Patents
Literature
62results about How to "Function is lost" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Novel synthetic triterpenoids and methods of use in the treatment and prevention of multiple scleroris
InactiveUS20090060873A1Improving glomerular filtration rateImproving creatinine clearanceBiocideSalicyclic acid active ingredientsDiseaseBipolar mood disorder
The present invention overcomes limitations of the prior art by providing new compounds and methods for the treatment of conditions, such as neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., multiple sclerosis), psychiatric disorders (e.g., psychosis, bipolar disorder, depression, neuropathic pain), conditions involving CNS-mediated chronic pain, spinal cord injuries, and other diseases or injuries.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE +1
Antioxidant inflammation modulators: oleanolic acid derivatives with saturation in the C-ring
ActiveUS7915402B2Suppresses demyelinationSuppresses transectionNervous disorderAntipyreticPerylene derivativesPharmaceutical Substances
This invention provides, but is not limited to, novel oleanolic acid derivatives having the formula:wherein the variables are defined herein. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions, kits and articles of manufacture comprising such compounds, methods and intermediates useful for making the compounds, and methods of using the compounds and compositions.
Owner:REATA PHARMA INC
Antioxidant inflammation modulators: C-17 homologated oleanolic acid derivatives
ActiveUS7943778B2Suppresses demyelinationSuppresses transectionAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderAntioxidantMedicinal chemistry
This invention provides, but is not limited to, novel oleanolic acid derivatives having the formula:wherein the variables are defined herein. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions, kits and articles of manufacture comprising such compounds, methods and intermediates useful for making the compounds, and methods of using the compounds and compositions.
Owner:REATA PHARMA INC
Antioxidant inflammation modulators: novel derivatives of oleanolic acid
ActiveUS20100048911A1Suppresses demyelinationSuppresses transectionBiocideNervous disorderAntioxidantCancer
Disclosed herein are novel oleanolic acid derivatives. Methods of preparing these compounds are also disclosed. The oleanolic acid derivatives of this invention may be used for the treatment and prevention of many diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, inflammation, and pathologies involving oxidative stress.
Owner:REATA PHARM INC
Antioxidant inflammation modulators: oleanolic acid derivatives with amino and other modifications at C-17
ActiveUS8124799B2Suppresses demyelinationSuppresses transectionSenses disorderNervous disorderAntioxidantInflammation
