Patents
Literature
71 results about "Airway wall" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
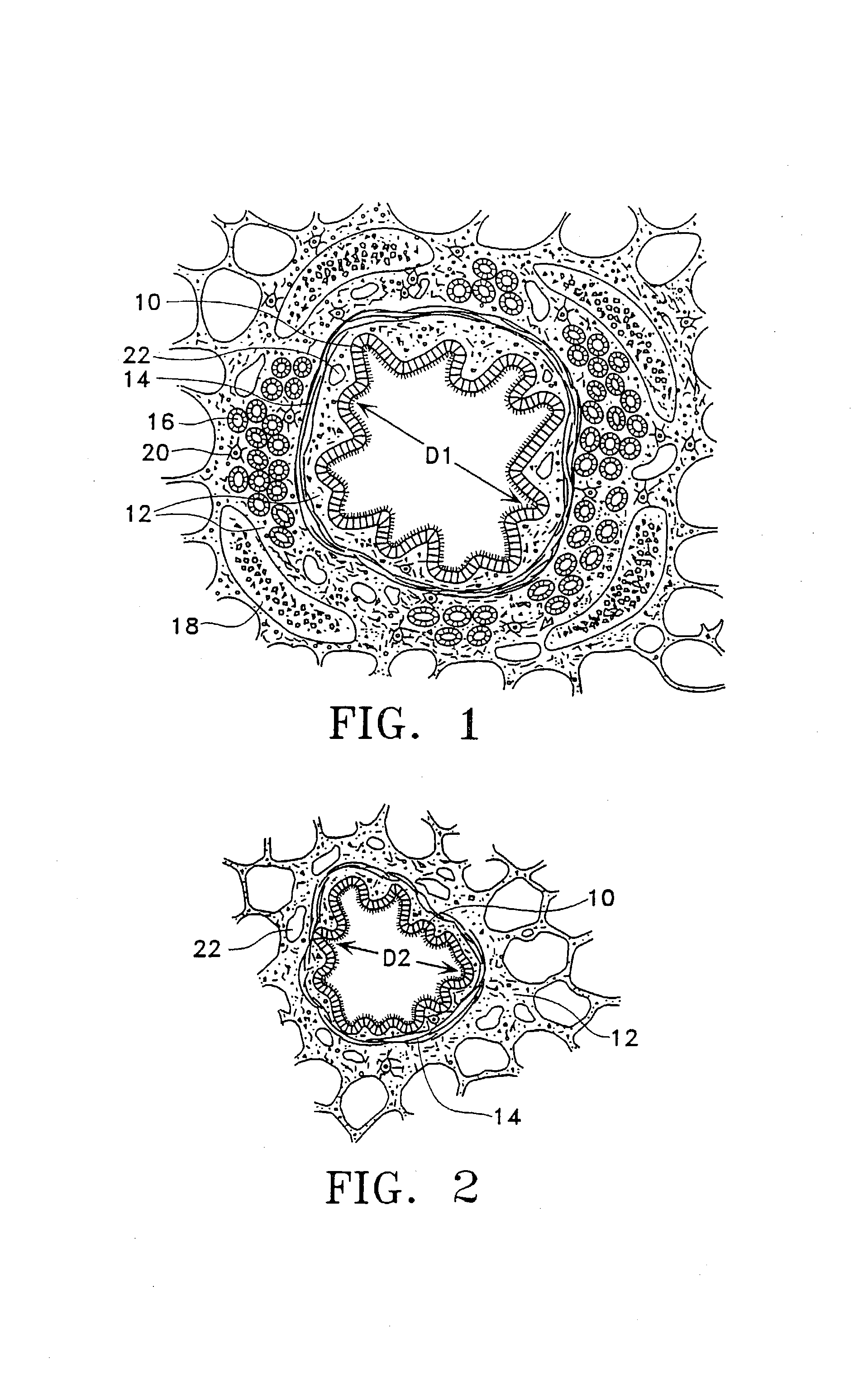
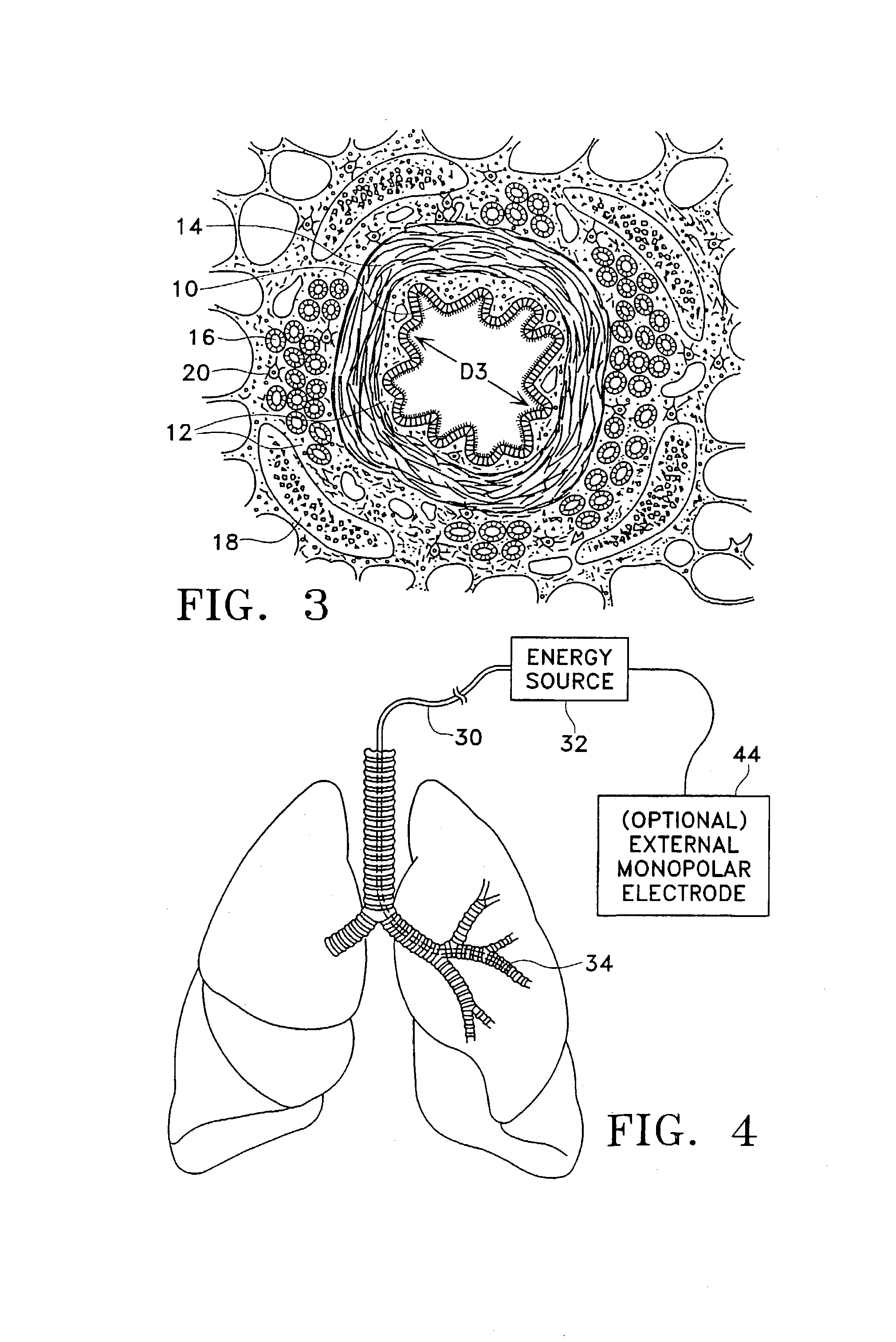
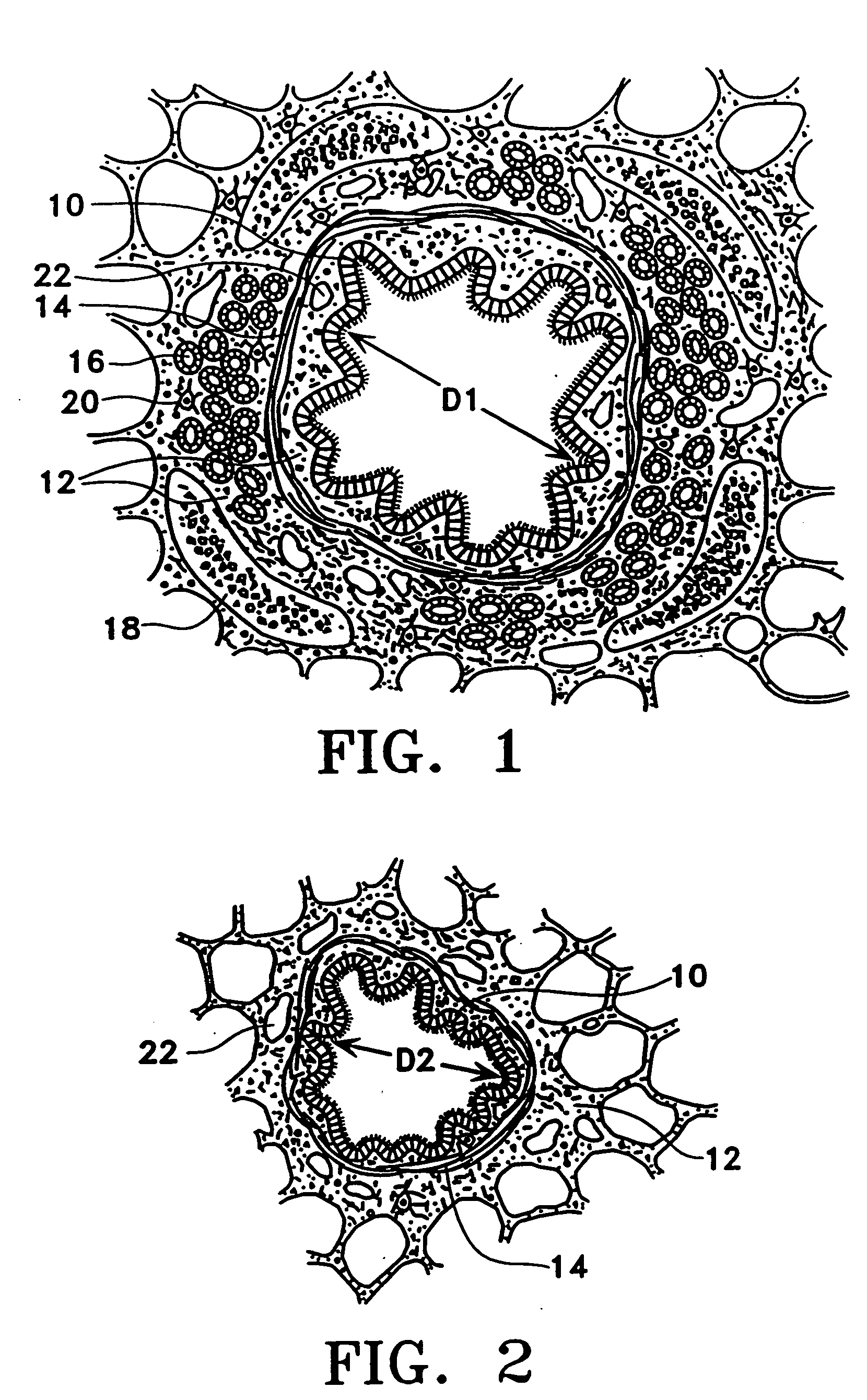
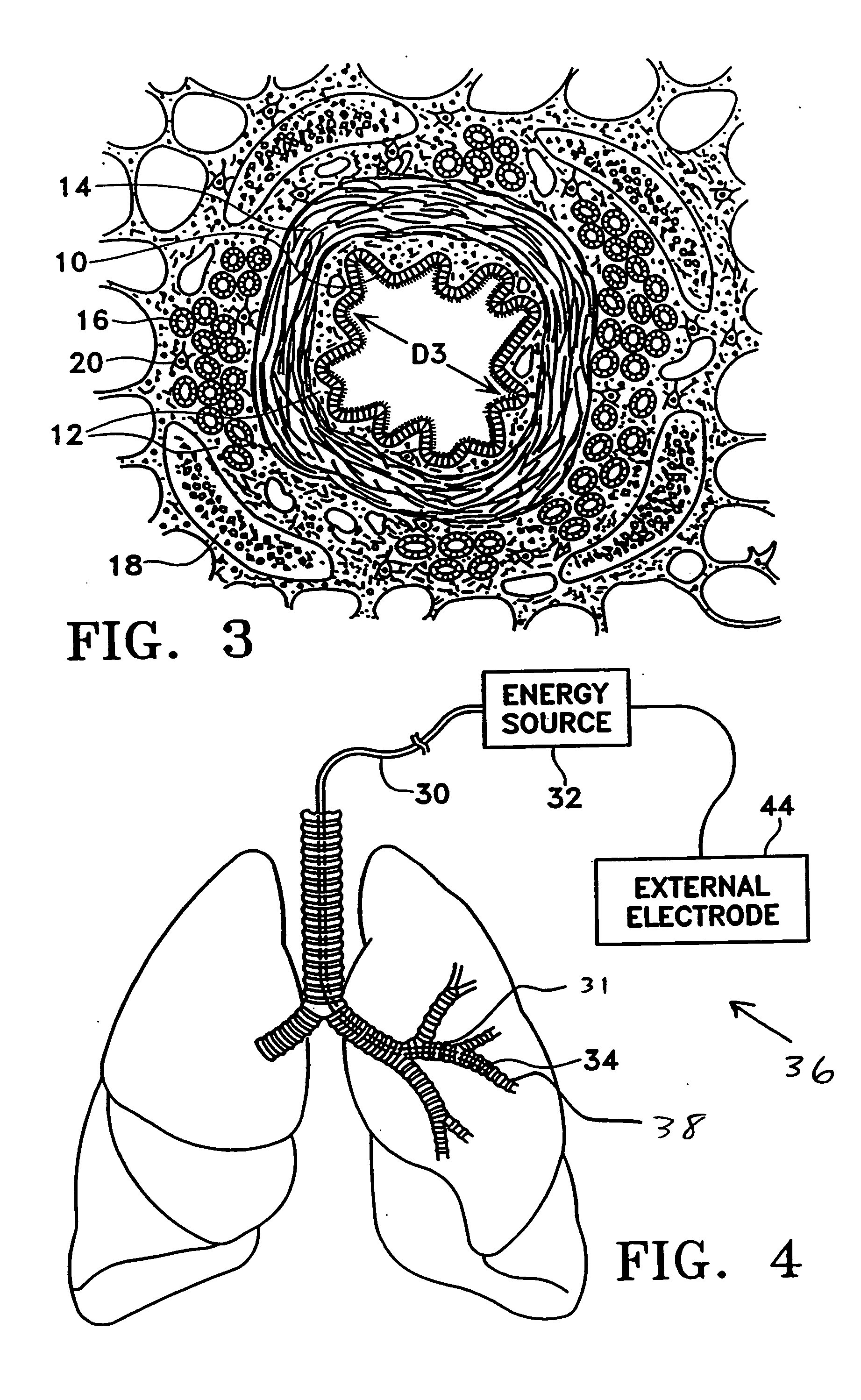
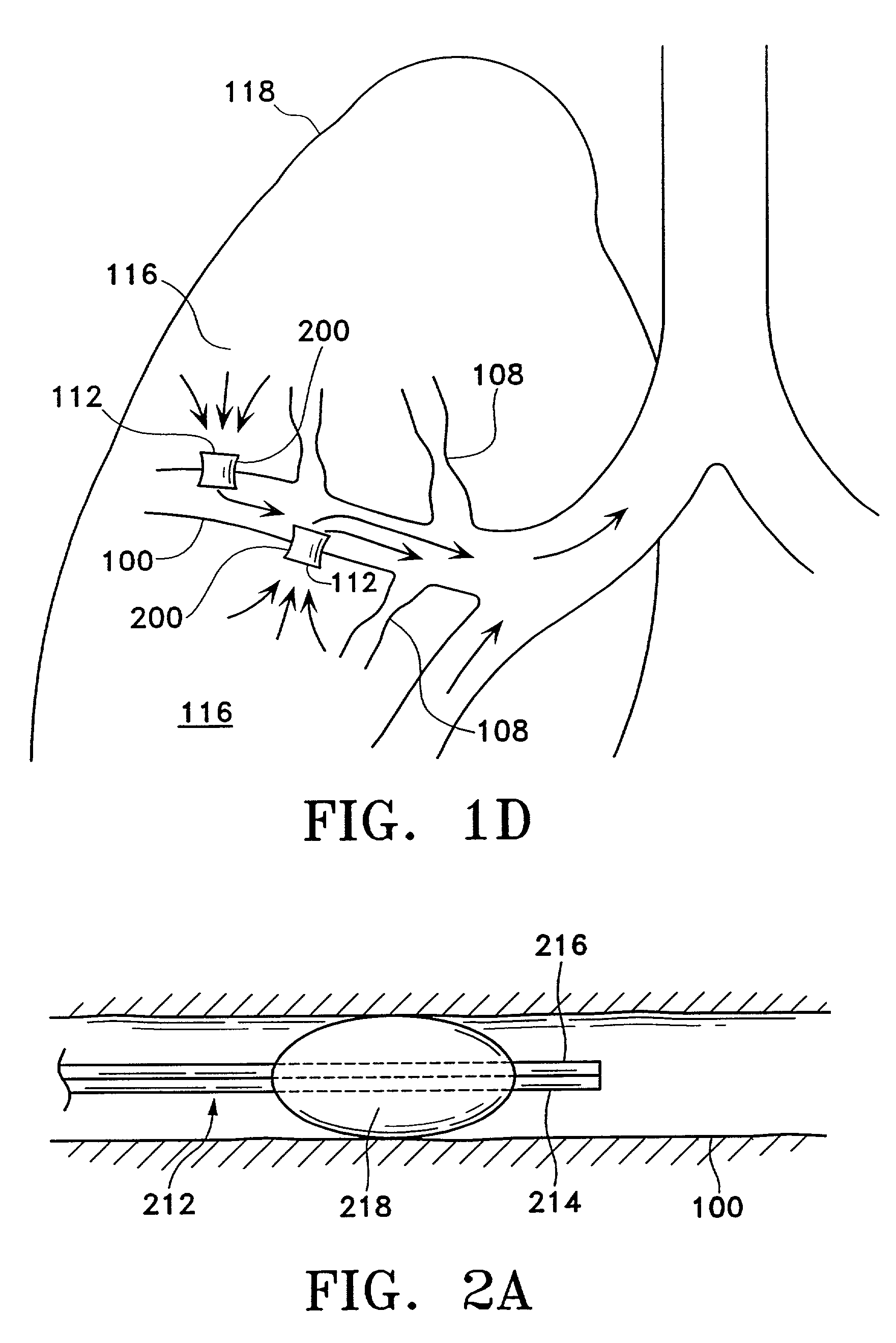
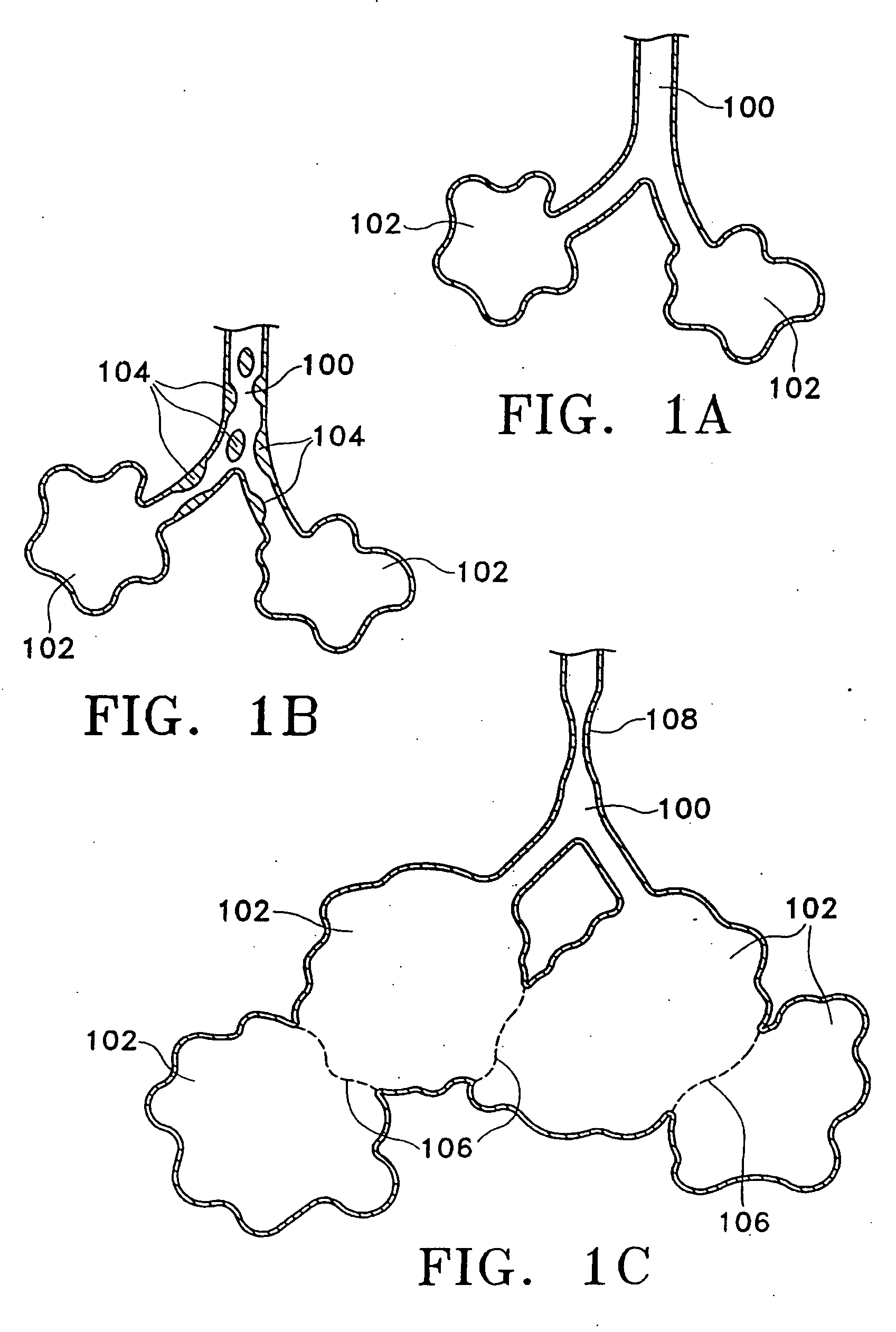
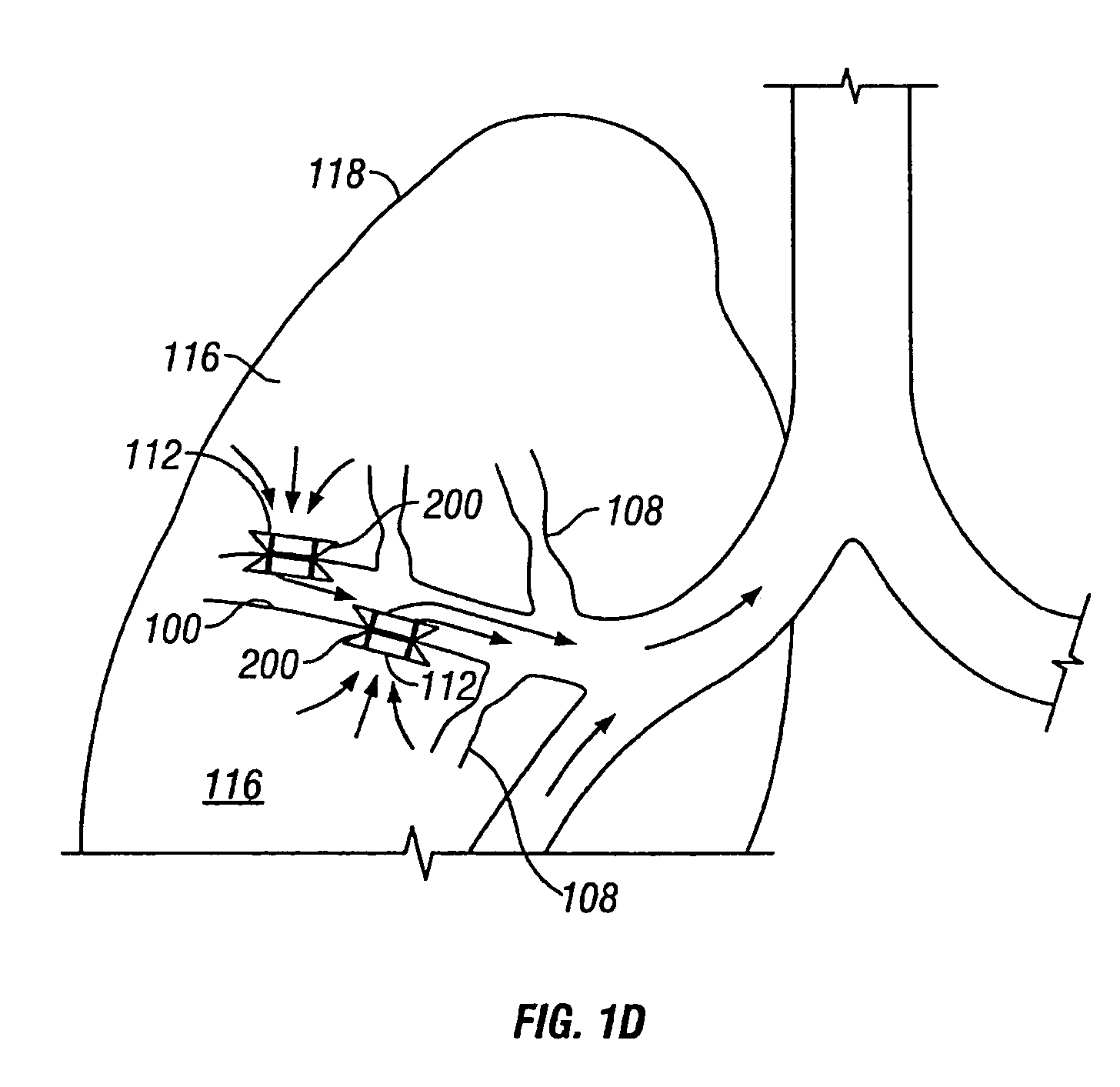
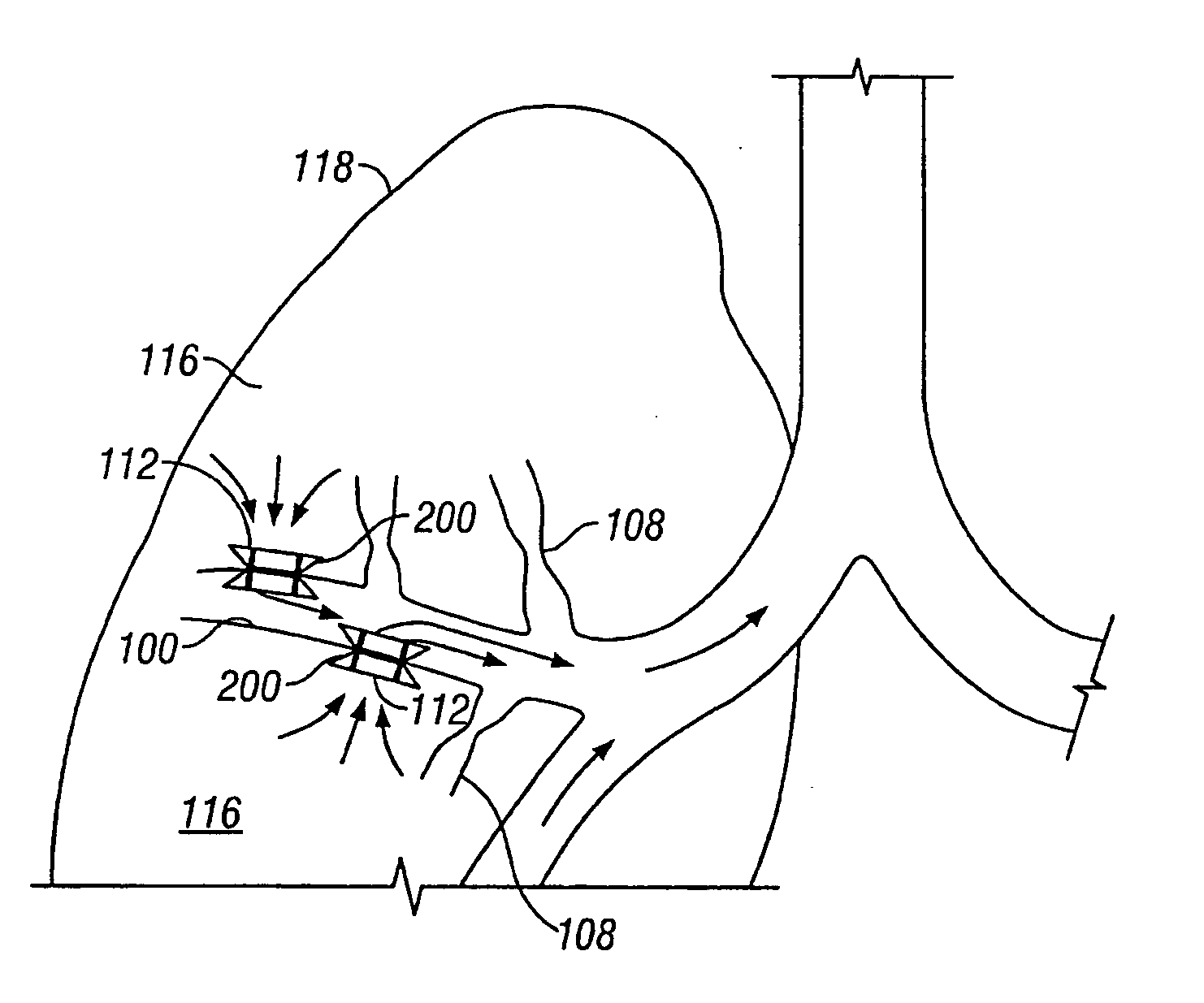
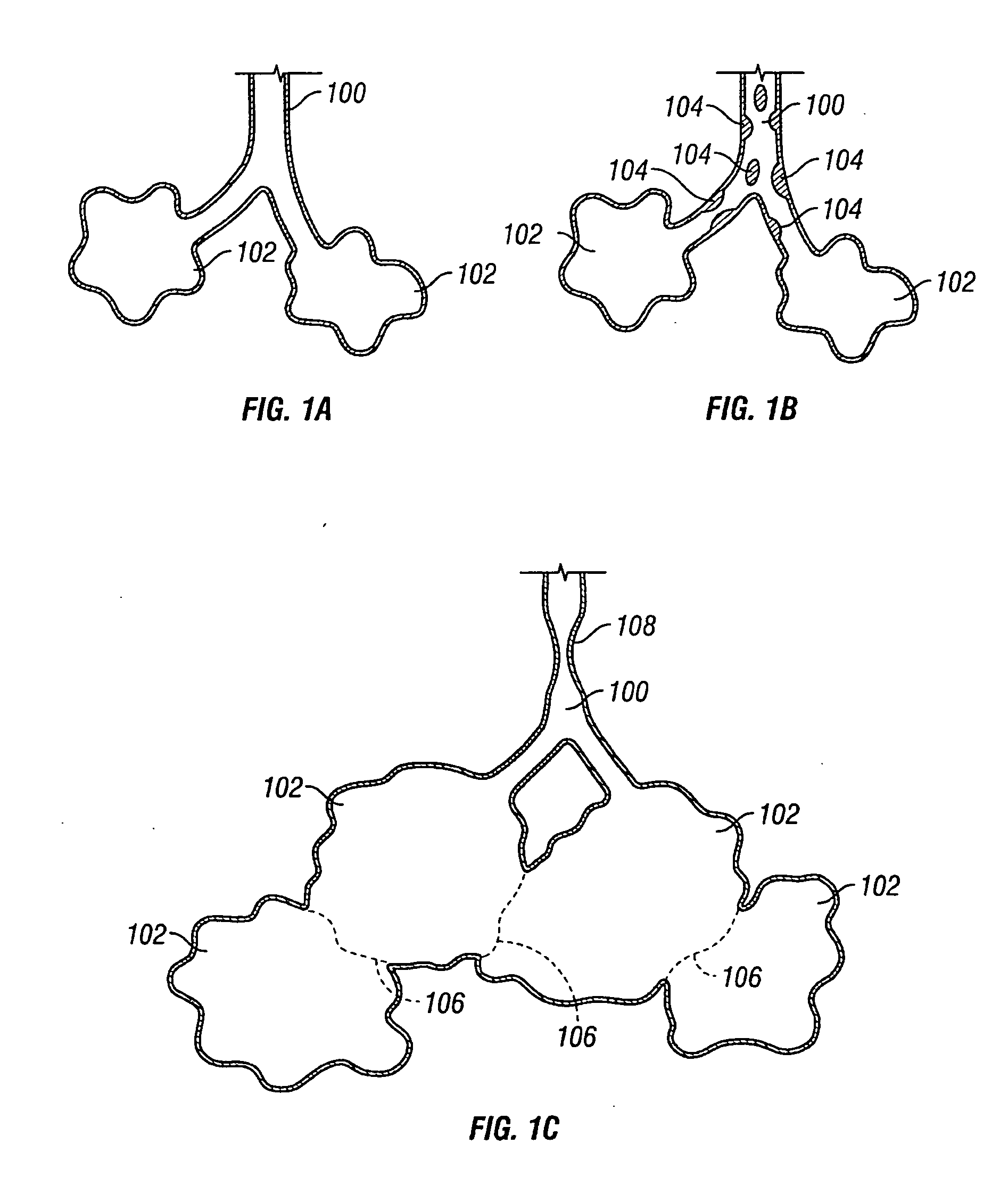
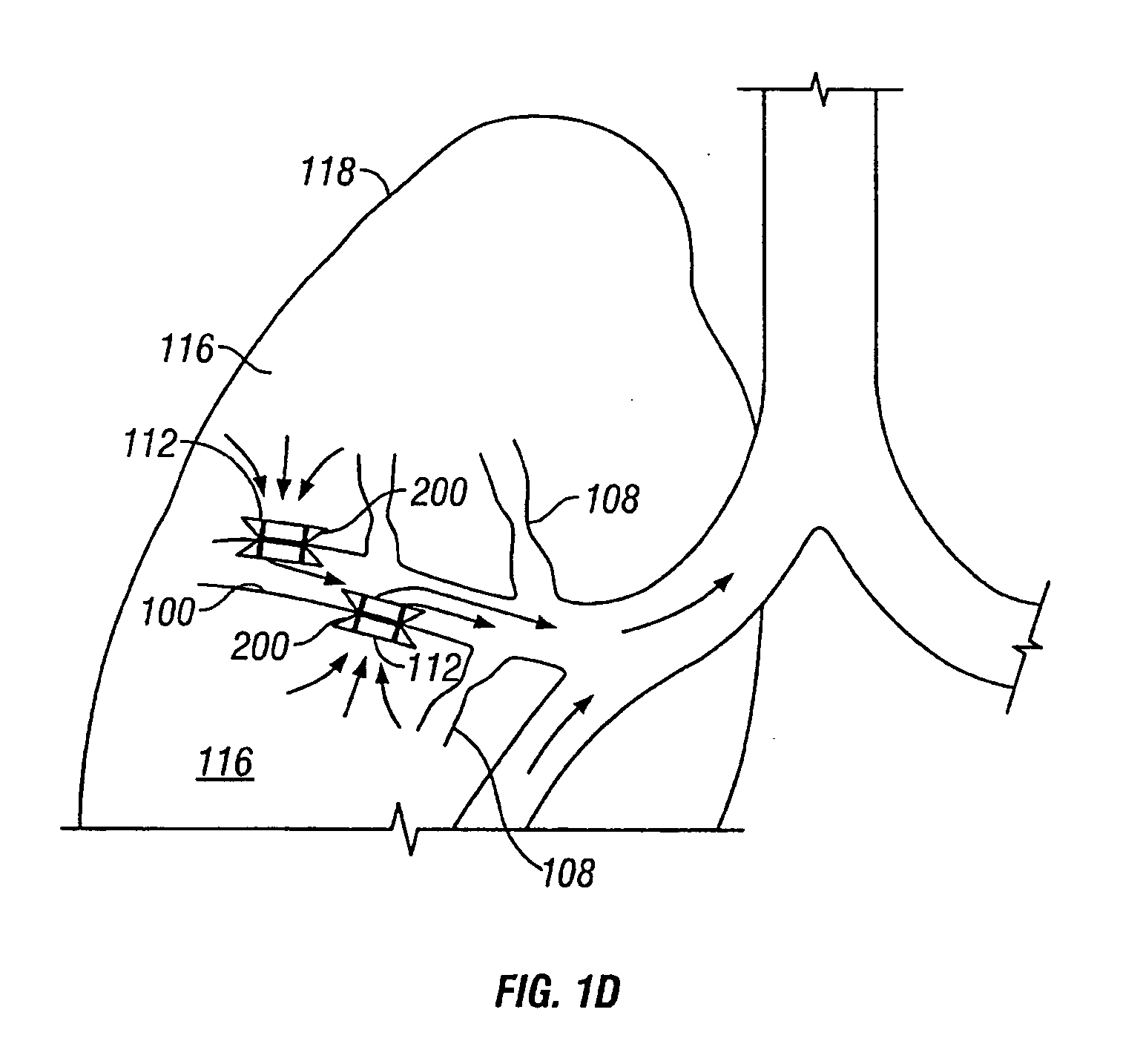
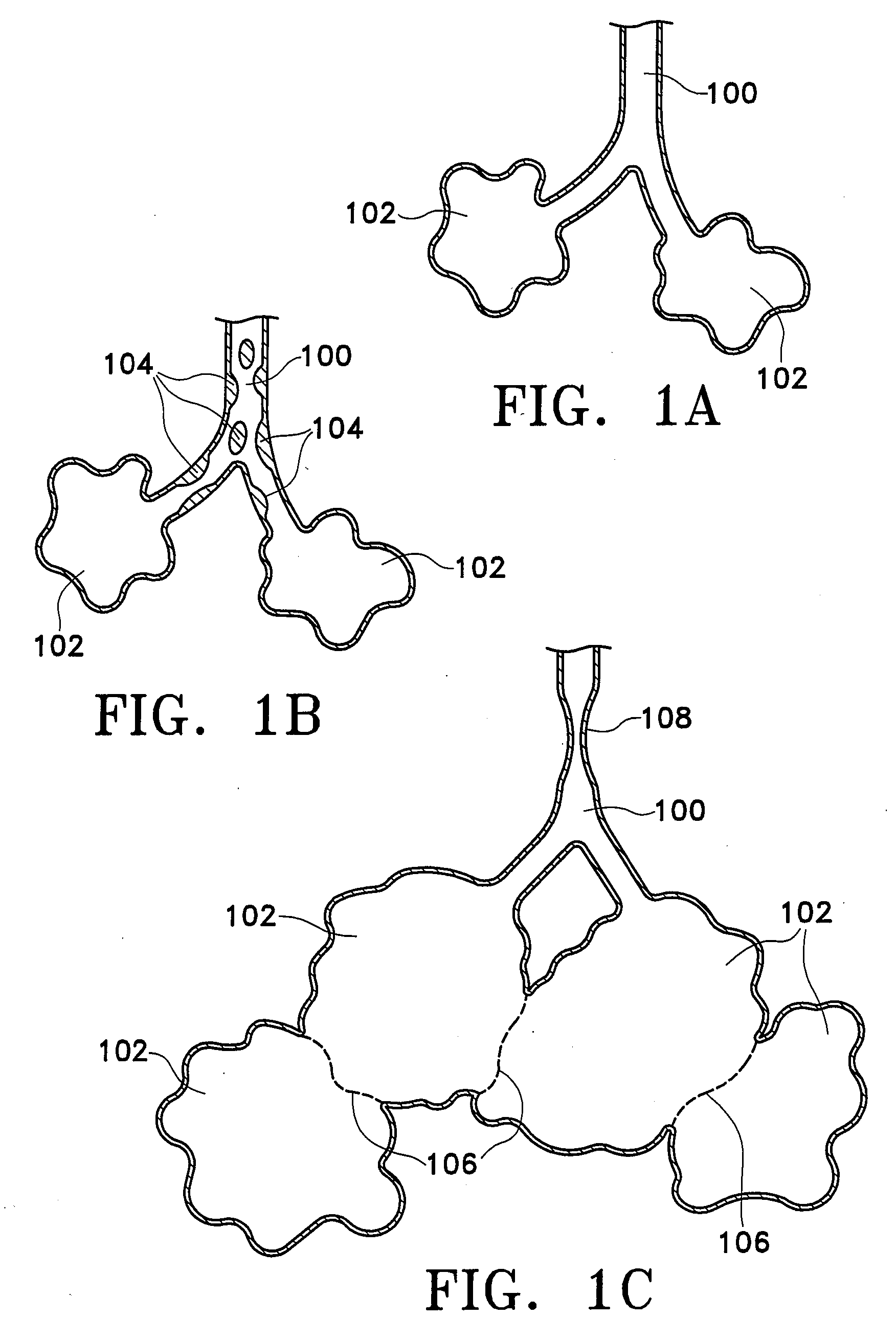
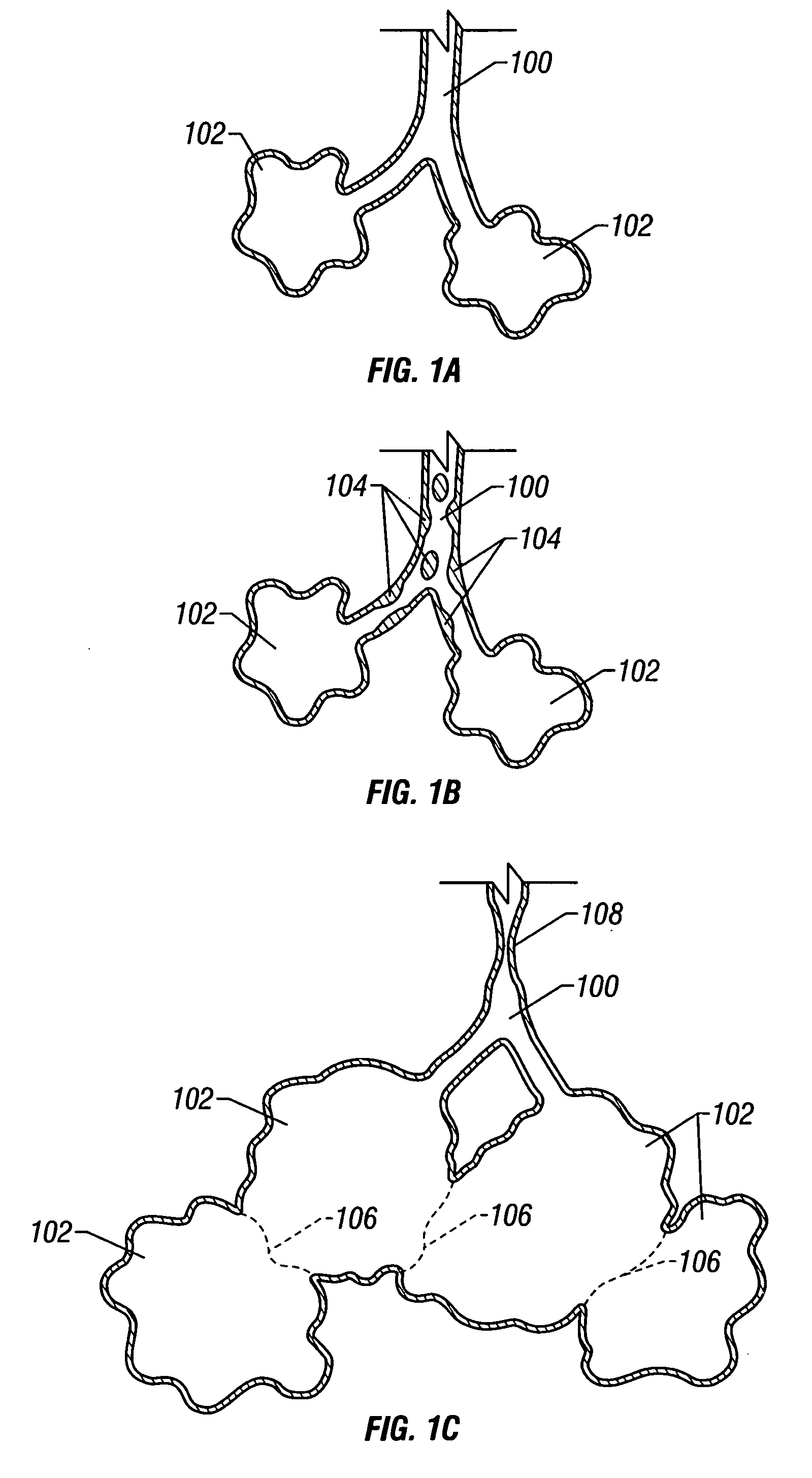
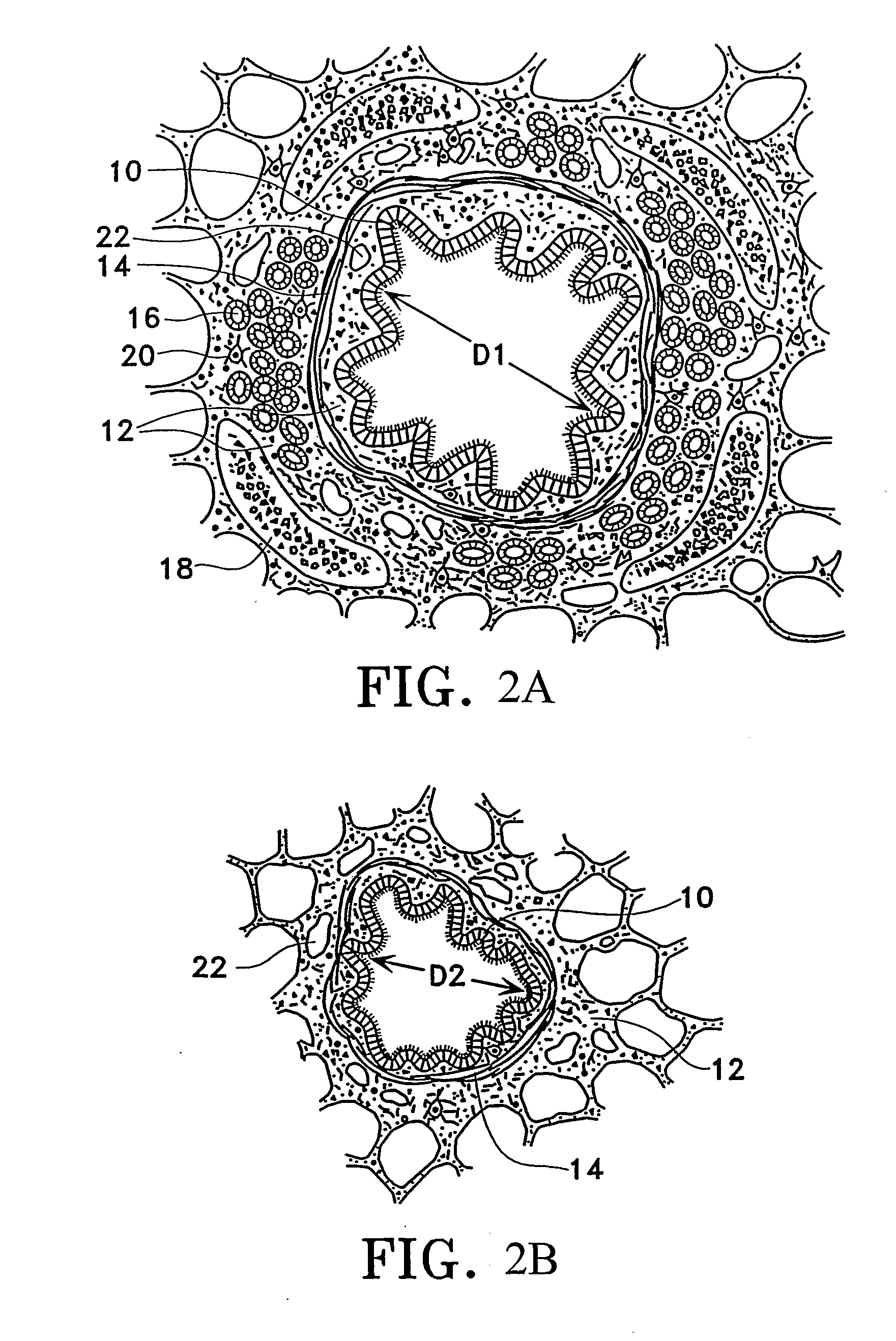
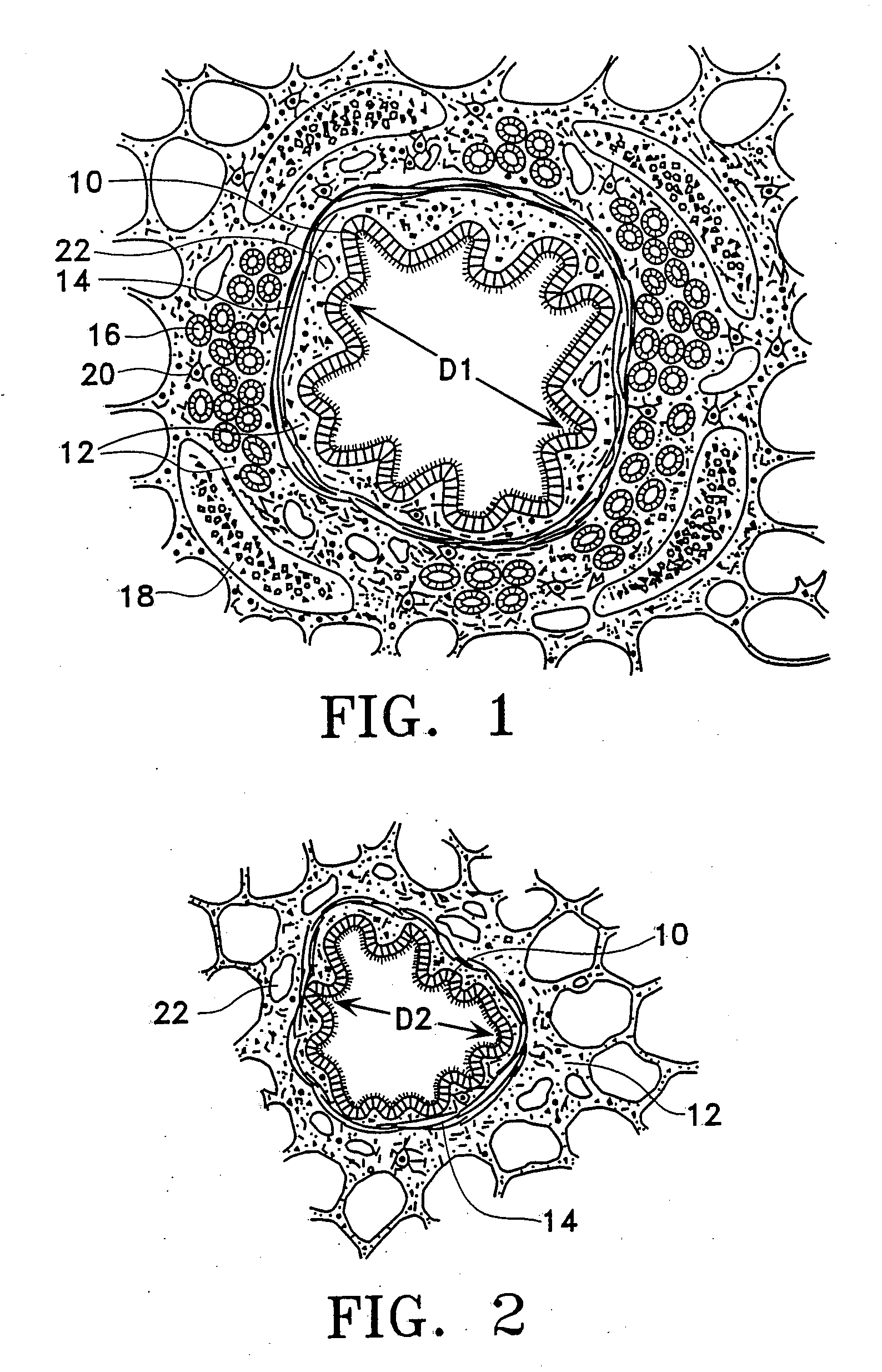
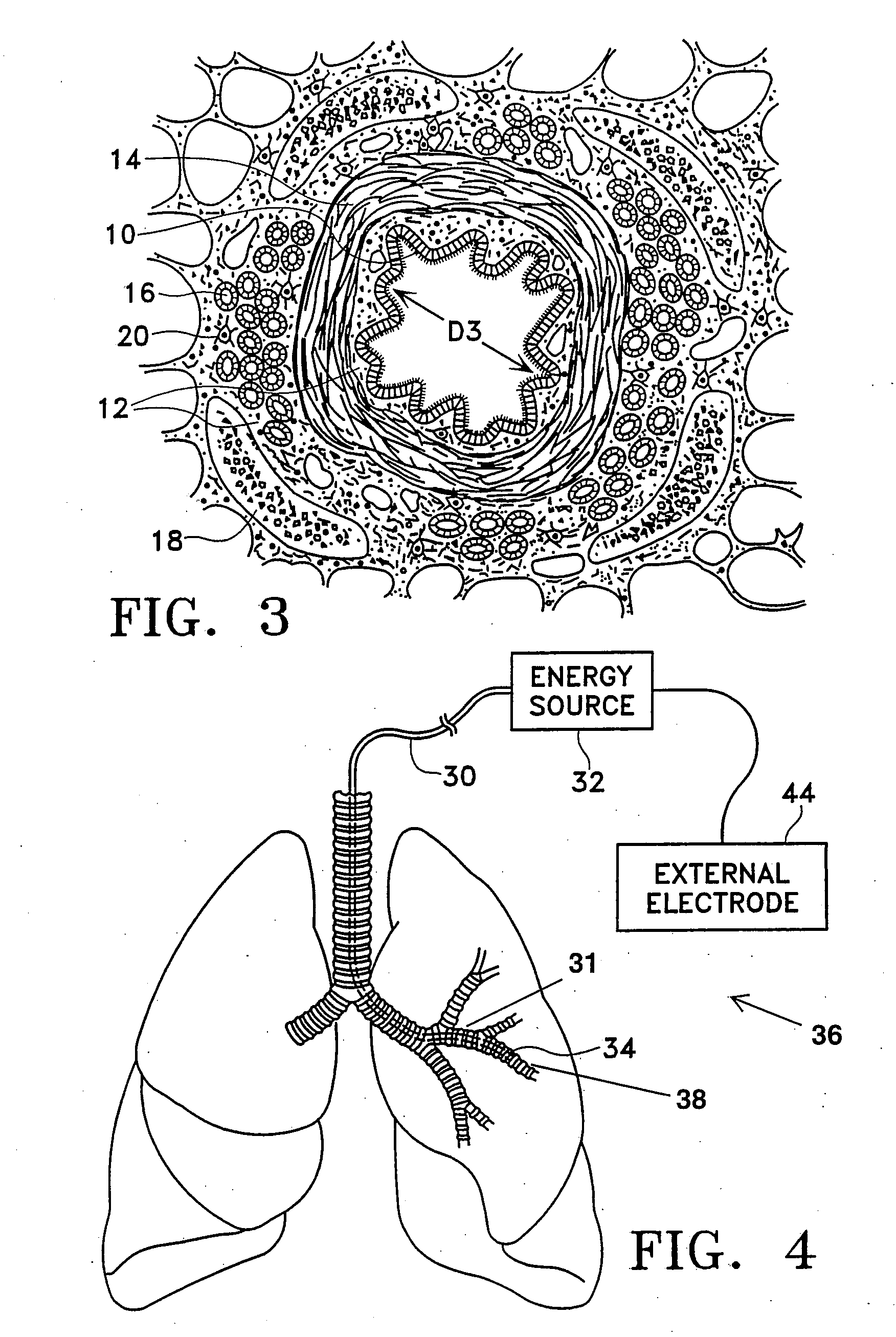
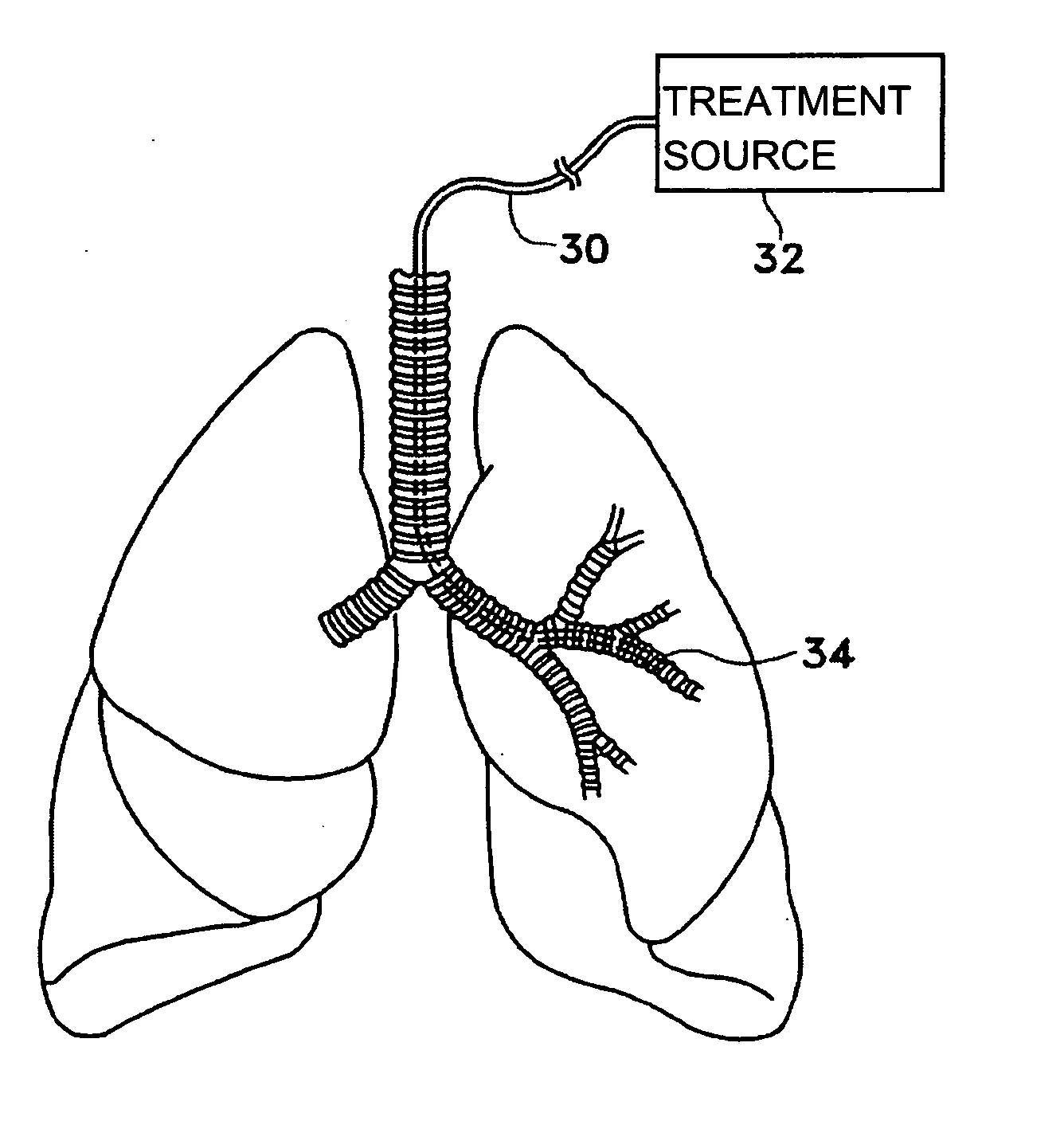
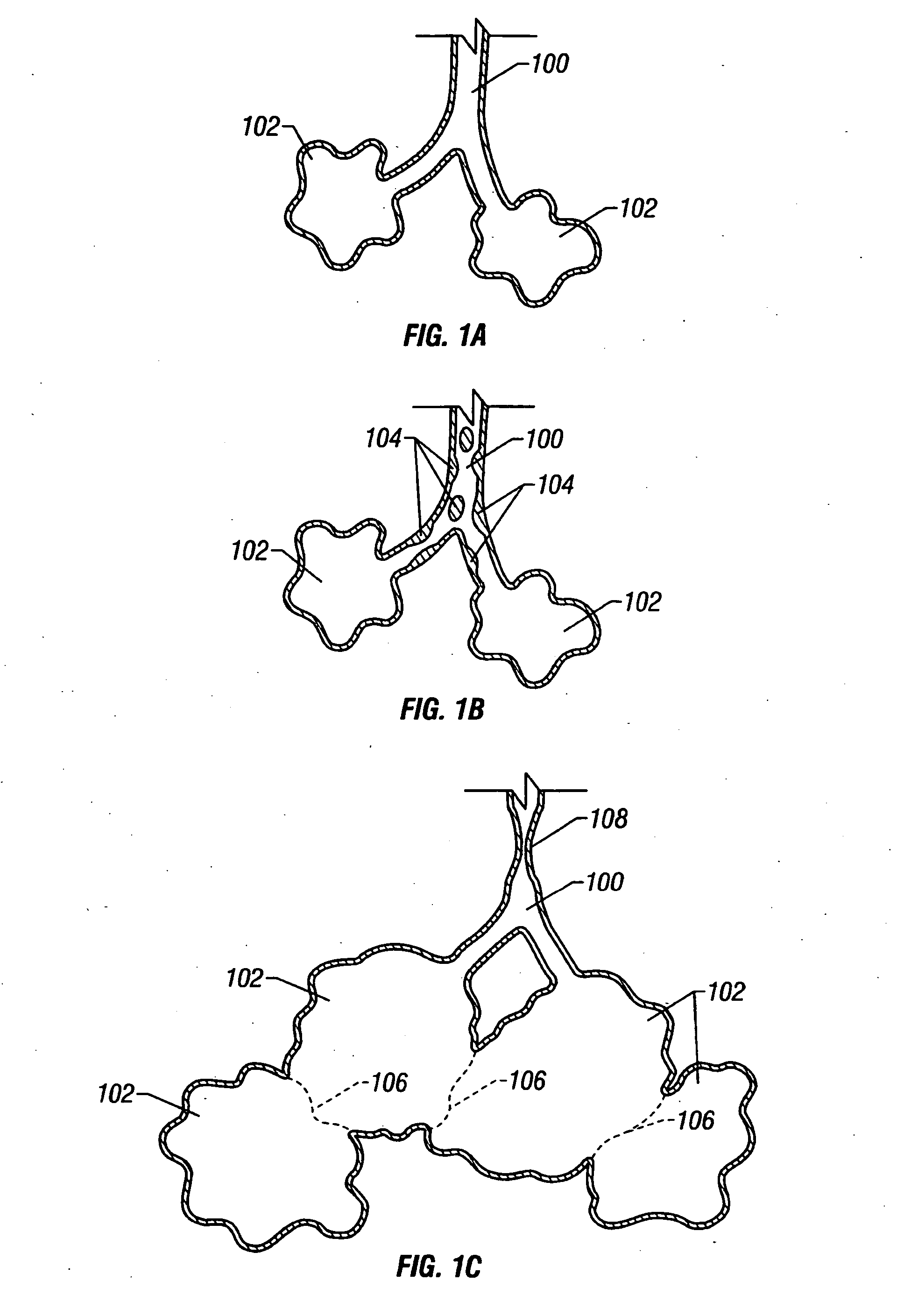
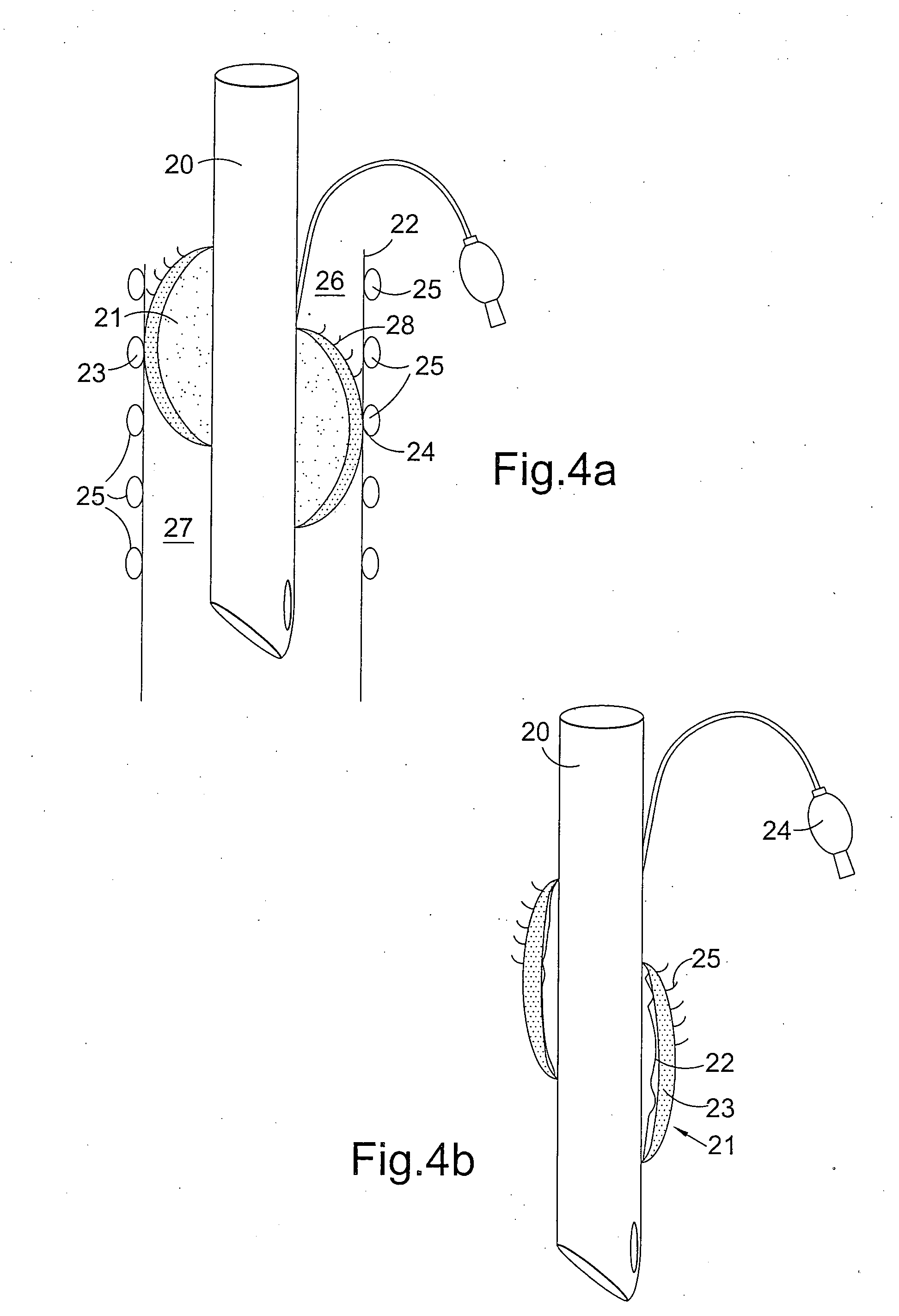
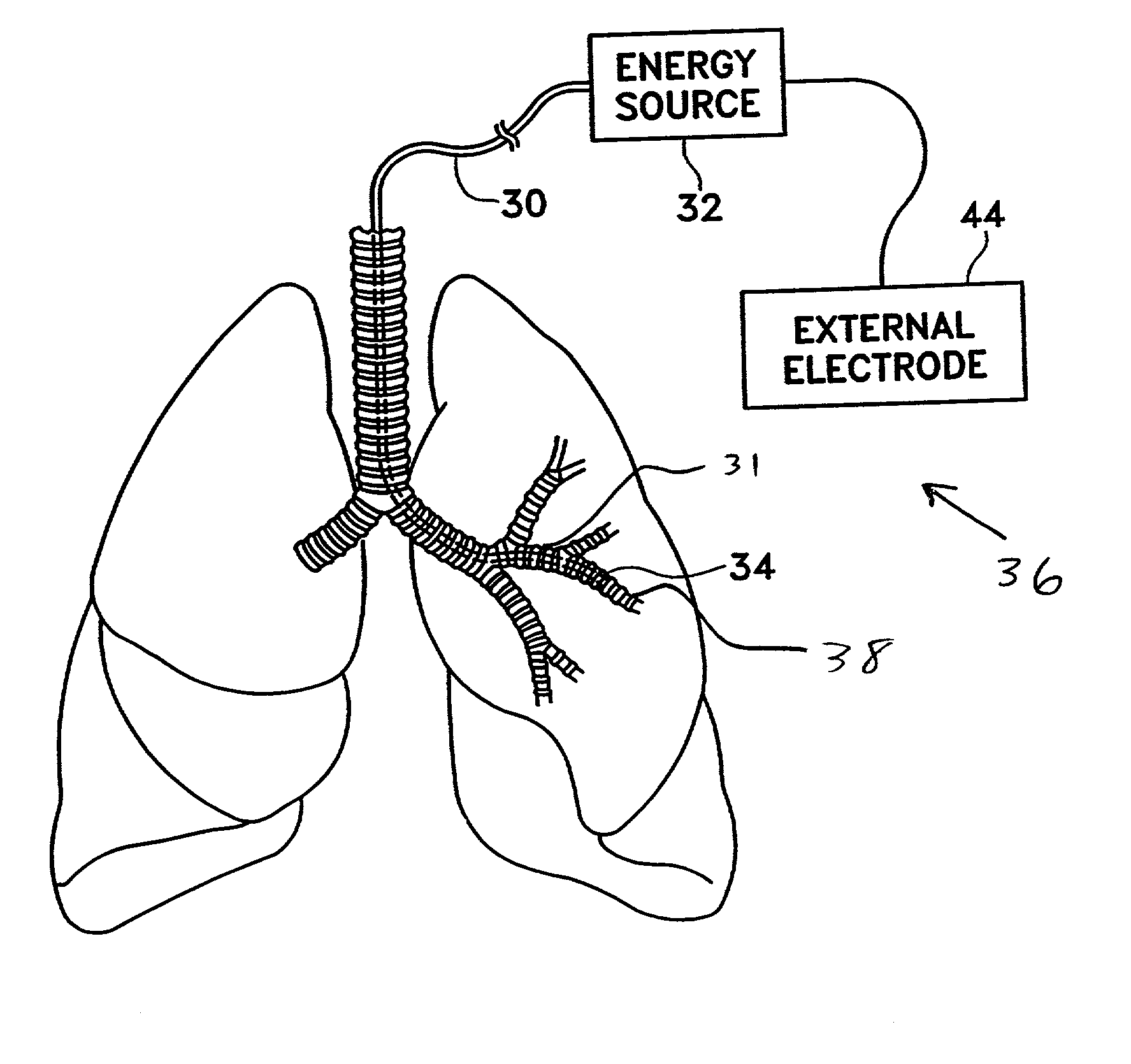
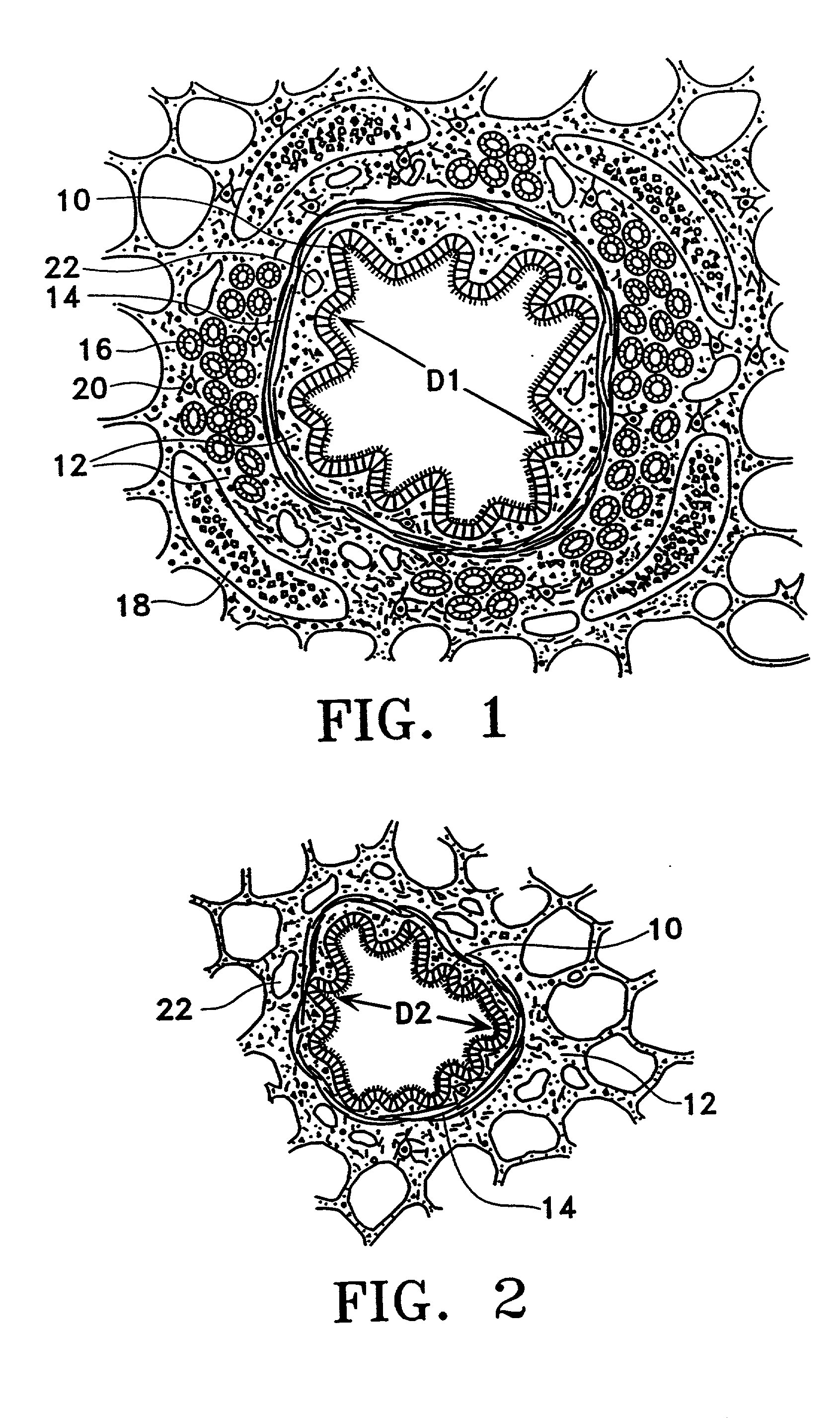
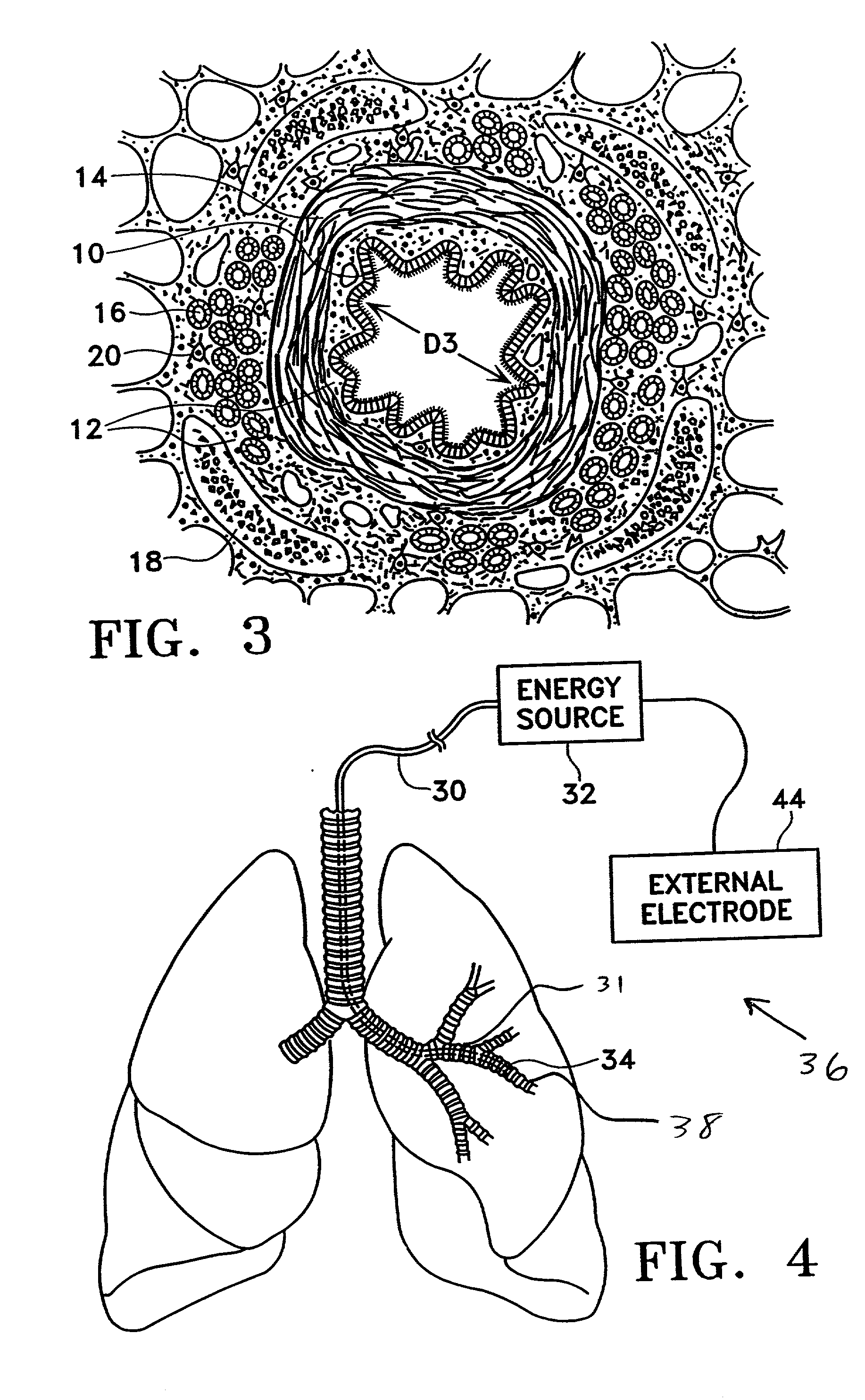
