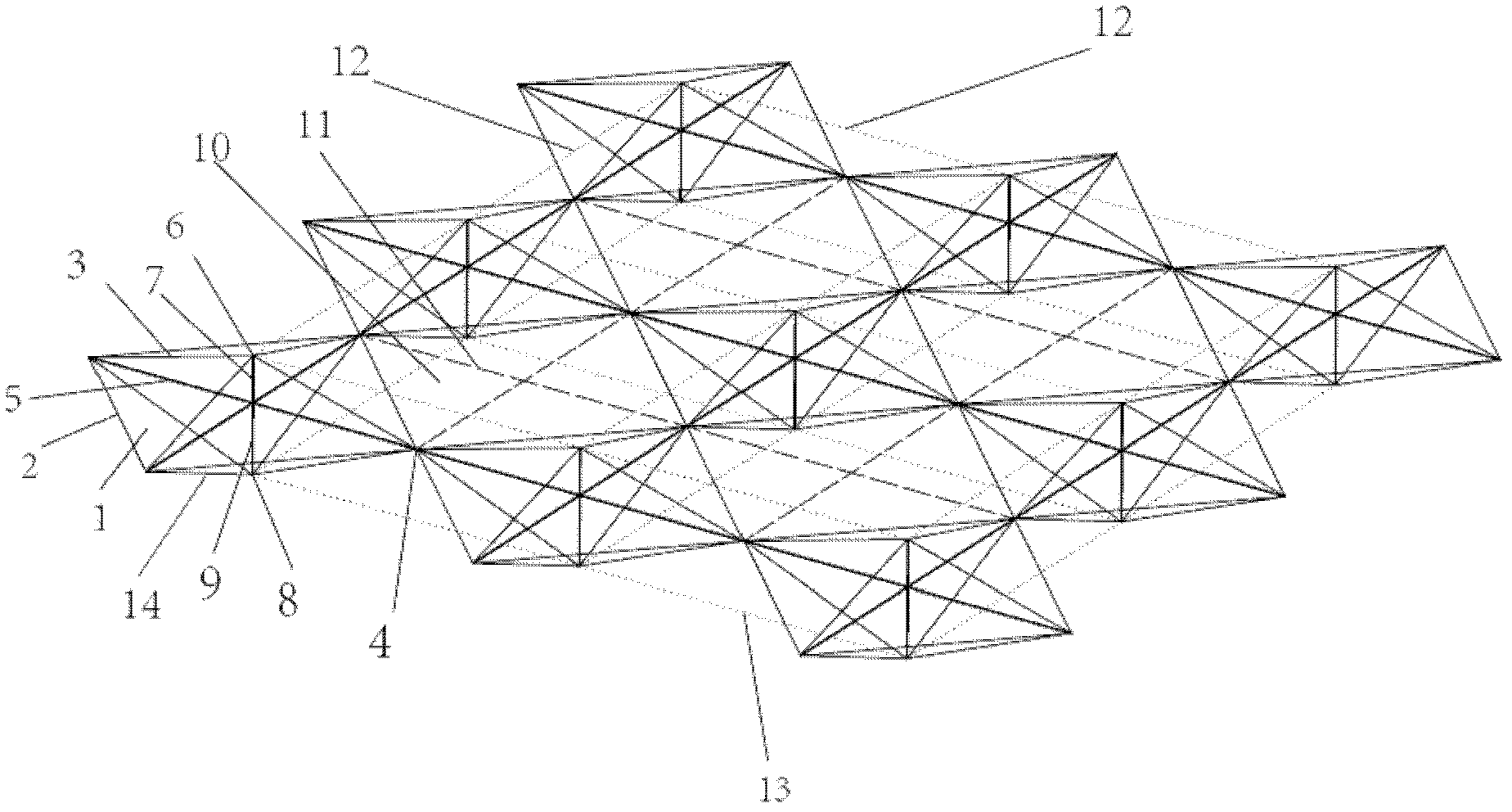
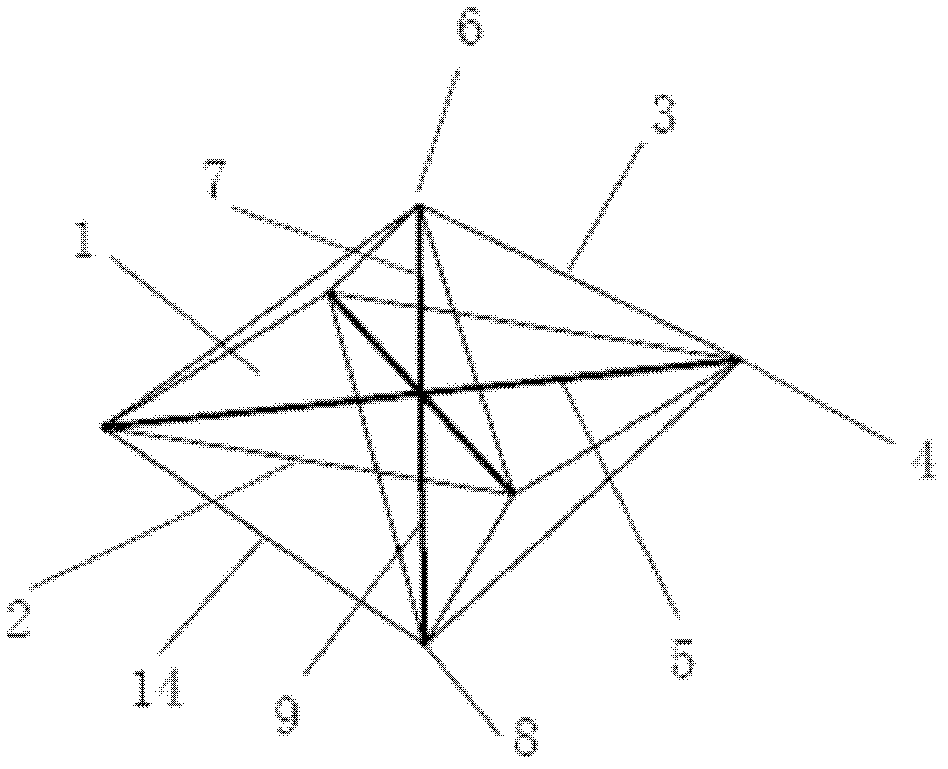
The invention discloses a cable-pole type deployable structure, obtained by mutual connection of octahedral basic units in two plane directions, wherein each octahedral base unit is composed of an inhaul cable and a pressure bar; the octahedral base unit is composed of an upper rectangular pyramid and a lower rectangular pyramid which