This invention provides, but is not limited to, novel oleanolic acid derivatives having the formula:wherein the variables are defined herein. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions, kits and articles of manufacture comprising such compounds, methods and intermediates useful for making the compounds, and methods of using the compounds and compositions.
Owner:REATA PHARM HLDG LLC
Antioxidant inflammation modulators: oleanolic acid derivatives with amino and other modifications at c-17
ActiveUS20100048892A1Improving glomerular filtration rateImproving creatinine clearanceSenses disorderNervous disorderAntioxidantInflammation
This invention provides, but is not limited to, novel oleanolic acid derivatives having the formula:wherein the variables are defined herein. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions, kits and articles of manufacture comprising such compounds, methods and intermediates useful for making the compounds, and methods of using the compounds and compositions.
Owner:REATA PHARM HLDG LLC
Compounds including an Anti-inflammatory pharmacore and methods of use
ActiveUS20100048887A1Suppresses demyelinationSuppresses transectionSenses disorderNervous disorderDrugAnti-inflammatory
Owner:REATA PHARMA INC
Antioxidant inflammation modulators: oleanolic acid derivatives with saturation in the c-ring
ActiveUS20100056777A1Suppresses demyelinationSuppresses transectionNervous disorderAntipyreticAntioxidantMedicinal chemistry
This invention provides, but is not limited to, novel oleanolic acid derivatives having the formula:wherein the variables are defined herein. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions, kits and articles of manufacture comprising such compounds, methods and intermediates useful for making the compounds, and methods of using the compounds and compositions.
Owner:REATA PHARMA INC
Antioxidant inflammation modulators: c-17 homologated oleanolic acid derivatives
ActiveUS20100041904A1Suppresses demyelinationSuppresses transectionAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderAntioxidantMedicinal chemistry
This invention provides, but is not limited to, novel oleanolic acid derivatives having the formula:wherein the variables are defined herein. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions, kits and articles of manufacture comprising such compounds, methods and intermediates useful for making the compounds, and methods of using the compounds and compositions.
Owner:REATA PHARMA INC
Antioxidant inflammation modulators: novel derivatives of oleanolic acid
InactiveUS20120238767A1Suppresses demyelinationSuppresses transectionNervous disorderSteroidsDiseaseOxidative stress