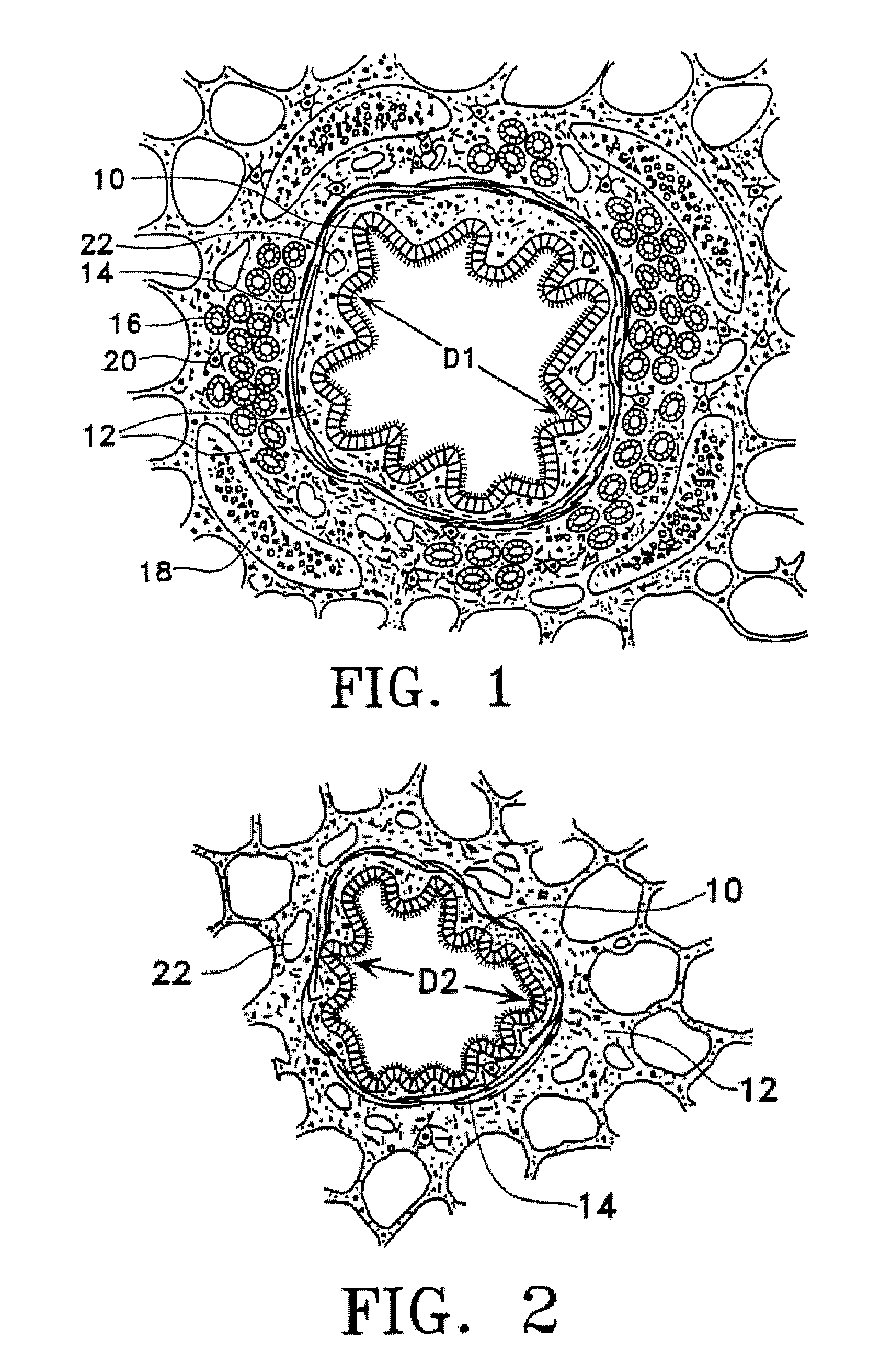
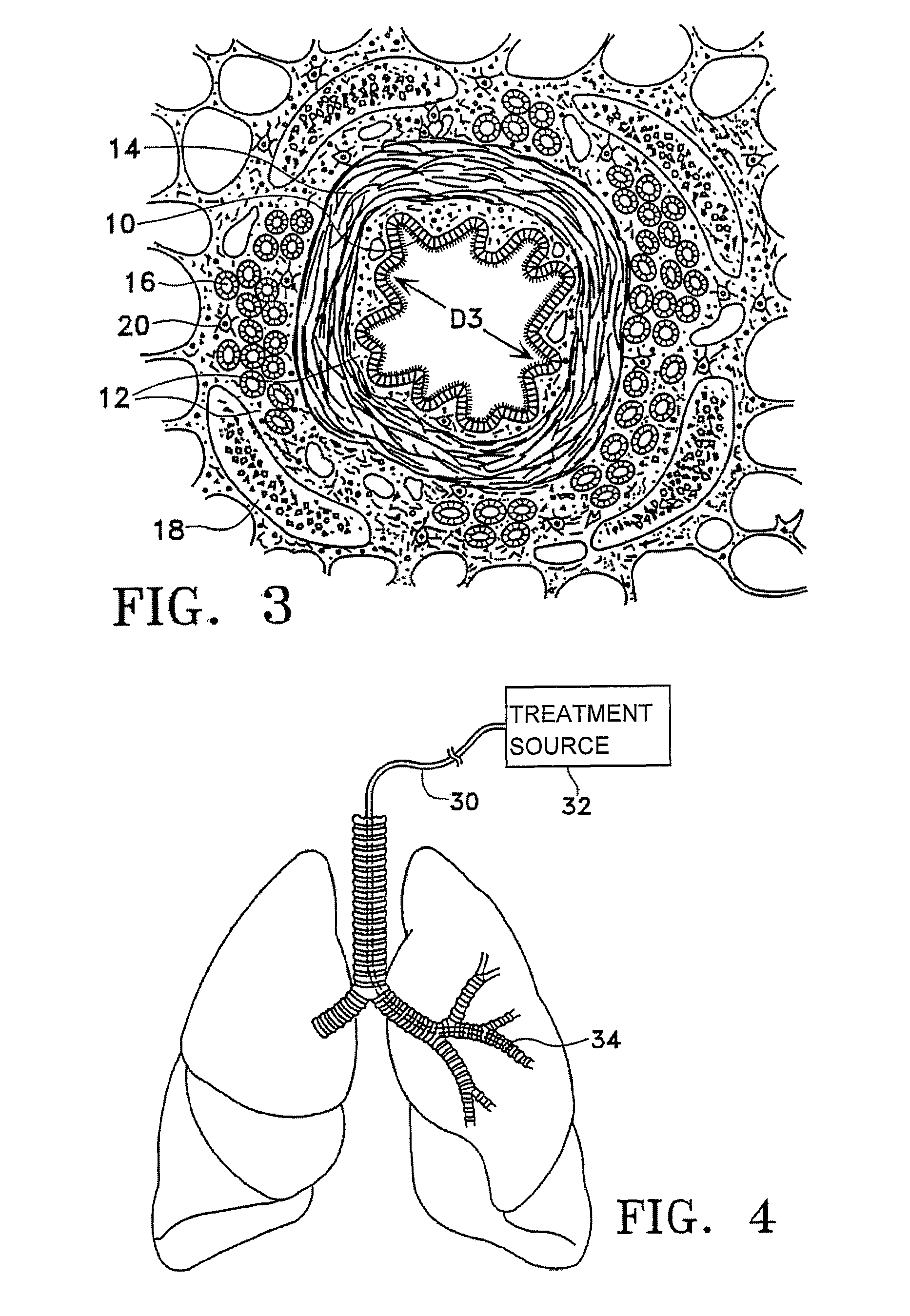
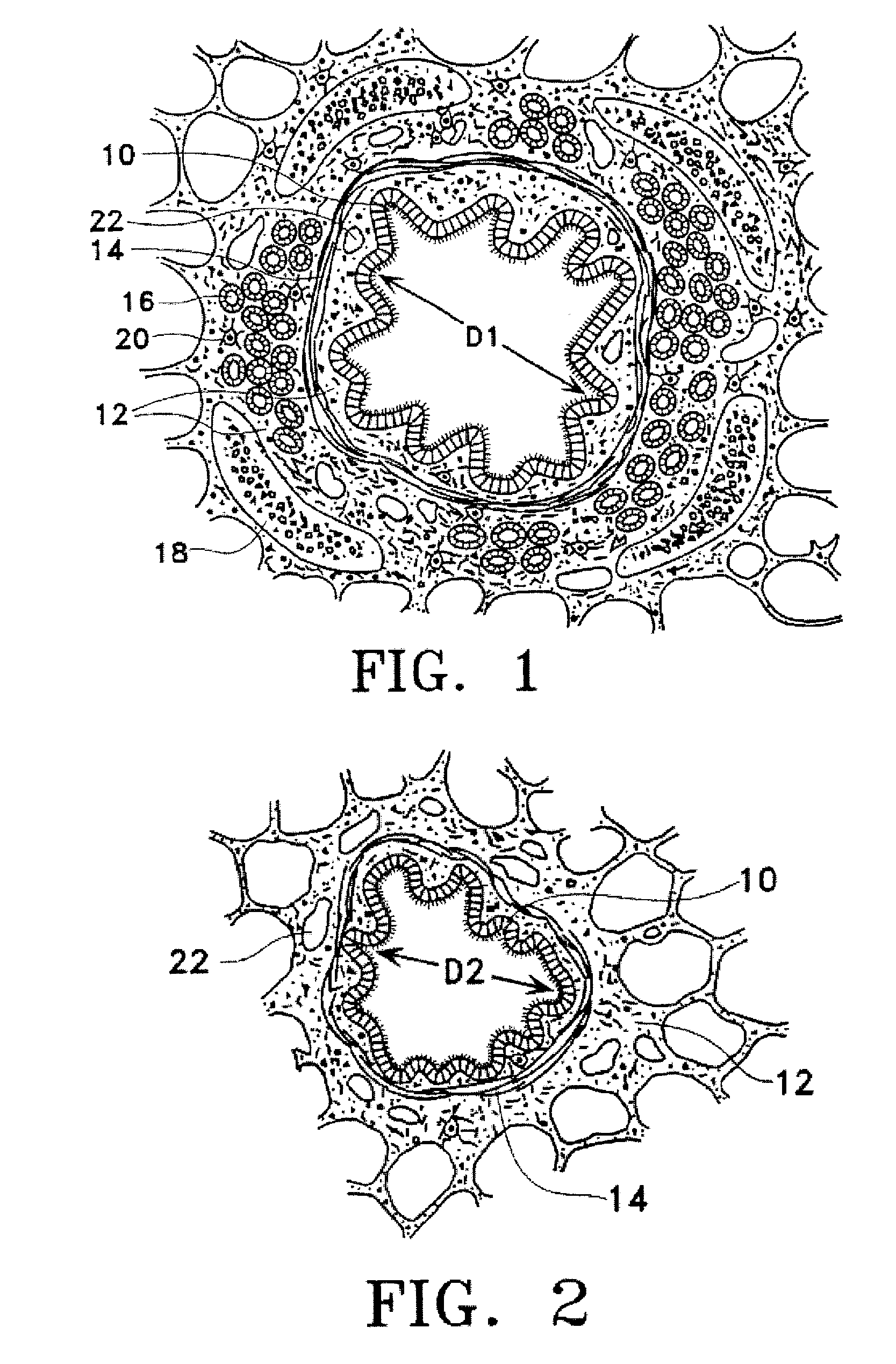
Modification of airways by application of energy
InactiveUS7198635B2Reduce plugging of the airwayPrevent the airway from being able to constrictElectrotherapySurgical needlesPatient complianceObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
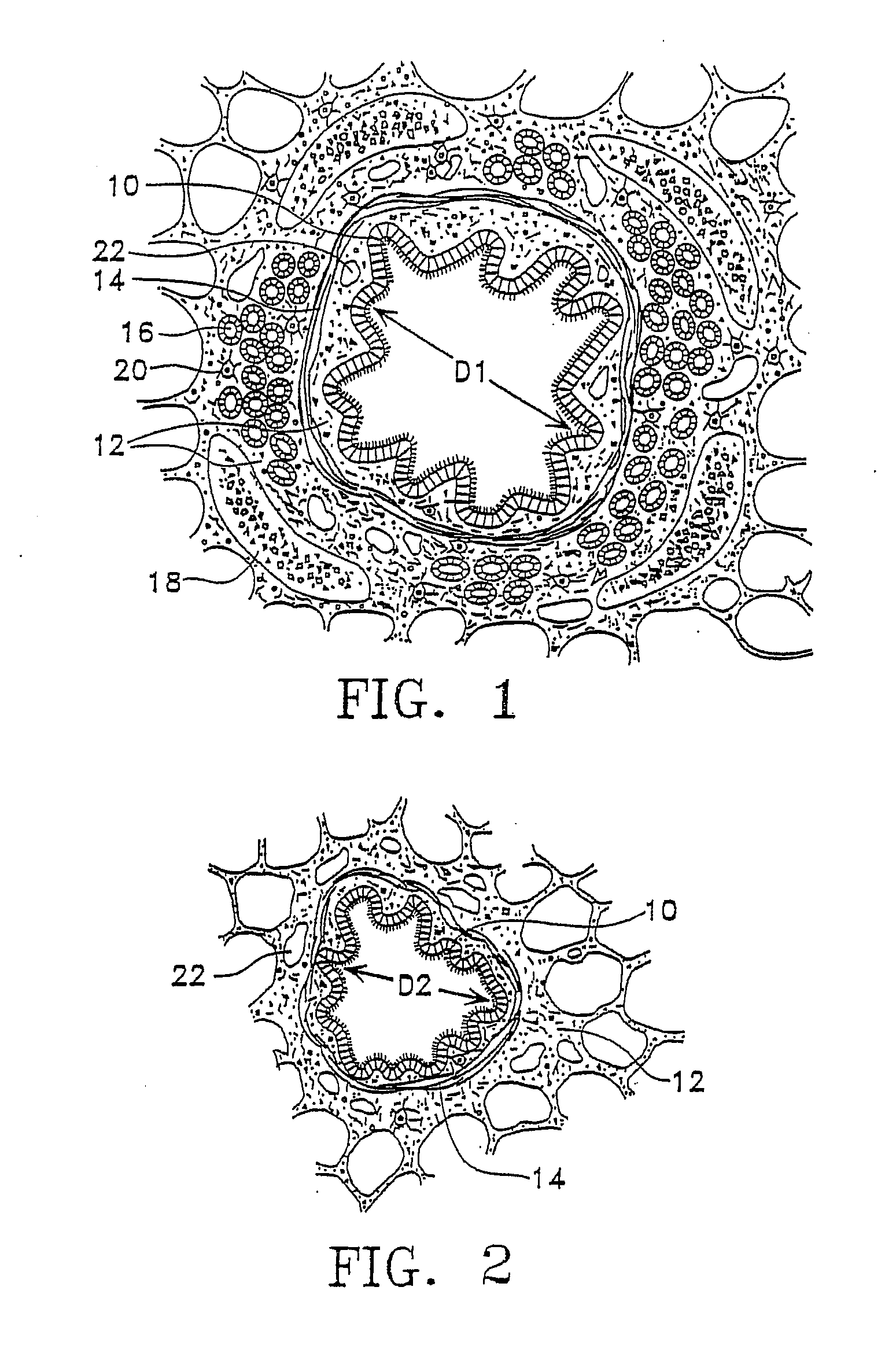
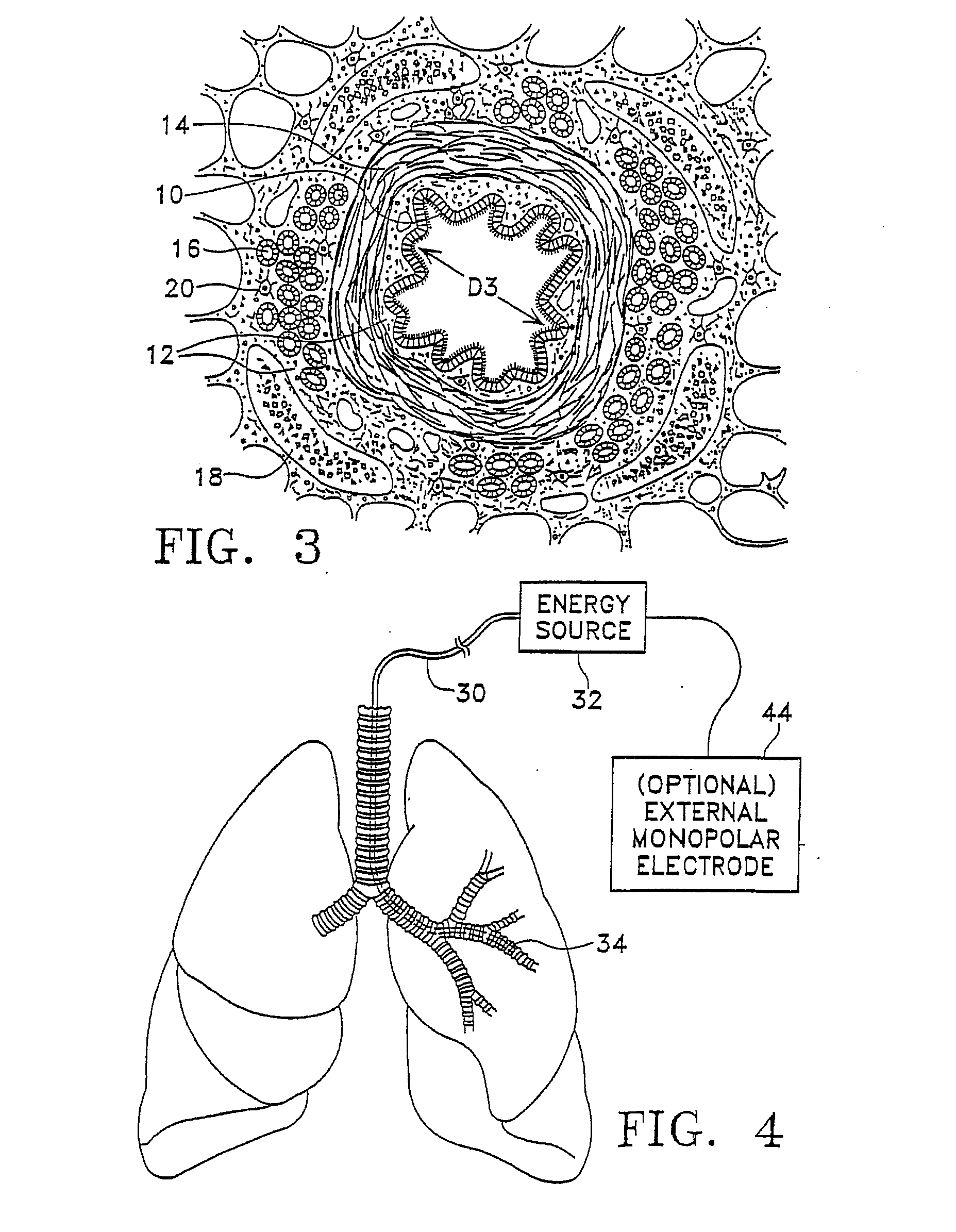
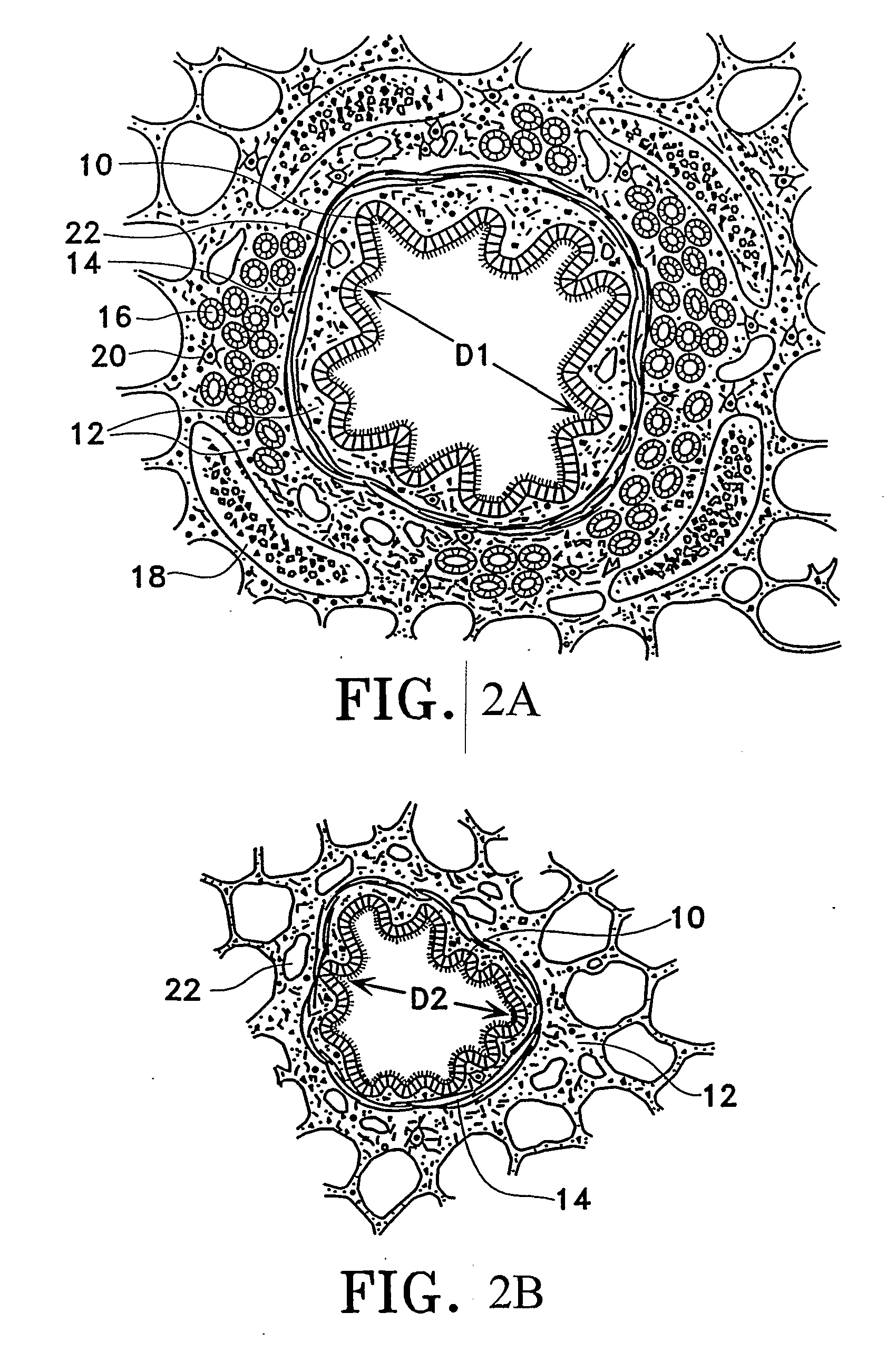
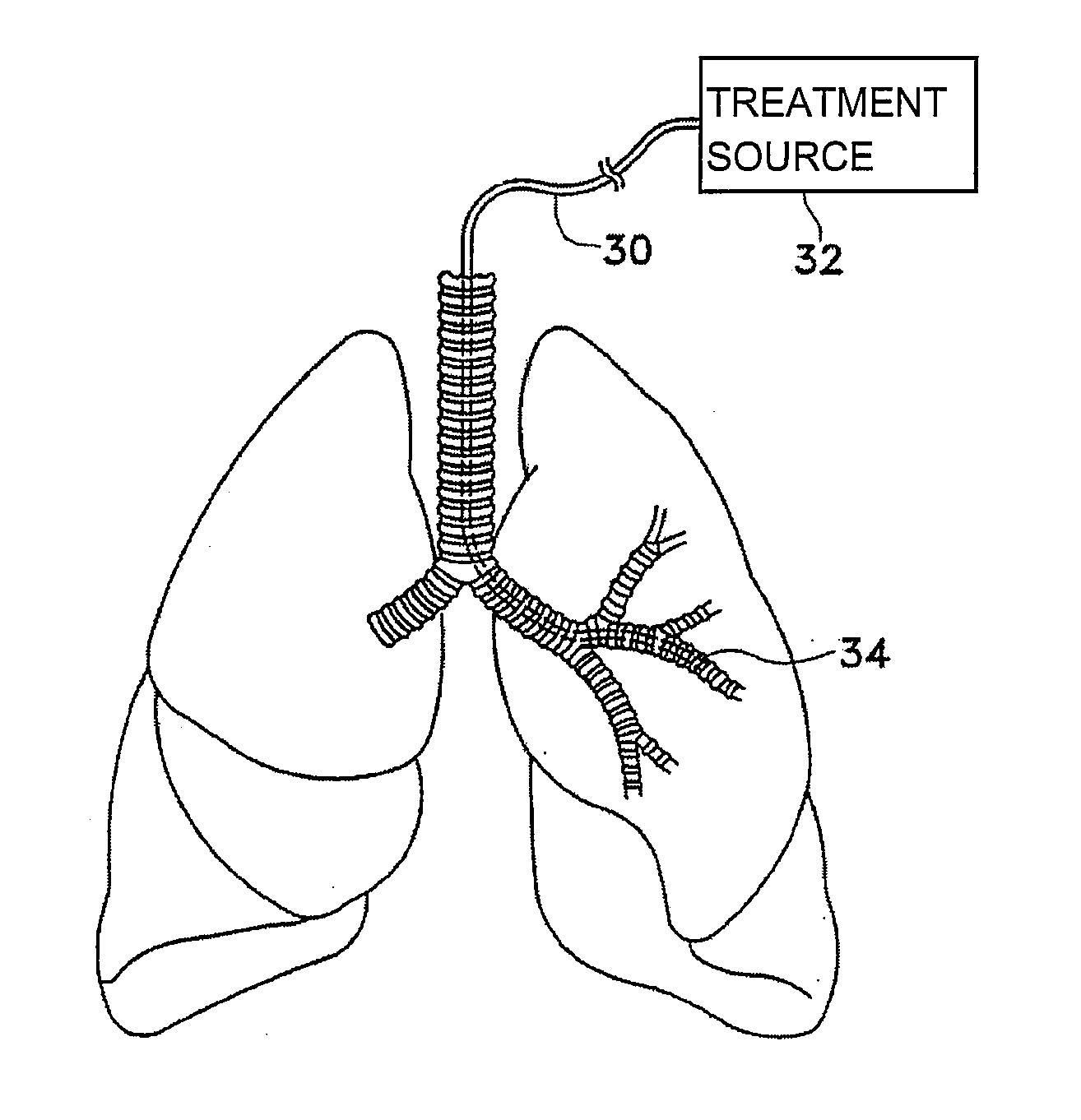
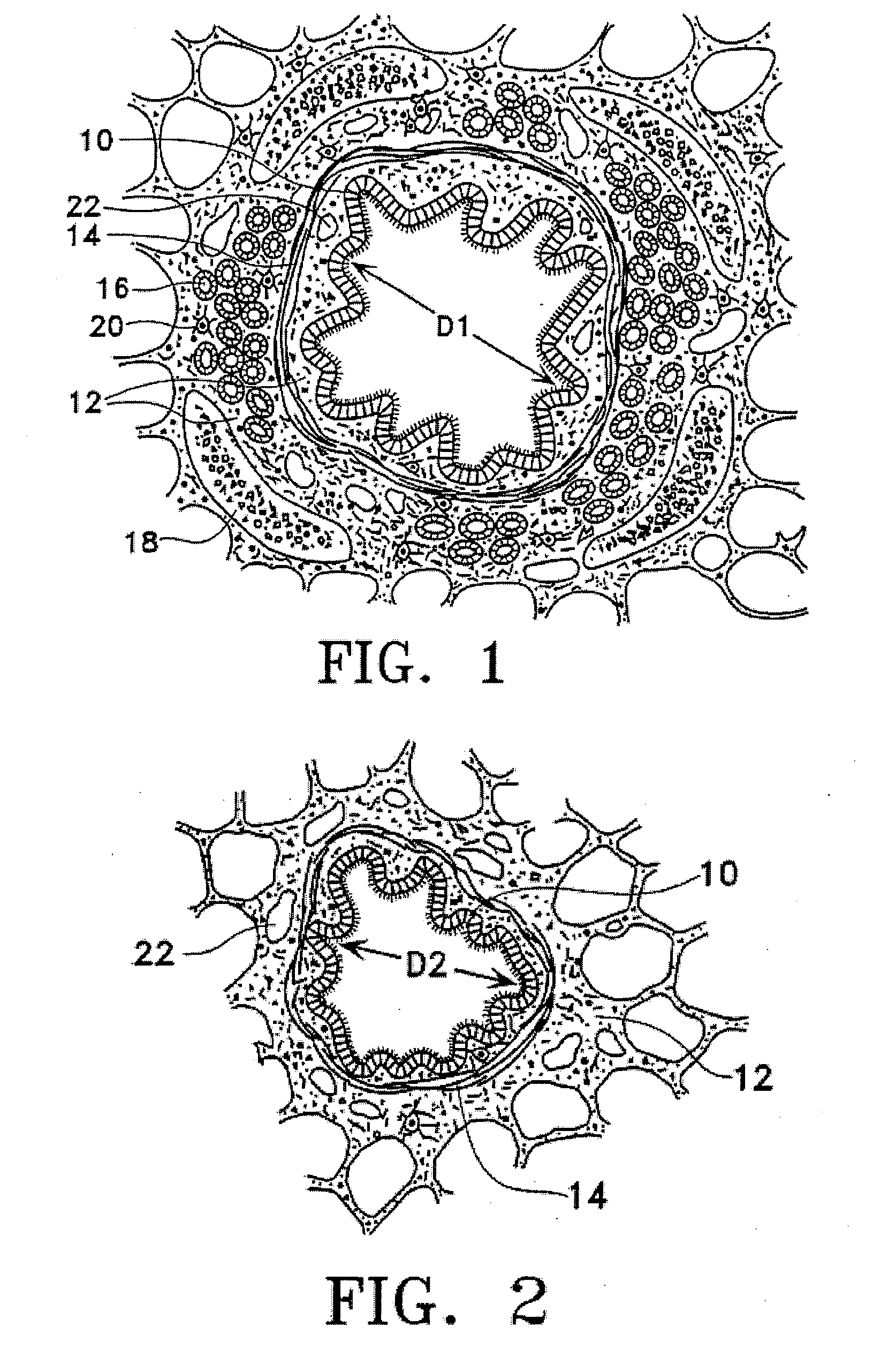
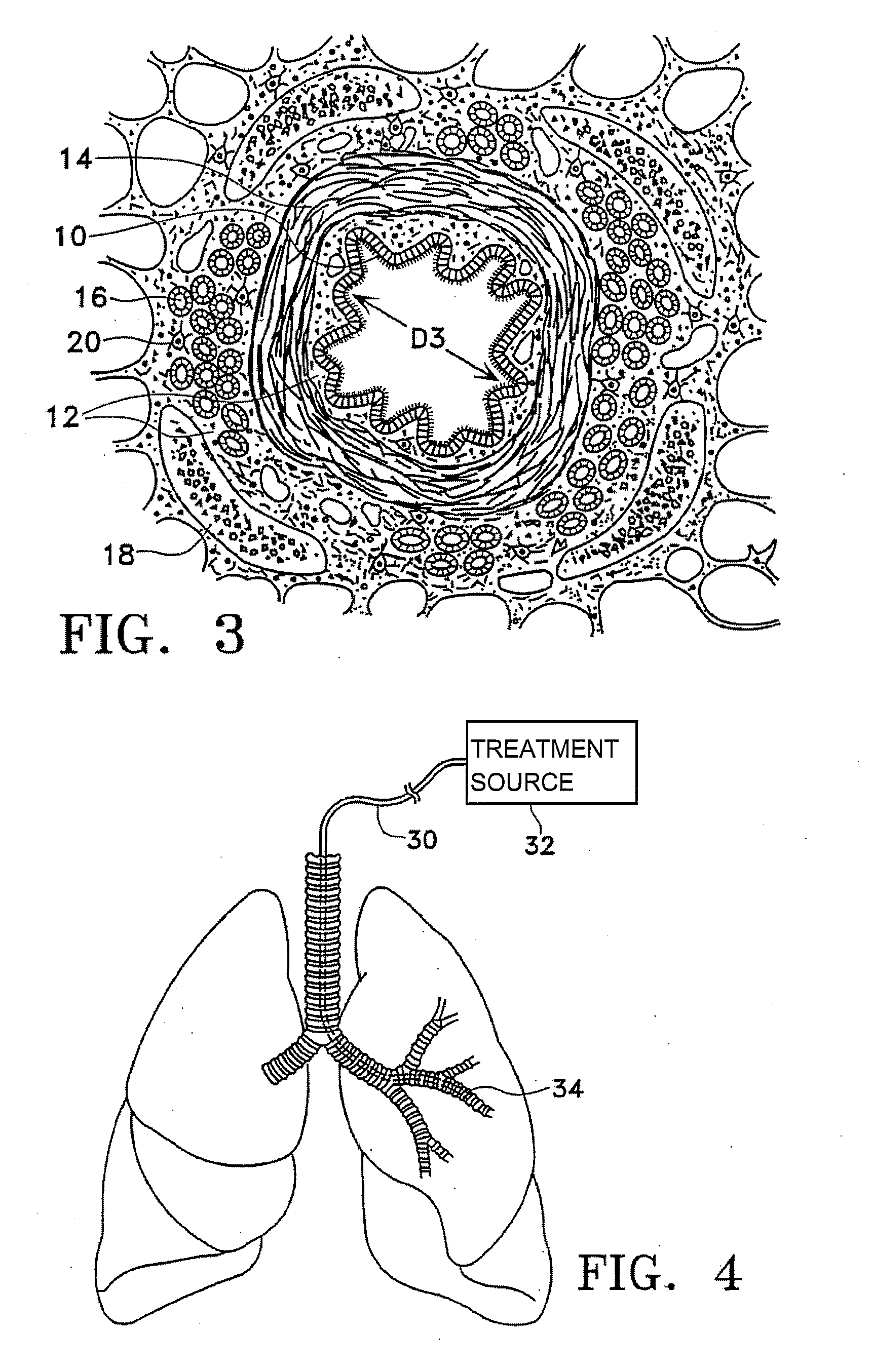
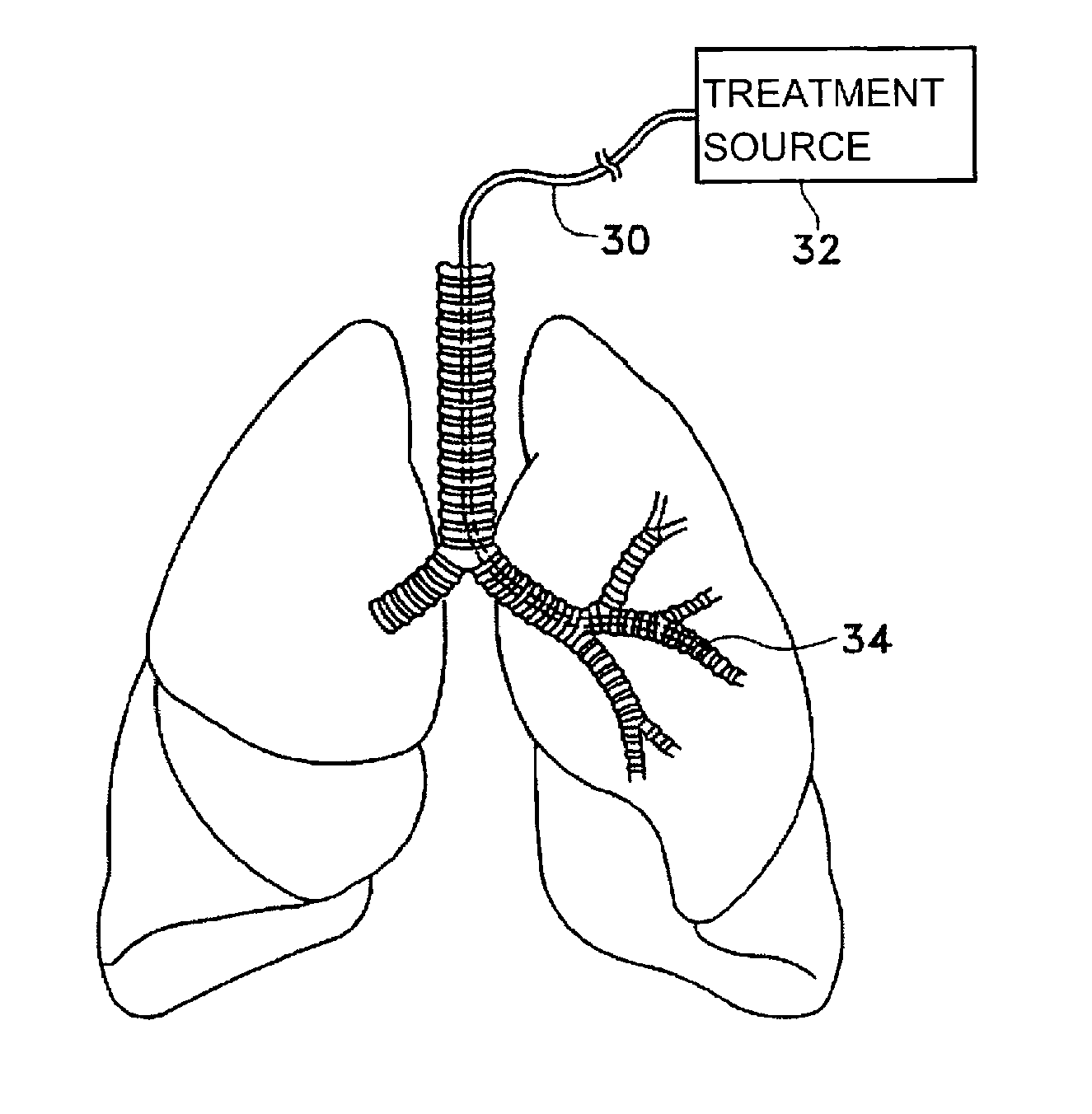
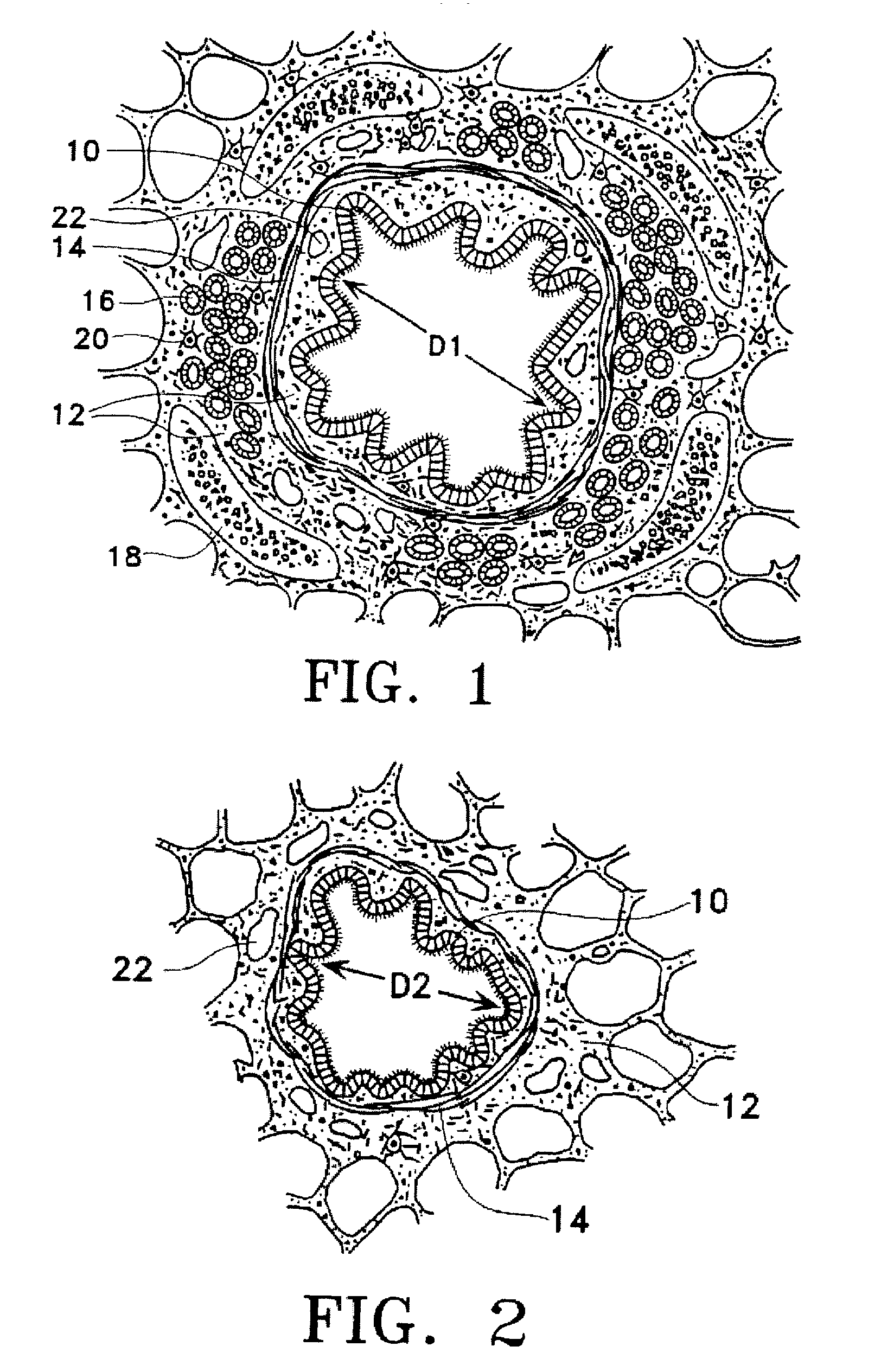
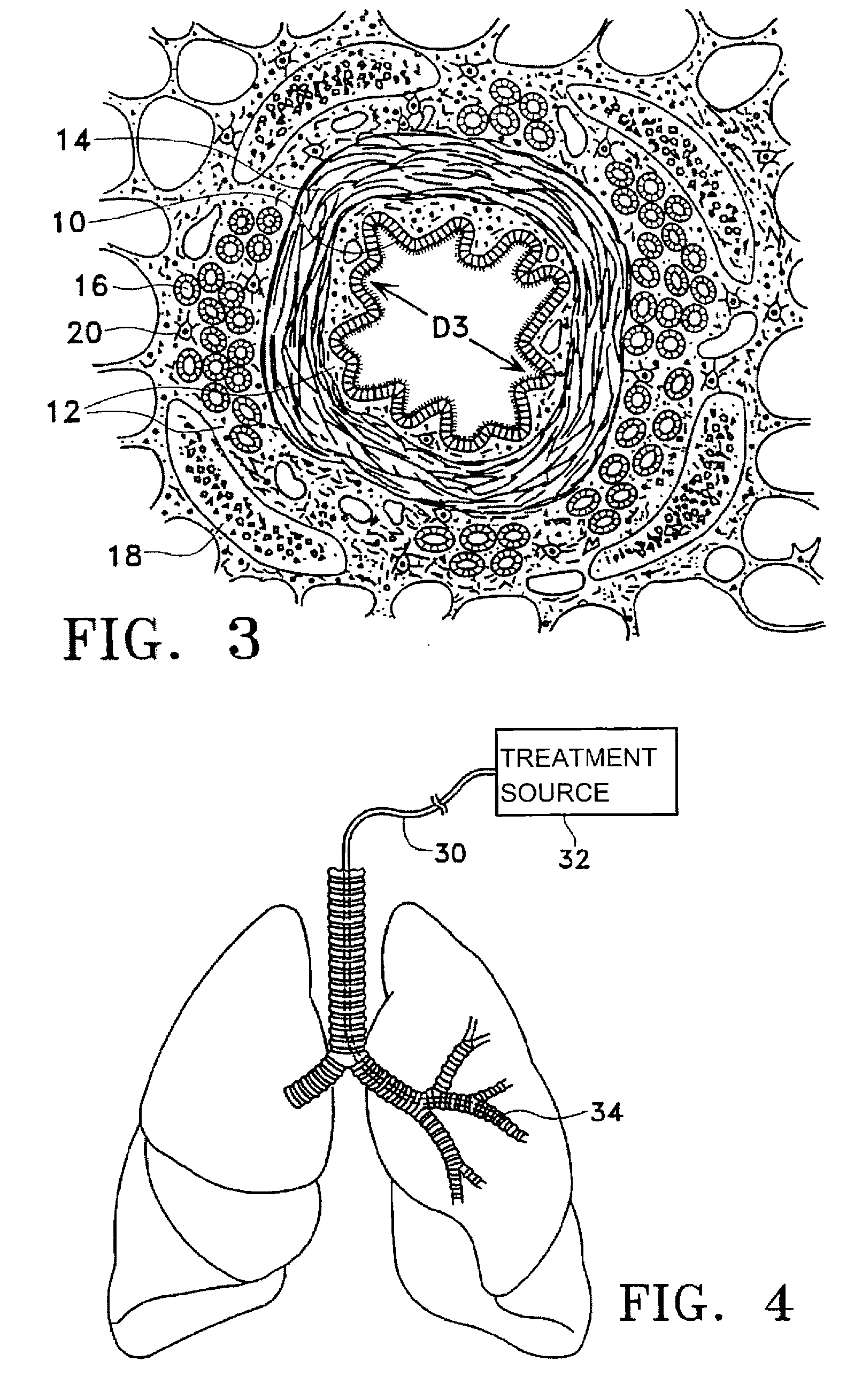
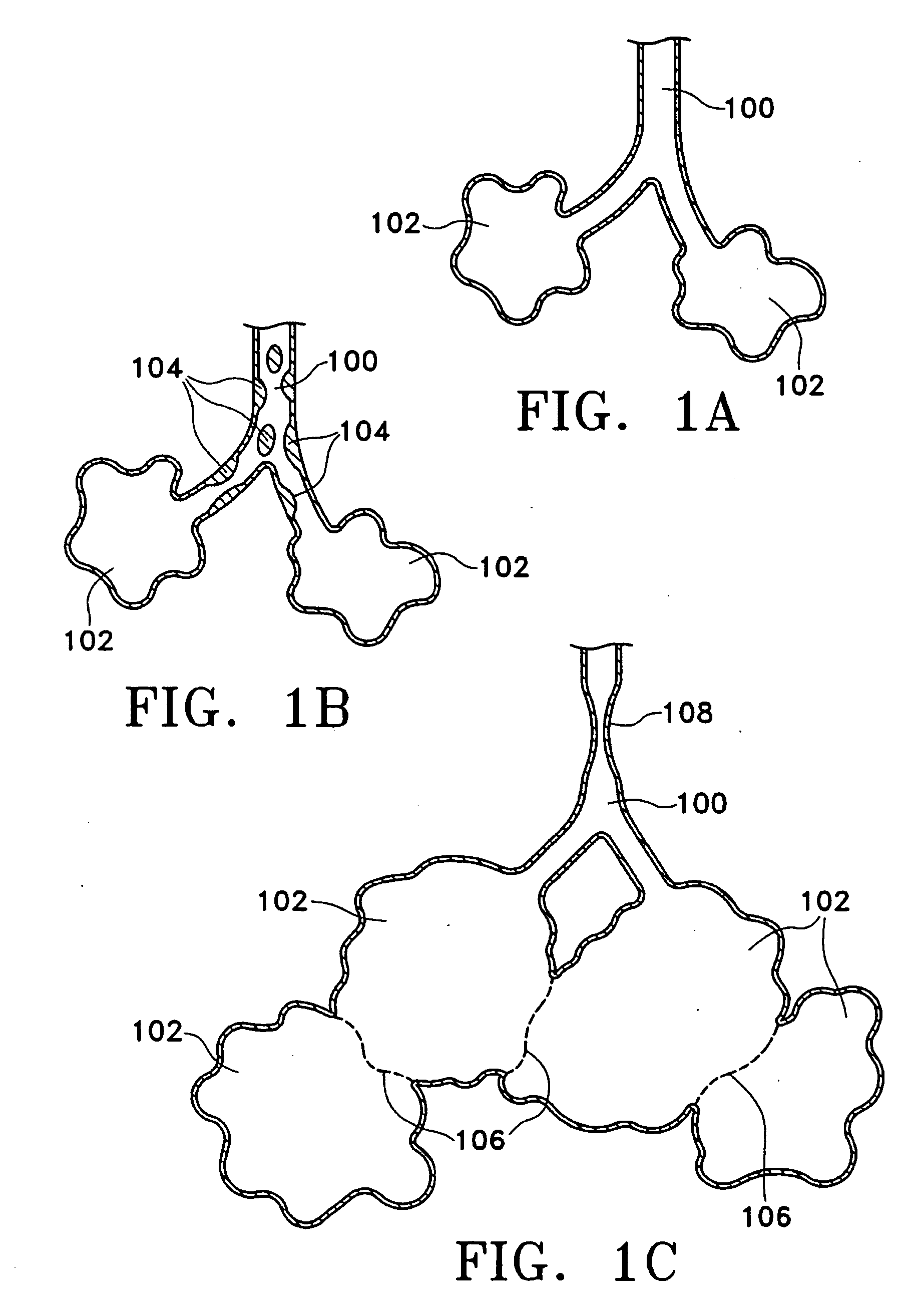
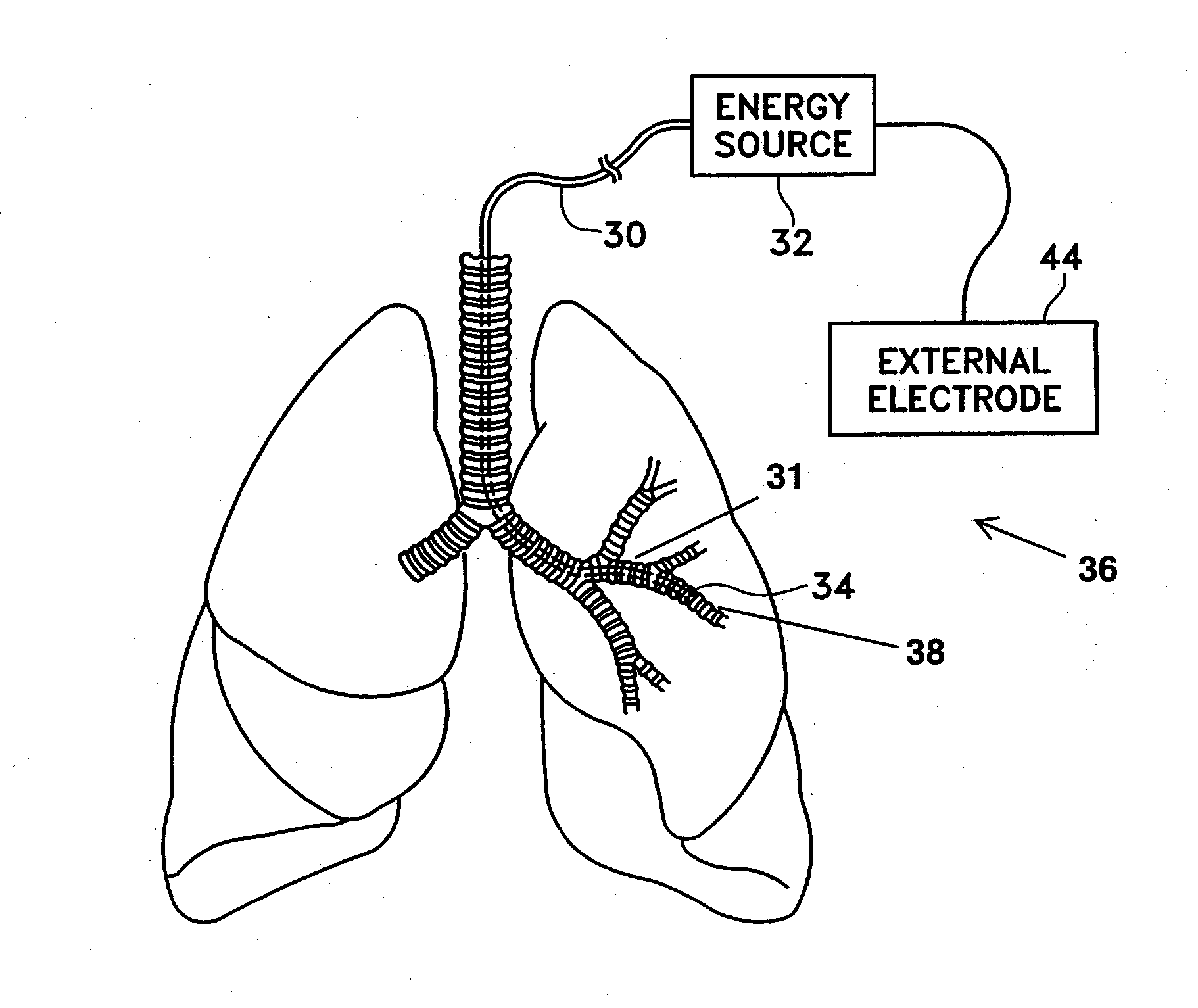
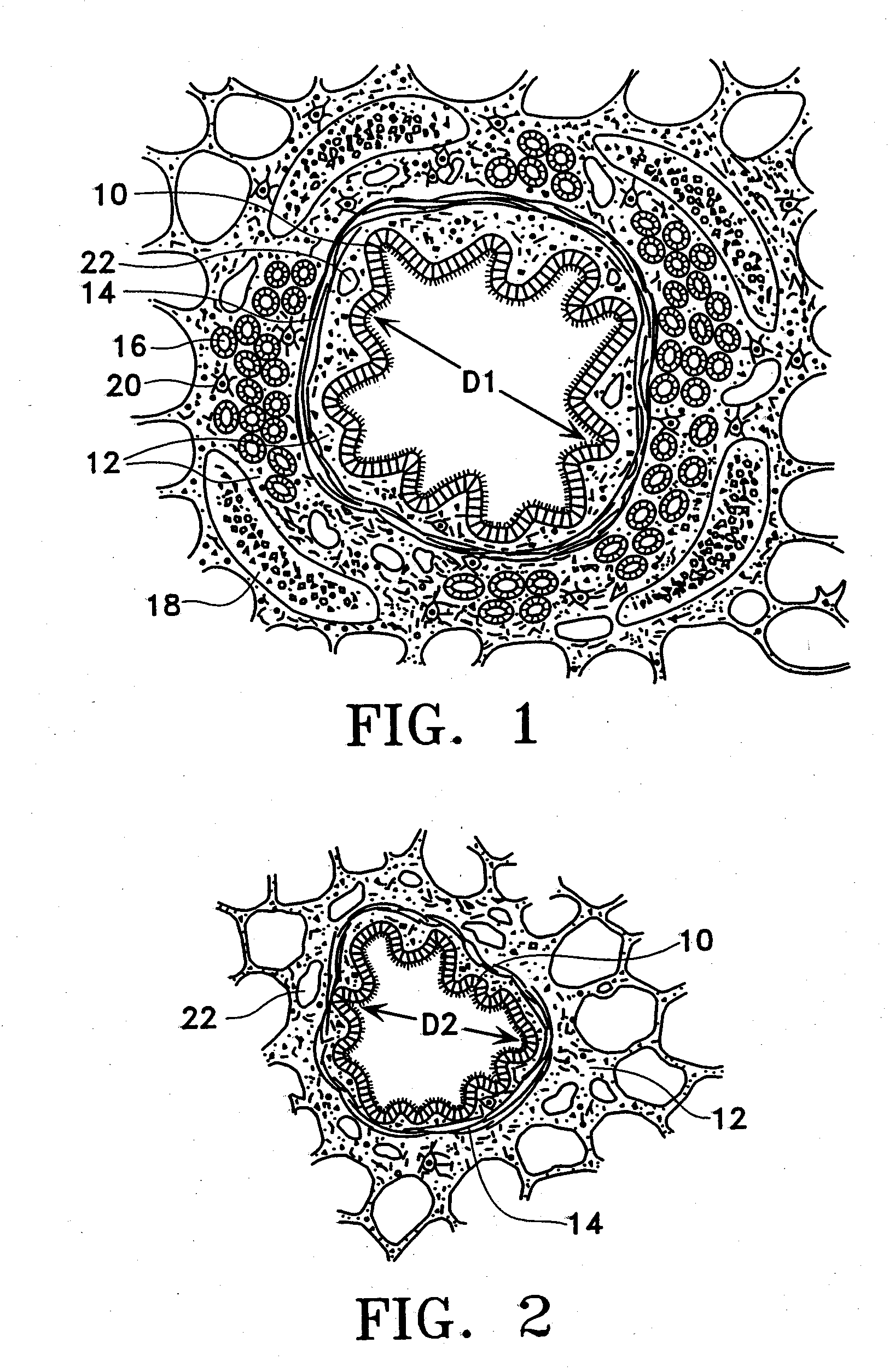
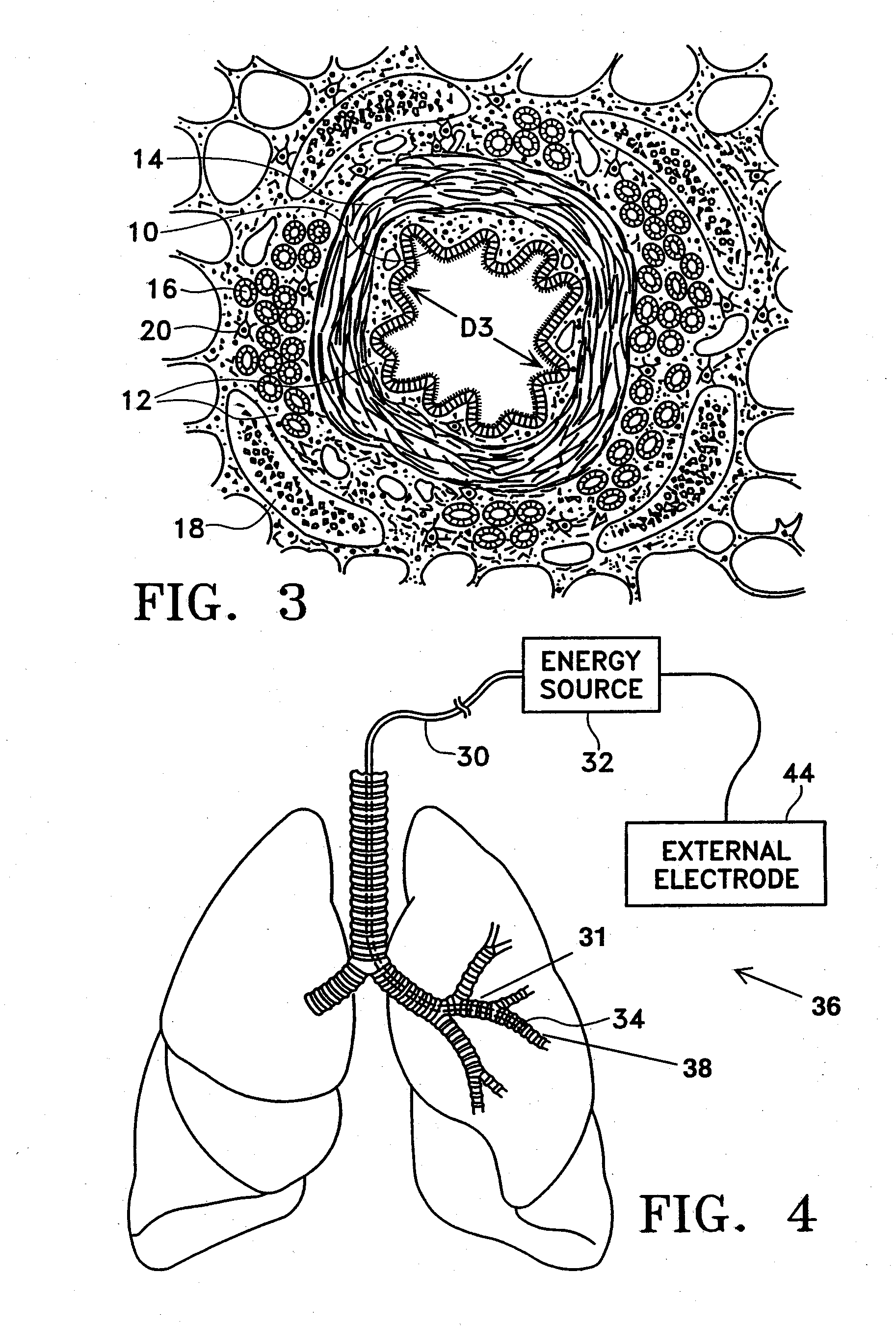
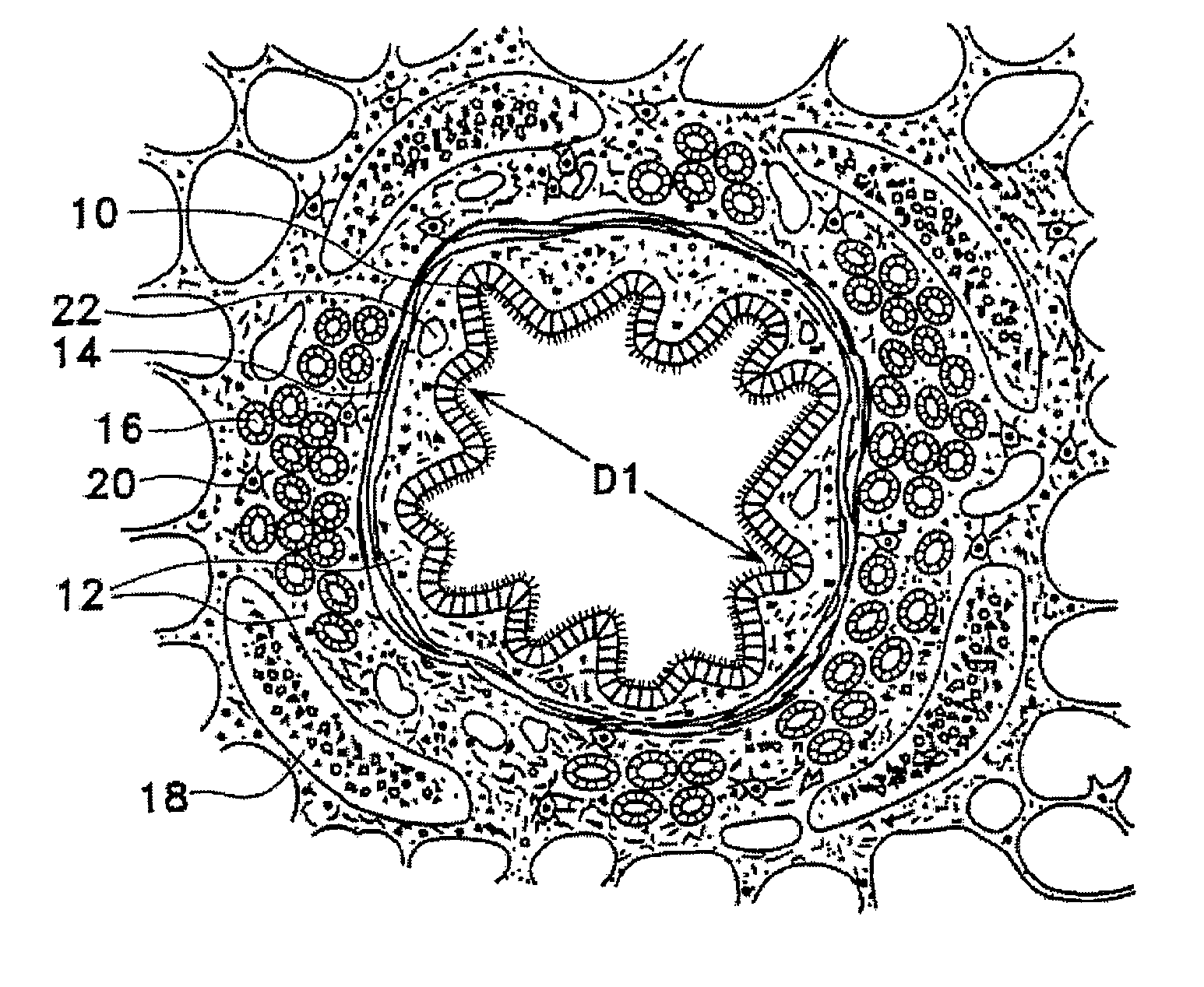