have the same bottom surface; four edges of the bottom surface quadrilateral of the rectangular pyramid are composed of travel cables for only bearing tension; four edges of the upper rectangular pyramid are four upper oblique cables; four edges of the lower rectangular pyramid are four lower oblique cables; four horizontal pressure bars are connected from the four top points of the bottom surface quadrilateral of the rectangular pyramid to a central point of the quadrilateral; the intersection point of the four horizontal pressure bars is connected with the top point of the upper rectangular pyramid through a first vertical pressure bar; the intersection point of four horizontal pressure bars is connected with the top point of the lower rectangular pyramid by a second vertical pressure bar; adjacent octahedral basic units are connected through the top points of the bottom surface quadrangle of the pyramid; and the upper oblique cables of all basic units in each line and row in the deployable structure assembled by octahedral basic units in the same plane are connected to an active cable.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
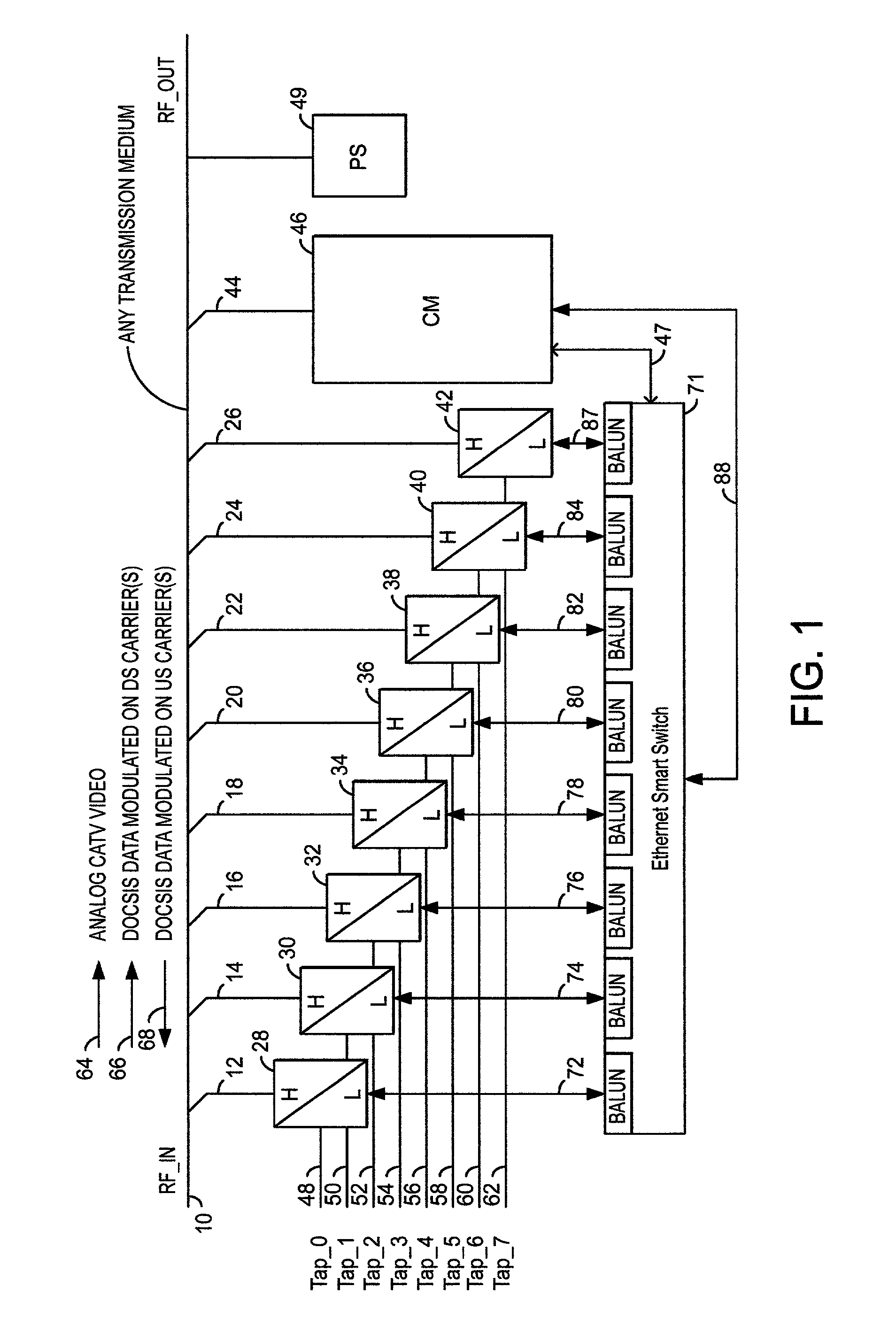
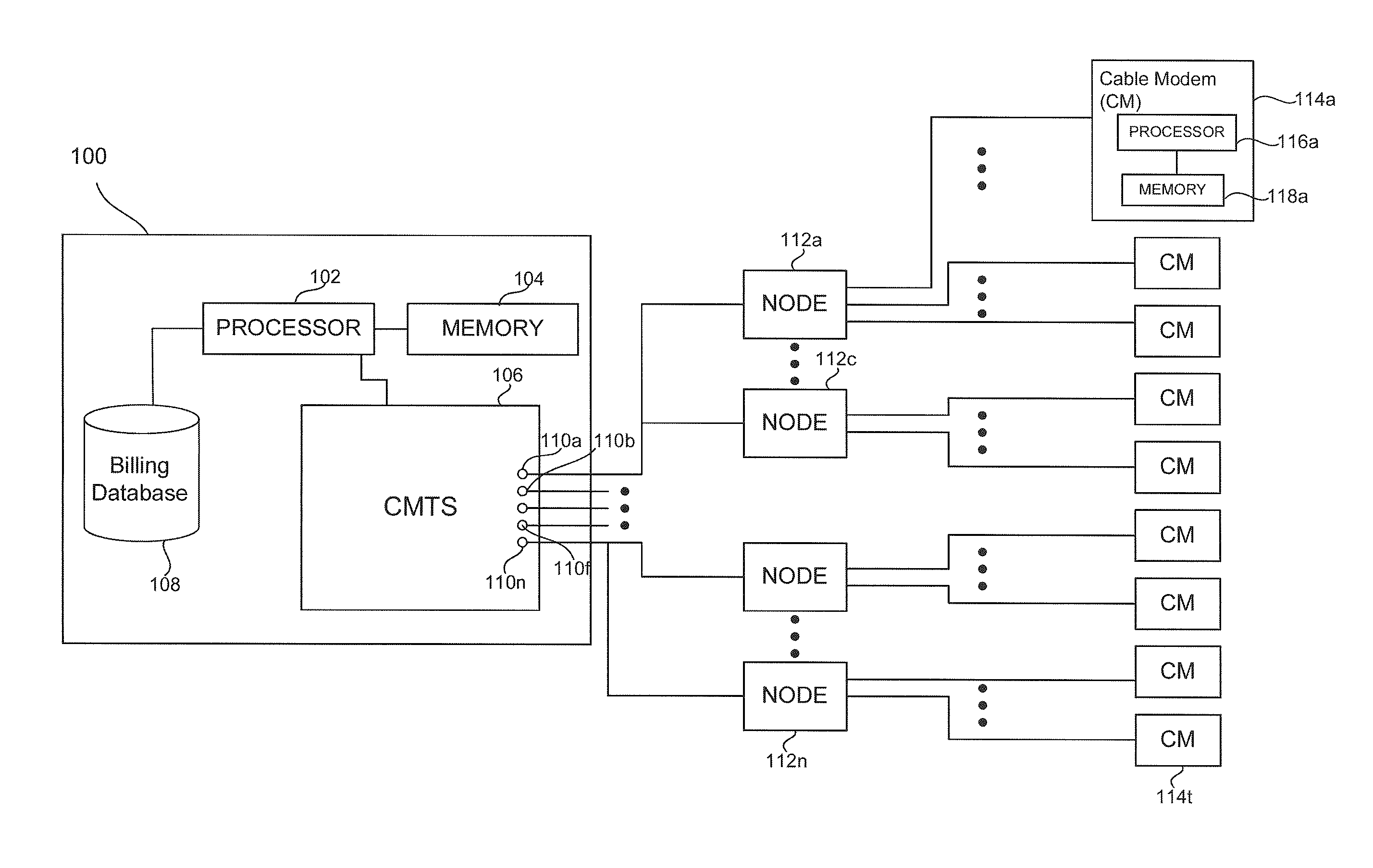