Disclosed herein are novel oleanolic acid derivatives. Methods of preparing these compounds are also disclosed. The oleanolic acid derivatives of this invention may be used for the treatment and prevention of many diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, inflammation, and pathologies involving oxidative stress.
Owner:REATA PHARMA INC
Antioxidant inflammation modulators: novel derivatives of oleanolic acid
ActiveUS8071632B2Suppresses demyelinationSuppresses transectionBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseMedicine
Owner:REATA PHARMA INC
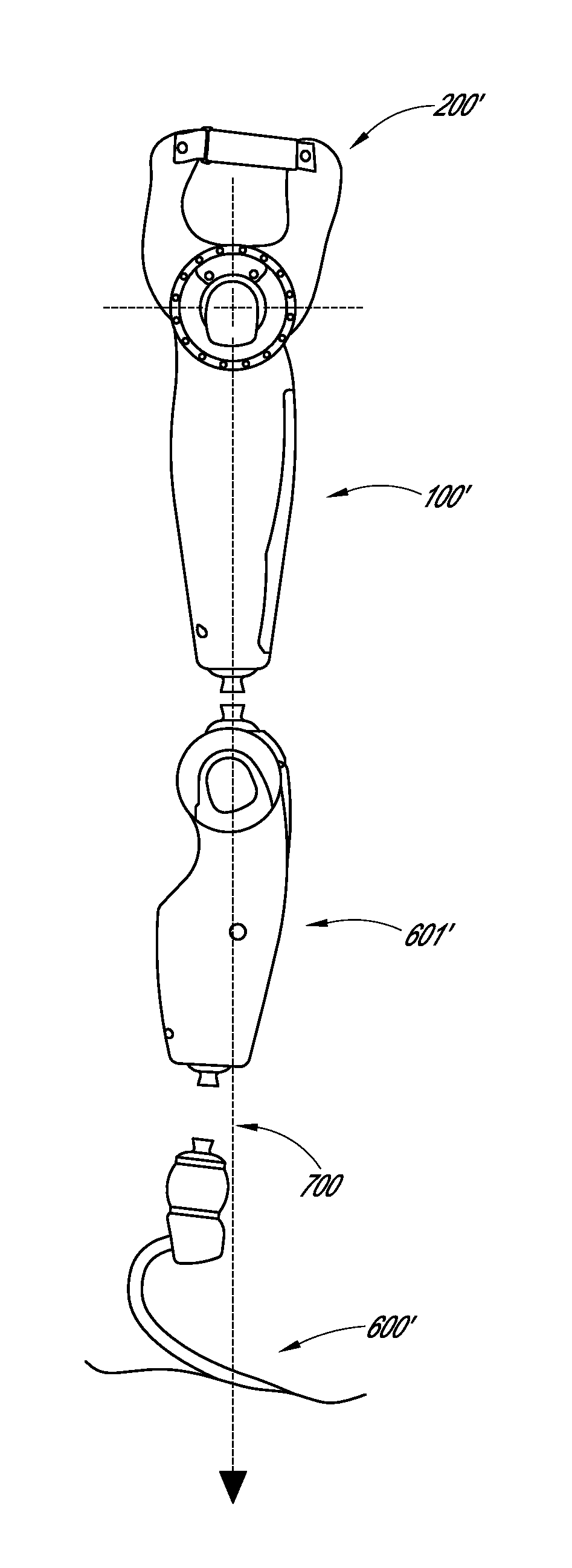
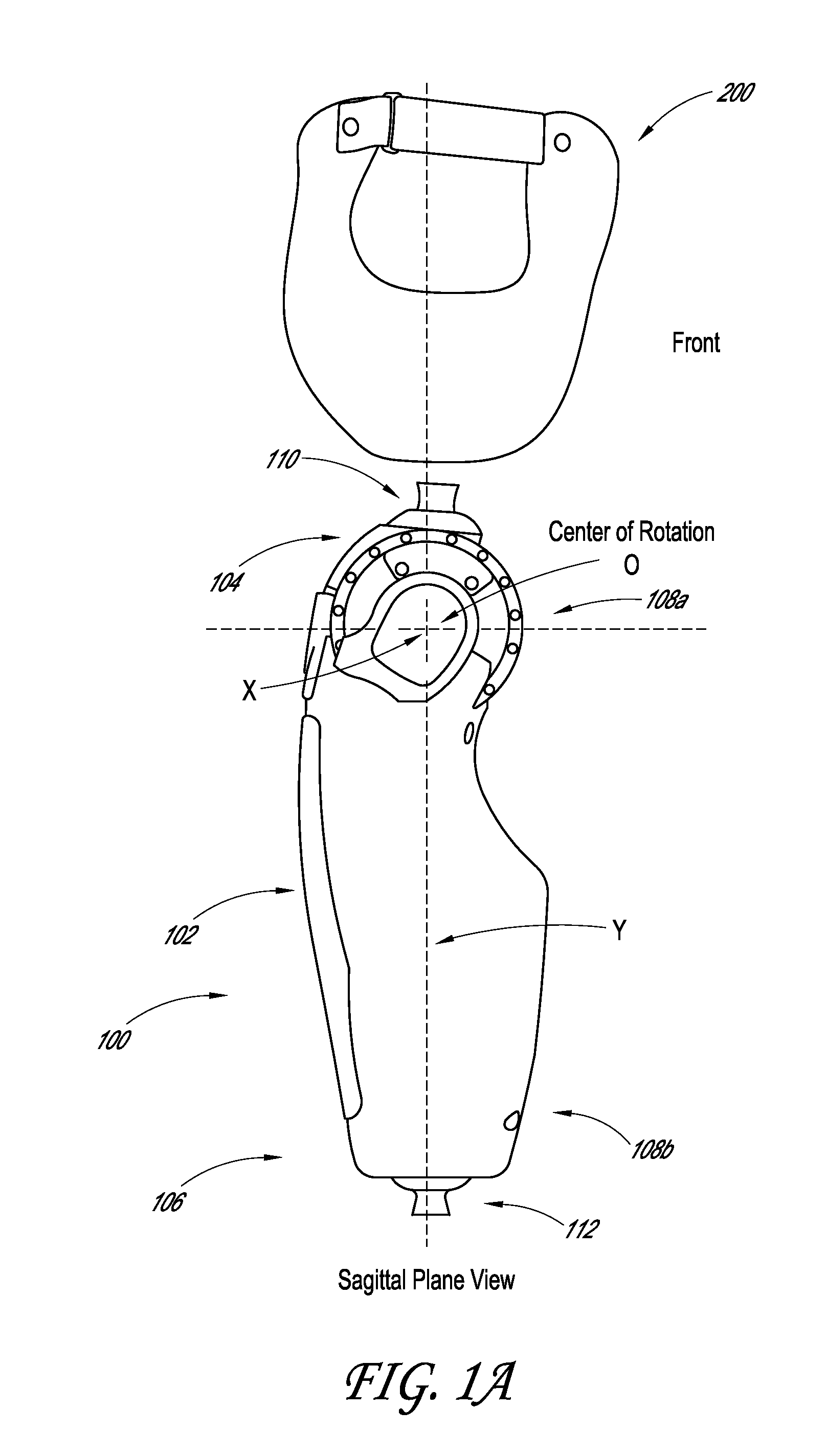
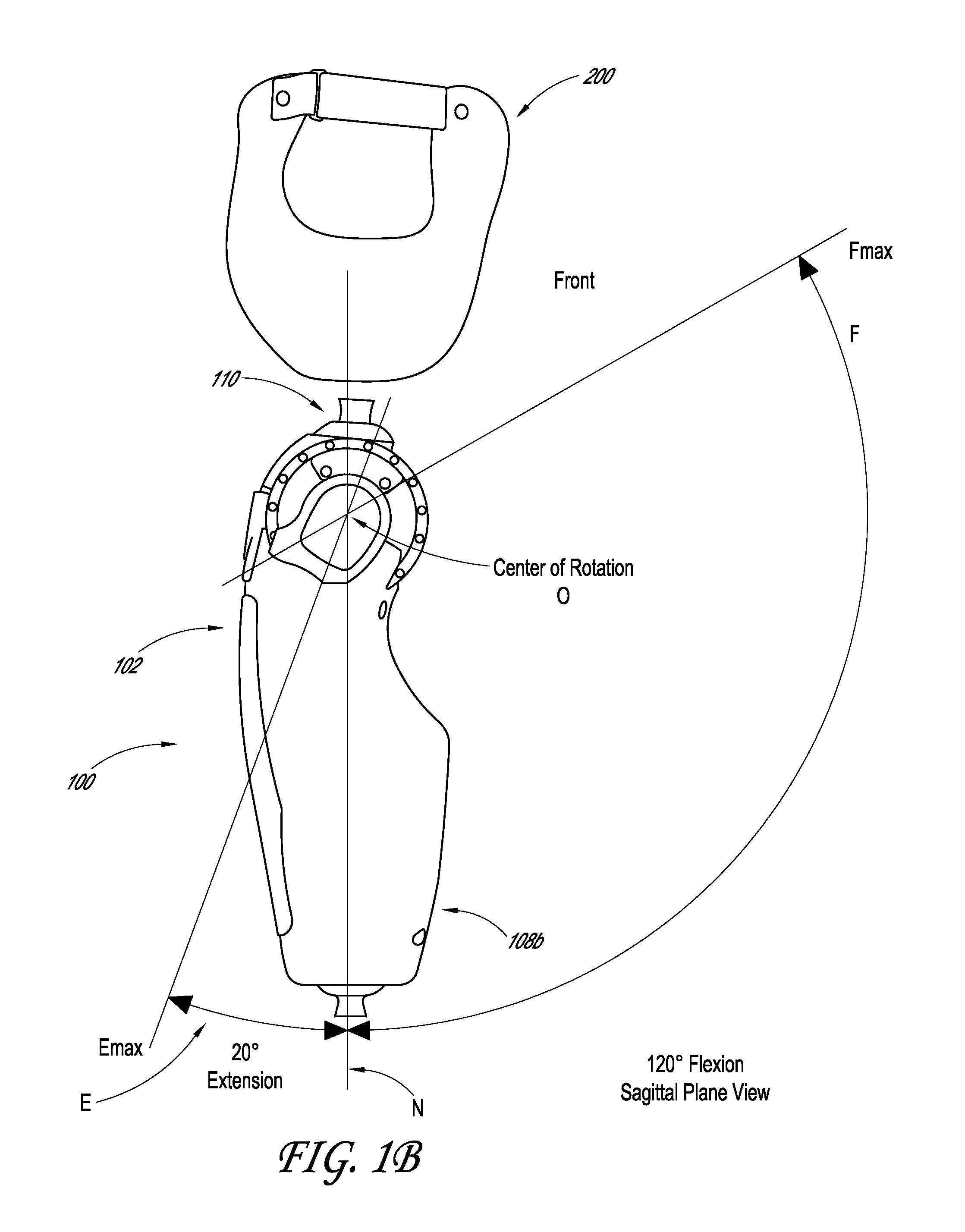
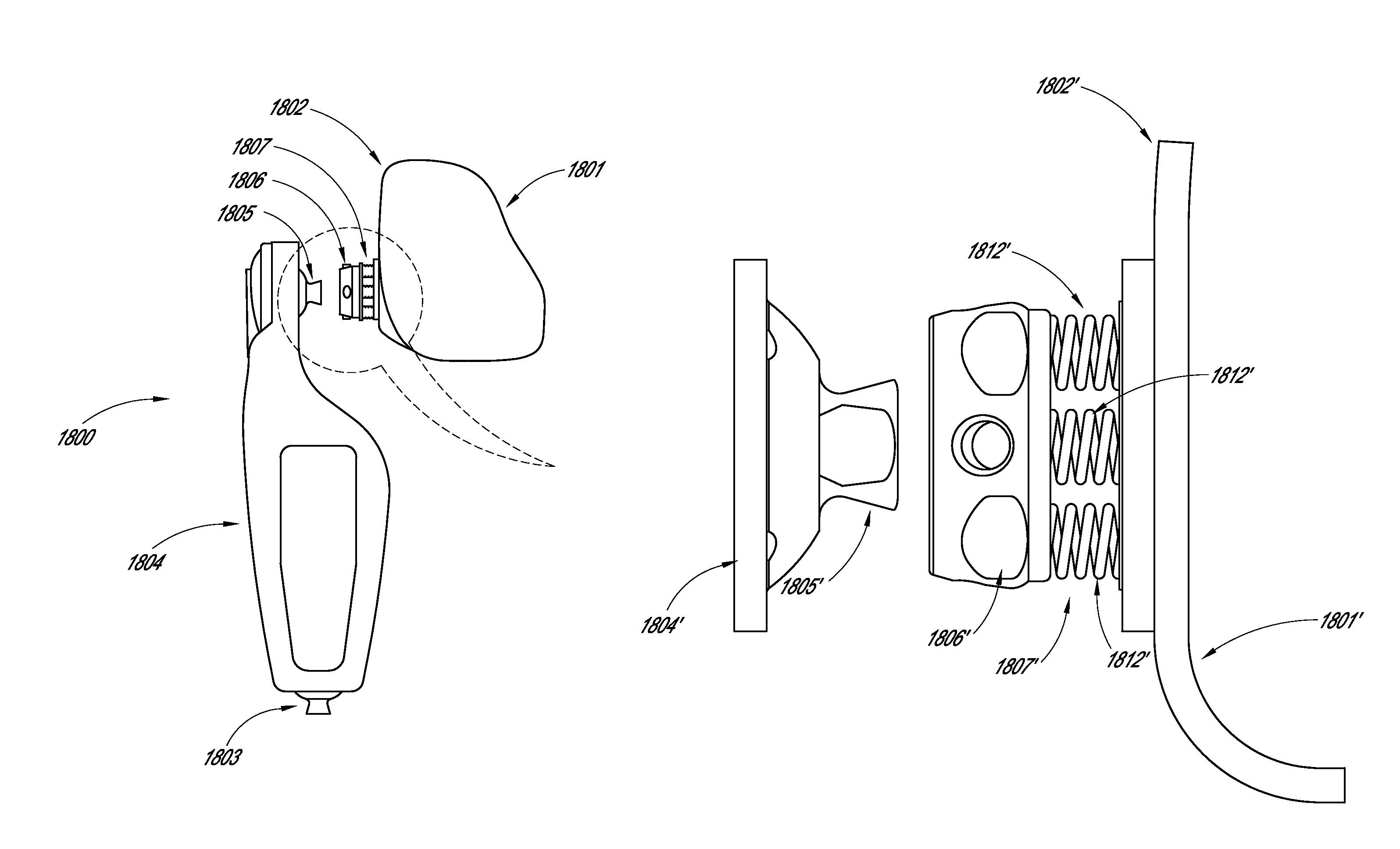
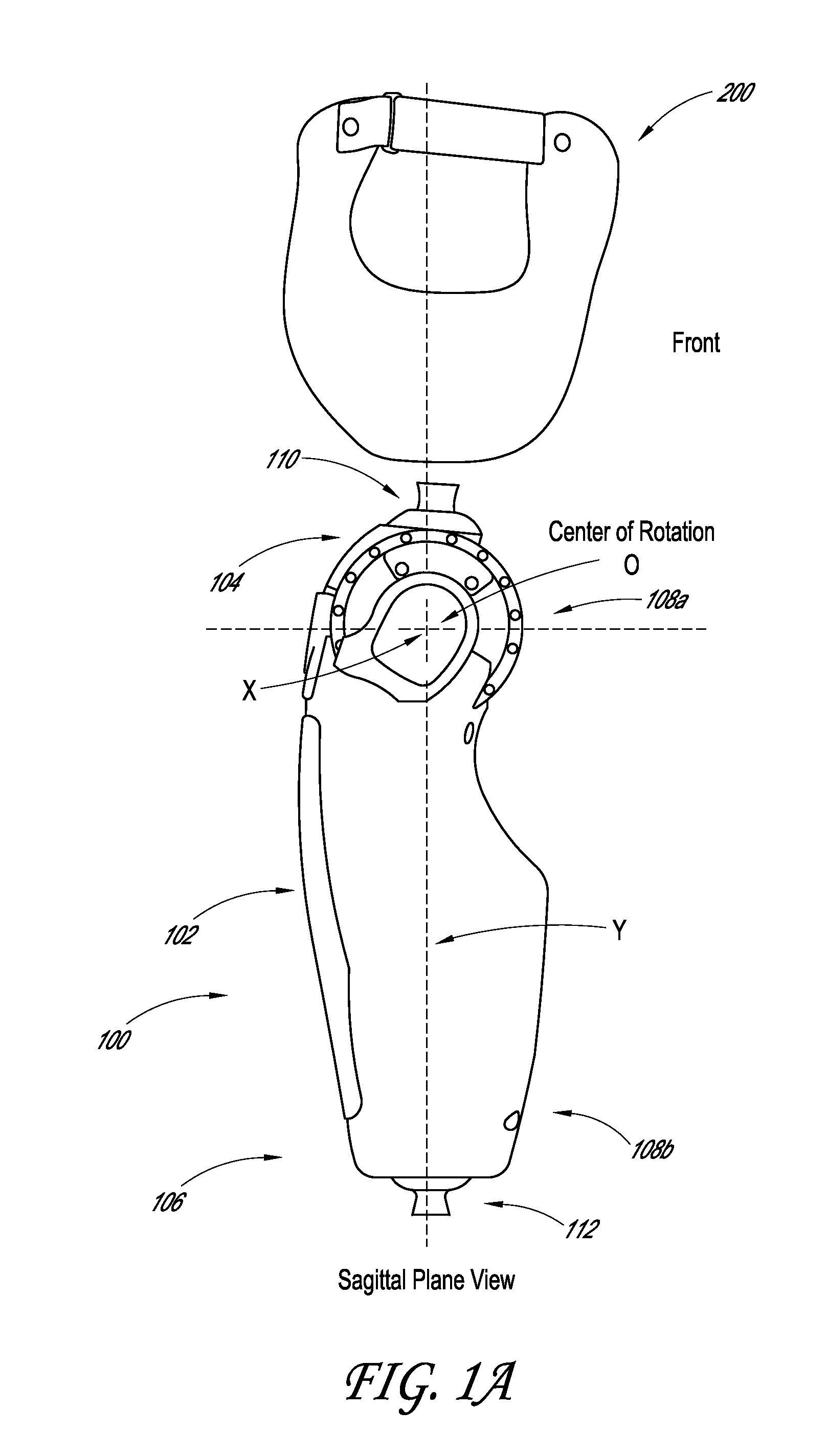
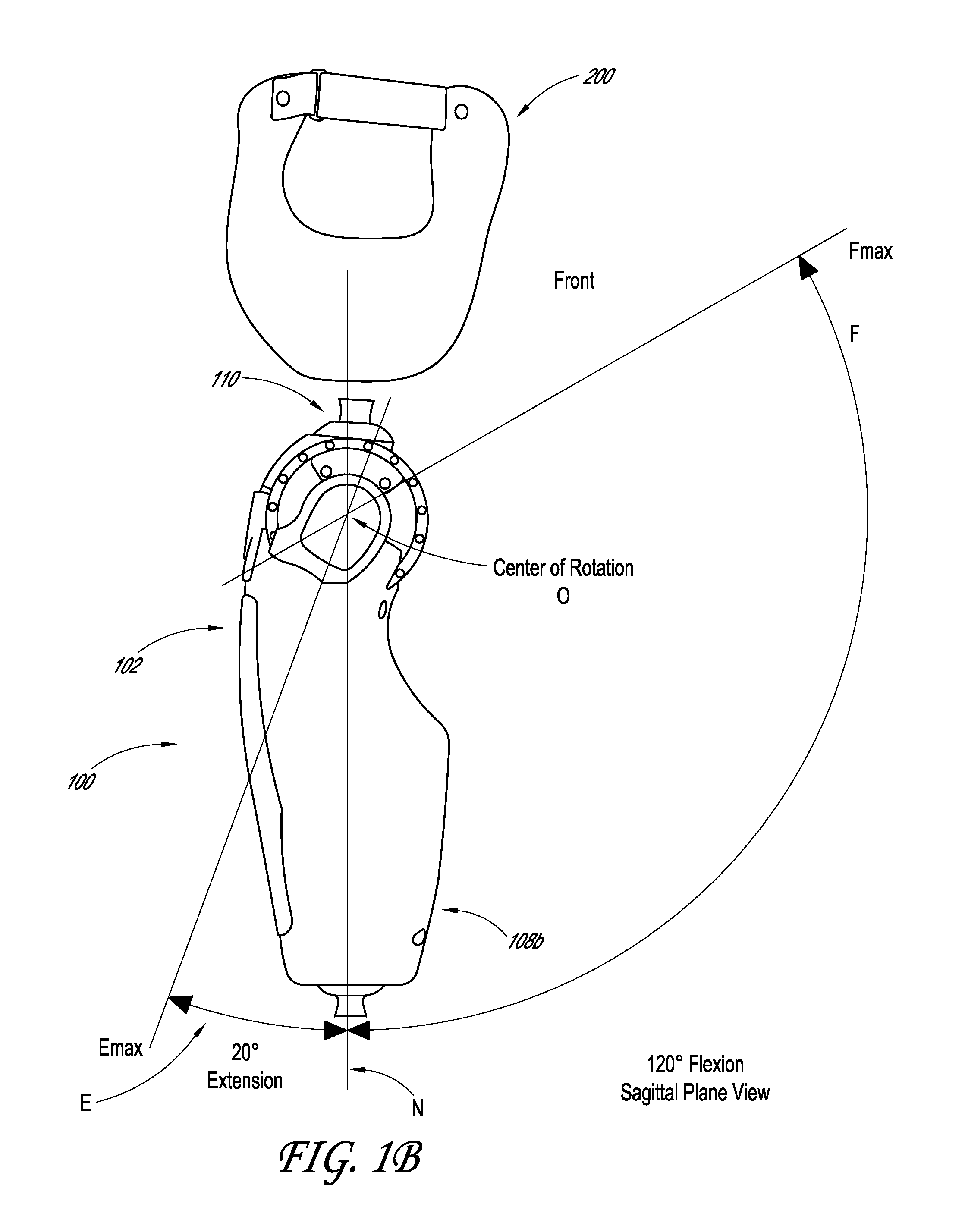
Powered prosthetic hip joint
ActiveUS20130261766A1Increase stiffnessDecrease in stiffnessArtificial legsDistal portionBiomedical engineering
A powered prosthetic thigh can have a proximal portion configured to couple to a prosthetic hip socket and can have a distal portion attached to the proximal portion. The distal portion can have a distal connector configured to couple to a prosthetic knee. The powered prosthetic thigh can also have a computer controlled actuator configured to rotate the prosthetic thigh relative to the prosthetic hip socket.
Owner:OSSUR HF
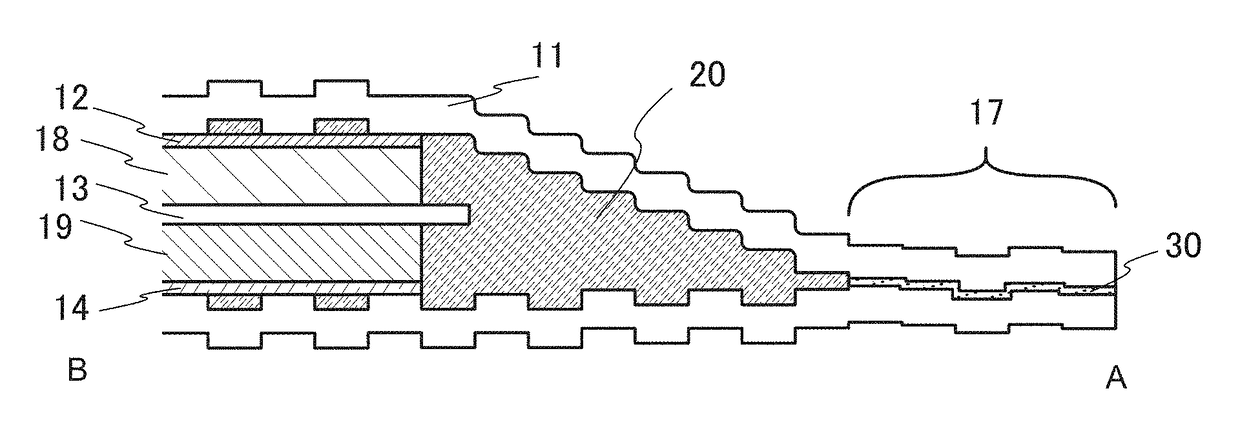
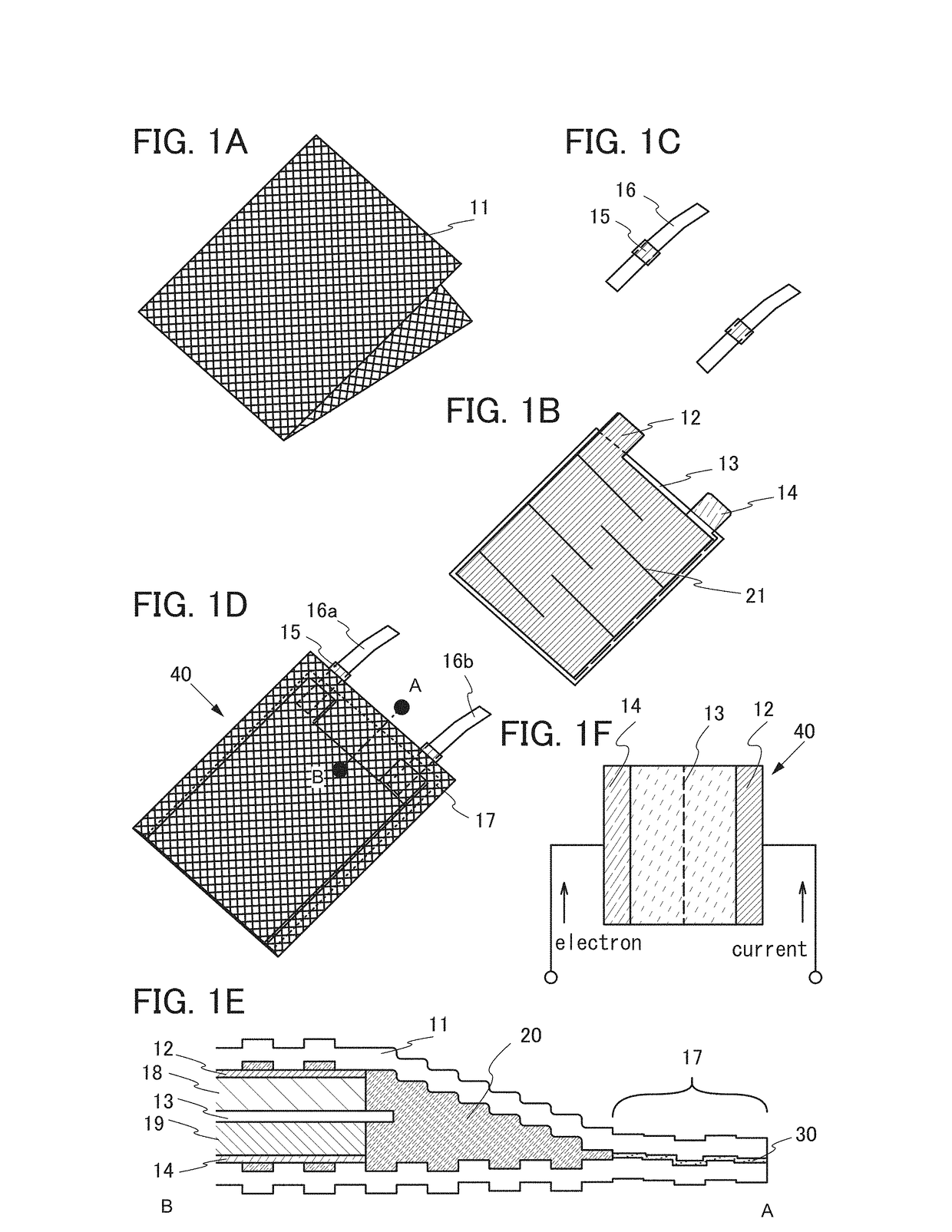
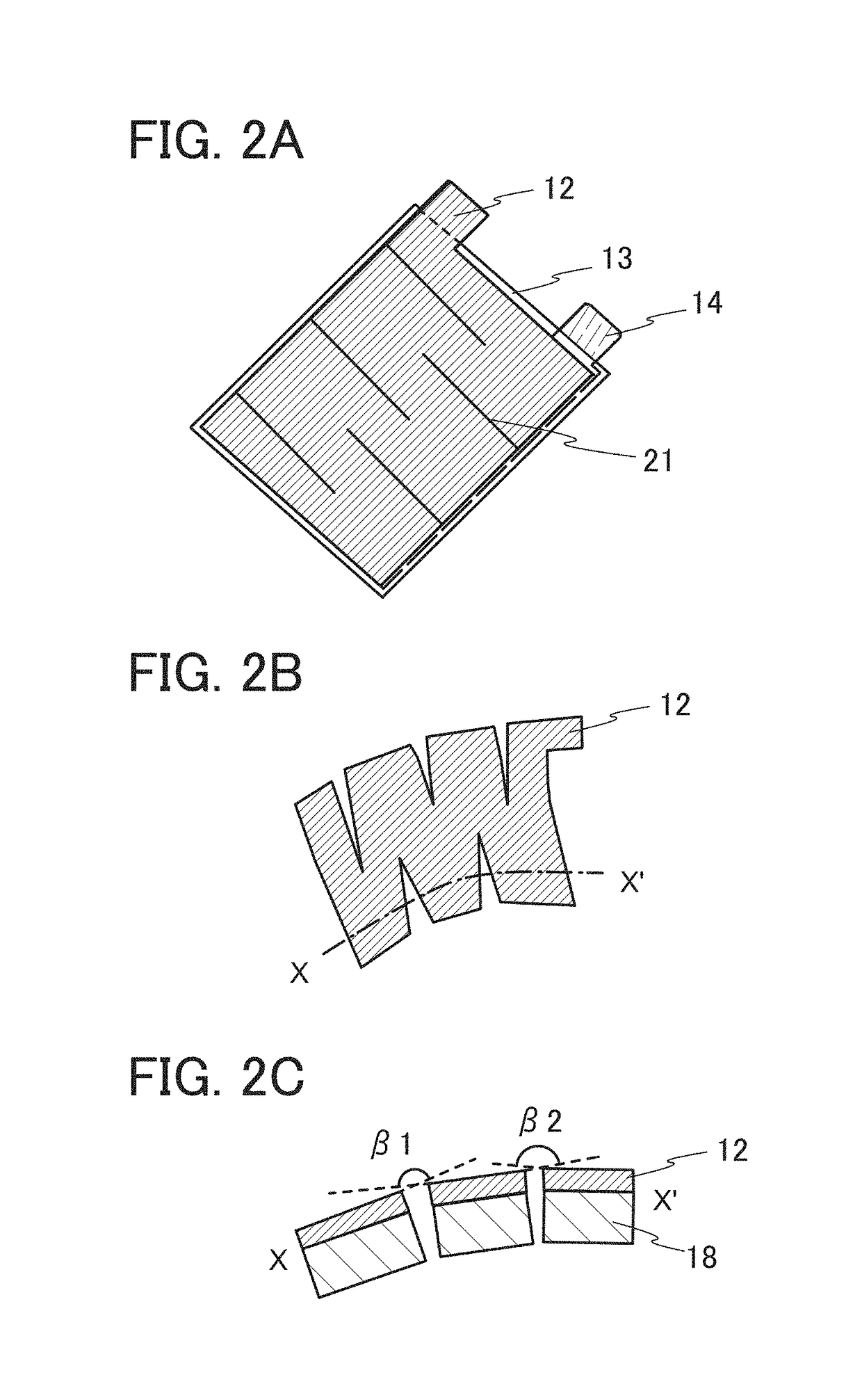
Current collector, secondary battery, electronic device, and manufacturing method thereof
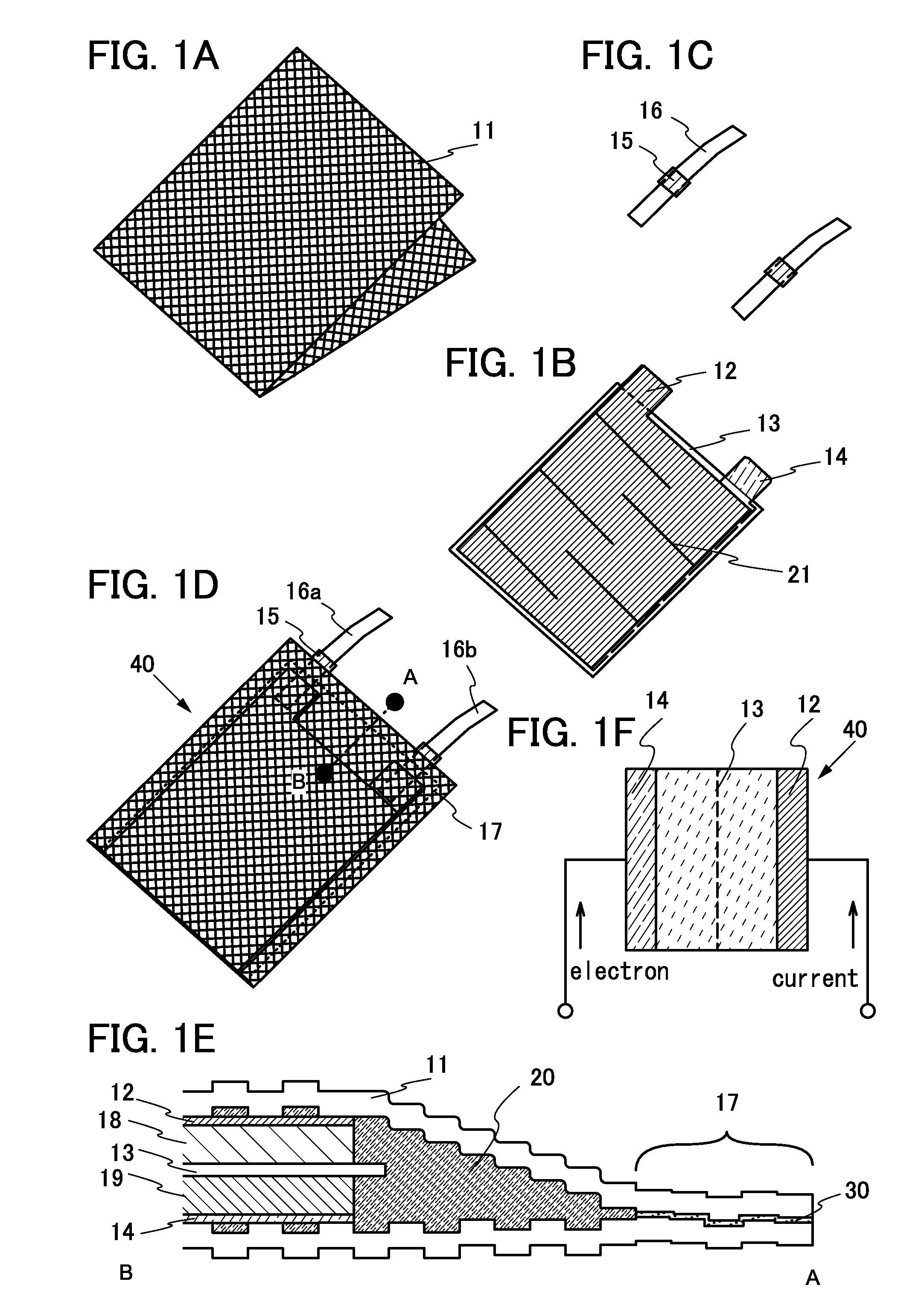
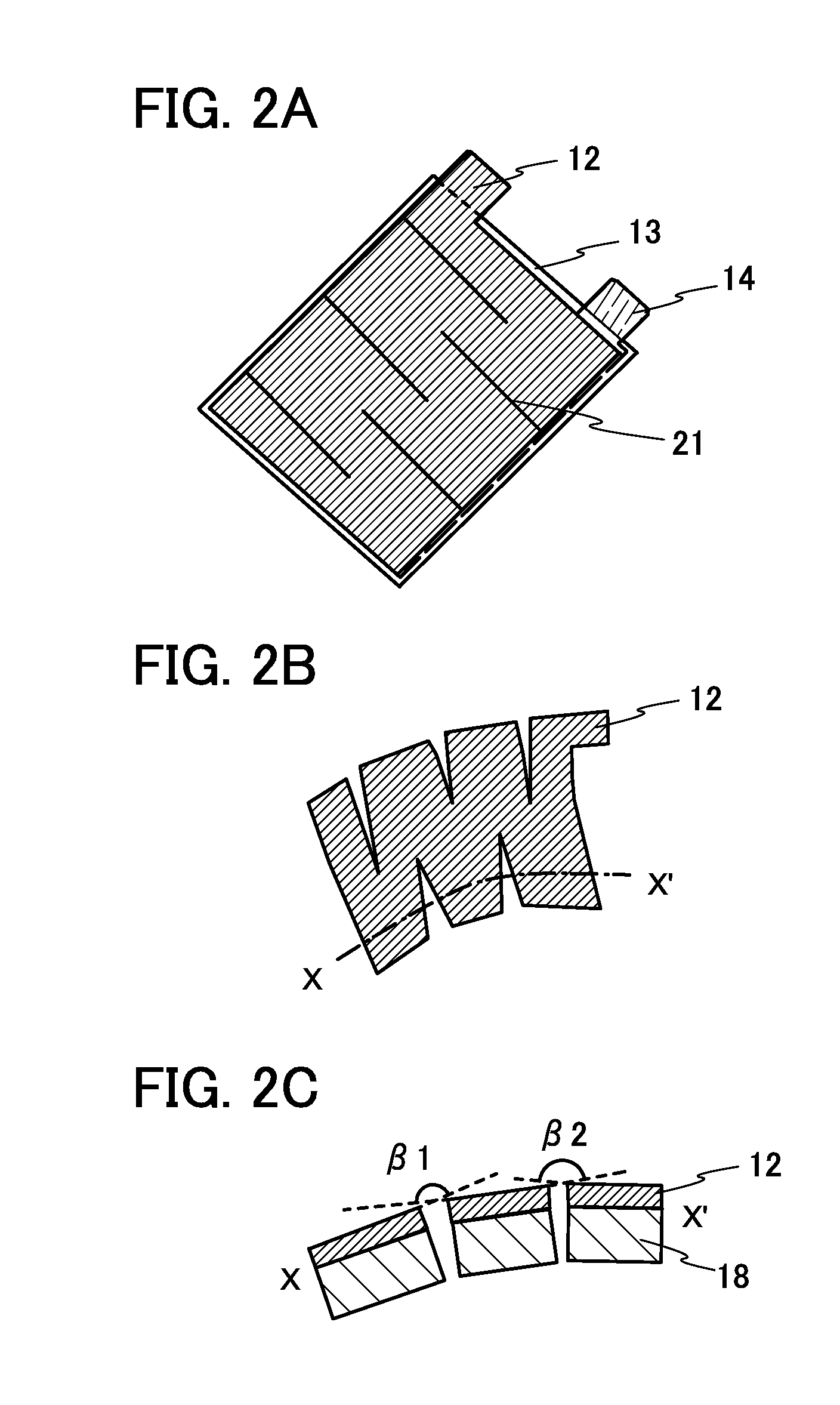
ActiveUS20150243962A1Suppress relative position shiftReduce tensionRadiation applicationsFinal product manufactureEngineeringElectron
An object is to provide a secondary battery suitable for a wearable device. Another object is to provide a novel power storage device. Part of an electrode, specifically a current collector and an active material layer, for a secondary battery is subjected to cutting processing to have a complex shape. This suppresses the positional shift of an end portion of an electrode far from a curvature center from an electrode close to the curvature center due to the larger degree of bending of the electrode far from the curvature center than that of the electrode close to the curvature center, or relieves tension to be applied to the electrode far from the curvature center.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Device and method to control volume of a ventricle
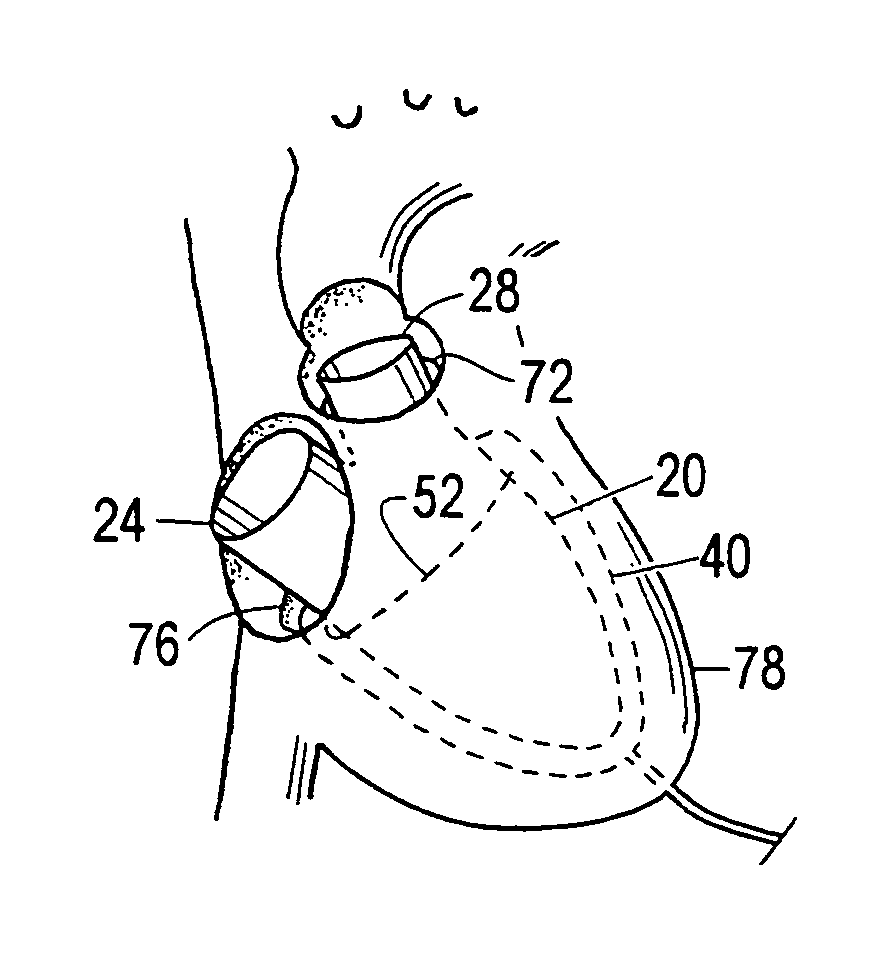
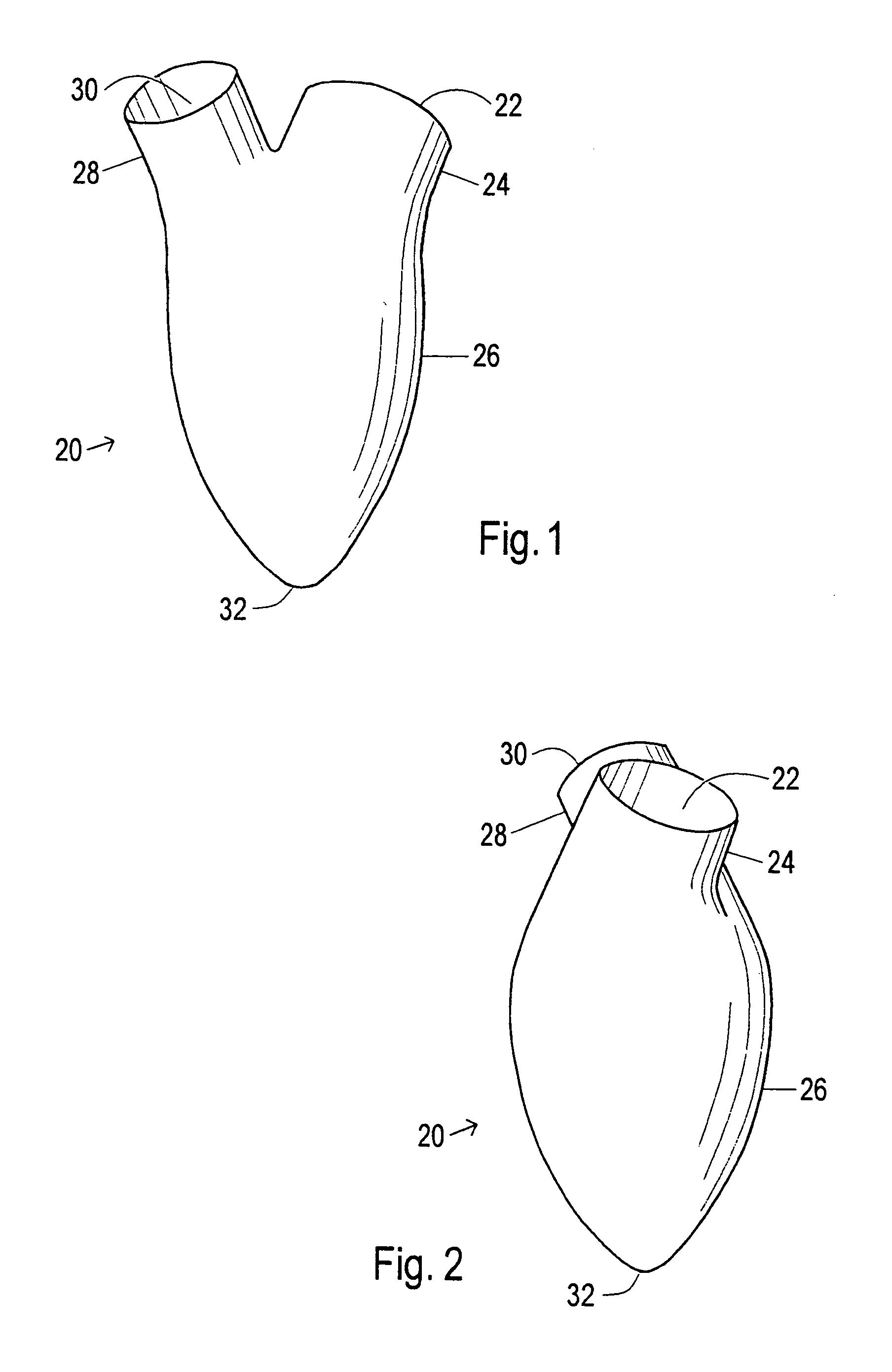
ActiveUS7530998B1Small sizePrevent further enlargement of a diseased heartHeart valvesHeart stimulatorsCardiac cycleReverse remodeling
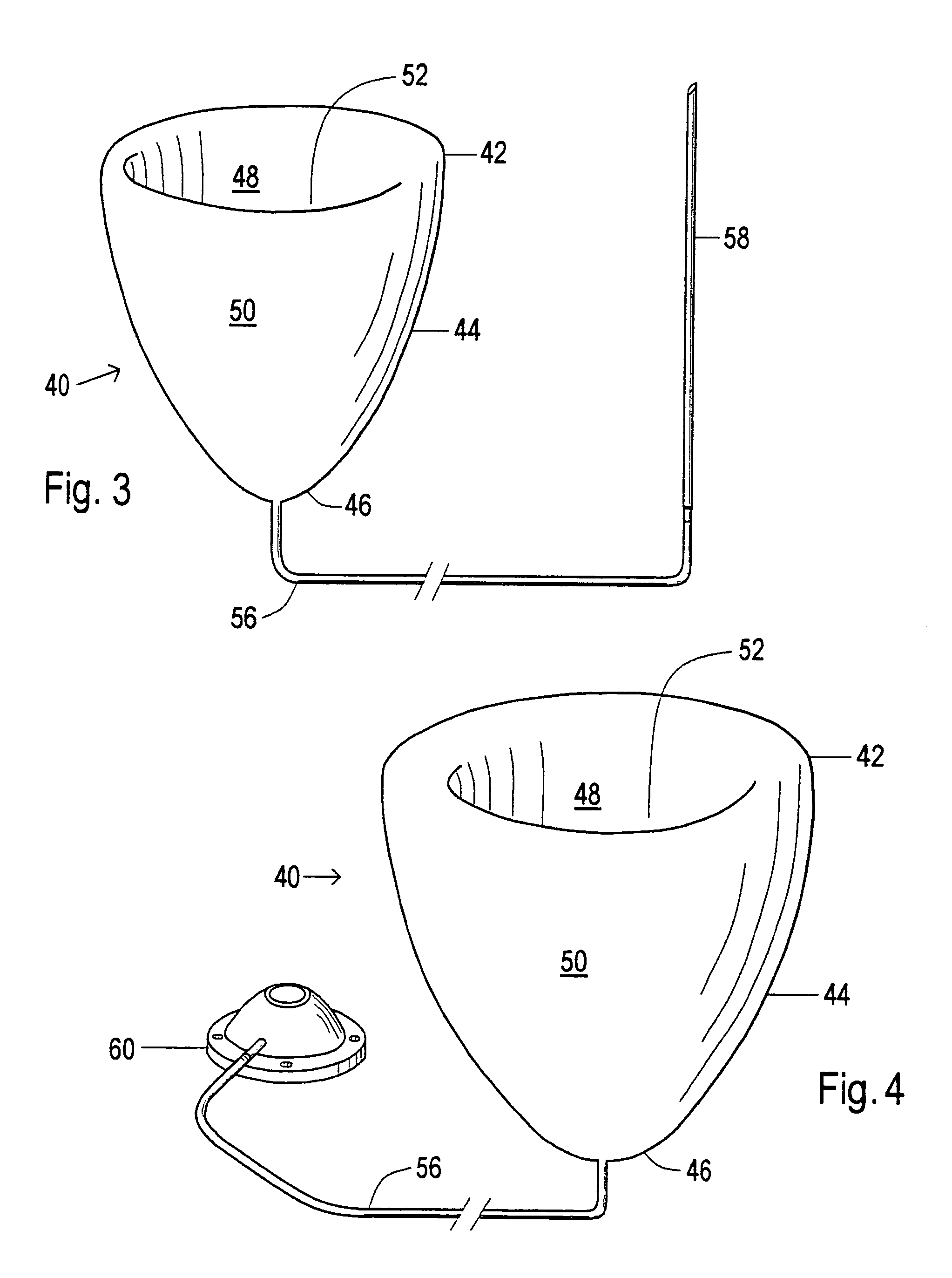
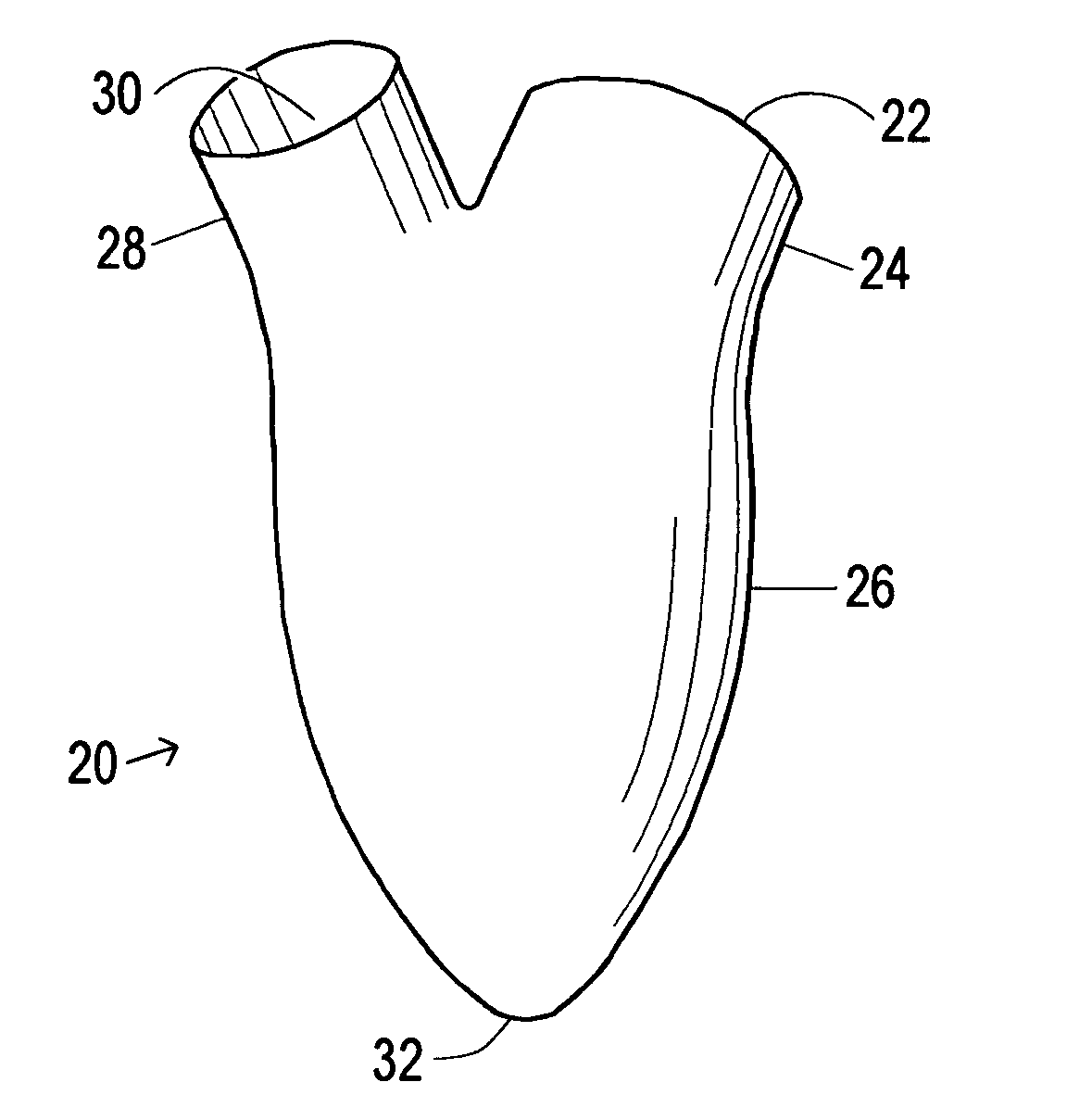
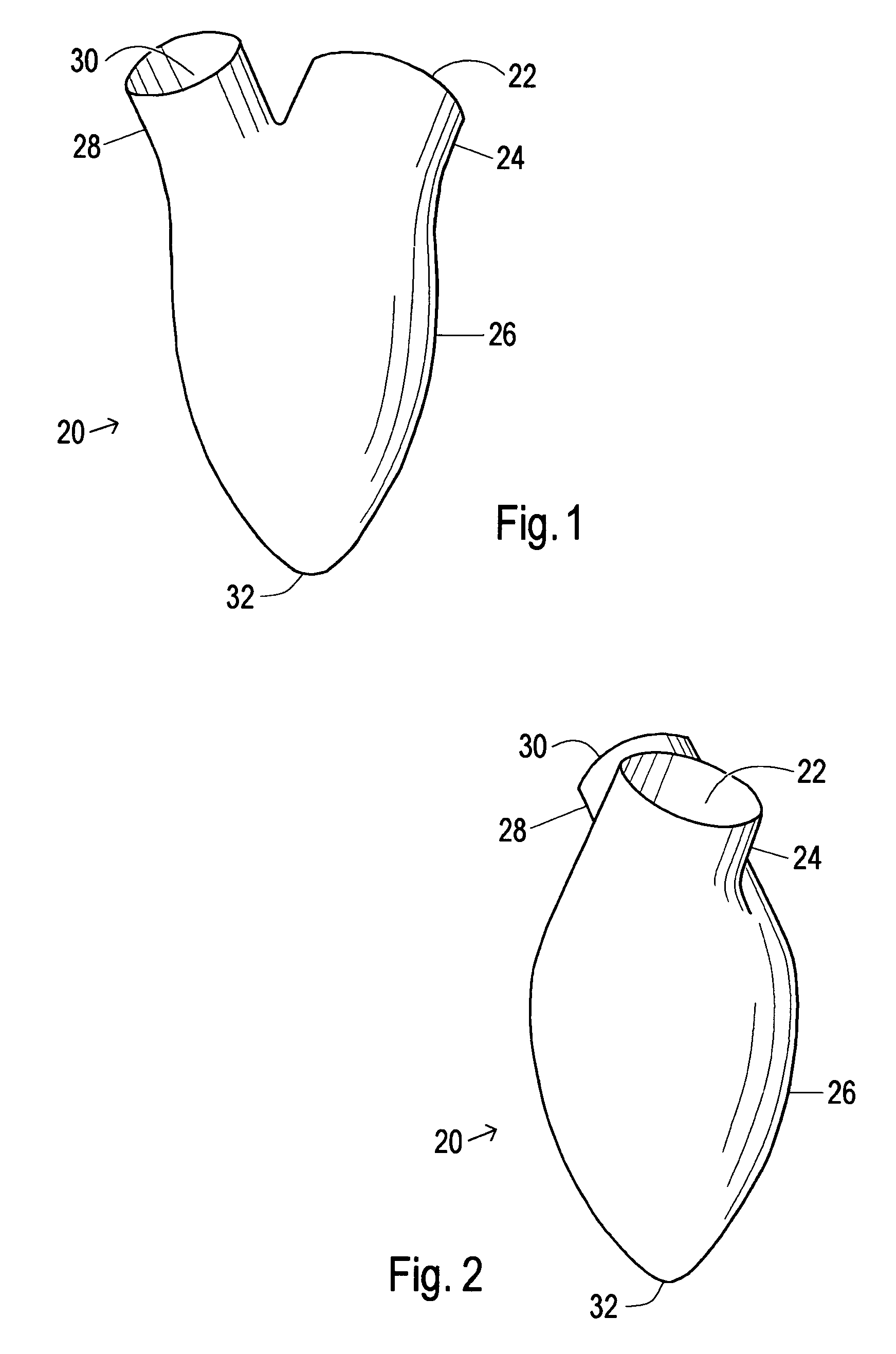
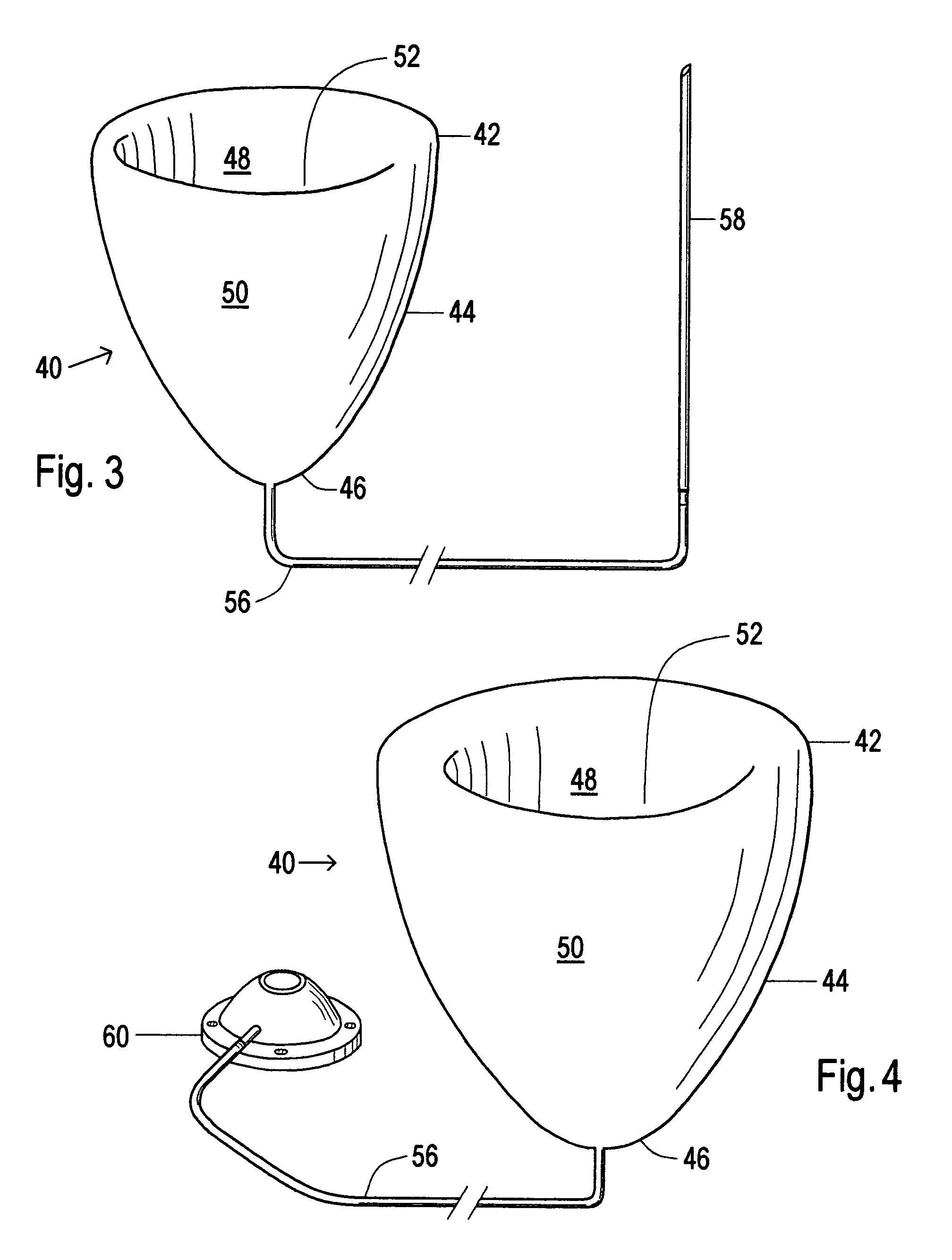