This relates to methods and devices for treating reversible chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and more particularly, relates to a device for exchanging energy with airway tissue such as that found in the airway of human lungs. The exchange of energy with this airway tissue in the airways reduces the ability of the air ways to constrict and / or reduces the resistance within the airway to the flow of air through the airway. This also relates to a method for decreasing responsiveness or decreasing resistance to airflow of airways involves the transfer of energy to or from the airway walls to prevent or reduce airway constriction and other symptoms of lung diseases. The treatment reduces the ability of the airway to contract during an acute narrowing of the airways, reduces mucus plugging of the airways, and / or increases the airway diameter. The methods according to the present invention provide a longer duration and / or more effective treatment for lung diseases than currently used drug treatments, and obviate patient compliance issues. This also includes additional steps that reduce the ability of the lung to produce at least one of the symptoms of reversible obstructive pulmonary disease and to reduce the resistance to the flow of air through a lung.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method for treating an asthma attack
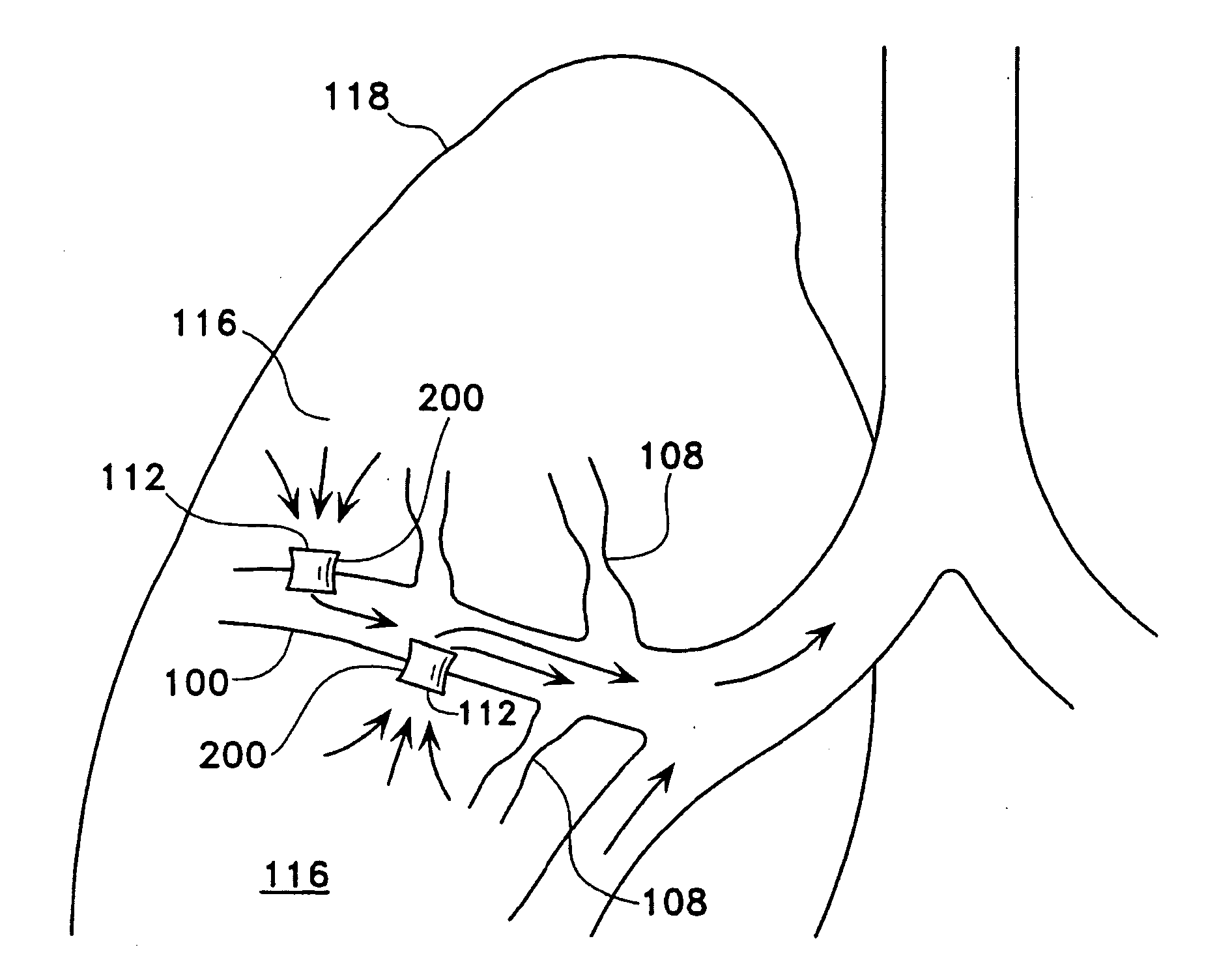
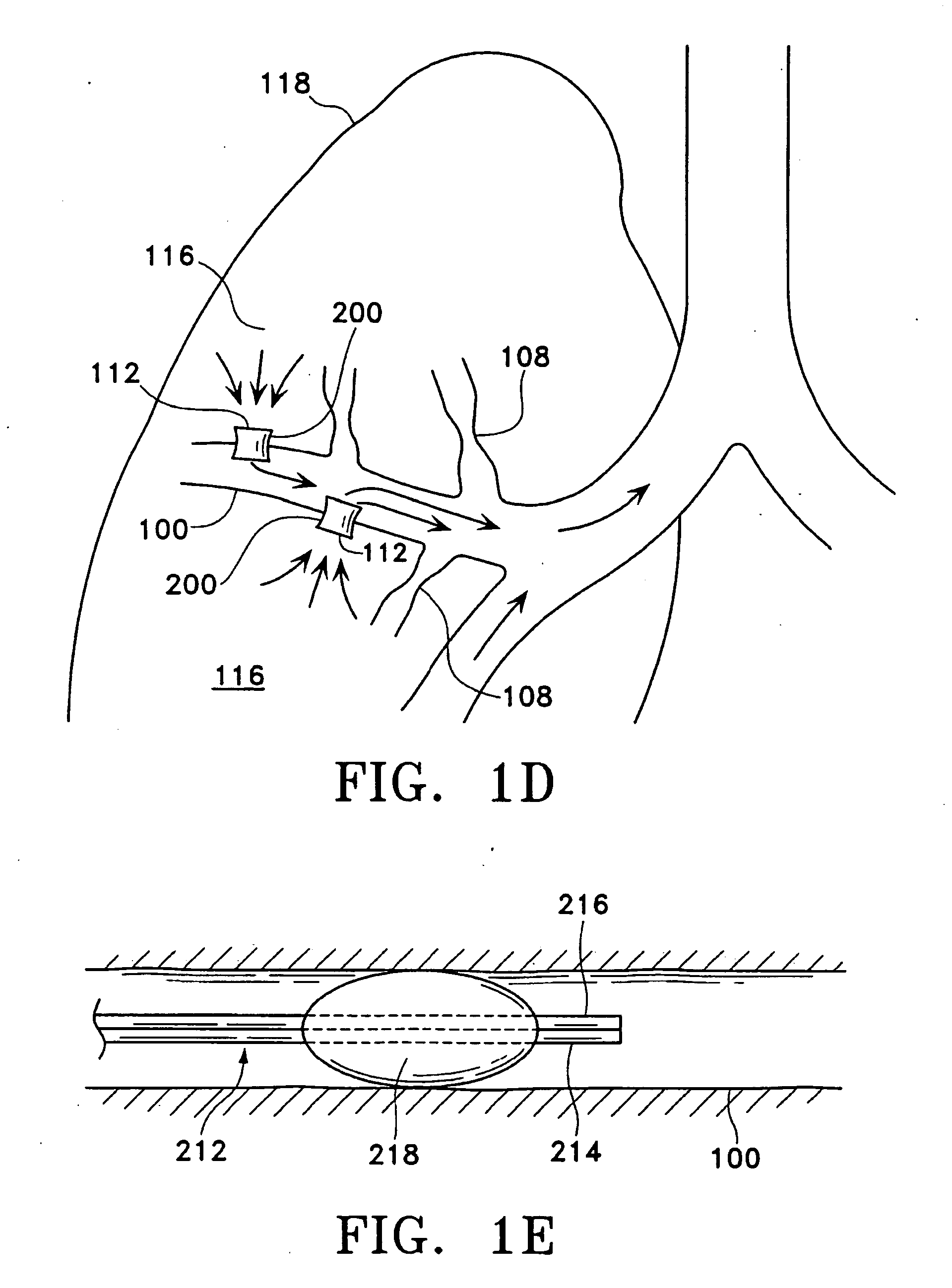
A method for treating the lung during an acute episode of reversible chronic obstructive pulmonary disease such as an asthma attack. The method comprises transferring energy to an airway wall of an airway such that a diameter of the airway is increased. The energy may be transferred to the airway wall prior to, during or after an asthma attack. The energy may be transferred in an amount sufficient to temporarily or permanently increase the diameter of the airway. The method may be performed while the airway is open, closed or partially closed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