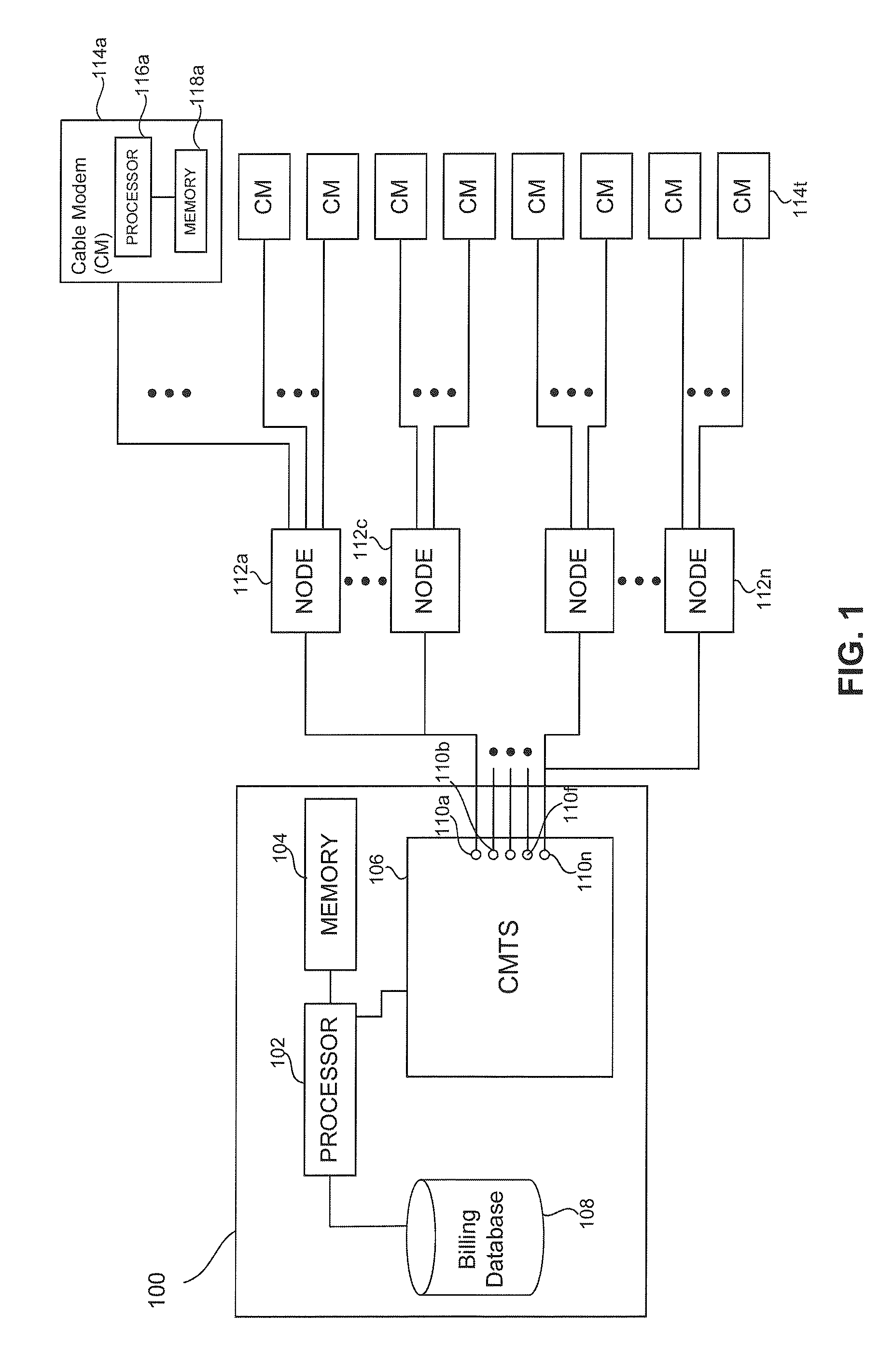
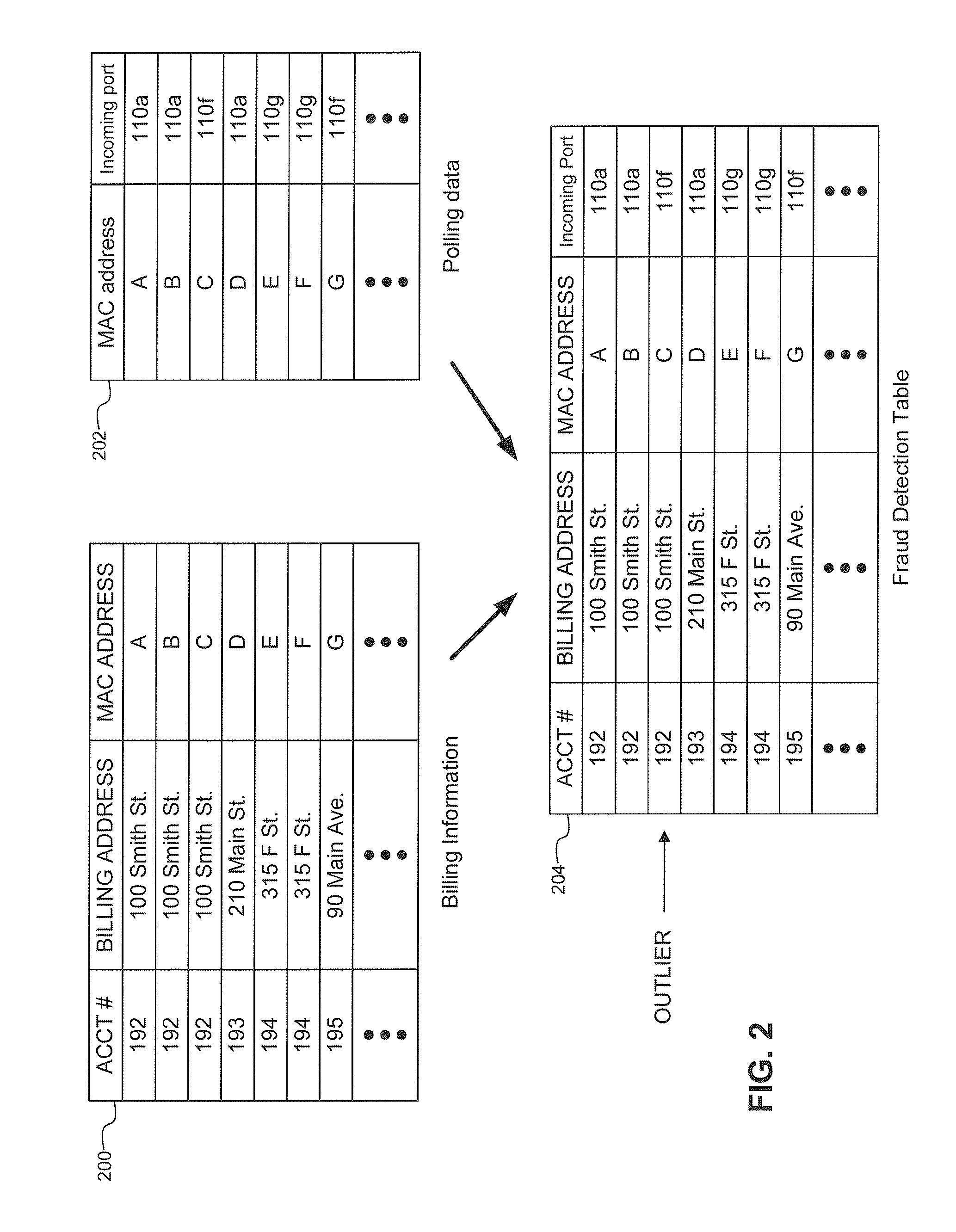
Topographic fraud detection
Methods and systems to detect topographic fraud are provided herein. The system includes a Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) to periodically poll active cable modems and generate polling data. The system also includes a processor and a memory coupled to the CMTS. The processor is configured to, based on instructions in the memory, periodically determine a current geographic location for each polled cable modem based on the polling data from the CMTS, determine a geographic radius within which each polled cable modem is to be operated in and determine cable modems whose current geographic location is outside of their geographic radius.
Owner:CSC HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com