A device used to treat heart disease by decreasing the size of a diseased heart, or to prevent further enlargement of a diseased heart. The device works by limiting the volume of blood entering the heart during each cardiac cycle. The device partitions blood within the heart, and protects the heart from excessive volume and pressure of blood. The device is placed within the interior of the heart, particularly within a ventricular cavity. The device is a hollow sac, with two openings, which simulates the shape and size of the interior lining of a ventricle of a normal heart. It allows the ventricle to fill through one opening juxtaposed to the annulus of the inflow valve to a predetermined, normal volume, and limits filling of the heart beyond that volume. It then allows blood to be easily ejected through the second opening through the outflow valve. By limiting the amount of blood entering the ventricle, the ventricle is not subjected to the harmful effect of excessive volume and pressure of blood during diastole, the period of the cardiac cycle when the heart is at rest. This allows the heart to decrease in size, or to reverse remodel, and to recover lost function. In some applications, a second device may be simultaneously placed inside the heart to take up excessive space between the heart and the primary device.
Owner:STARKEY THOMAS DAVID
Device and method to limit filling of the heart
ActiveUS7341584B1Small sizeLimiting volume of bloodHeart valvesSurgical instrument detailsCardiac cycleReverse remodeling
A device used to treat heart disease by decreasing the size of a diseased heart, or to prevent further enlargement of a diseased heart. The device works by limiting the volume of blood entering the heart during each cardiac cycle. The device partitions blood within the heart, and protects the heart from excessive volume and pressure of blood. The device is placed within the interior of the heart, particularly within a ventricular cavity. The device is a hollow sac, with two openings, which simulates the shape and size of the interior lining of a ventricle of a normal heart. It allows the ventricle to fill through one opening juxtaposed to the annulus of the inflow valve to a predetermined, normal volume, and limits filling of the heart beyond that volume. It then allows blood to be easily ejected through the second opening through the outflow valve. By limiting the amount of blood entering the ventricle, the ventricle is not subjected to the harmful effect of excessive volume and pressure of blood during diastole, the period of the cardiac cycle when the heart is at rest. This allows the heart to decrease in size, or to reverse remodel, and to recover lost function. In some applications, a second device may be simultaneously placed inside the heart to take up excessive space between the heart and the primary device.