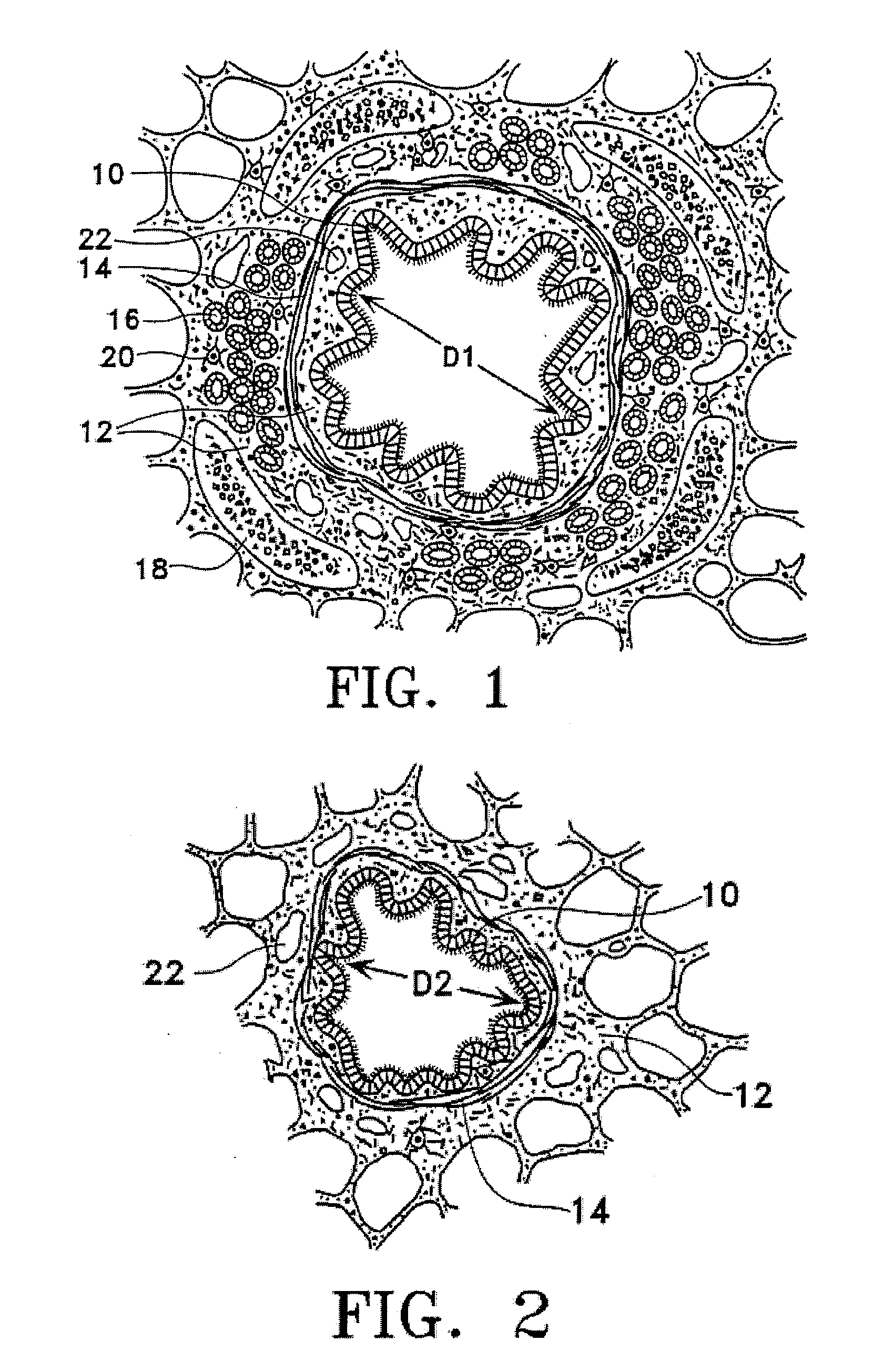
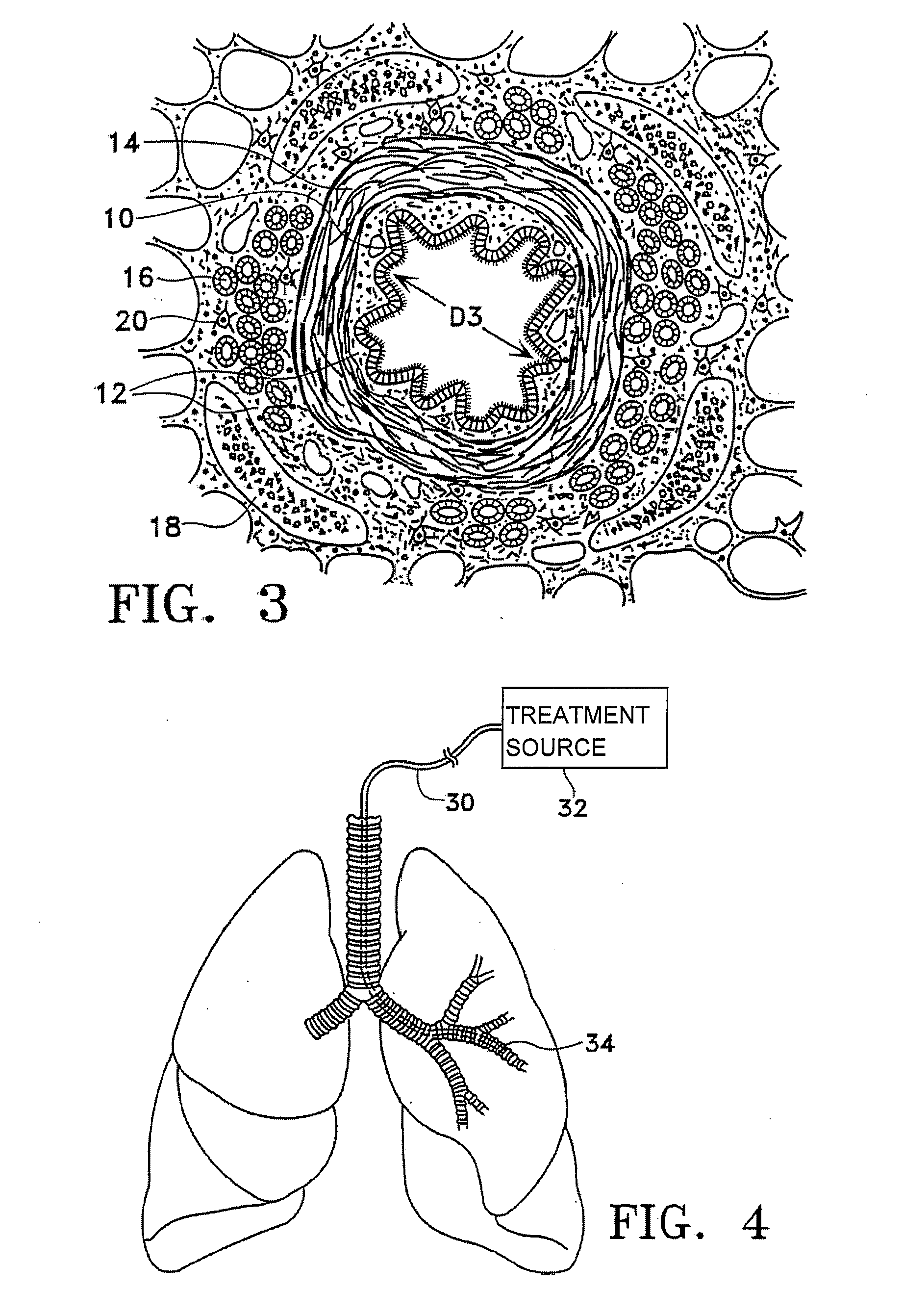
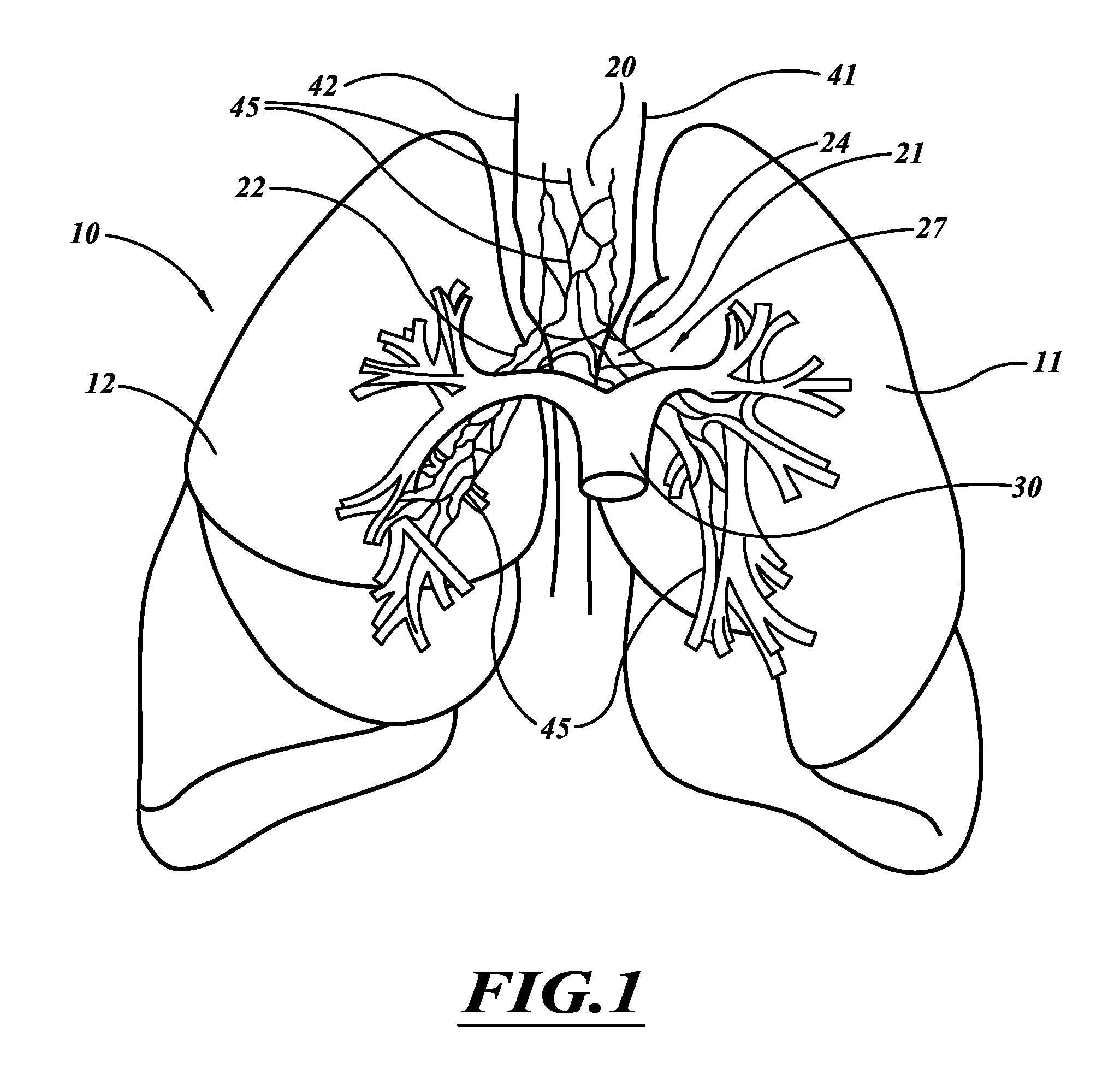
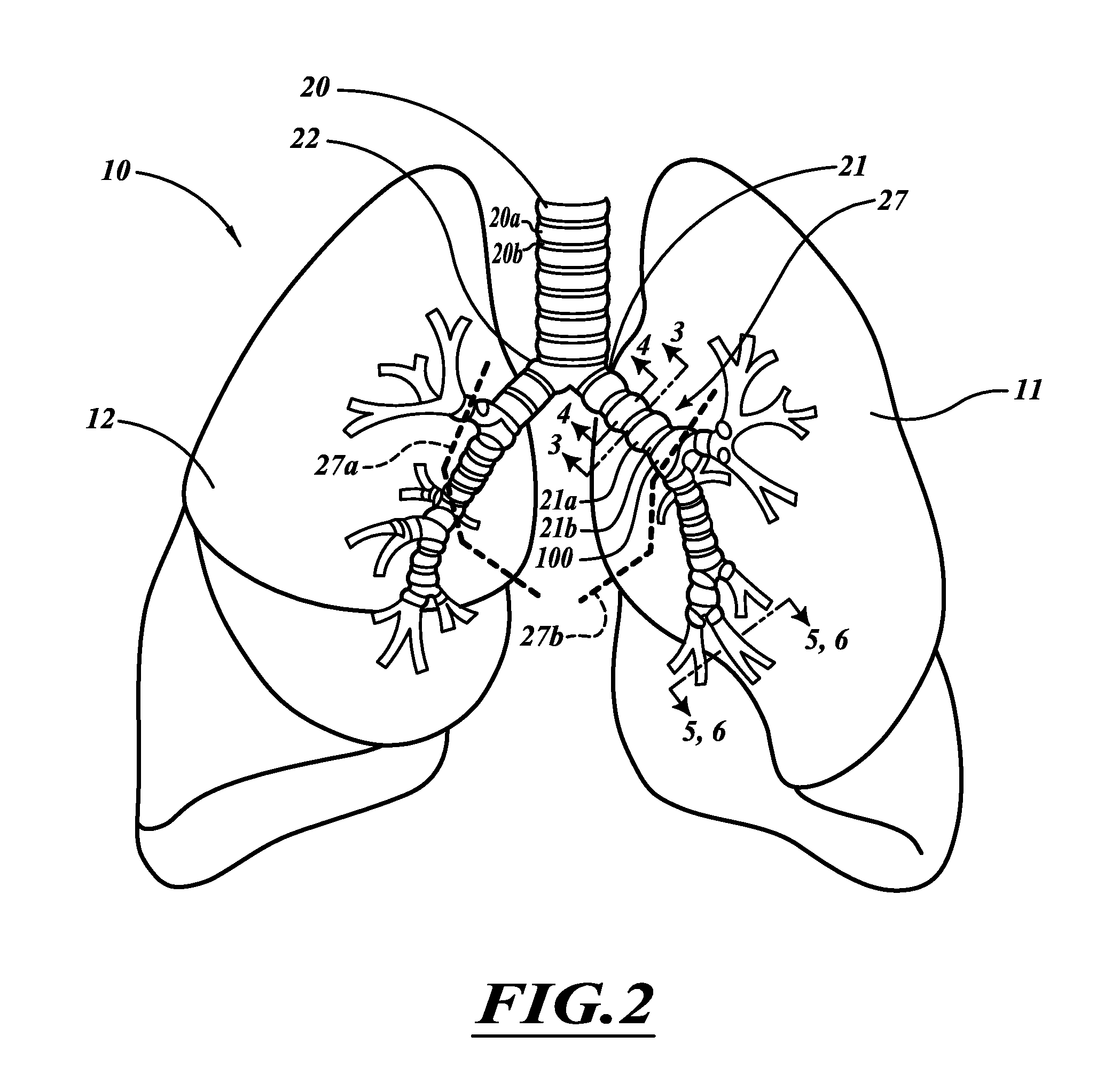
Devices and methods for maintaining collateral channels in tissue
The devices and methods of placement of such devices disclosed herein are directed to altering gaseous flow within a lung to improve the expiration cycle of, for instance, an individual having Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. More particularly, these devices produce and maintain collateral openings or channels through the airway wall so that oxygen depleted / carbon dioxide rich air is able to pass directly out of the lung tissue to facilitate both the exchange of oxygen ultimately into the blood and / or to decompress hyper-inflated lungs. The medical kits disclosed herein are also directed to produce and maintain collateral openings through airway walls.