Owner:STARKEY THOMAS DAVID
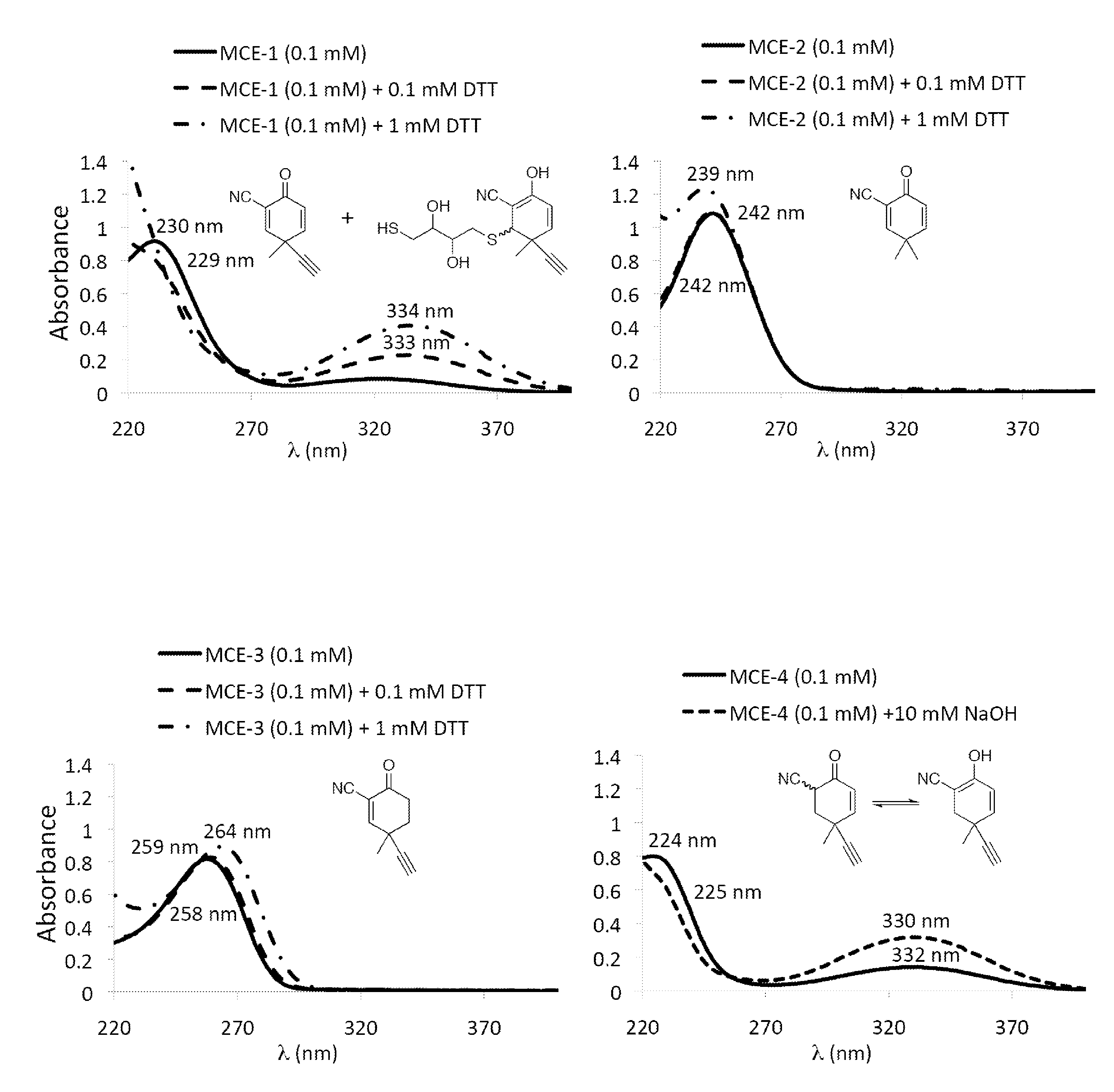
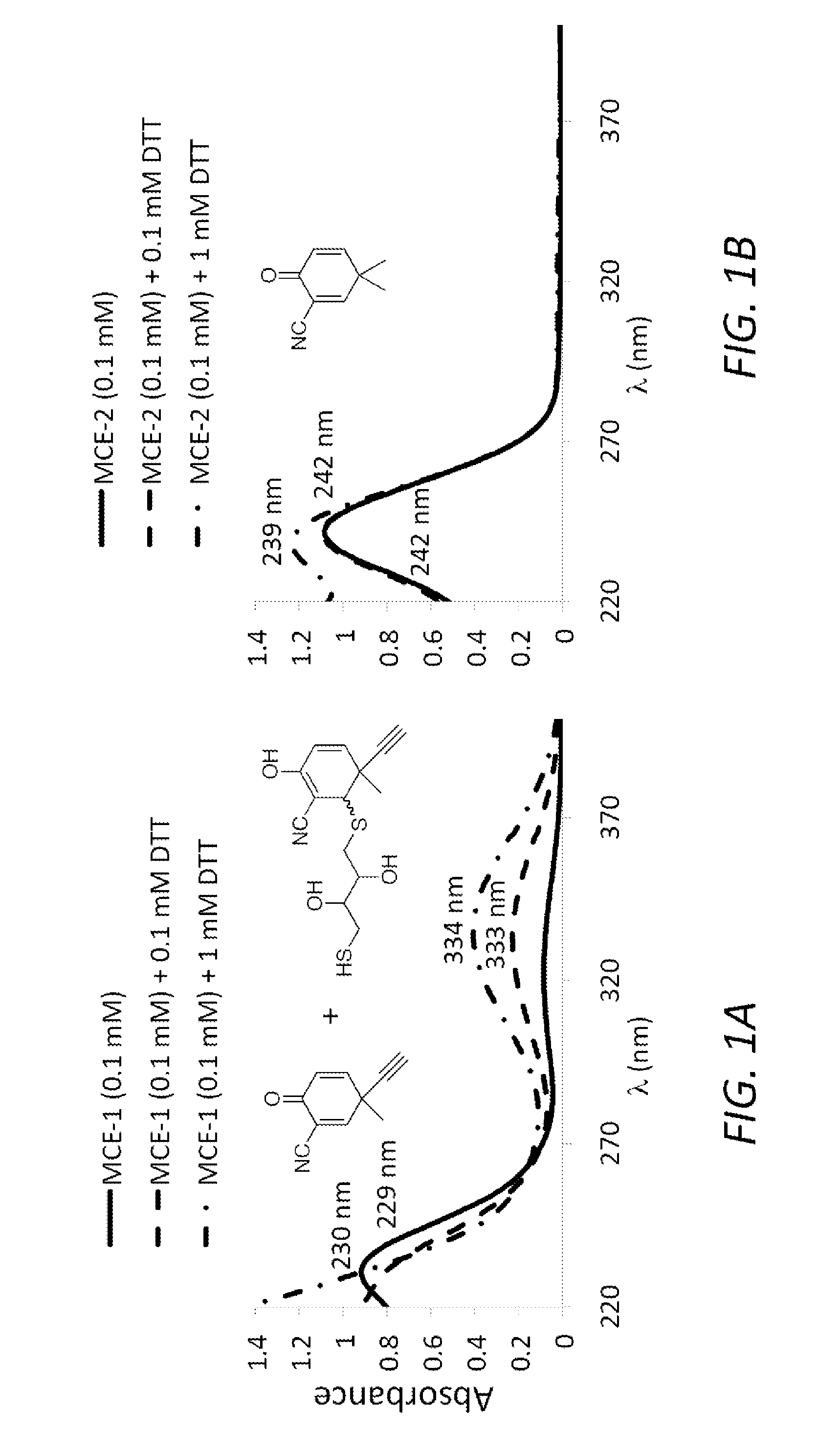
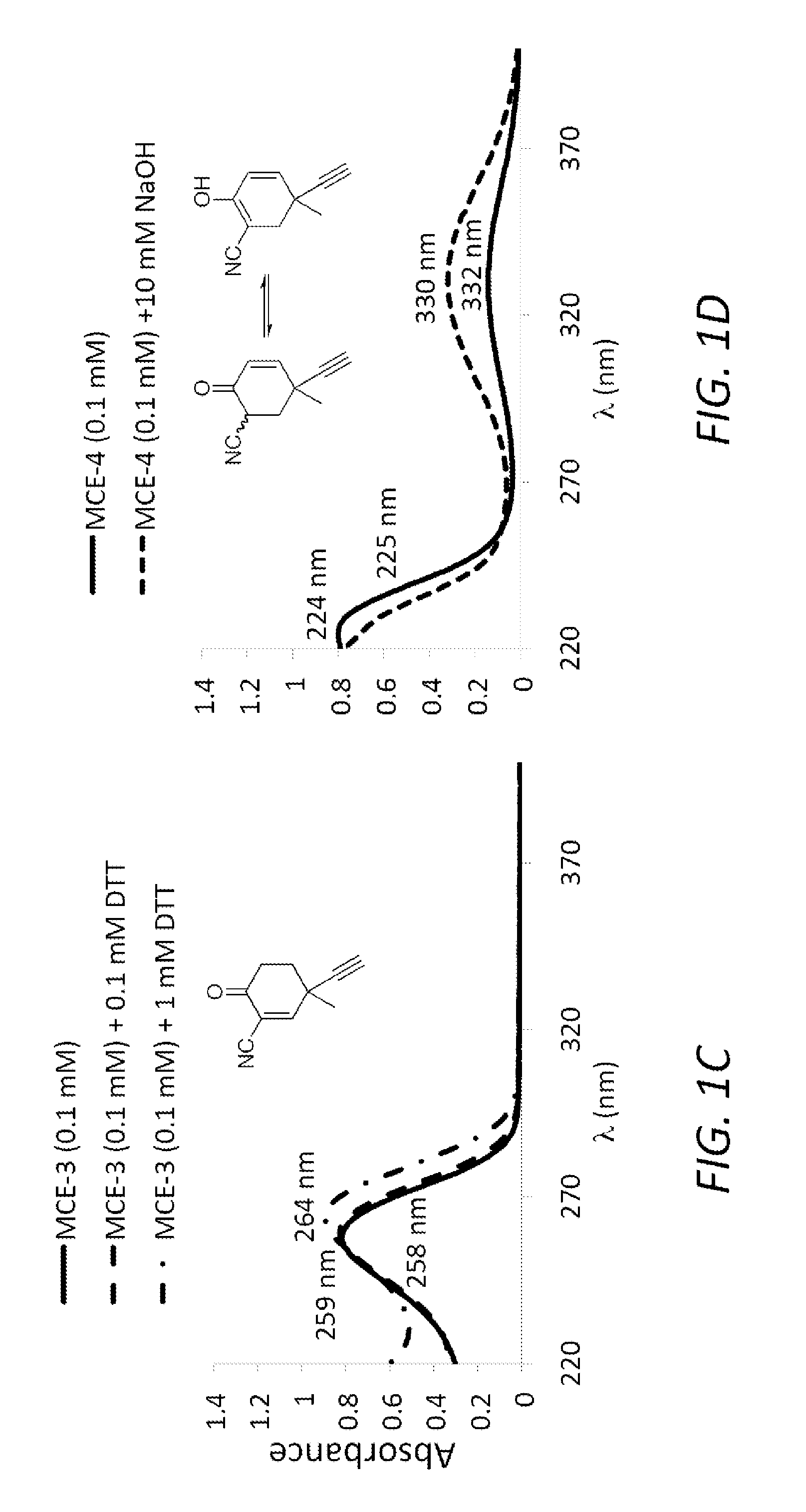
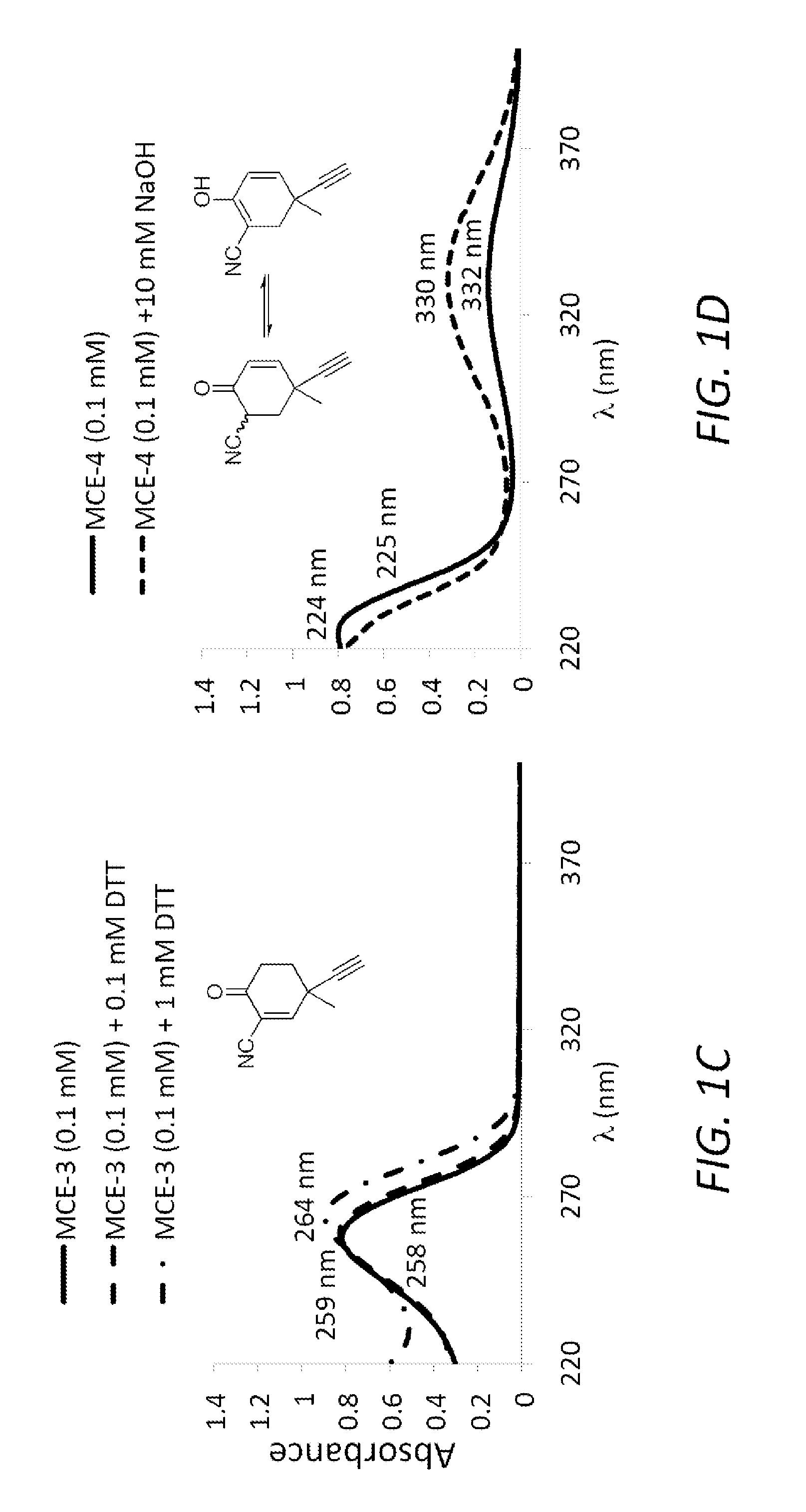
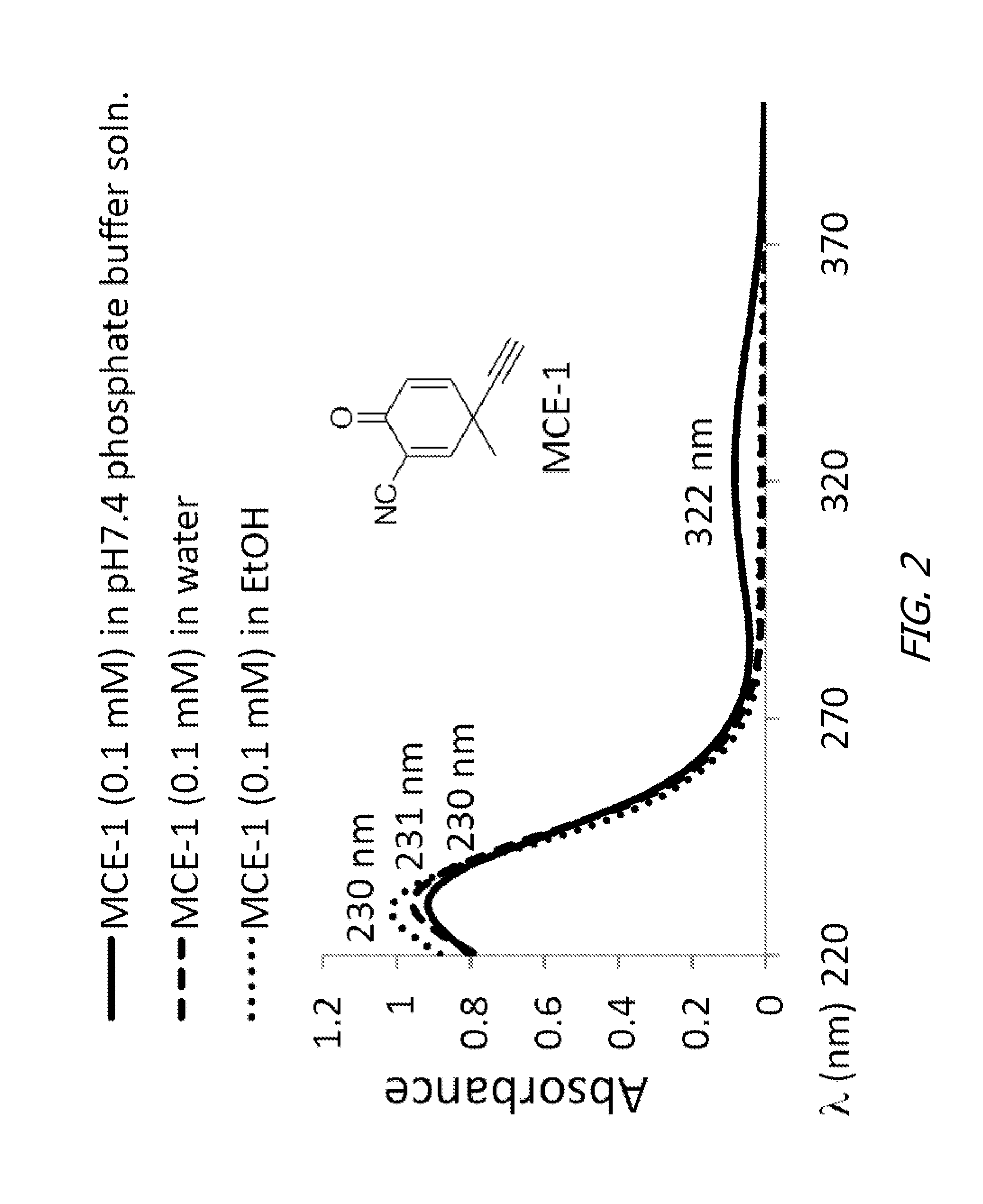
Monocyclic cyanoenones and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20110196007A1Improving glomerular filtration rateImproving creatinine clearanceBiocideSenses disorderMedicineNeuro-degenerative disease
The present invention features monocyclic cyanoenone compositions and methods for using the same in the treatment of diseases such as cancer, inflammatory diseases and neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
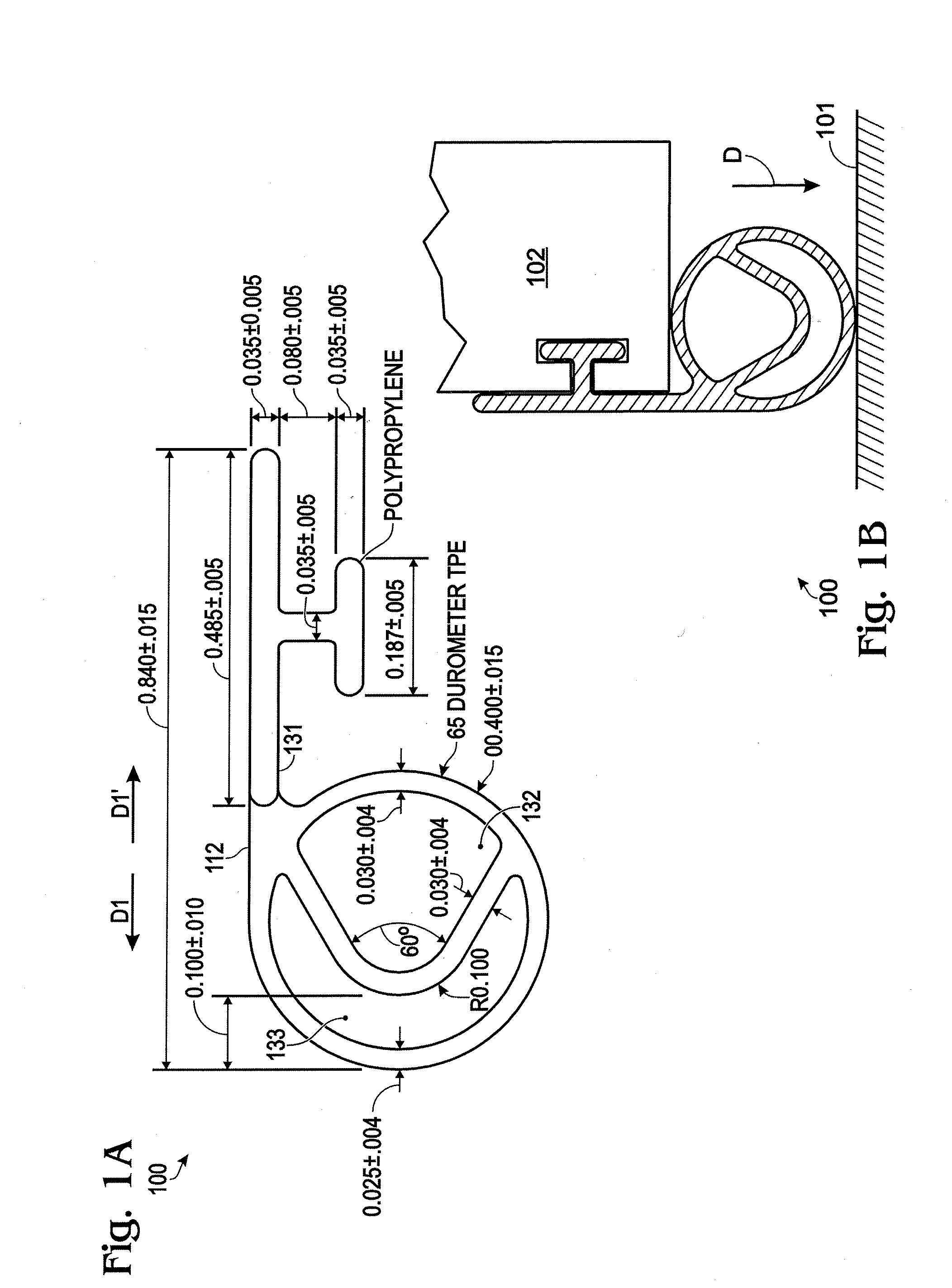
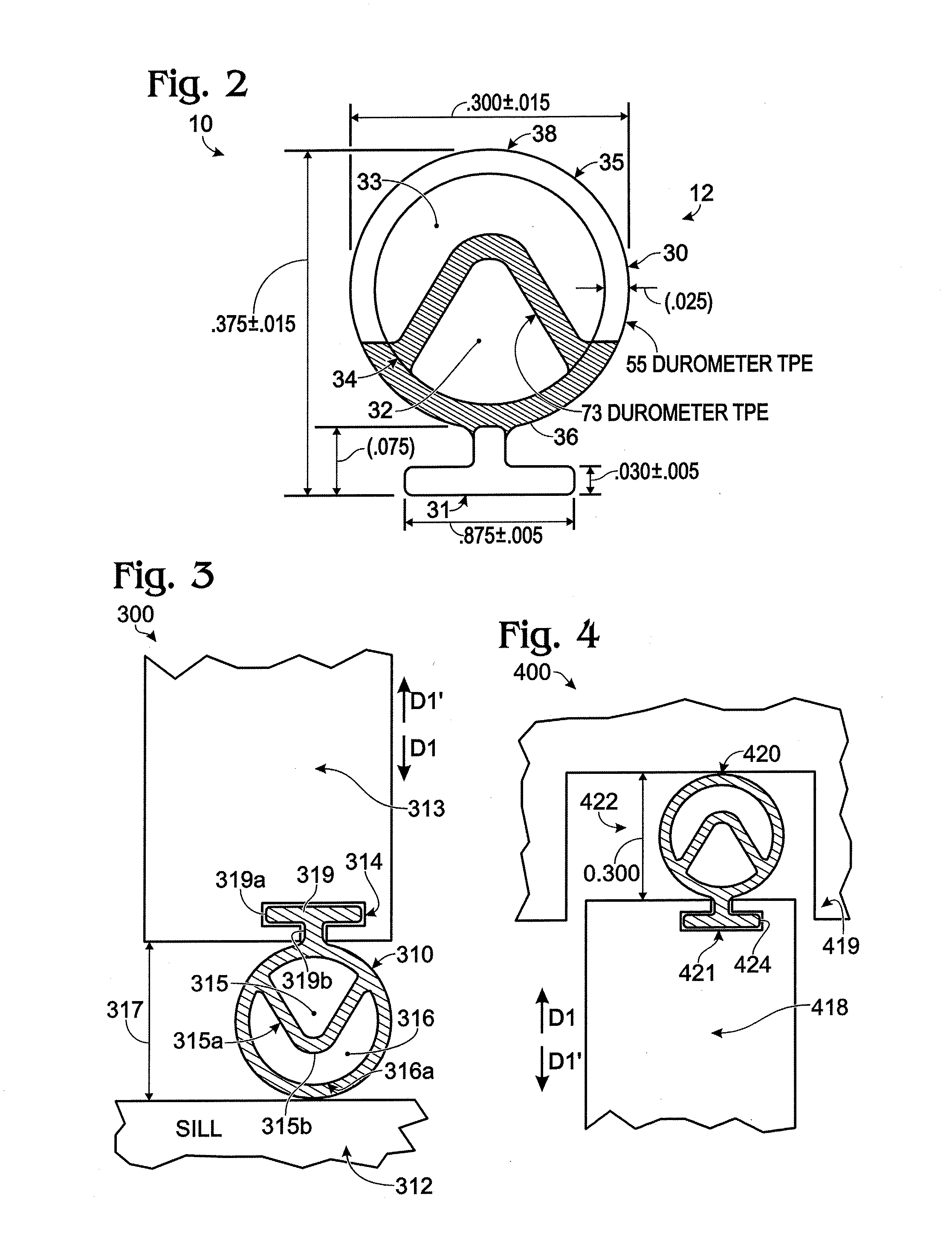
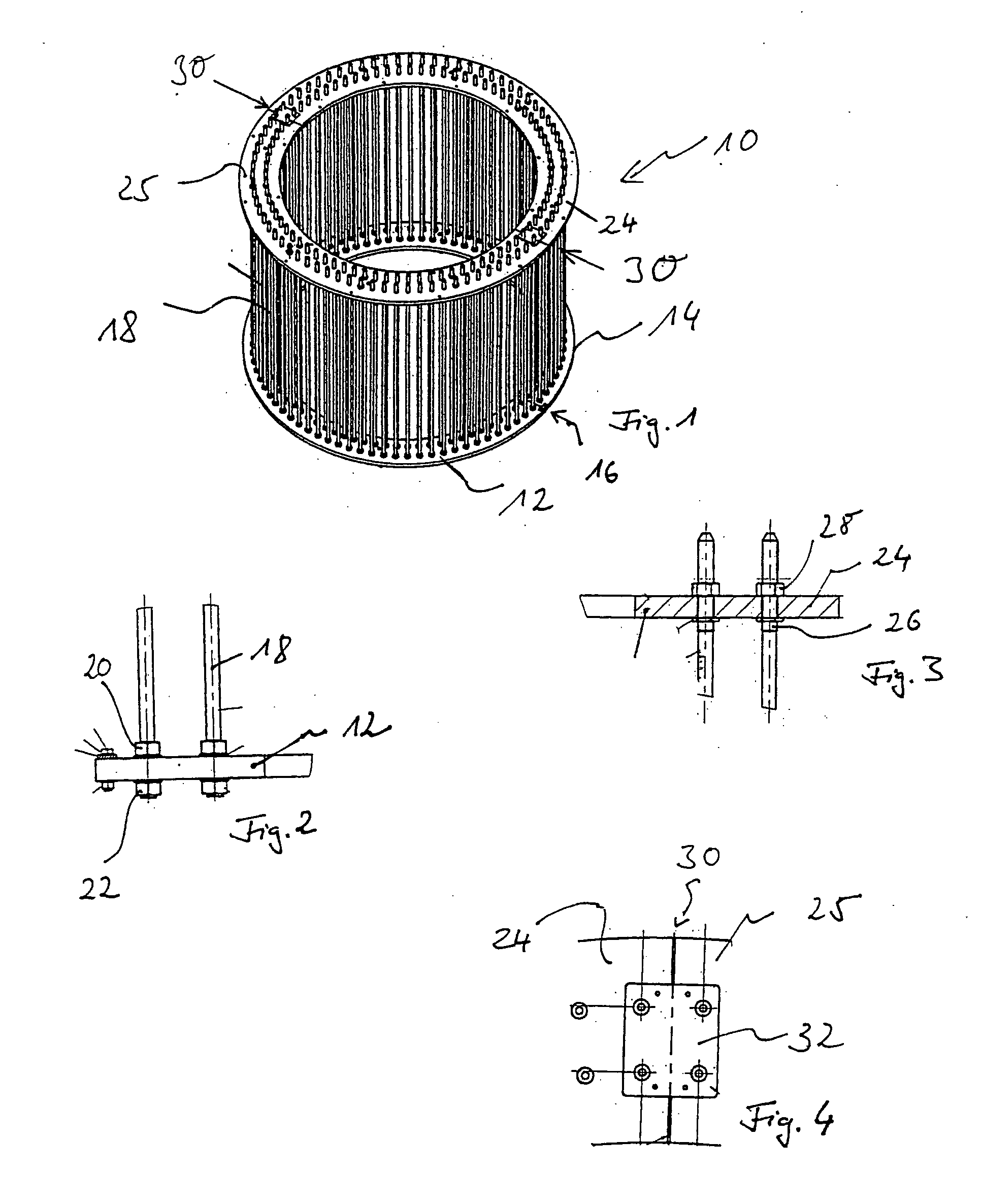
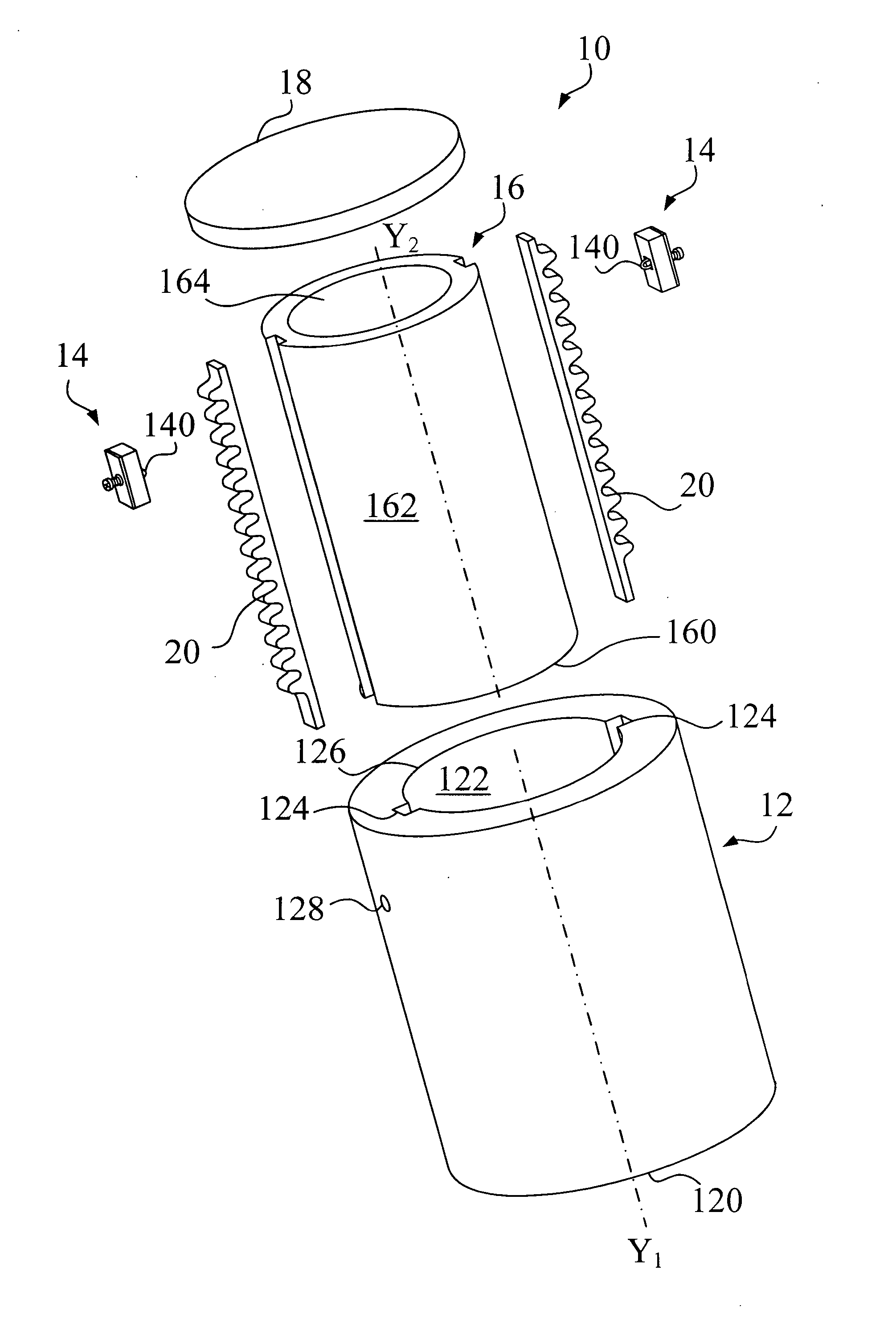
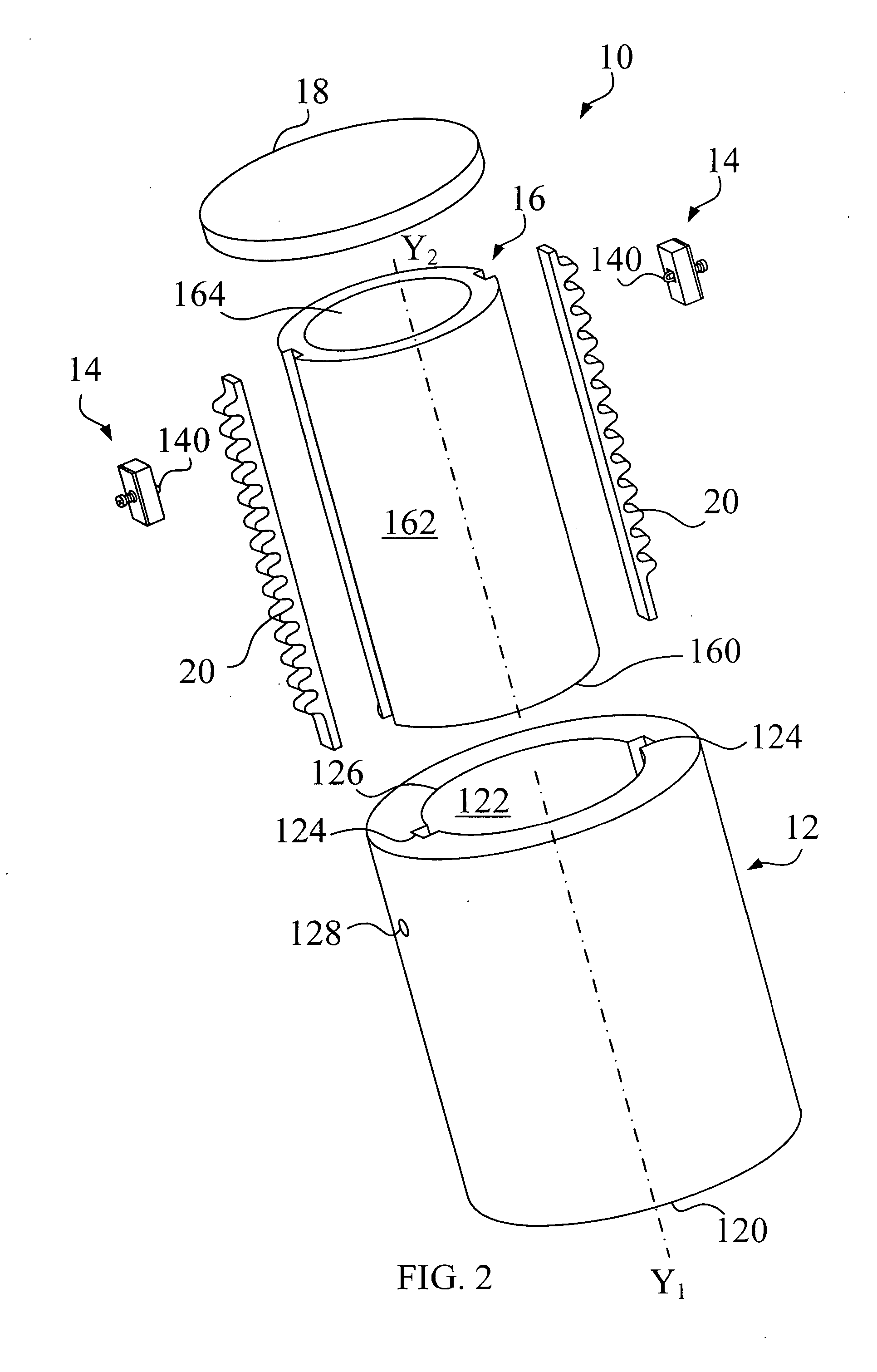
Multiple Hollow Bulb Seal
A seal that includes a hollow bulb that defines an interior space, and further includes at least one solid divider wall located in the interior space in order to divide the interior space so that it includes at least a first chamber and a second chamber, where the first and second chambers are not in fluid communication with one another. In some preferred embodiments: (i) the interior wall is generally V-Shaped in transverse cross-section; (ii) the first chamber is generally triangular in transverse cross-section; and (iii) the second chamber is generally U-shaped in transverse cross-section. Some preferred embodiments further include a seal base (for example, a T-shaped base), with the hollow bulb being mechanically connected to the base at the bottom of the T-shape so that an open end of the V-shaped interior wall is oriented to directly face the seal base. In some preferred embodiments, the first and second chambers are hollow.