Owner:BRONCUS MEDICAL
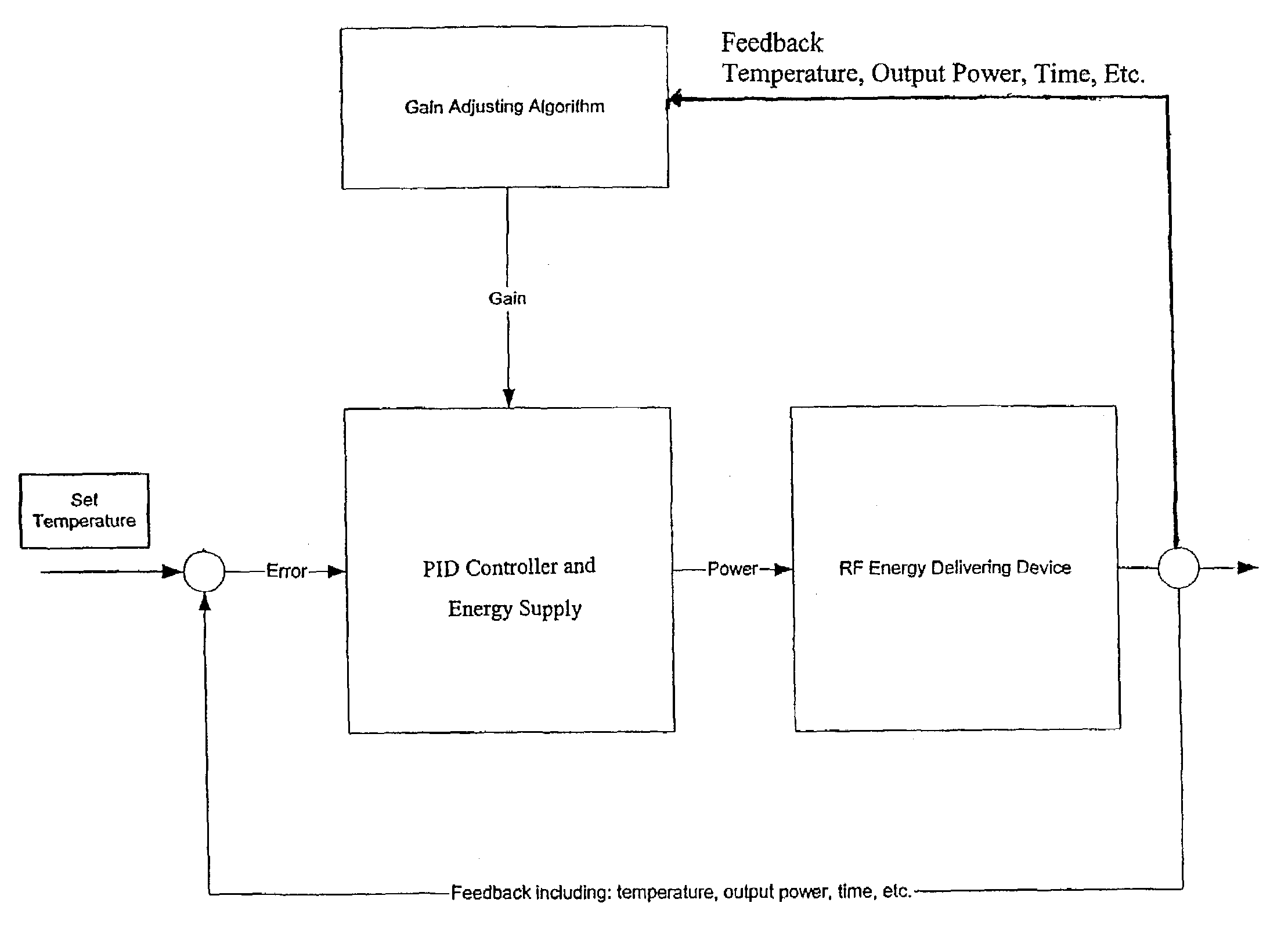
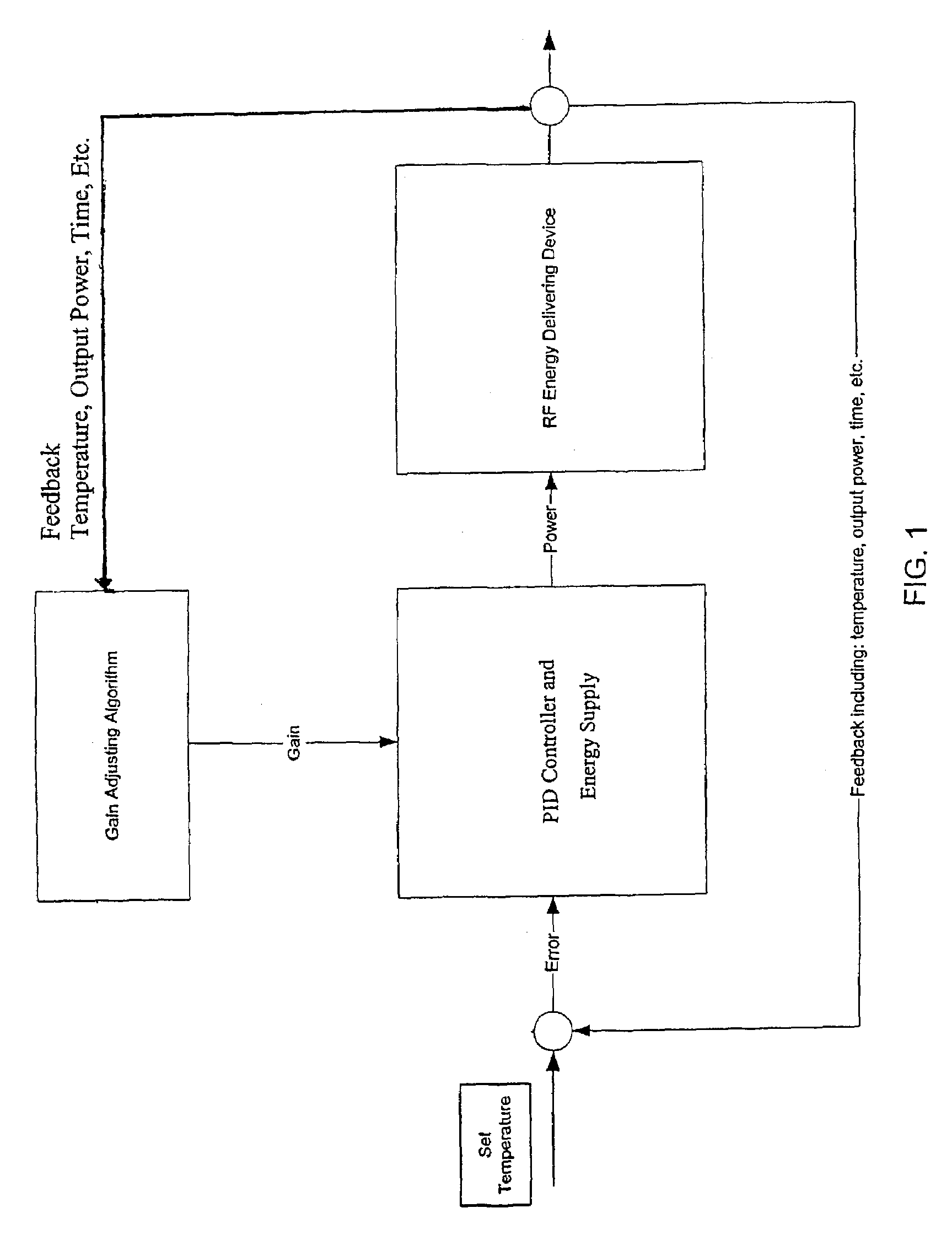
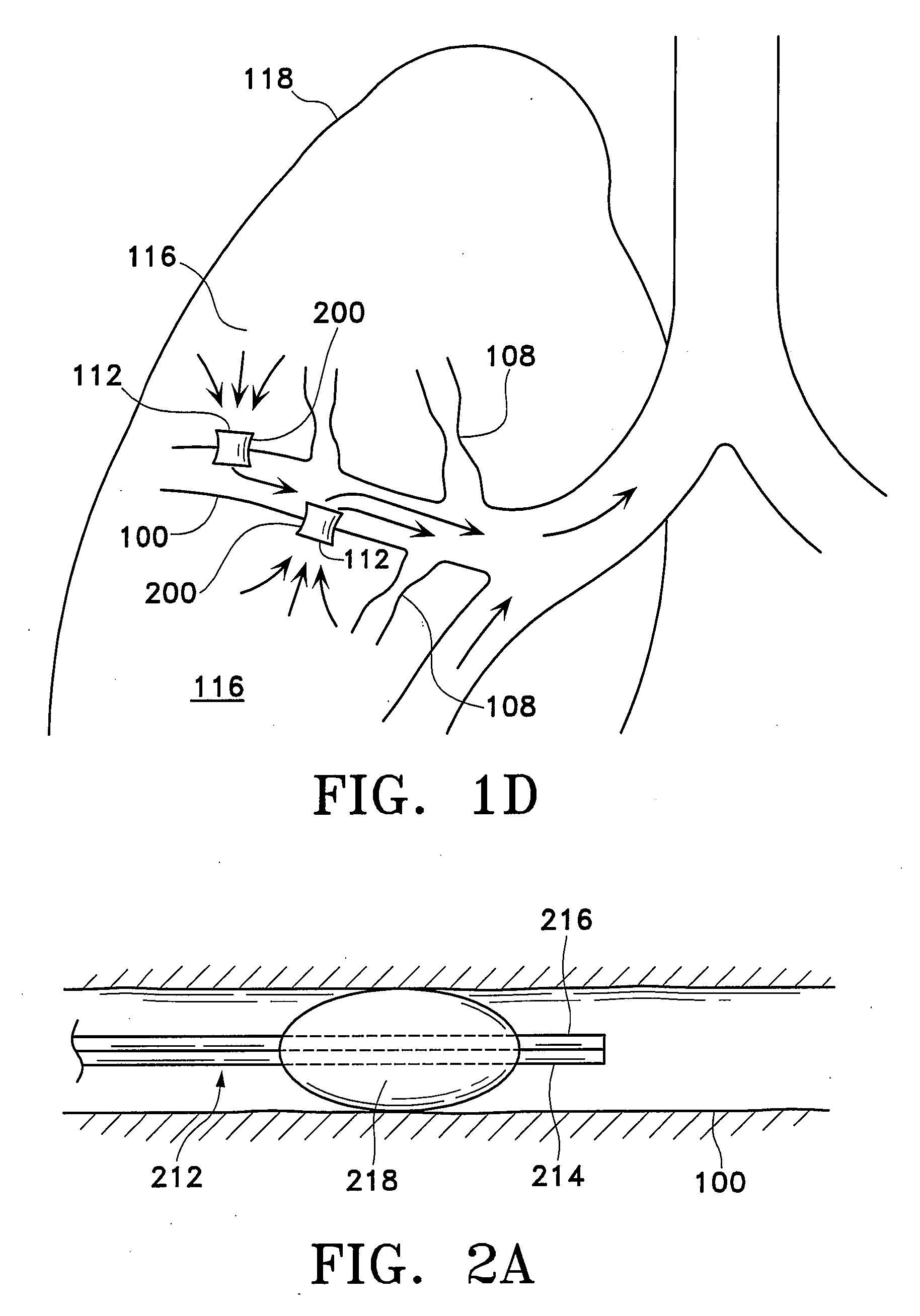
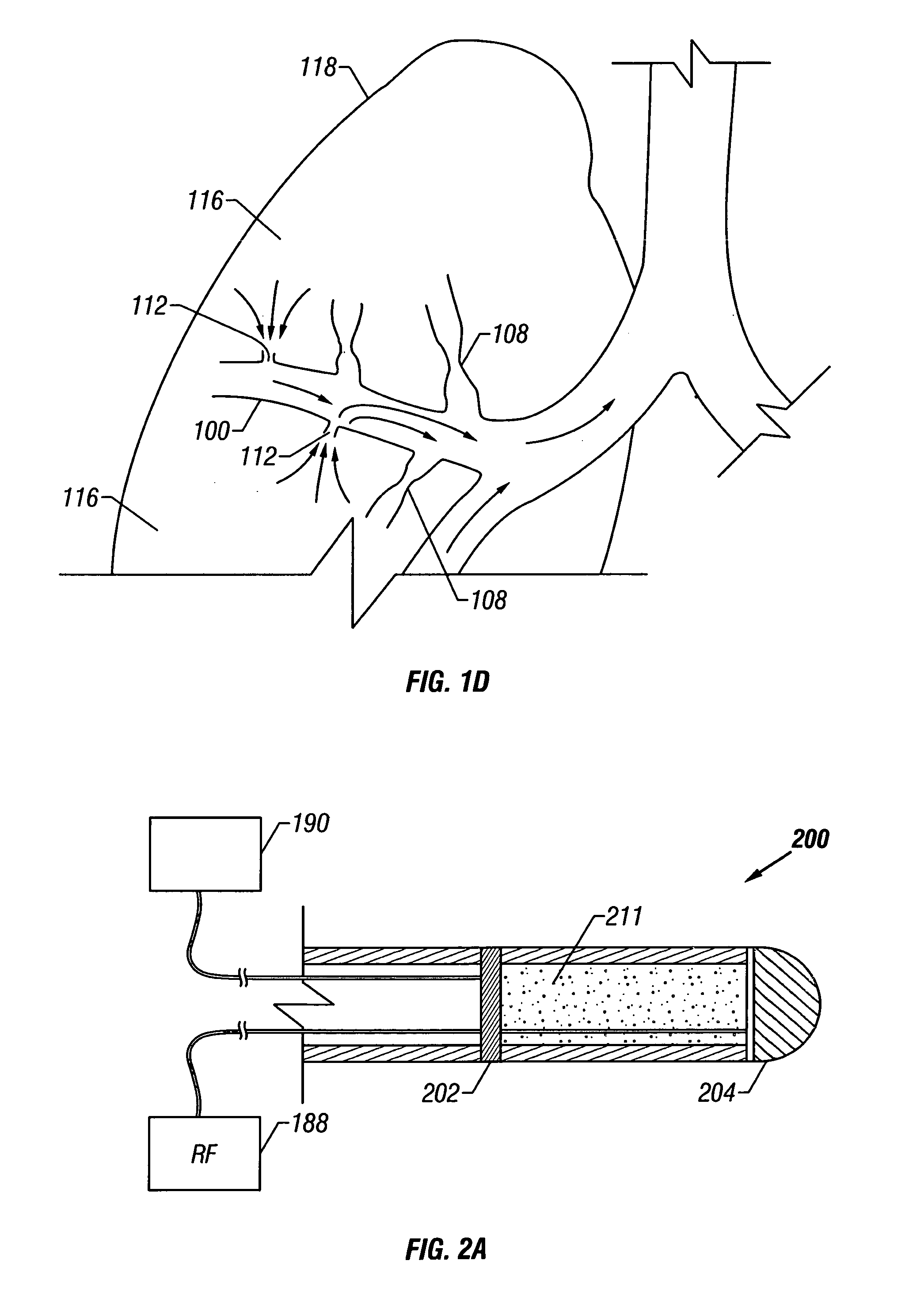
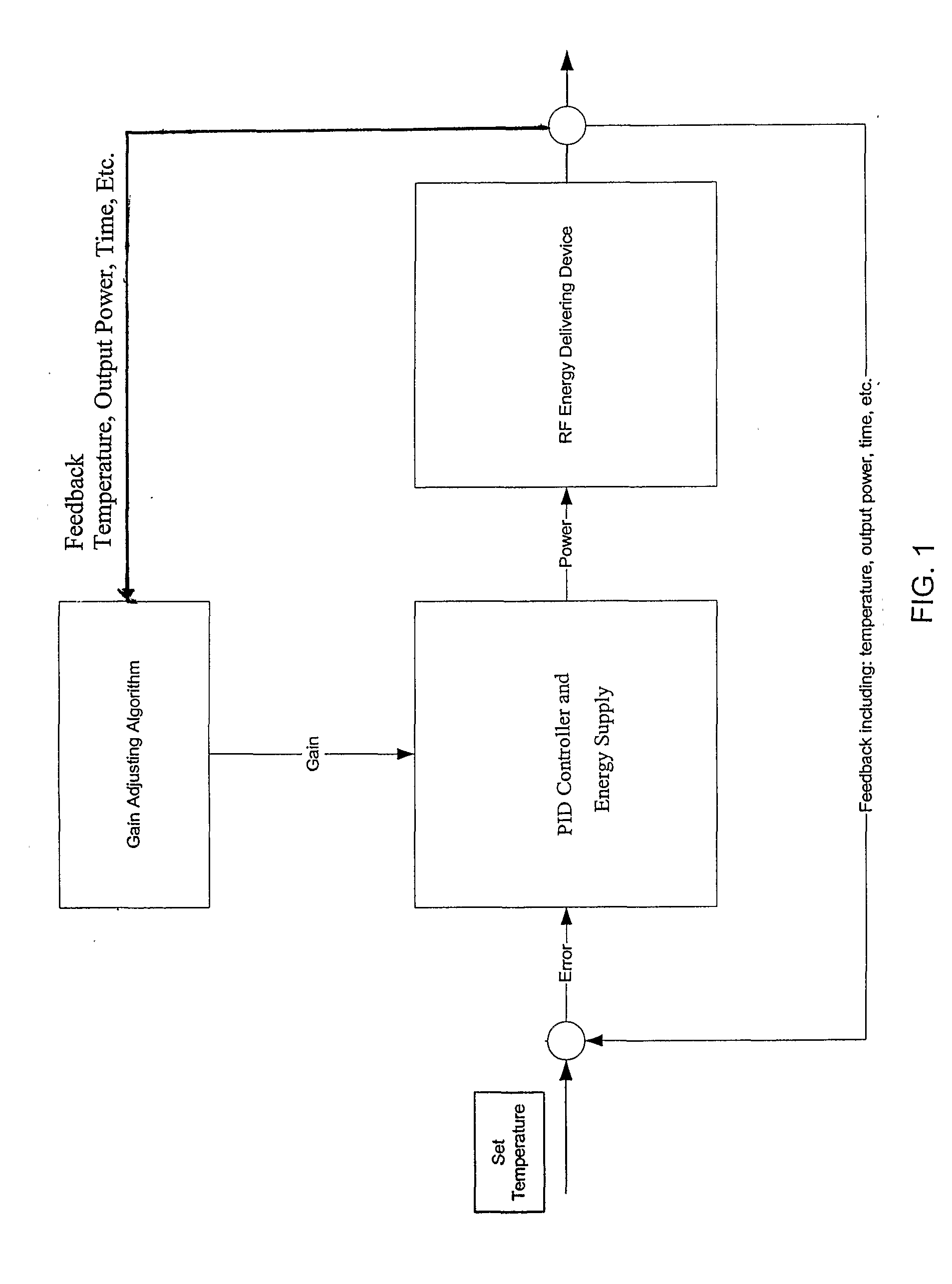
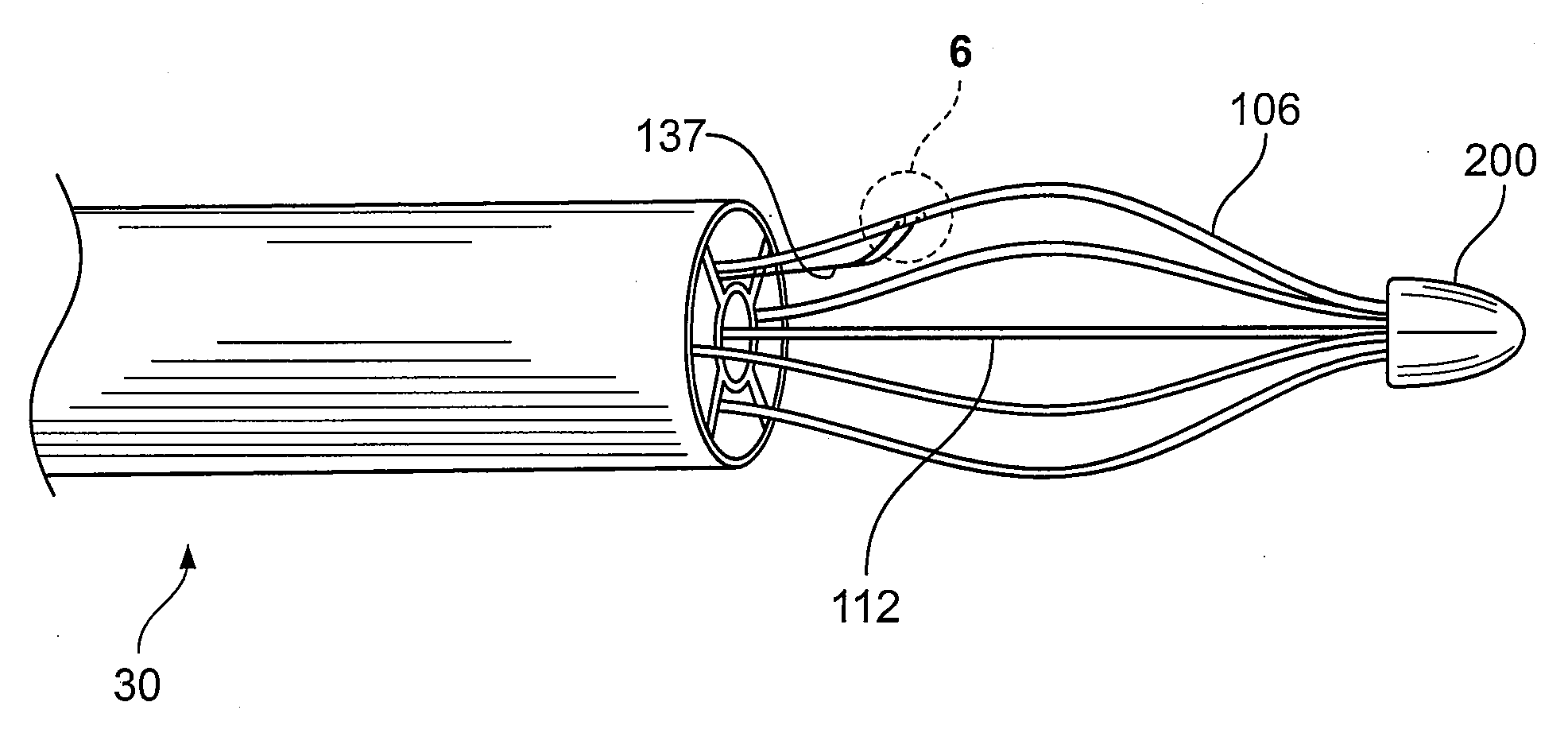
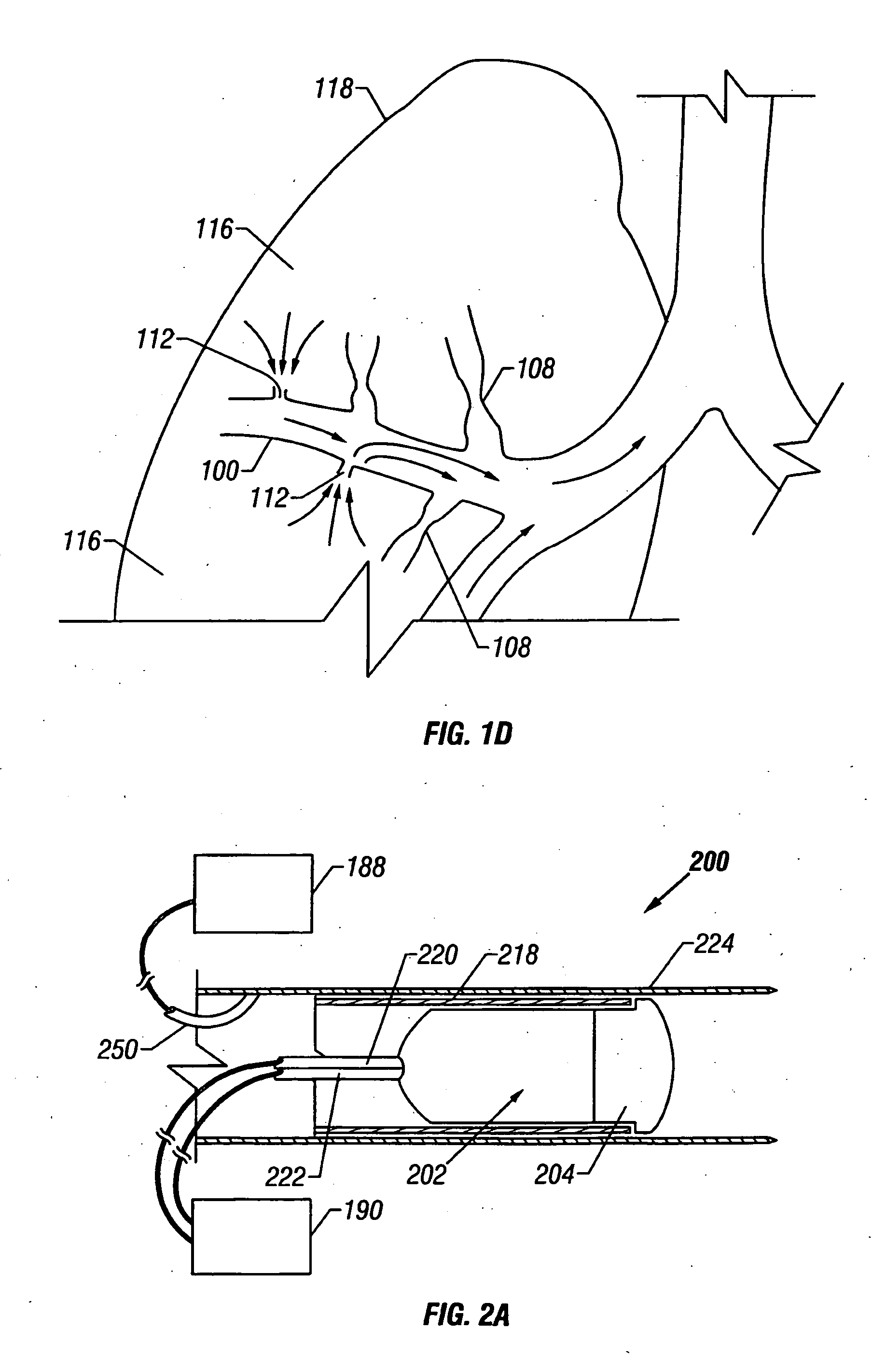
Control system and process for application of energy to airway walls and other mediums
InactiveUS7104987B2Improve conductivityElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingAirway wallSet point
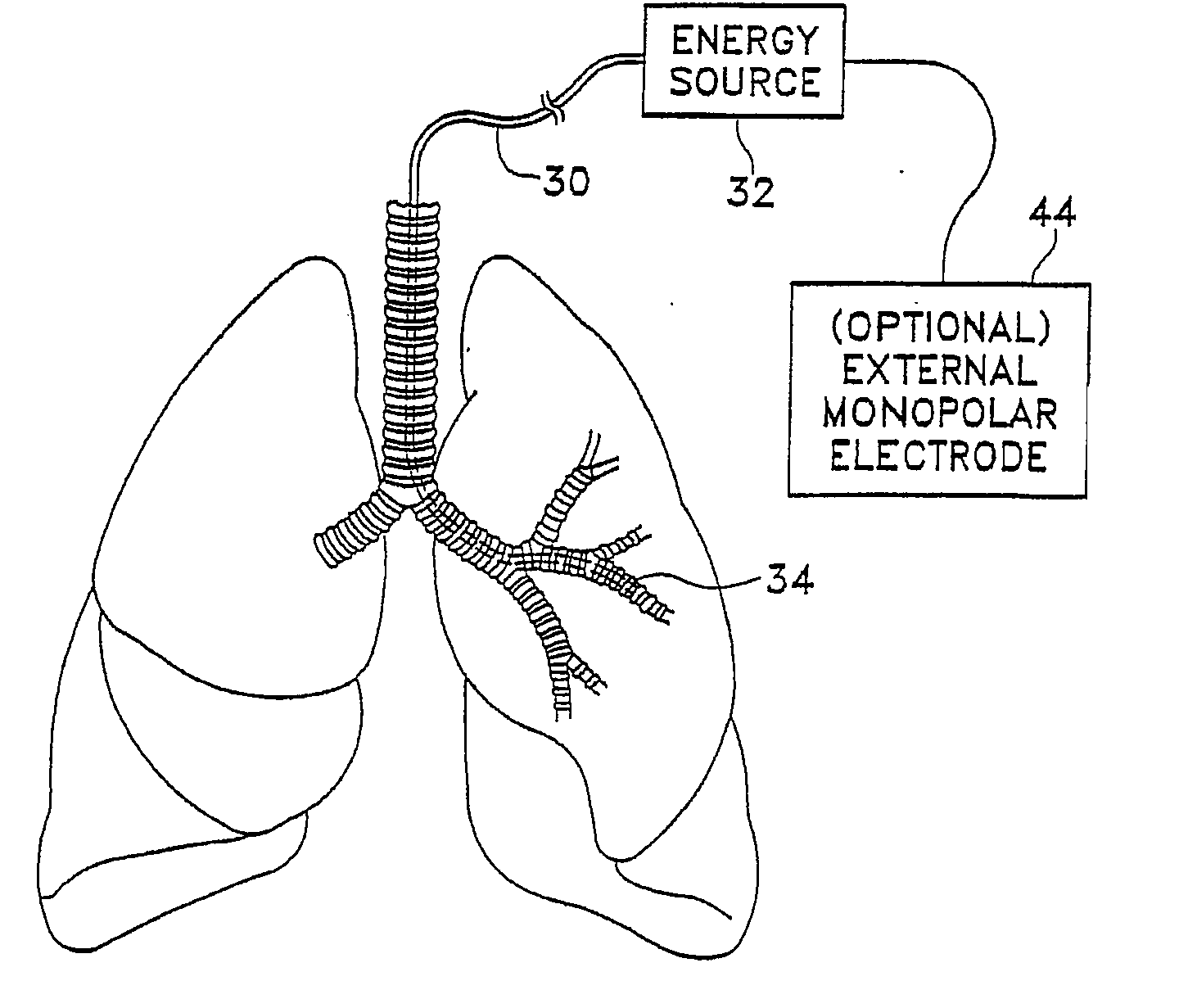
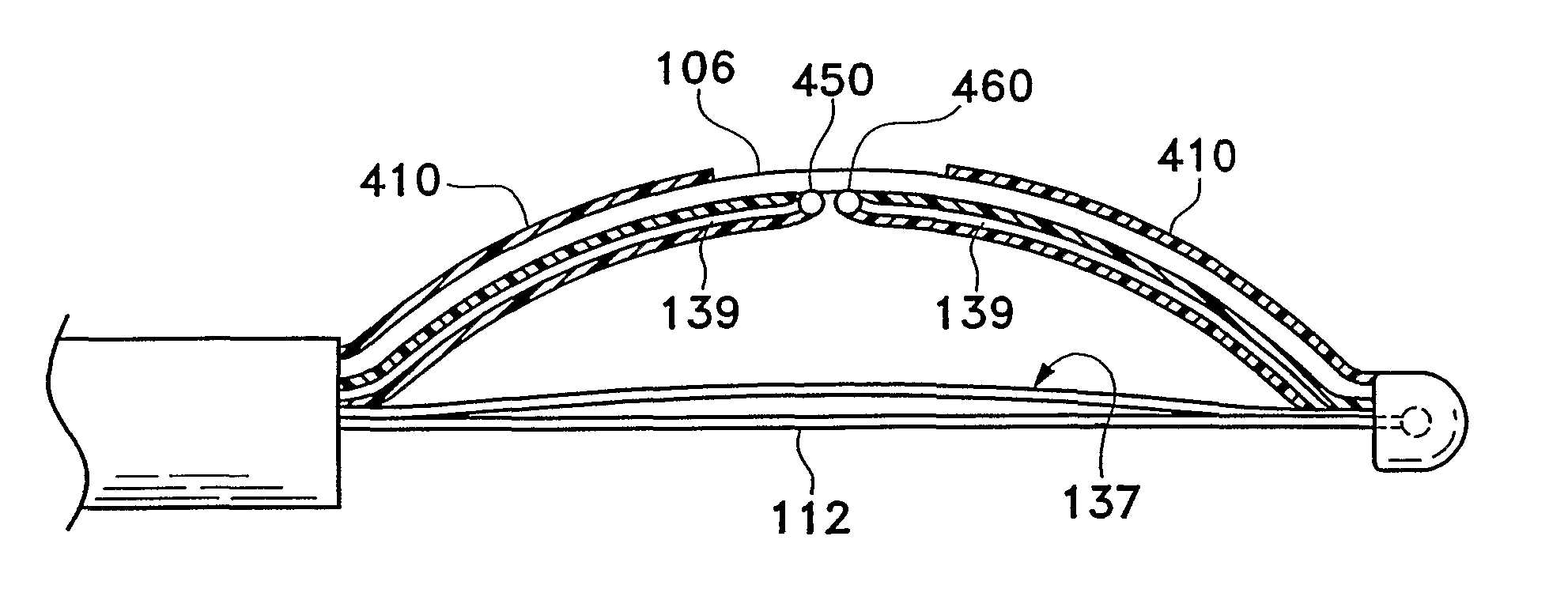
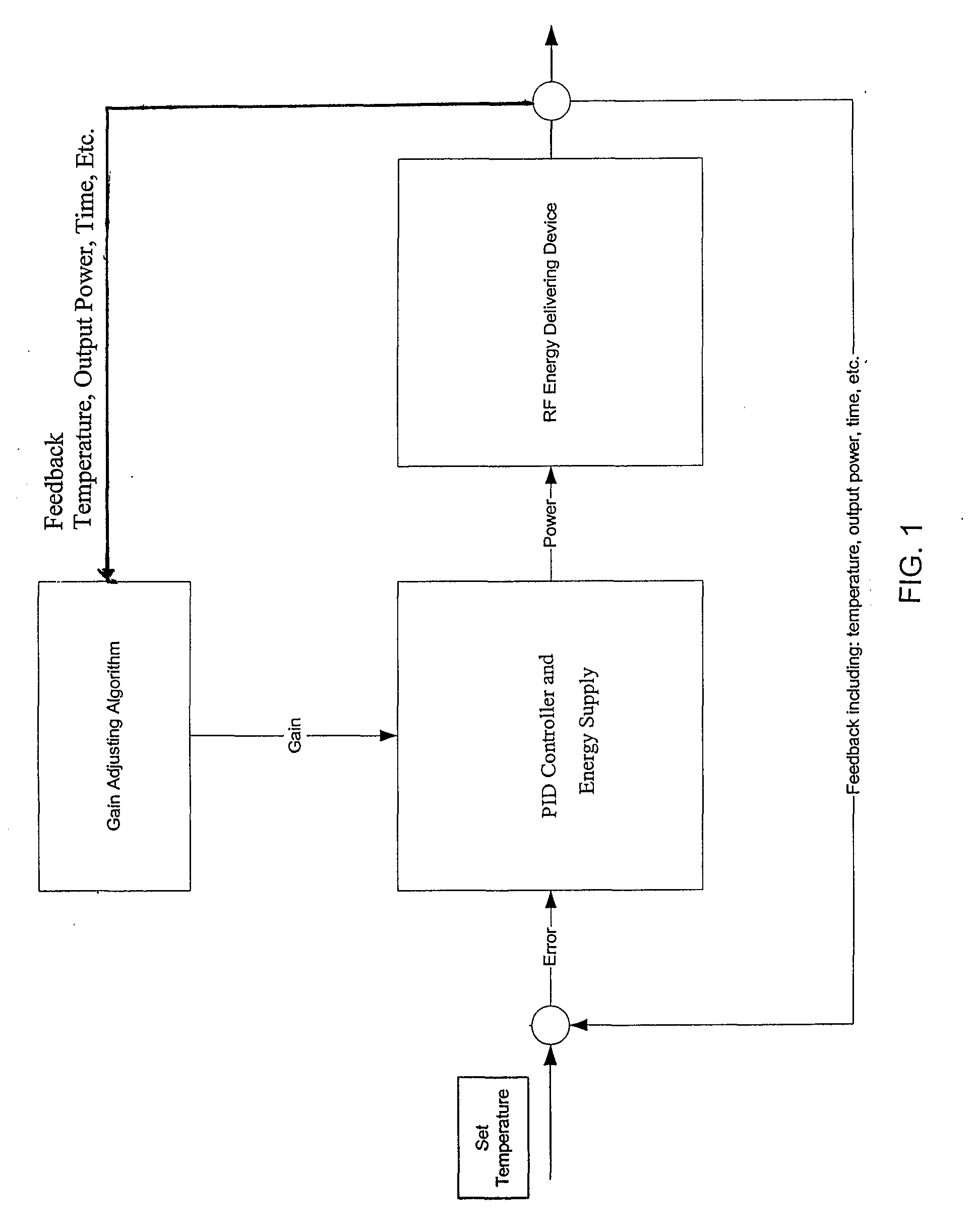
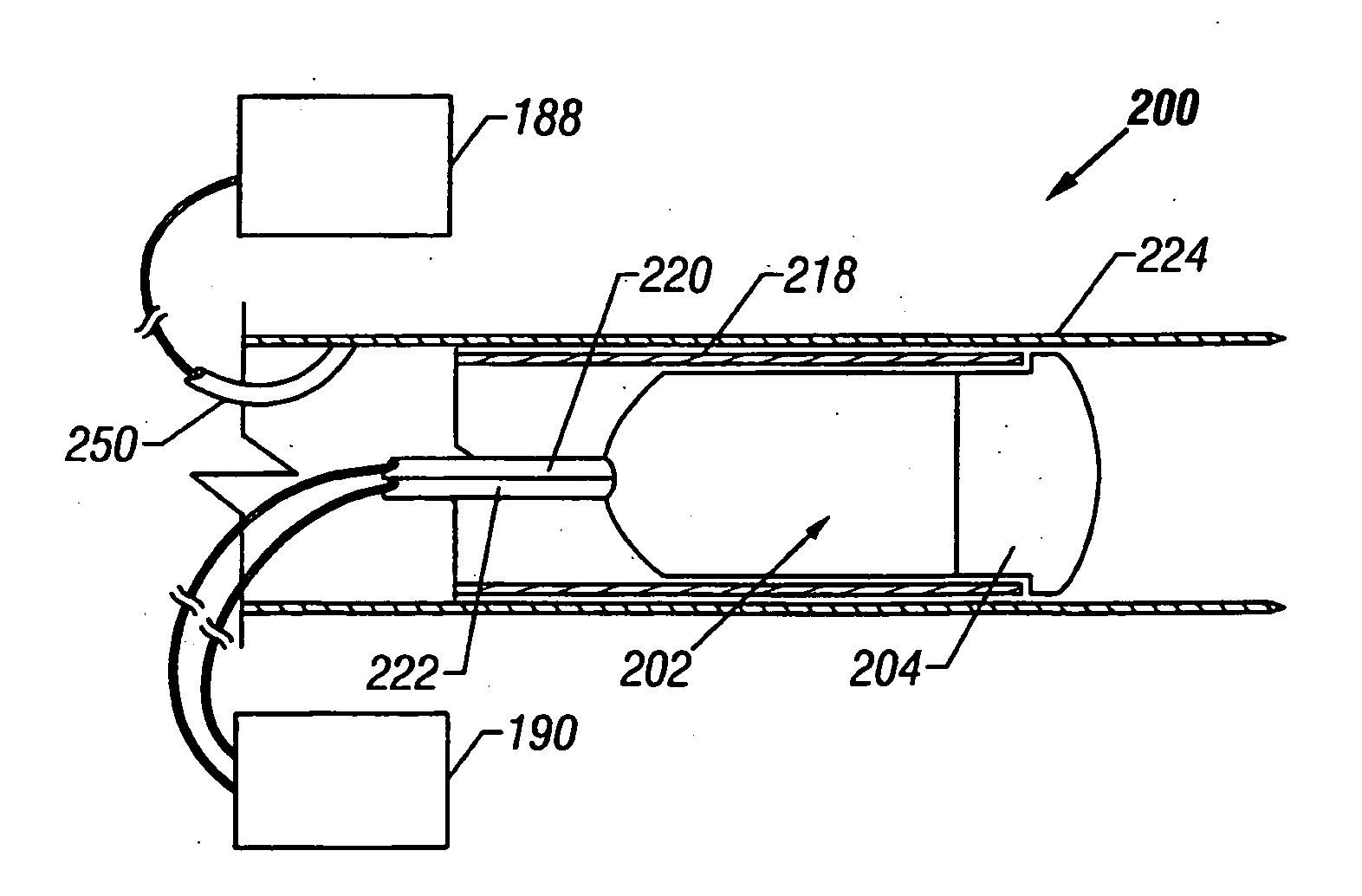
The present invention includes a system for delivering energy to an airway wall of a lung comprising an energy delivering apparatus and a PID controller having one or more variable gain factors which are rest after energy deliver has begun. The energy delivering apparatus may include a flexible elongated member and a distal expandable basket having at least one electrode for transferring energy to the airway wall and at least one temperature sensor for measuring temperature. The PID controller determines a new power set point base on an error between a preset temperature and the measured temperature. The algorithm can be Pi+1=Pi+G(αei+βei−1+γei−2) where α, β and γ are preset values and α is from 1 to 2; βis from −1 to −2; and γ is from −0.5 to 0−5. In another variation, the controller is configured to shut down if various measured parameters are exceeded such as, for example, energy, impedance, temperature, temperature differences, activation time and combinations thereof. Methods for treating a target medium using a PID algorithm are also provided.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Devices for applying energy to tissue
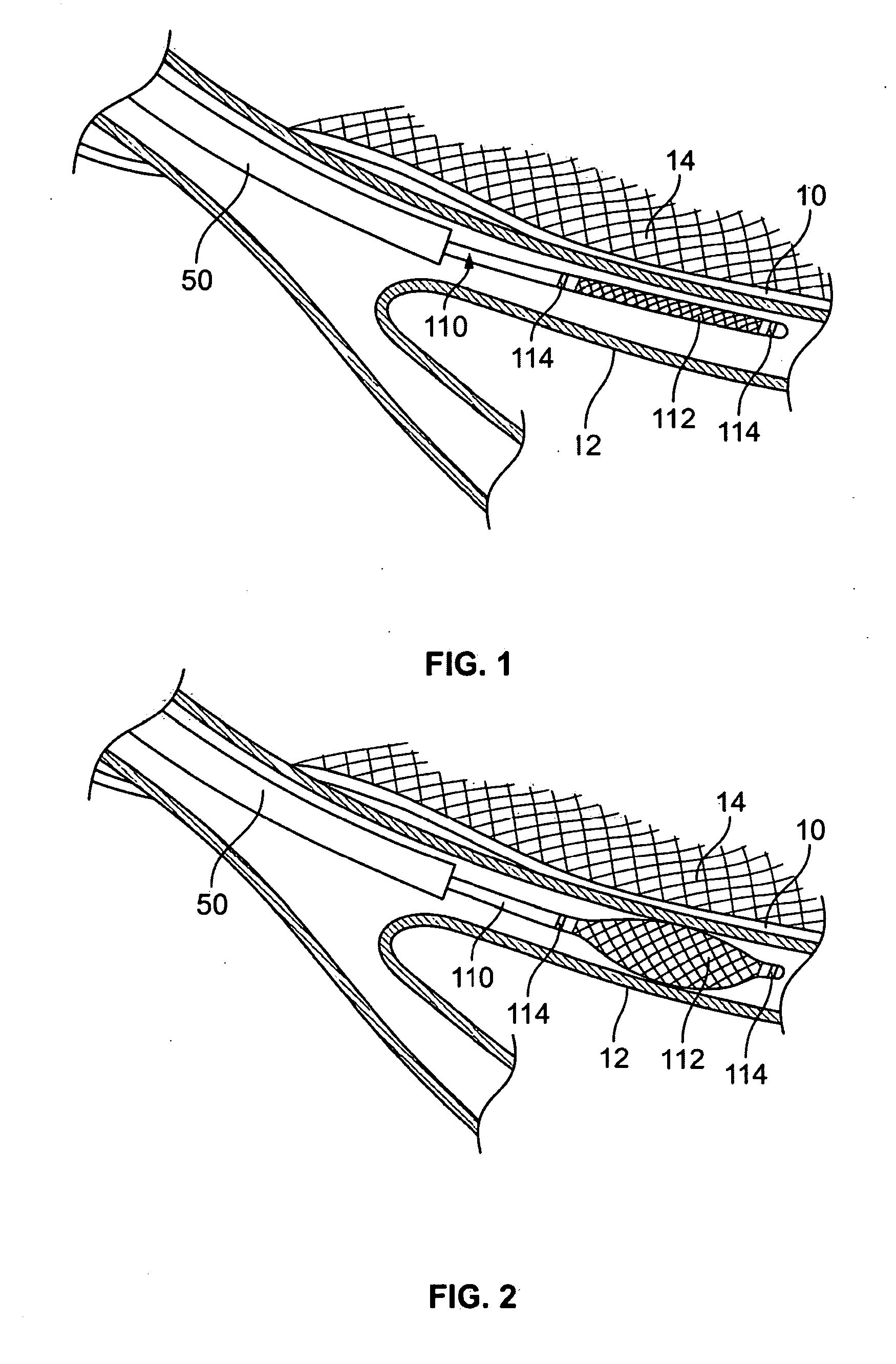
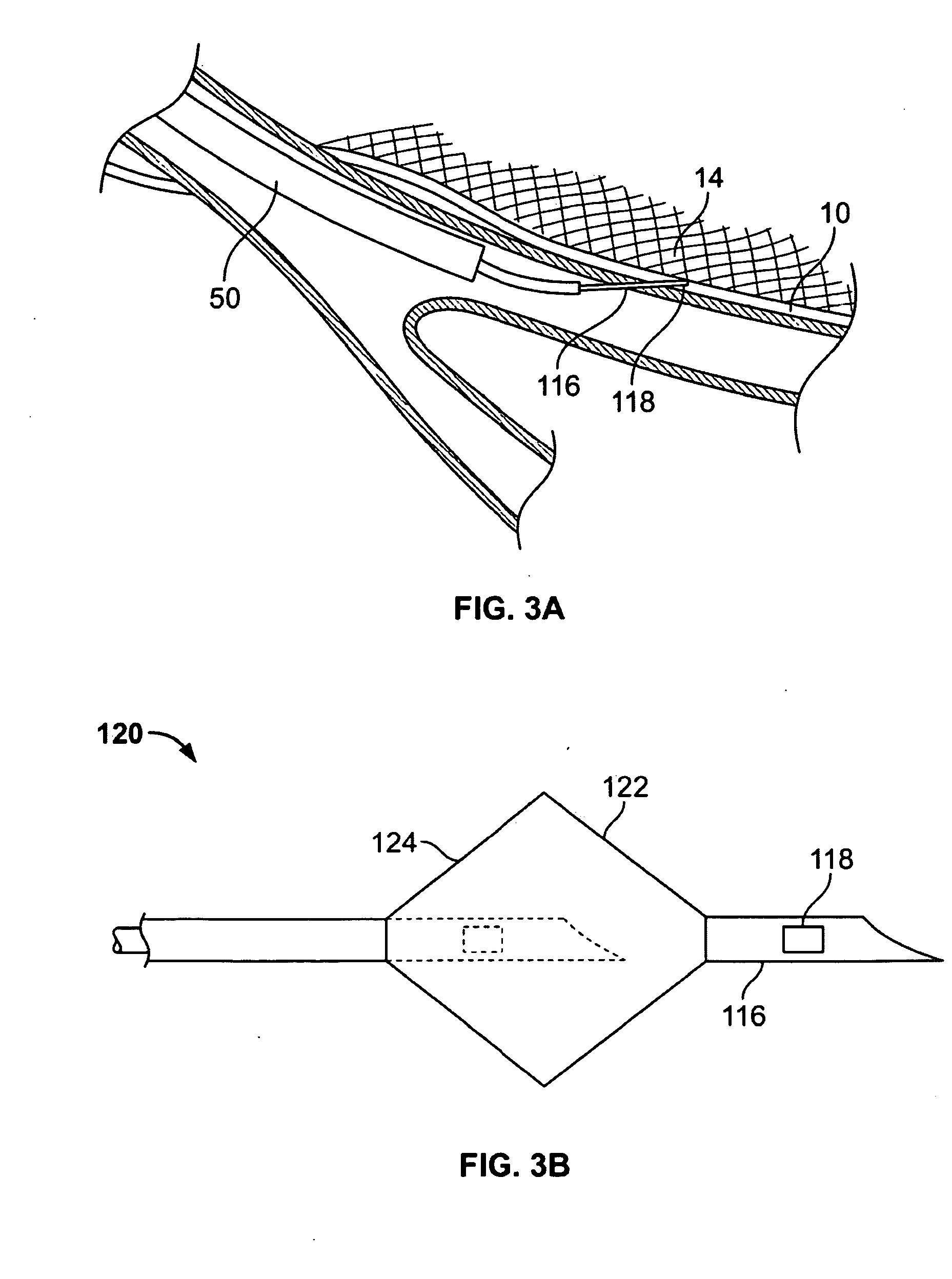
Disclosed herein are devices for altering gaseous flow within a lung to improve the expiration cycle of an individual, particularly individuals having chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). More particularly, a medical catheter is disclosed to detect the presence of blood vessels and to produce collateral openings or channels through the airway wall so that air is able to pass directly out of the lung tissue to facilitate both the exchange of oxygen ultimately into the blood and / or to decompress hyper-inflated lungs.
Owner:BRONCUS MEDICAL
Devices for maintaining surgically created openings
InactiveUS20050137518A1Simple processImprove scalabilityStentsBronchiCatheterObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Devices and methods are directed to improving the gaseous exchange in a lung of an individual having, for instance, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. More particularly, conduits may be deployed in the lung to maintain collateral openings (or channels) surgically created through airway walls. This tends to facilitate both the exchange of oxygen ultimately into the blood and decompress hyper-inflated lungs. The conduit includes a radially expandable center section having a first end, a second end, and a passageway extending from the first end to the second end. A control segment may be associated with the conduit to limit the degree of radial expansion. The conduit further includes a plurality of deflectable members extending from the ends of the center section. A tissue barrier may coaxially surround the conduit such that tissue ingrowth is prevented. The conduits may also include hold-down members and bioactive coatings that serve to prevent ejection of the conduit as well as prevent narrowing of the passageway due to tissue ingrowth.
Owner:BRONCUS TECH
Devices for maintaining surgically created openings
InactiveUS20050192526A1Simple processImprove scalabilityStentsBronchiCatheterObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Devices and methods are directed to improving the gaseous exchange in a lung of an individual having, for instance, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. More particularly, conduits may be deployed in the lung to maintain collateral openings (or channels) surgically created through airway walls. This tends to facilitate both the exchange of oxygen ultimately into the blood and decompress hyper-inflated lungs.
Owner:BIGGS MICHAEL +12
Modification of airways by application of energy
InactiveUS20070100390A1Reduce plugging of the airwayPrevent the airway from being able to constrictElectrotherapySurgical needlesPatient complianceObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
This relates to methods and devices for treating reversible chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and more particularly, relates to a device for exchanging energy with airway tissue such as that found in the airway of human lungs. The exchange of energy with this airway tissue in the airways reduces the ability of the air ways to constrict and / or reduces the resistance within the airway to the flow of air through the airway. This also relates to a method for decreasing responsiveness or decreasing resistance to airflow of airways involves the transfer of energy to or from the airway walls to prevent or reduce airway constriction and other symptoms of lung diseases. The treatment reduces the ability of the airway Lo contract during an acute narrowing of the airways, reduces mucus plugging of the airways, and / or increases the airway diameter. The methods according to the present invention provide a longer duration and / or more effective treatment for lung diseases than currently used drug treatments, and obviate patient compliance issues. This also includes additional steps that reduce the ability of the lung to produce at least one of the symptoms of reversible obstructive pulmonary disease and to reduce the resistance to the flow of air through a lung.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Devices for maintaining surgically created openings
InactiveUS20050137712A1Simple processImprove scalabilityStentsBronchiCatheterObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Devices and methods are directed to improving the gaseous exchange in a lung of an individual having, for instance, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. More particularly, conduits may be deployed in the lung to maintain collateral openings (or channels) surgically created through airway walls. This tends to facilitate both the exchange of oxygen ultimately into the blood and decompress hyper-inflated lungs.
Owner:BIGGS MICHAEL +12
Devices and methods for maintaining collateral channels in tissue
The devices and methods of placement of such devices disclosed herein are directed to altering gaseous flow within a lung to improve the expiration cycle of, for instance, an individual having Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. More particularly, these devices produce and maintain collateral openings or channels through the airway wall so that oxygen depleted / carbon dioxide rich air is able to pass directly out of the lung tissue to facilitate both the exchange of oxygen ultimately into the blood and / or to decompress hyper-inflated lungs. The medical kits disclosed herein are also directed to produce and maintain collateral openings through airway walls.
Owner:BRONCUS TECH
Methods of evaluating individuals having reversible obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20070102011A1Reduce capacityReduce resistanceElectrotherapyMedical devicesObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesAirway wall
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Control system and process for application of energy to airway walls and other mediums
InactiveUS20060247726A1Improve conductivityElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingControl systemEngineering
The present invention includes a system for delivering energy to an airway wall of a lung comprising an energy delivering apparatus and a PID controller having one or more variable gain factors which are rest after energy deliver has begun. The energy delivering apparatus may include a flexible elongated member and a distal expandable basket having at least one electrode for transferring energy to the airway wall and at least one temperature sensor for measuring temperature. The PID controller determines a new power set point base on an error between a preset temperature and the measured temperature. The algorithm can be Pii+1=Pi+G(αei+βei-1+γei-2) where α, β and γ are preset values and a is from 1 to 2; β is from −1 to −2; and 7 is from −0.5 to 0-5. In another variation, the controller is configured to shut down if various measured parameters are exceeded such as, for example, energy, impedance, temperature, temperature differences, activation time and combinations thereof. Methods for treating a target medium using a PID algorithm are also provided.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Multifunctional tip catheter for applying energy to tissue and detecting the presence of blood flow
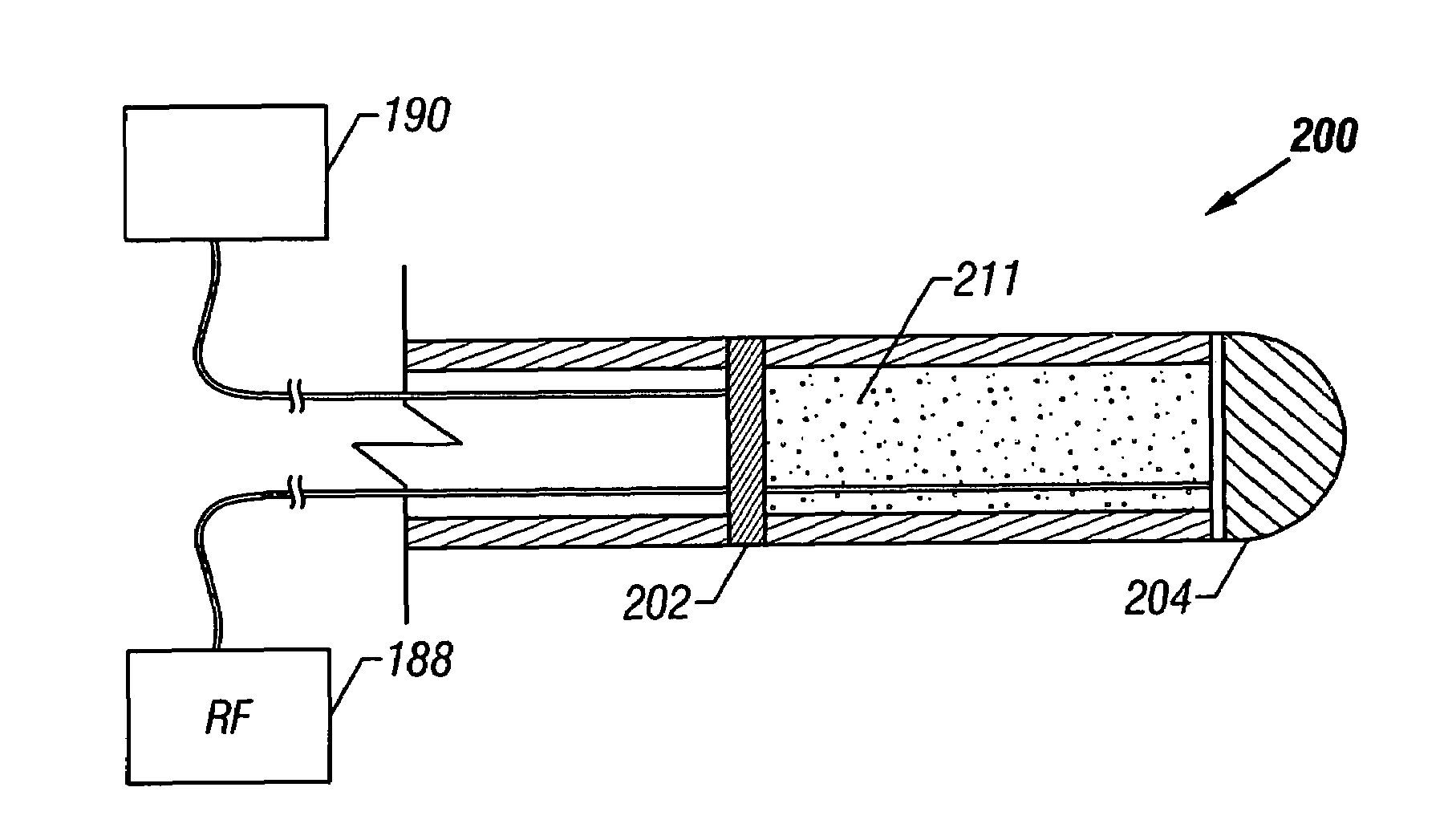
InactiveUS7422563B2Minimized in sizeEliminate needBronchiHeart valvesObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesAirway wall
Disclosed herein are devices for altering gaseous flow within a lung to improve the expiration cycle of an individual, particularly individuals having Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). More particularly, devices are disclosed to produce collateral openings or channels through the airway wall so that expired air is able to pass directly out of the lung tissue to facilitate both the exchange of oxygen ultimately into the blood and / or to decompress hyper-inflated lungs.
Owner:BRONCUS MEDICAL
Control system and process for application of energy to airway walls and other mediums
InactiveUS20060247727A1Improve conductivityElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingControl systemEngineering
The present invention includes a system for delivering energy to an airway wall of a lung comprising an energy delivering apparatus and a PID controller having one or more variable gain factors which are rest after energy deliver has begun. The energy delivering apparatus may include a flexible elongated member and a distal expandable basket having at least one electrode for transferring energy to the airway wall and at least one temperature sensor for measuring temperature. The PID controller determines a new power set point base on an error between a preset temperature and the measured temperature. The algorithm can be Pi+1=Pi+G(αei+βei−1+γei−2) where α, β and γ are preset values and α is from 1 to 2; β is from −1 to −2; and γ is from −0.5 to 0-5. In another variation, the controller is configured to shut down if various measured parameters are exceeded such as, for example, energy, impedance, temperature, temperature differences, activation time and combinations thereof. Methods for treating a target medium using a PID algorithm are also provided.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method for treating an asthma attack
InactiveUS20070083197A1Increase the diameterIncrease the effective diameterElectrotherapyDiagnosticsAsthma attackAirway wall
A method for treating the lung during an acute episode of reversible chronic obstructive pulmonary disease such as an asthma attack. The method comprises transferring energy to an airway wall of an airway such that a diameter of the airway is increased. The energy may be transferred to the airway wall prior to, during or after an asthma attack. The energy may be transferred in an amount sufficient to temporarily or permanently increase the diameter of the airway. The method may be performed while the airway is open, closed or partially closed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
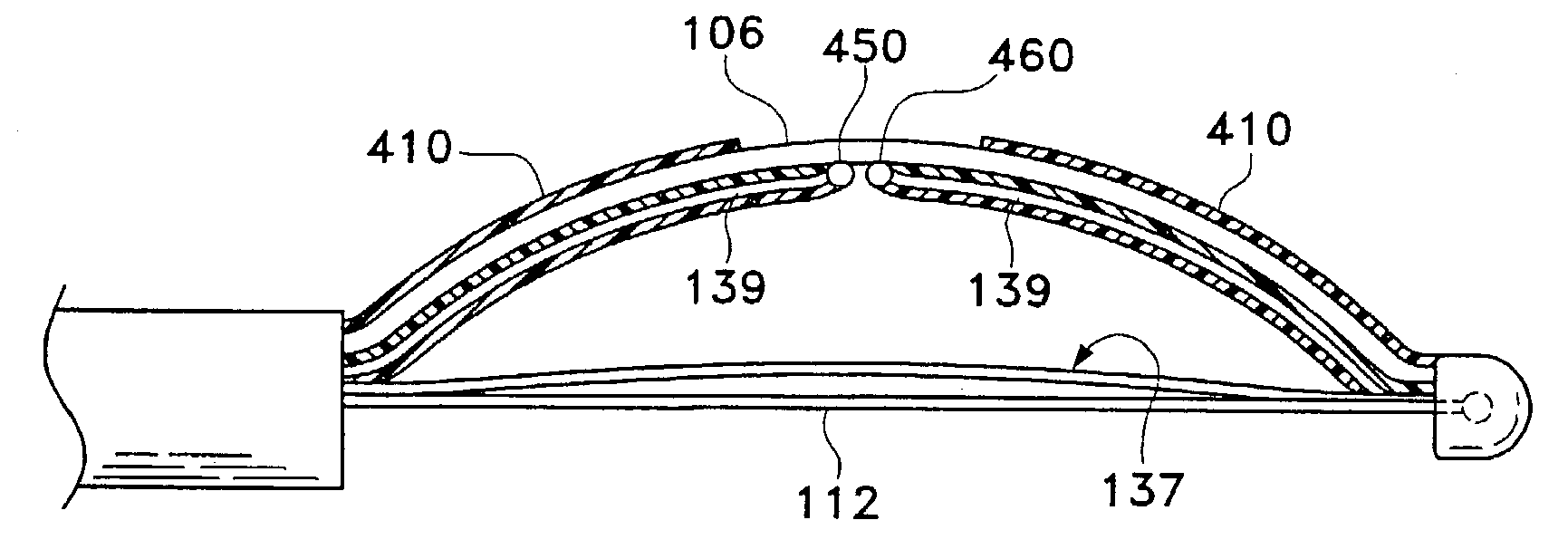
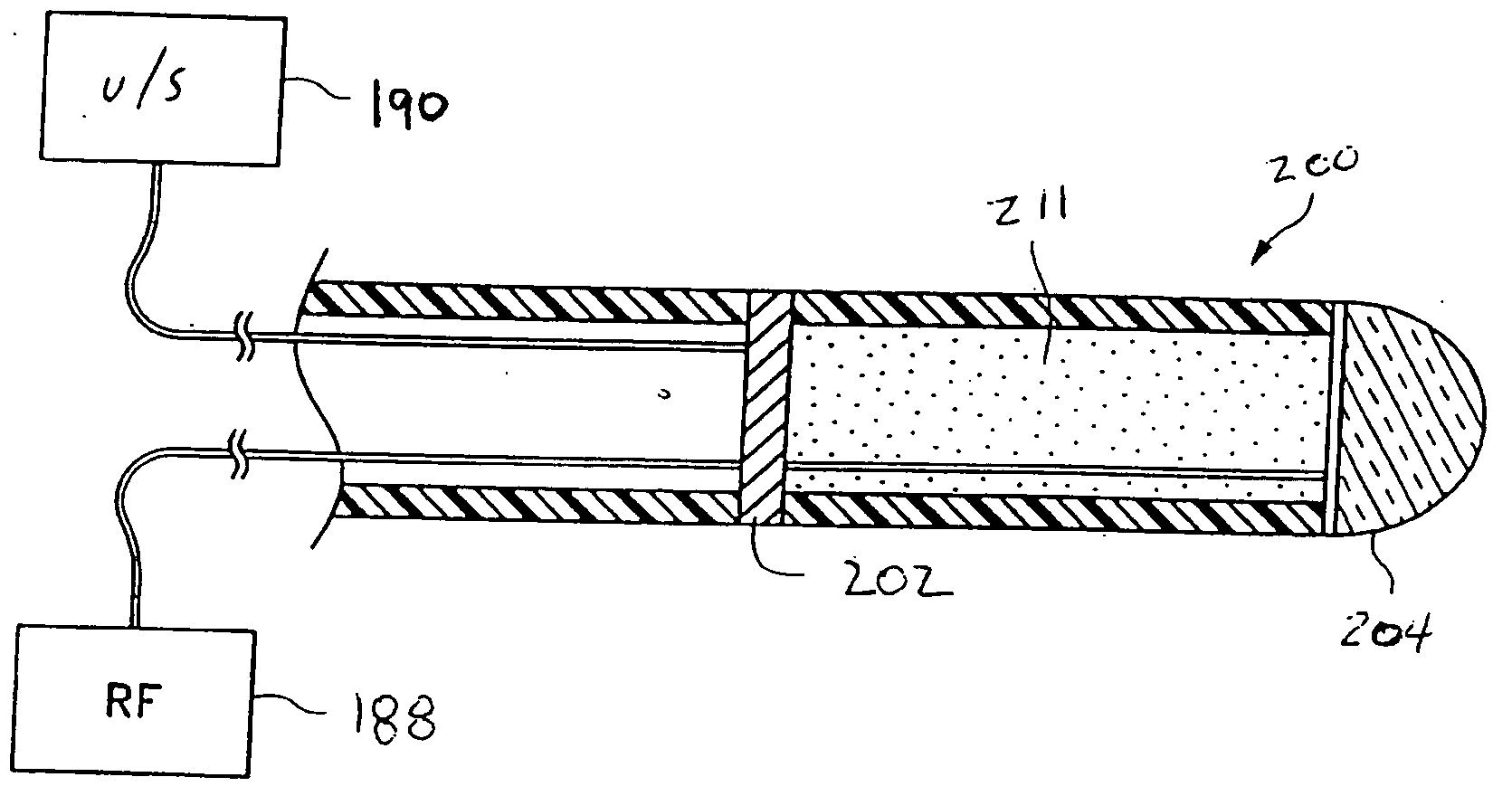
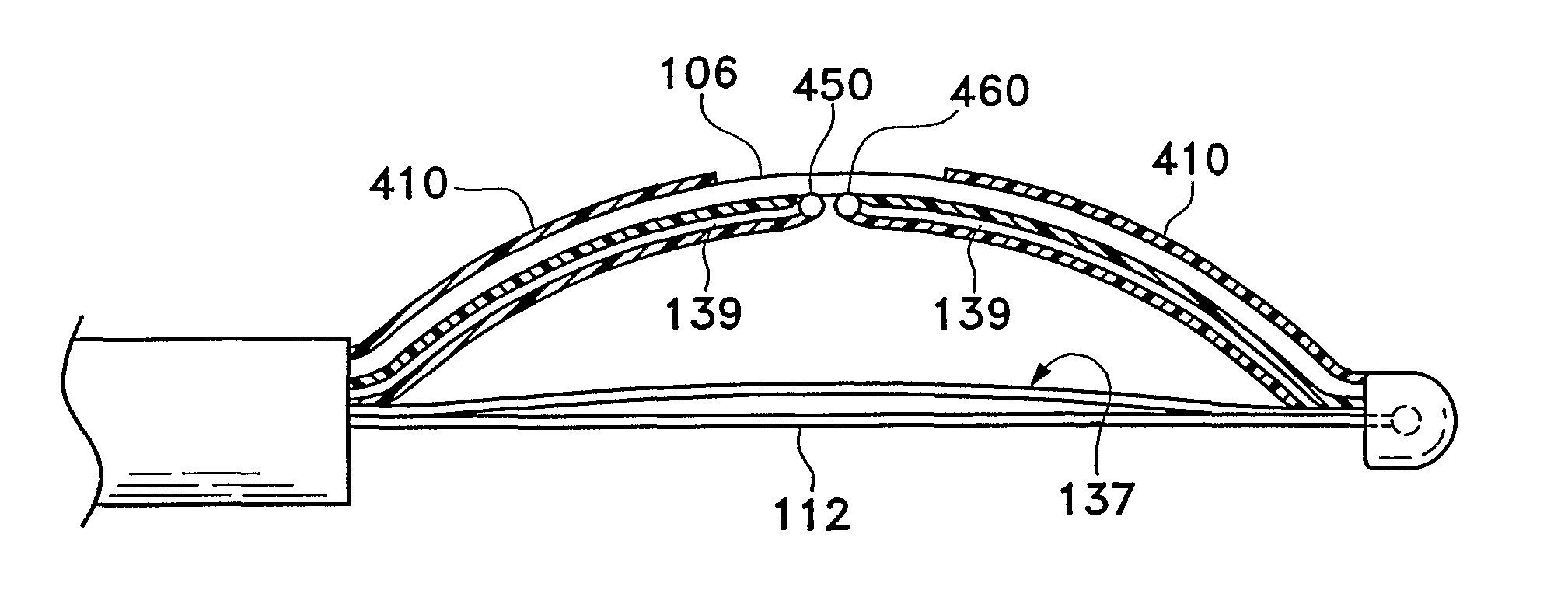
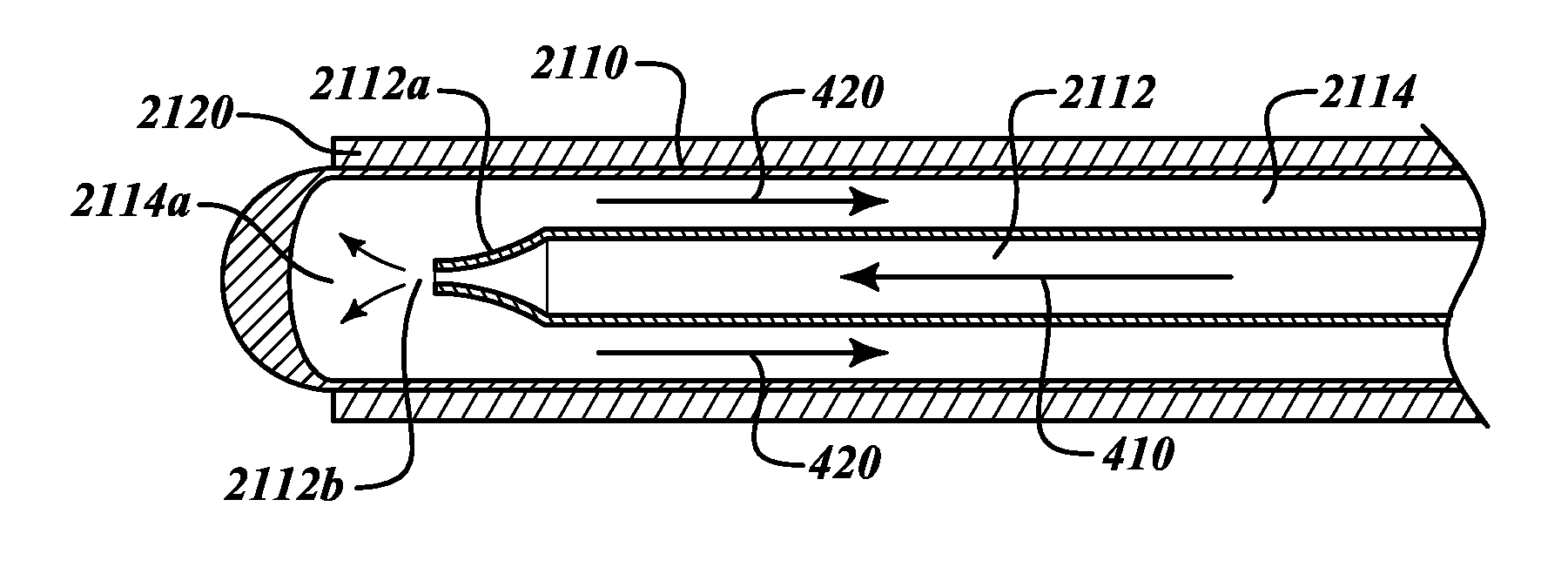
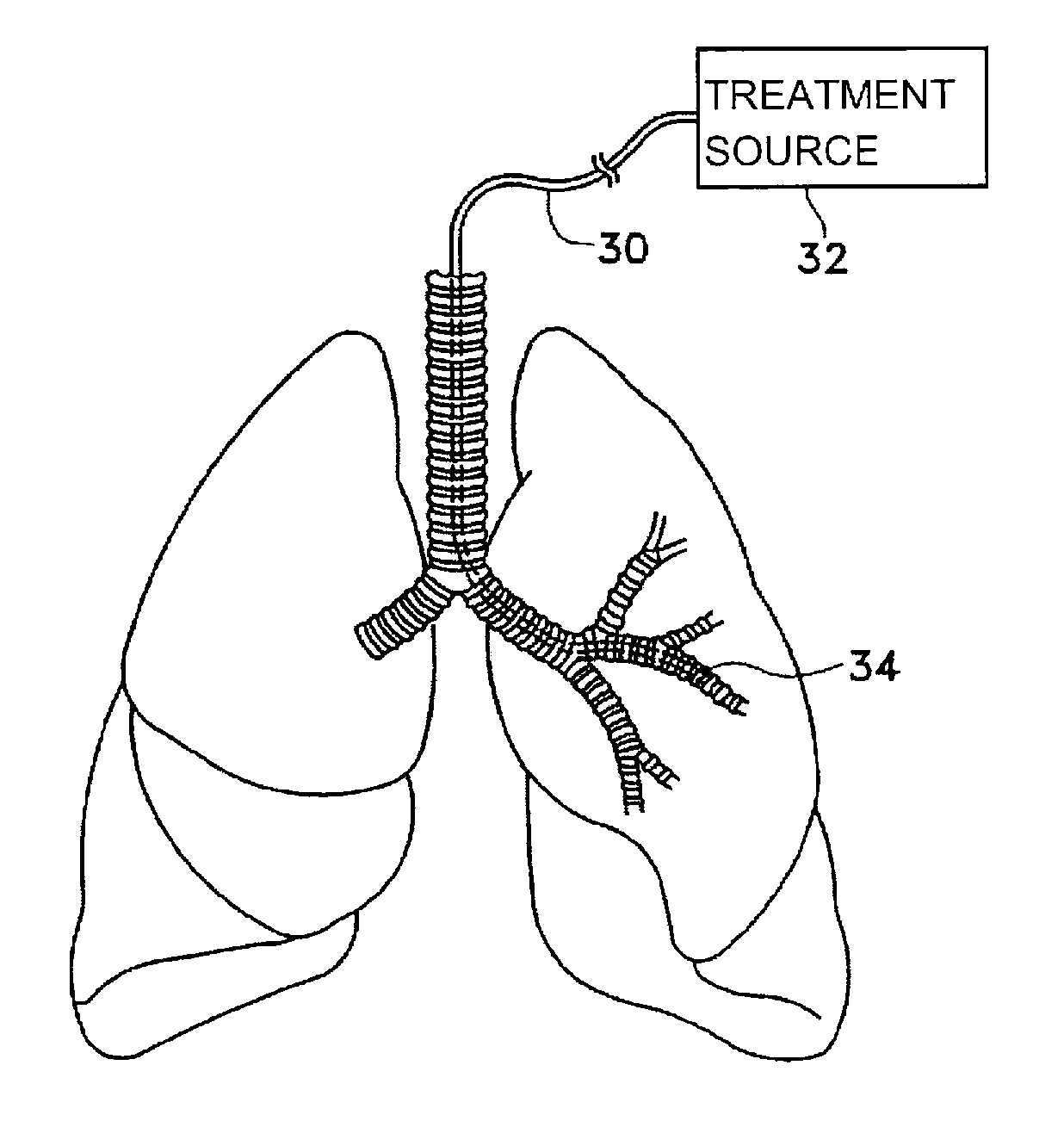
Compact delivery pulmonary treatment systems and methods for improving pulmonary function
InactiveUS20130310822A1Large inflexibilityIncrease in sizeUltrasound therapySurgical instruments for heatingAirway wallIntensive care medicine
A pulmonary treatment system includes a compact configuration for delivery to a first airway of a patient. An energy delivery system of the pulmonary treatment system delivers energy to target tissue in or along an airway wall of the first airway to reduce airway resistance in a second airway distal to the first airway. The pulmonary treatment system protects tissue in the airway wall of the first airway located between the target tissue and the energy delivery system by at least one of thermodynamically cooling, circulating a liquid coolant through the pulmonary treatment system, and shielding a portion of the energy delivery system.