Owner:ULTRTAFAB INC
Dehydroandrosterone analogs including an anti-inflammatory pharmacore and methods of use
ActiveUS8258329B2Suppresses demyelinationSuppresses transectionSenses disorderNervous disorderStereochemistryAnti-inflammatory analgesics
Owner:REATA PHARMA INC
Powered prosthetic hip joint
A powered prosthetic thigh can have a proximal portion configured to couple to a prosthetic hip socket and can have a distal portion attached to the proximal portion. The distal portion can have a distal connector configured to couple to a prosthetic knee. The powered prosthetic thigh can also have a computer controlled actuator configured to rotate the prosthetic thigh relative to the prosthetic hip socket.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Monocyclic cyanoenones and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS8314137B2Suppresses demyelinationSuppresses transectionBiocideSenses disorderMedicineDisease cause
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
System and methods for promoting health
InactiveUS20080070210A1Structural degradationImmediate resultChiropractic devicesVibration massageBone densitySacroiliac joint
A system made up of methods and techniques designed to improve the body's postural alignment, joint range, muscle hydration, bone density, and overall musculoskeletal health. The system combines a series of exercised designed to lengthen and strengthen muscles, fascial and myofascial tissue. The system is used in combination with a vibrating roller device, which can also be used with a head cradle. The application of the vibrational motion to the body in combination with the techniques described herein work to stimulate fascial tissue and confer benefits on the user which will improve the overall quality of life.
Owner:HITZMANN SUE
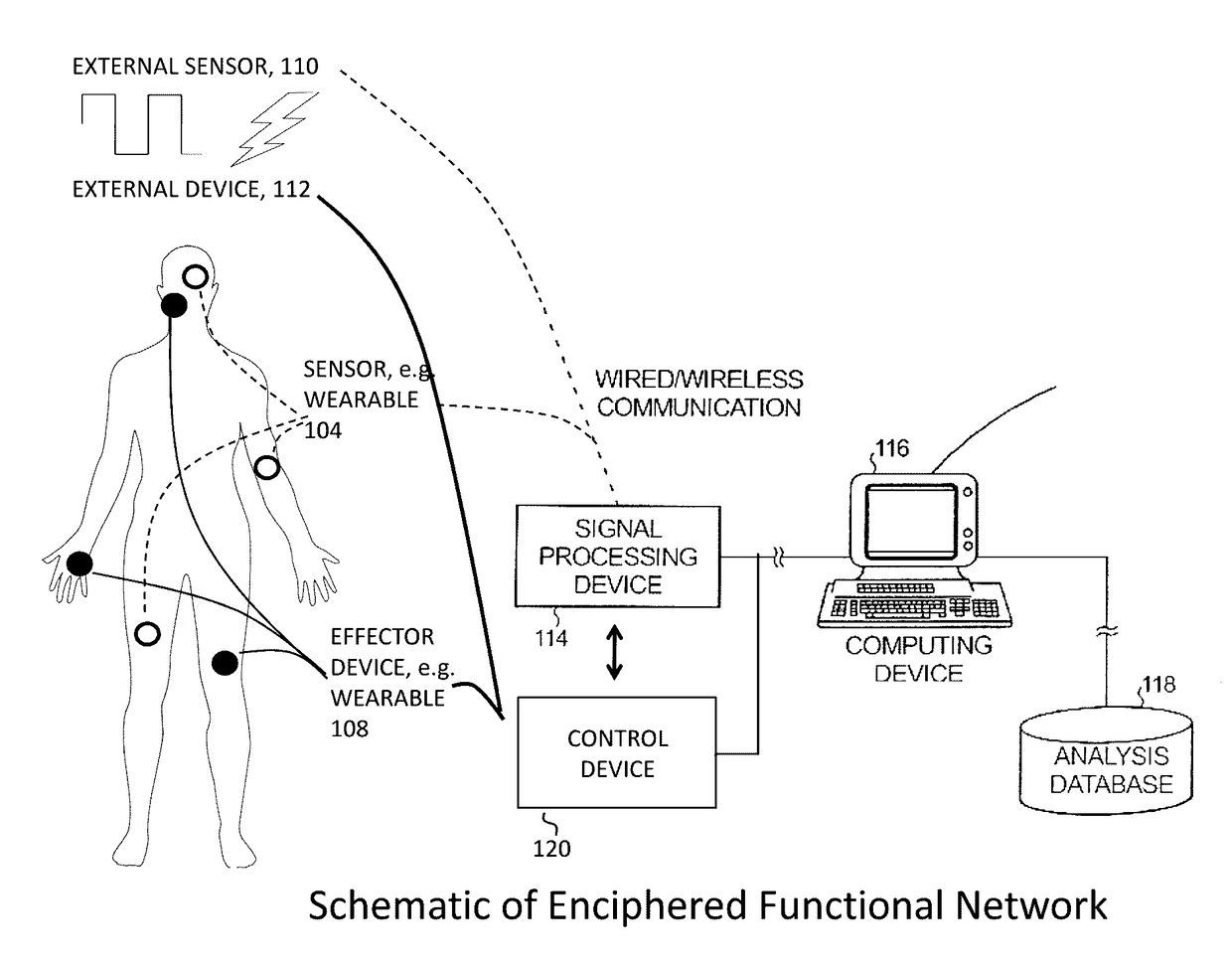
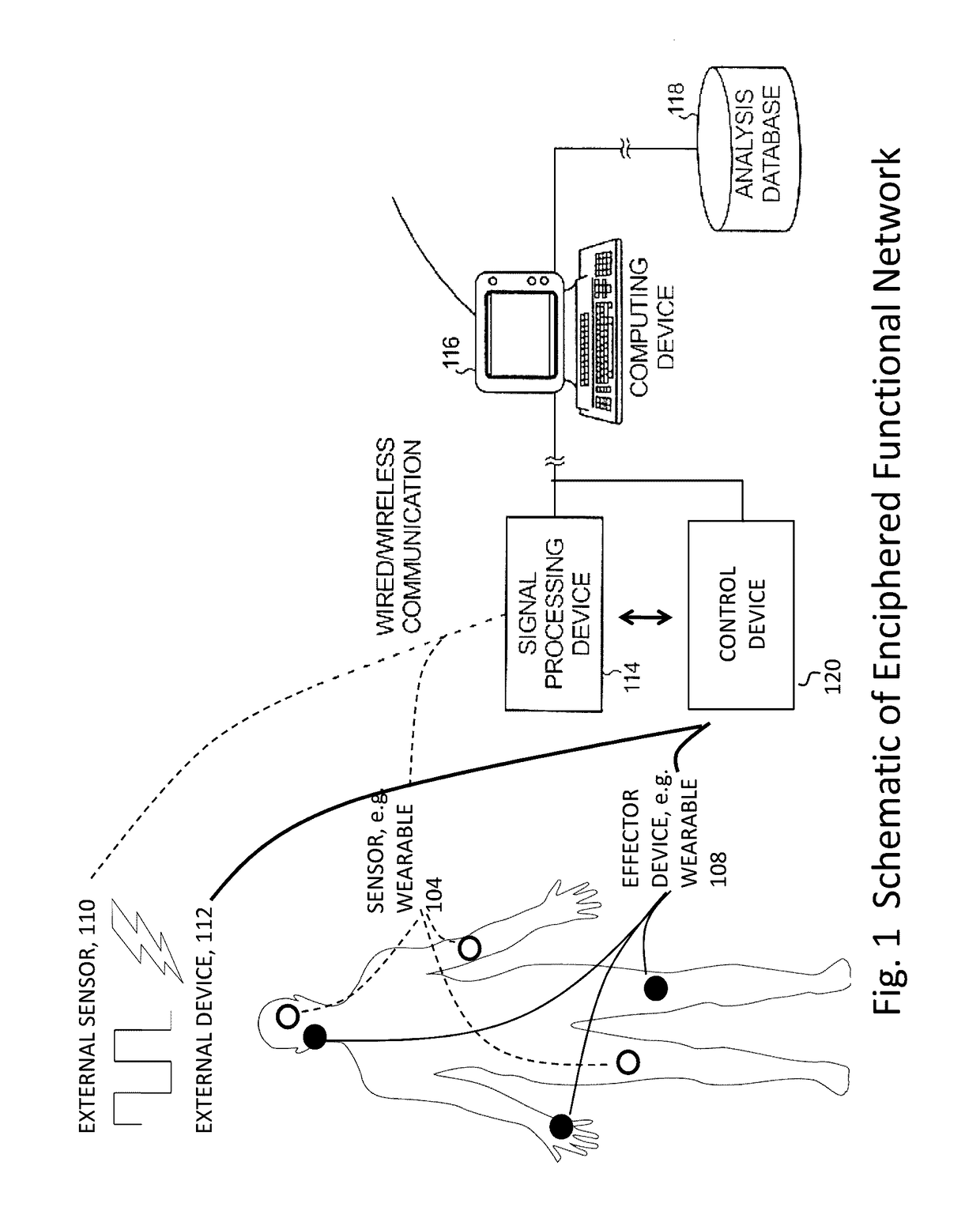
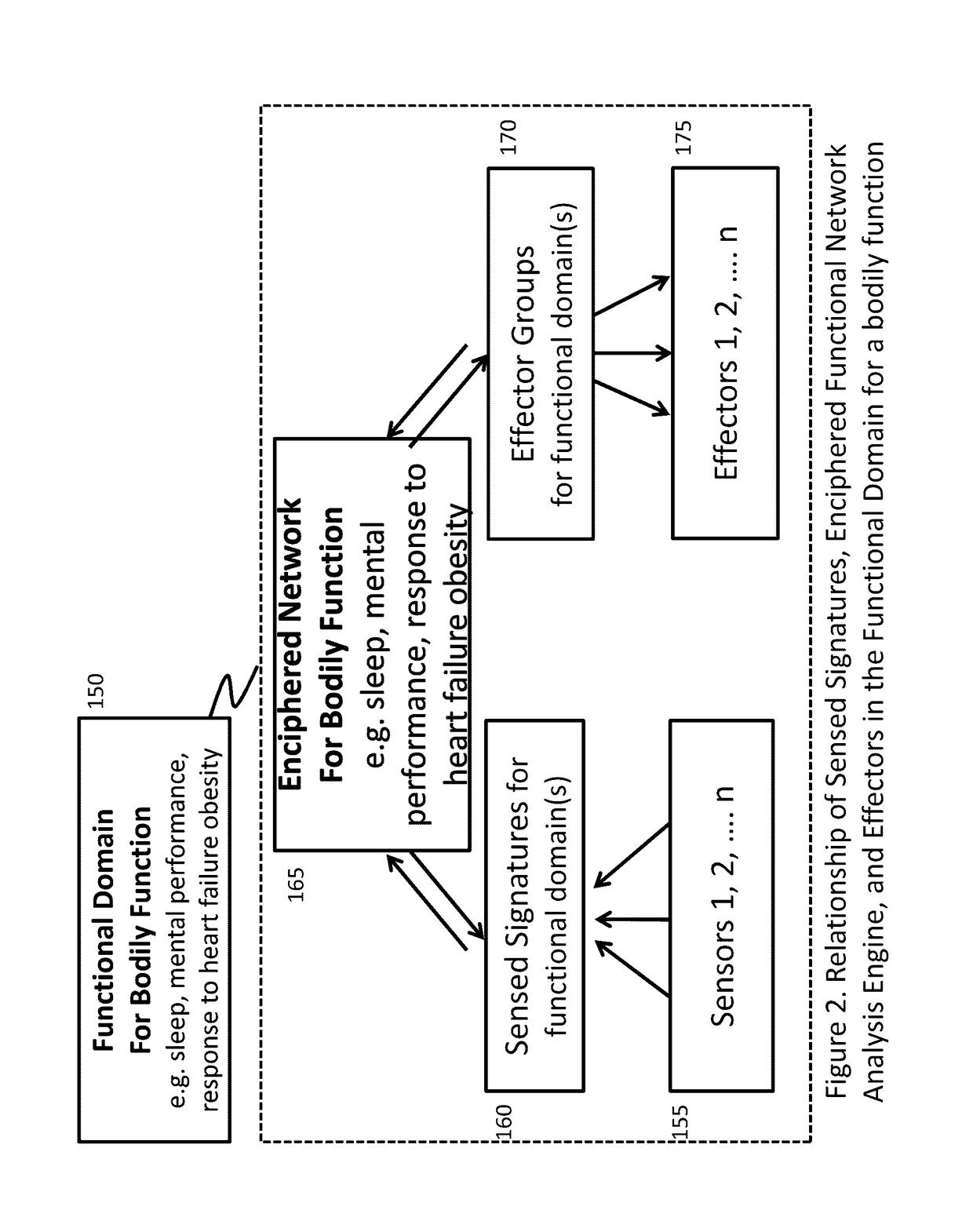
Method and system for combining physiological and machine information to enhance function
InactiveUS20170164893A1Monitor and modulate complex bodily functionImprove performanceMedical data miningElectrocardiographyMedicine
The present invention relates generally and specifically to combining biological sensors with external machines using machine learning to form computerized representations that can control effectors to deliver therapy or enhance performance.
Owner:RESONEA INC
Joint-protecting beverages and/or foods and their preparations
InactiveUS20040198695A1Overcome low absorptionPromote absorptionBiocideVitamin food ingredientsAdditive ingredientMedicine
A series of beverages and / or foods, which have protecting and enhancing effects on human's joints and bones and can therefore prevent and treat osteoarthritis, is provided. The beverages and / or foods comprise one or more cartilage- and synovial fluid-enhancing active ingredients or combinations of these ingredients with bone-enhancing calcium and phosphorus additives. Active ingredients in these beverages and / or foods are taken in liquid forms. So they can be easily absorbed and utilized thoroughly by human body.