Owner:NUVAIRA INC
Methods for treating airways
InactiveUS20060137698A1Reduce capacityReduce resistanceDiagnosticsInternal electrodesAirway wallAnesthesia
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Visualizing different types of airway wall abnormalities
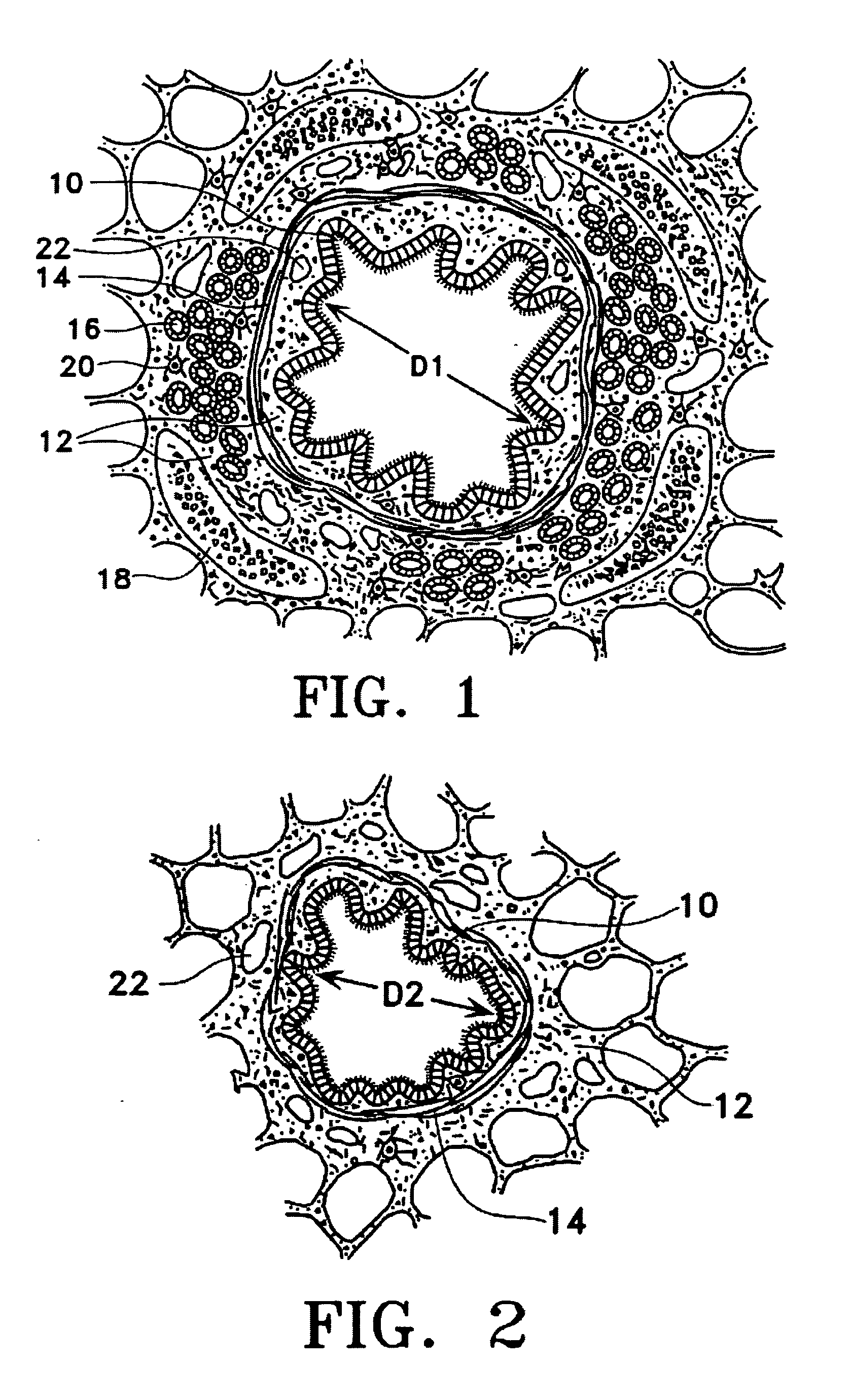
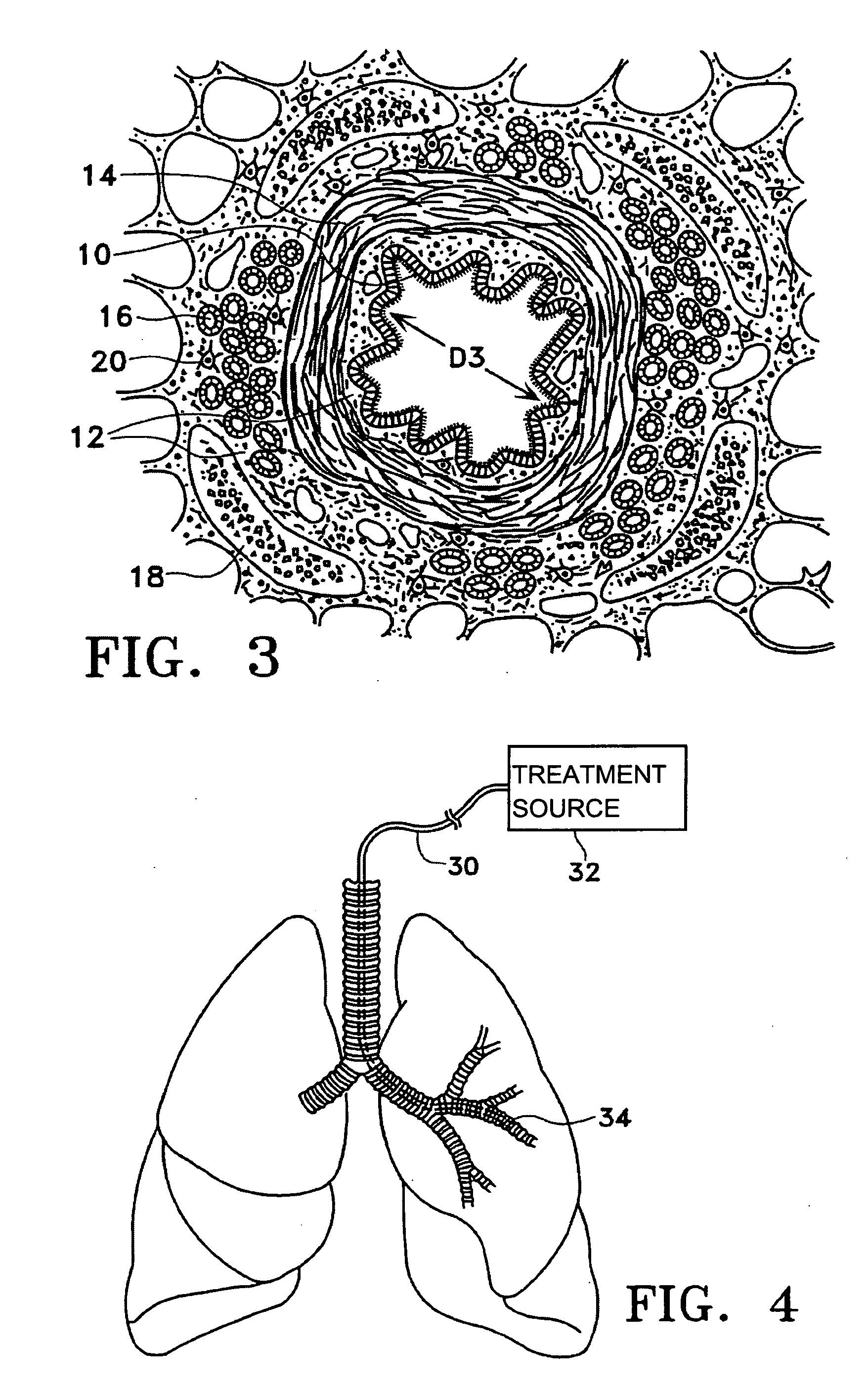
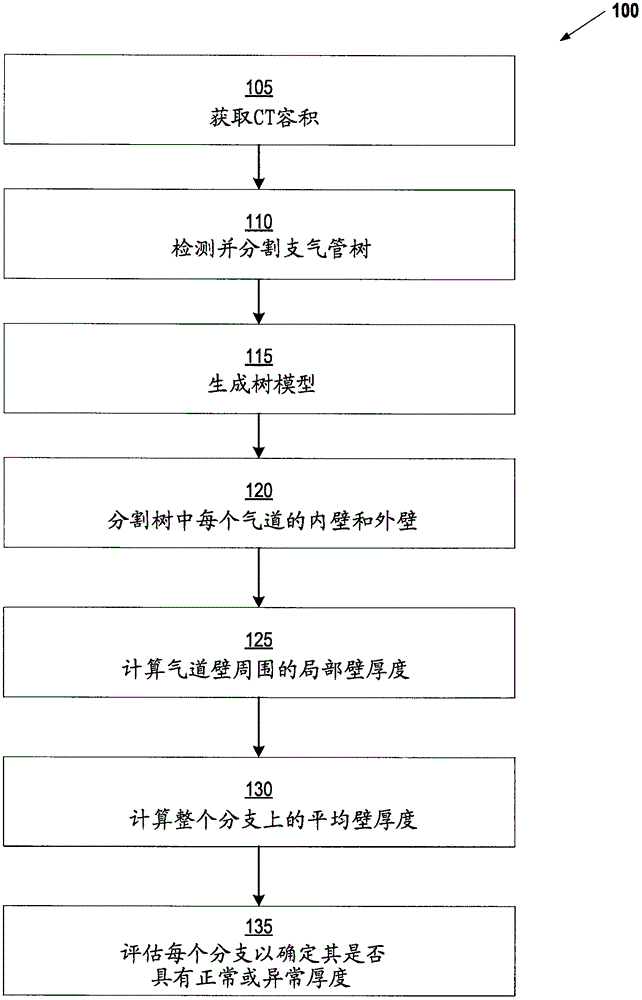
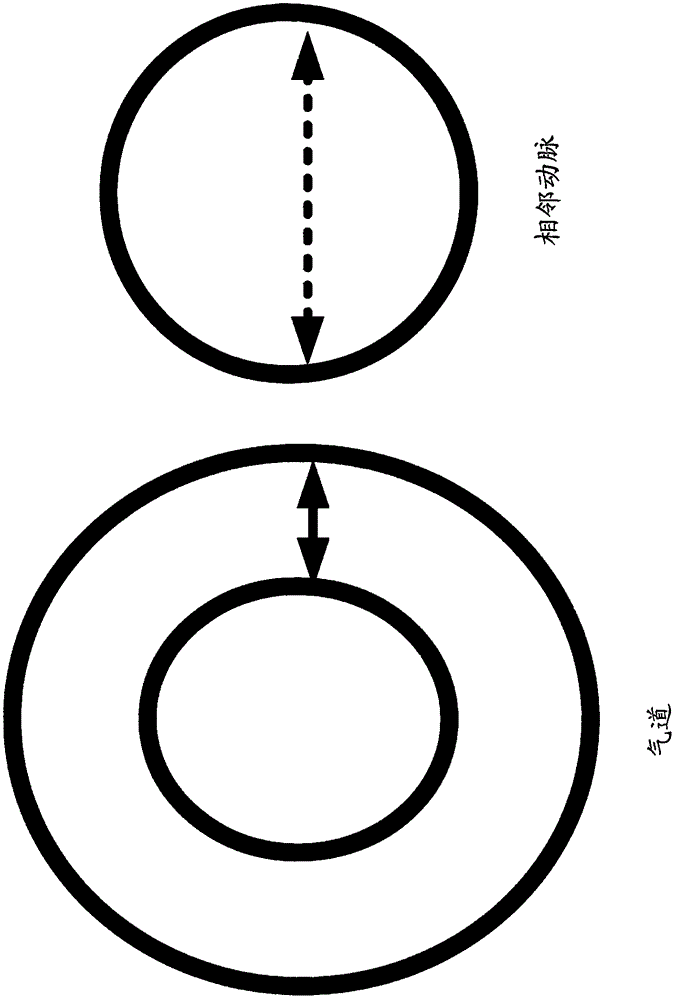
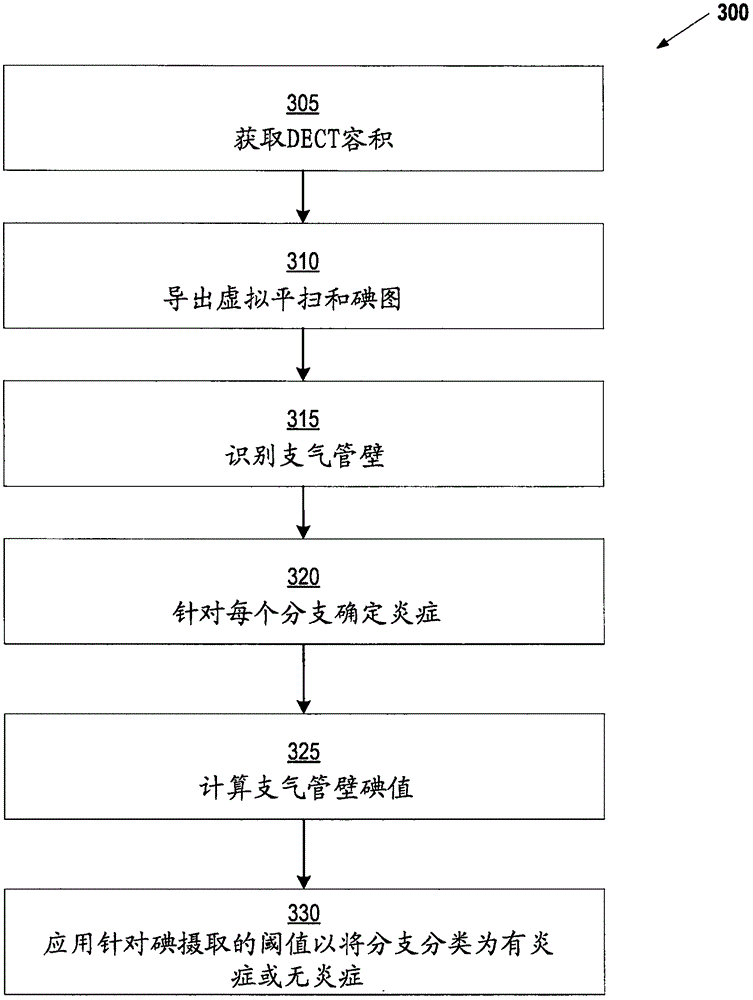
The invention relates to visualizing different types of airway wall abnormalities. A method for visualizing airway wall abnormalities includes acquiring Dual Energy Computed Tomography (DECT) imaging data comprising one or more image volumes representative of a bronchial tree. An iodine map is derived using the DECT imaging data and the bronchial tree is segmented from the image volume(s). A tree model representative of the bronchial tree is generated. Then, for each branch, this tree model is used to determine an indicator of normal or abnormal thickness. Locations corresponding to bronchial walls in the bronchial tree using the tree model are identified. Next, for each branch, the locations corresponding to bronchial walls in the bronchial tree and the iodine map are used to determine an indicator of normal or abnormal inflammation. A visualization of the bronchial tree may be presented with visual indicators at each of the locations corresponding to bronchial walls indicating whether a bronchial wall is thickened and / or inflamed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Methods of treating inflammation in airways
InactiveUS20060278243A1Reduce capacityReduce resistanceDiagnosticsInternal electrodesAirway wallAnesthesia
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Devices for applying energy to tissue
InactiveUS20060142672A1Minimized in sizeEliminate needBronchiHeart valvesRadiologyObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Disclosed herein are devices for altering gaseous flow within a lung to improve the expiration cycle of an individual, particularly individuals having Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). More particularly, devices are disclosed to produce collateral openings or channels through the airway wall so that expired air is able to pass directly out of the lung tissue to facilitate both the exchange of oxygen ultimately into the blood and / or to decompress hyper-inflated lungs.
Owner:BRONCUS MEDICAL
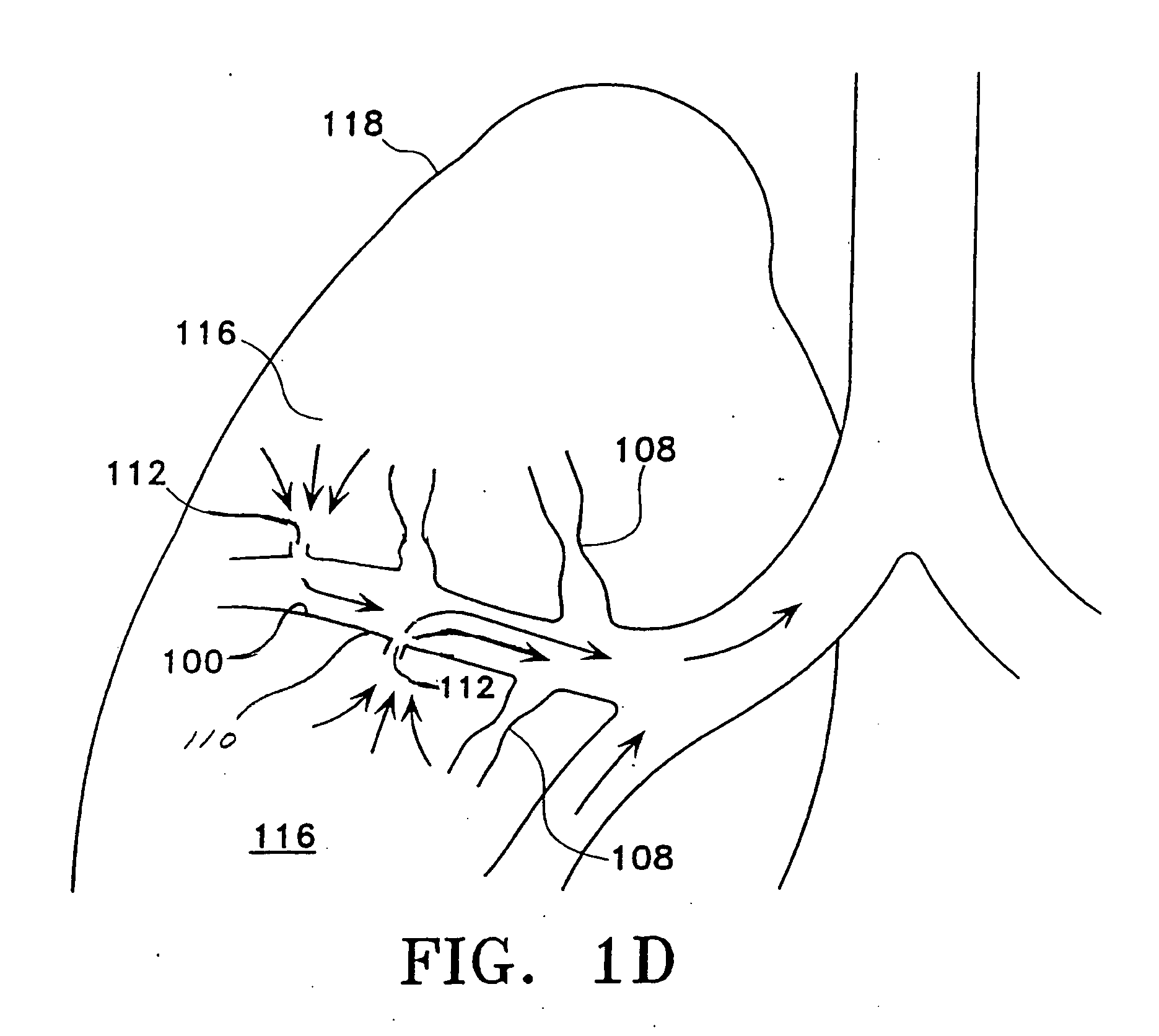
Method and system for measuring pulmonary artery circulation information
Minimally invasive systems and methods are described for measuring pulmonary circulation information from the pulmonary arteries. A transbronchial Doppler ultrasound catheter is advanced through the airways and in the vicinity of the pulmonary artery. Doppler ultrasound energy is sent through the airway wall and across the pulmonary artery to obtain velocity information of blood flowing through the artery. The velocity information is used to compute pulmonary circulation information including but not limited to flowrate.
Owner:EKOS CORP
Devices for applying energy to tissue
InactiveUS20020128647A1Minimized in sizeEliminate needBronchiHeart valvesRadiologyObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Disclosed herein are devices for altering gaseous flow within a lung to improve the expiration cycle of an individual, particularly individuals having Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). More particularly, devices are disclosed to produce collateral openings or channels through the airway wall so that expired air is able to pass directly out of the lung tissue to facilitate both the exchange of oxygen ultimately into the blood and / or to decompress hyper-inflated lungs.
Owner:BRONCUS MEDICAL
Methods for maintaining the patency of collateral channels in the lungs using cryo-energy
InactiveUS20090076491A1Enhance the imageSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesAirway wall
The methods disclosed herein are directed to altering gaseous flow within a lung to improve the expiration cycle of, for instance, an individual having Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. More particularly, these methods produce and maintain collateral openings or channels through the airway wall so that expired air is able to pass directly out of the lung tissue to facilitate both the exchange of oxygen ultimately into the blood and / or to decompress hyper-inflated lungs. Devices and methods apply cryo-energy to maintain the patency of the surgically created openings.
Owner:BRONCUS MEDICAL
Measurement of pulmonary hypertension from within the airways
InactiveUS20080312543A1Control bleedingElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesBronchial balloon catheterAirway wall
This is directed to methods and devices suited for airway based measurements of pressure in a pulmonary artery. A device is advanced into an airway and in the vicinity of the pulmonary artery. Physical properties of the pulmonary artery are observed through the airway wall using one or more minimally invasive modalities. In a variation, a bronchial balloon catheter measures pressure of the pulmonary artery.
Owner:PNEUMRX
Airway device
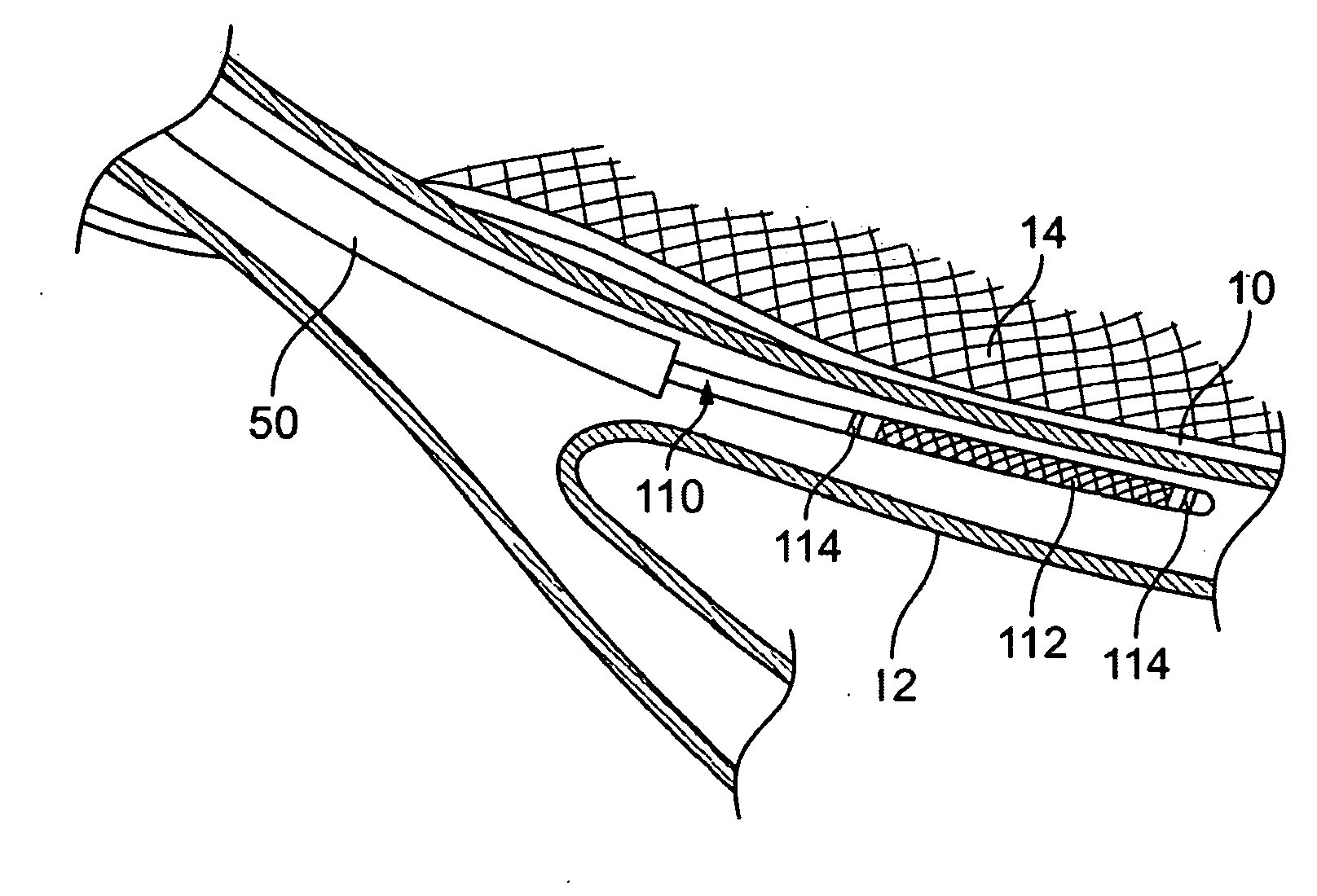
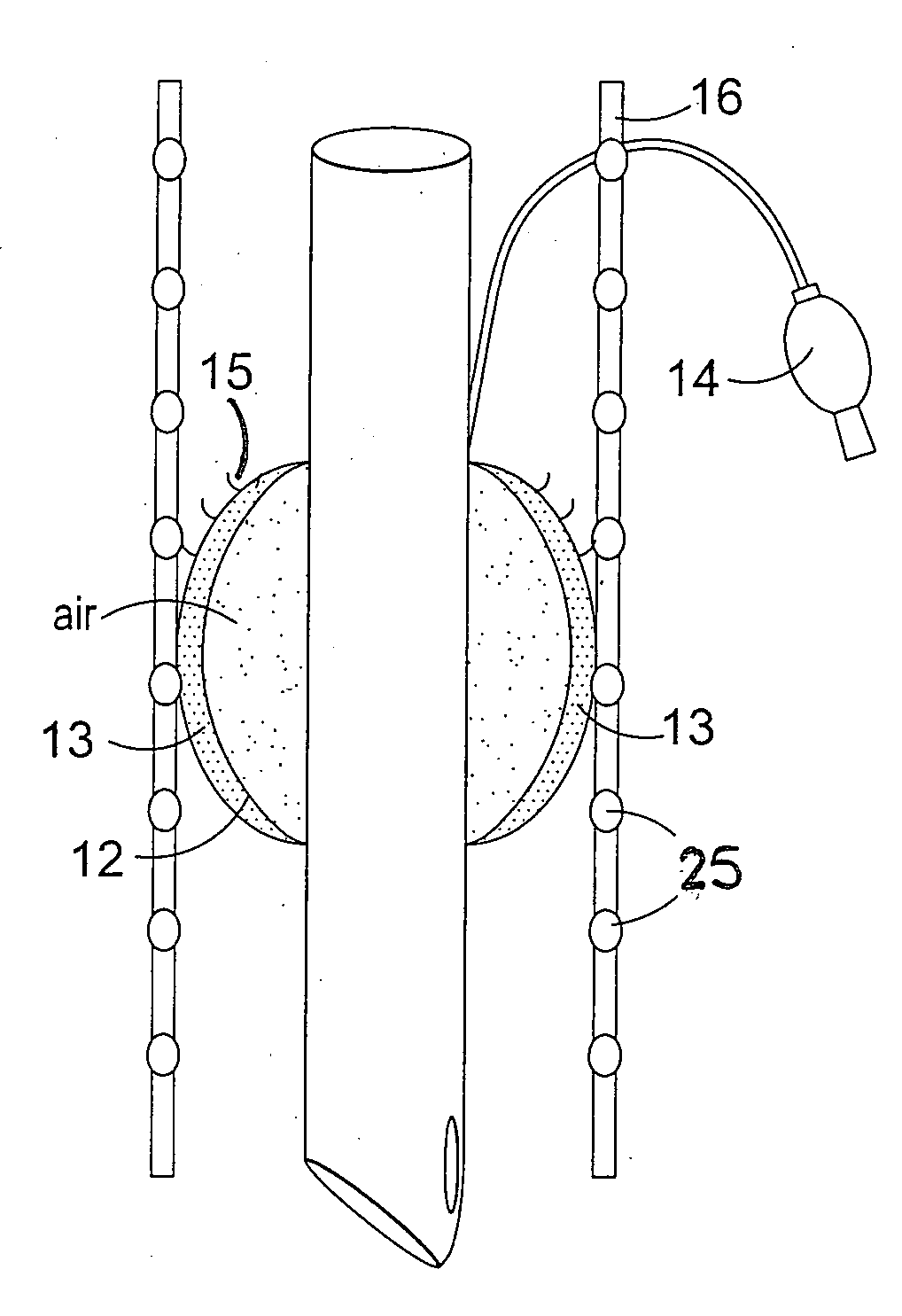
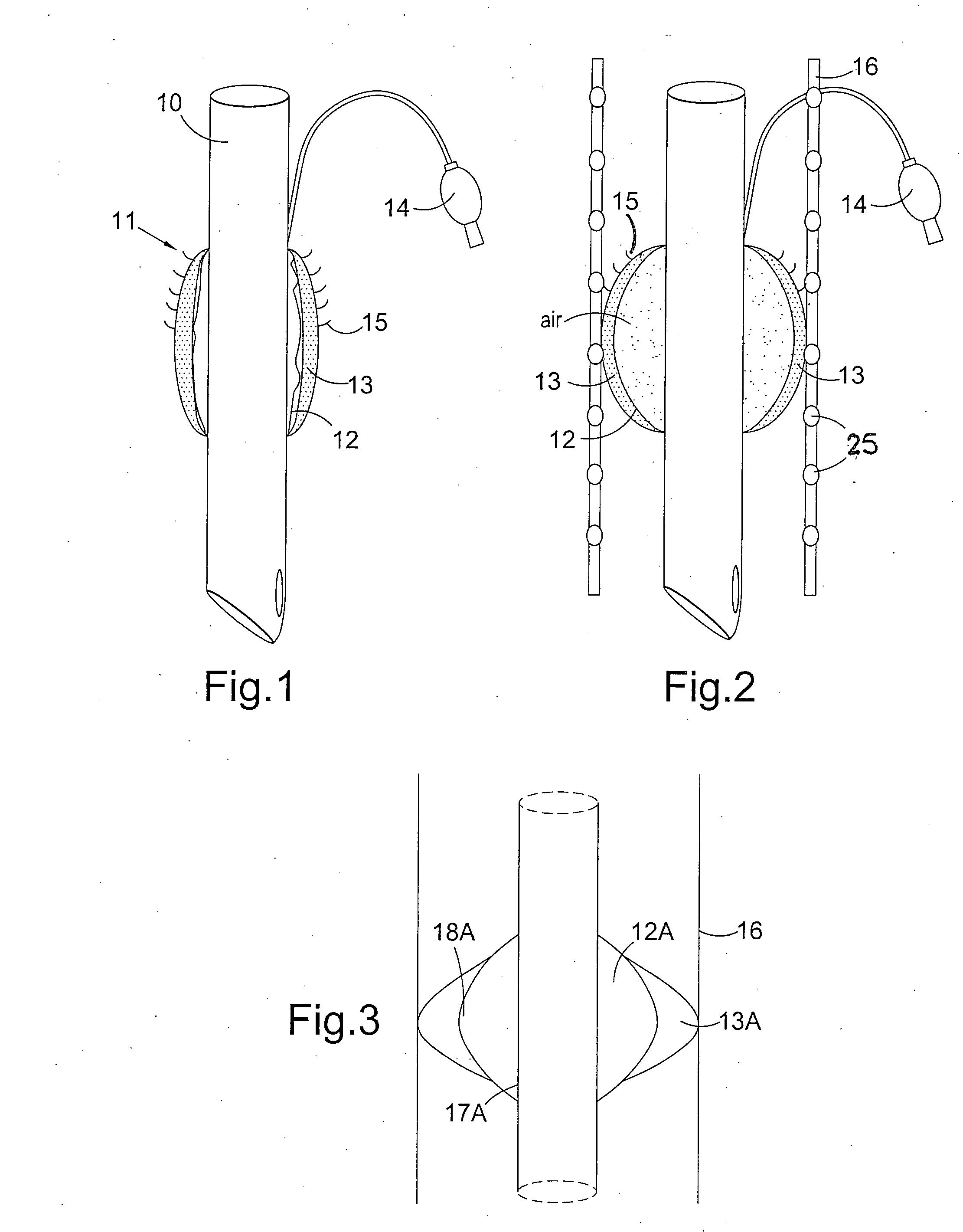
InactiveUS20100288289A1Direct contact guaranteeNot to damageTracheal tubesTeeth fillingAnatomyAirway wall
An airway device for insertion into the trachea or bronchi of a human or animal, comprising an elongate flexible tube (10) having a distal end, a proximal end and a lumen therethrough, the device further comprising a cuff (11) located at or near the distal end of the flexible tube, wherein the cuff comprises an inner inflatable region (12) and an outer soft barrier region (13) adapted to prevent the walls of the airway coming into direct contact with the inner inflatable region when the cuff is in position and inflated.
Owner:NASIR MUHAMMED ASLAM
Method for treating an asthma attack
InactiveUS20050159736A9Increase the diameterIncrease the effective diameterElectrotherapyDiagnosticsAcute onsetAirway wall
A method for treating the lung during an acute episode of reversible chronic obstructive pulmonary disease such as an asthma attack. The method comprises transferring energy to an airway wall of an airway such that a diameter of the airway is increased. The energy may be transferred to the airway wall prior to, during or after an asthma attack. The energy may be transferred in an amount sufficient to temporarily or permanently increase the diameter of the airway. The method may be performed while the airway is open, closed or partially closed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method for treating an asthma attack
A method for treating the lung during an acute episode of reversible chronic obstructive pulmonary disease such as an asthma attack. The method comprises transferring energy to an airway wall of an airway such that a diameter of the airway is increased. The energy may be transferred to the airway wall prior to, during or after an asthma attack. The energy may be transferred in an amount sufficient to temporarily or permanently increase the diameter of the airway. The method may be performed while the airway is open, closed or partially closed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods of evaluating individuals having reversible obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS7992572B2Reduce capacityReduce resistanceElectrotherapyMedical devicesObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesAirway wall
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods of regenerating tissue in airways
InactiveUS20070062545A1Reduce capacityReduce resistanceDiagnosticsInternal electrodesAirway wallAnesthesia
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com