Owner:LI ANHU +1
Semiconductor apparatus for fingerprint recognition
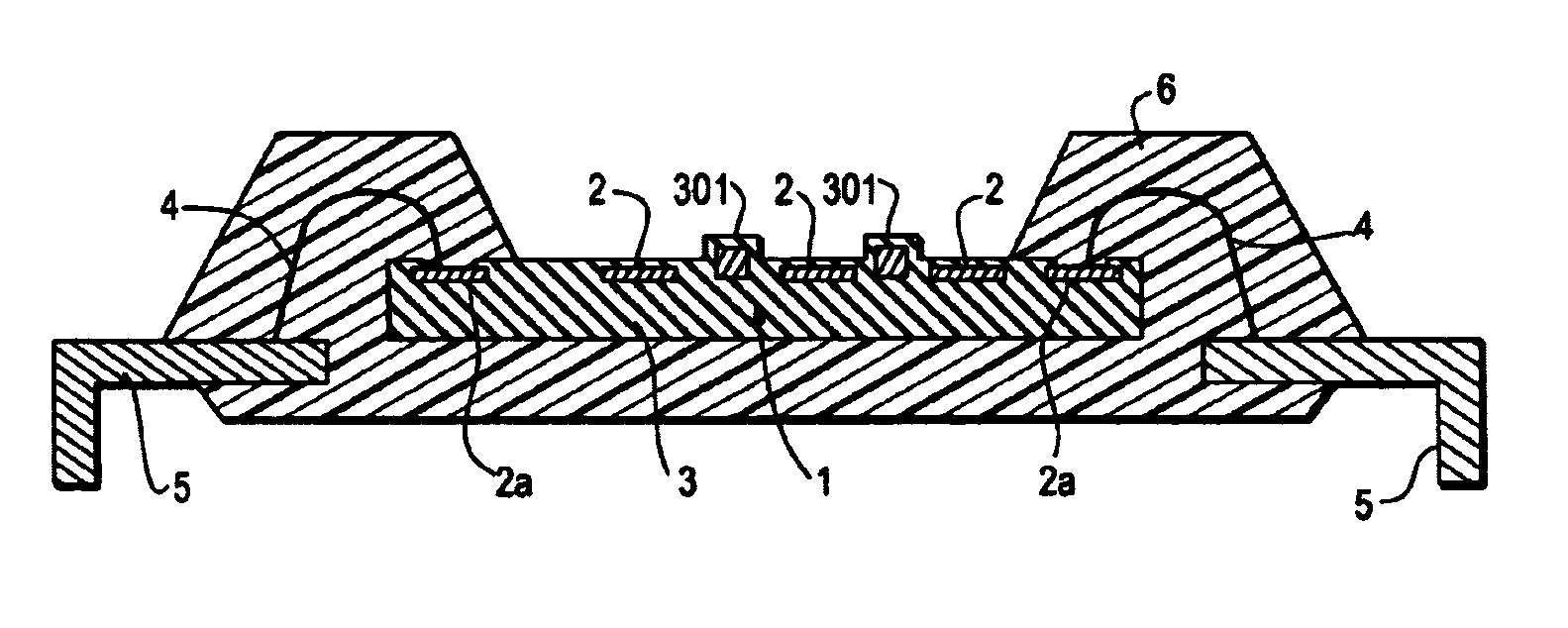
InactiveUS7031500B1Function is lostSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPerson identificationElectricitySemiconductor
A semiconductor apparatus, which comprises: a substrate having a transistor; a first electrode formed on the substrate and connected to the transistor; a second electrode formed on the substrate and electrically separated from the first electrode; and an insulating film formed on the substrate so as to cover the first electrode, wherein, when a plane of the insulating film which is not on a side of the substrate is taken as a first plane, a surface facing the first plane of the first electrode is taken as a first surface, and a surface facing the first plane of the second electrode is taken as a second surface, a distance between a surface of the substrate and the second surface is larger than a distance between the surface of the substrate and the first surface. By virtue of having the above unique structure, the semiconductor apparatus of the present invention is advantageous in that, when a finger or any other material which is electrostatically charged is brought closer to the substrate, the static electricity is not discharged into the electrode but into the static-electricity drawing wiring and then drawn out of the semiconductor device, so that the semiconductor devices, the circuits and the like which are connected to the electrode can be prevented from suffering a damage due to the static electricity and from losing the functions thereof.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method for the earthwork of a foundation sunk for a wind energy facility
InactiveUS20070065234A1Avoid inaccuraciesFunction is lostWind motor supports/mountsBuilding repairsEnergy facilitiesLoad distribution
A method for the earthwork of a foundation sunk for a wind energy facility, which has the following steps: an anchor cage is provided, consisting of an anchor plate and several anchoring bolts which are connected with the anchor plate, the free ends of the anchoring bolts are guided through bores in at least one load distribution plate the load distribution plate lays on at least three bolt nuts, which are screwed on the anchoring bolts, a reinforcement for the foundation sunk is mounted and the anchor cage is poured in with the reinforcement, the anchoring bolts protruding with the bolt nuts in this, upon subsequent tightening of the anchoring bolts between anchor plate and load distribution plate, the bolt nuts are stripped over the thread of the anchoring bolt and loose their supporting capability.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY
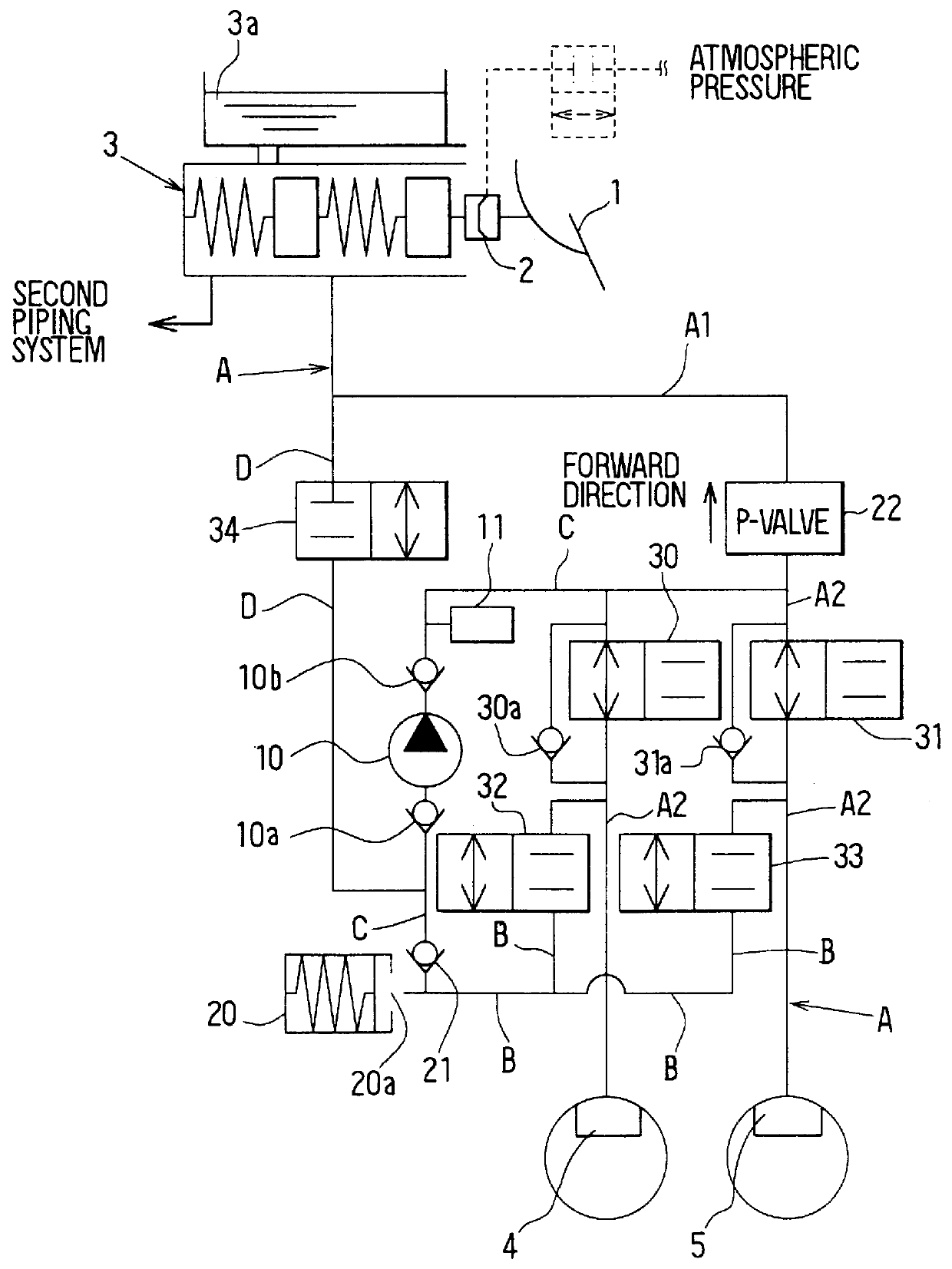
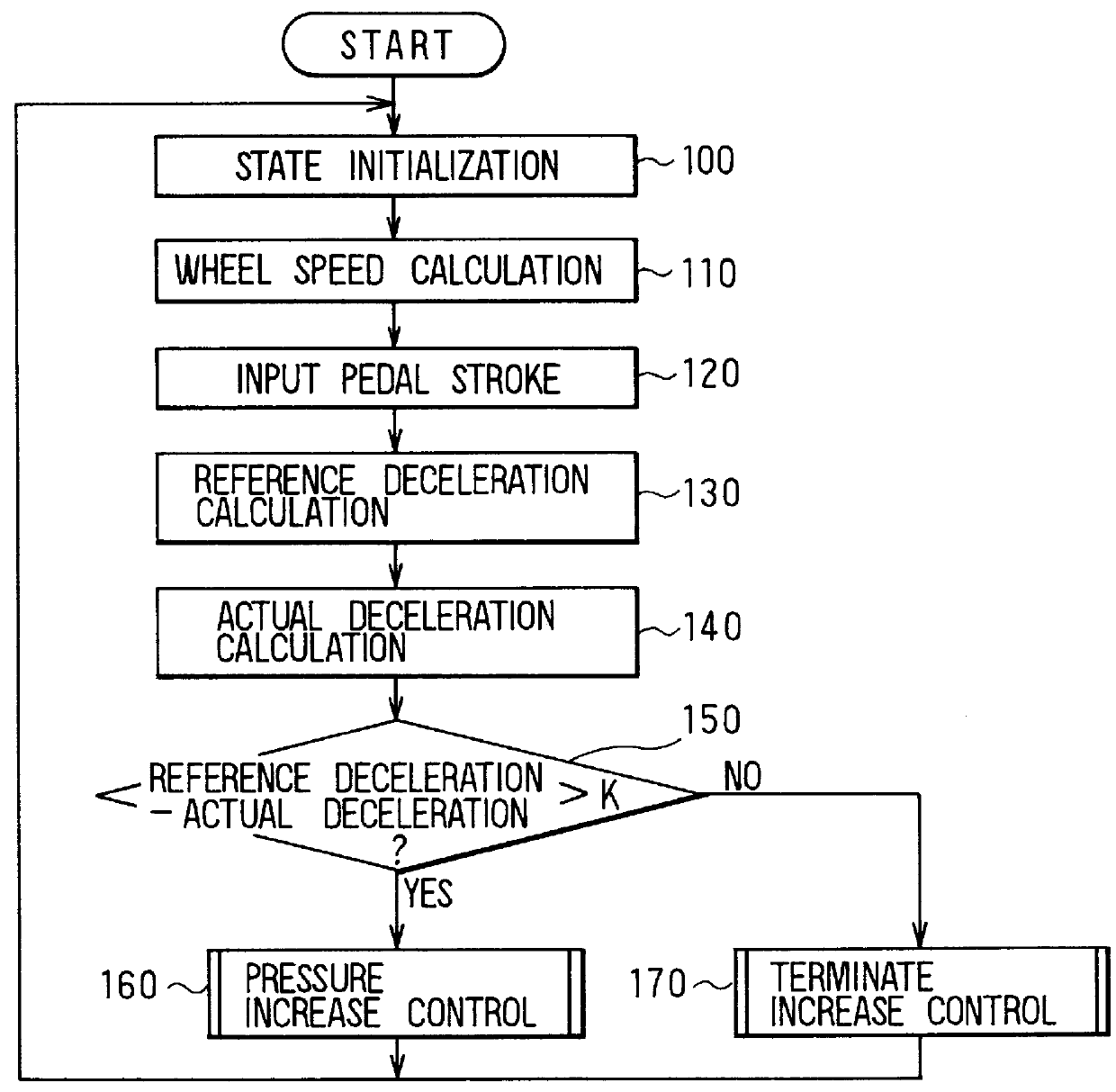
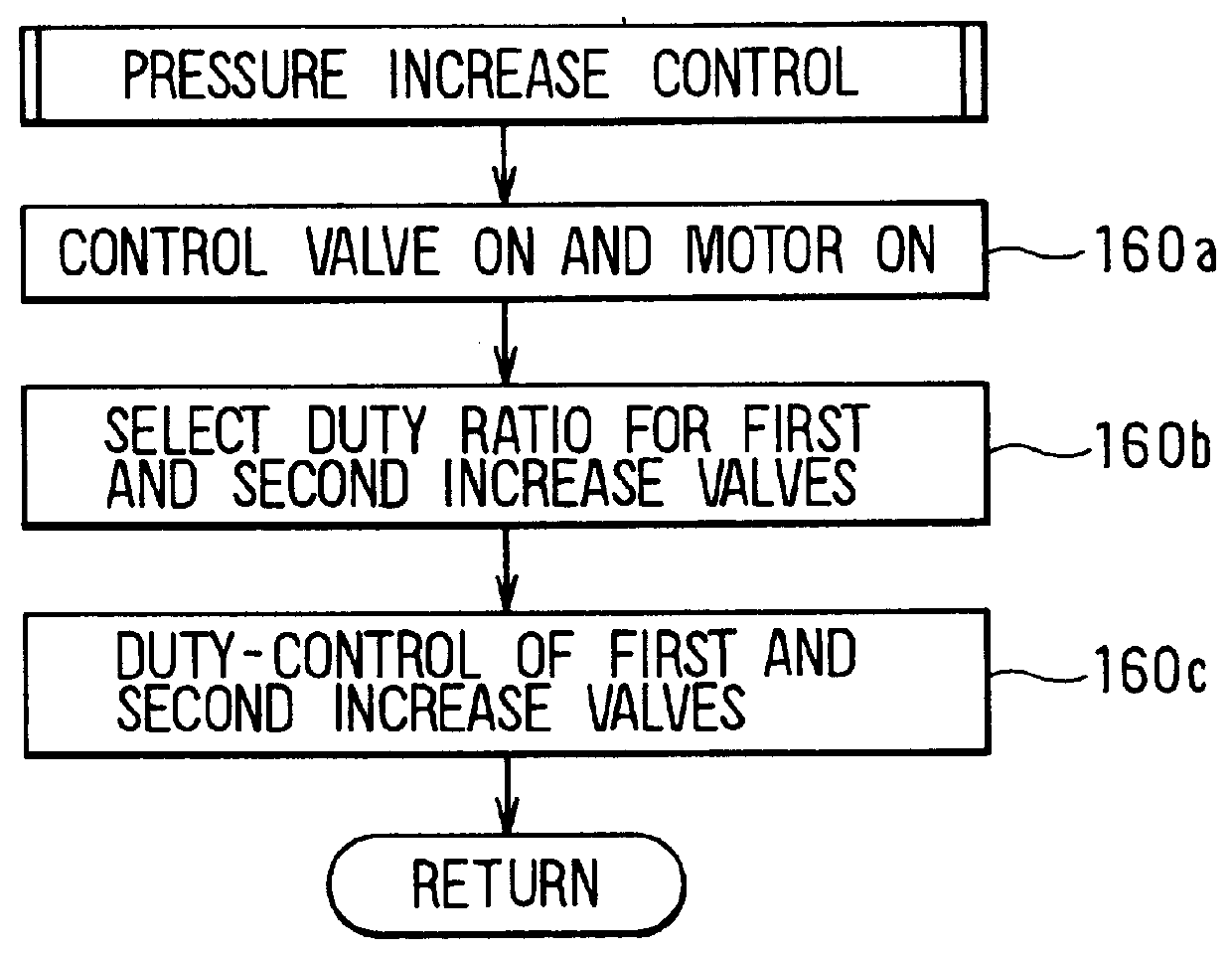
Braking system for a vehicle
InactiveUS6019438AIncrease braking powerAmple vehicle braking forceBraking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsDriver/operatorBrake force
A vehicle braking system can, for example when the performance of a booster has deteriorated, reduce a brake pedal depressing force required to obtain a sufficient braking force and thereby lighten the burden on the driver. A booster and a master cylinder generate a brake fluid pressure in correspondence with an operation of a brake pedal. Wheel cylinders connected to the master cylinder generate wheel braking forces in wheels of the vehicle. It is determined if a vehicle braking state corresponds to a state of operation of the brake pedal, and when it is determined that the vehicle braking state does not correspond to the brake pedal operation brake fluid pressure in the wheel cylinders is increased with a pump. In this way, it is possible to obtain a predetermined braking force corresponding to the brake pedal operation at all times.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Adjustable lift support apparatus
ActiveUS20060175512A1Lower costSimple structureRod connectionsLifting devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:BENQ CORP
Current collector, secondary battery, electronic device, and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS9941506B2Suppress relative position shiftReduce tensionFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsElectronElectrical and Electronics engineering
Part of an electrode, specifically a current collector and an active material layer, for a secondary battery is subjected to cutting processing to have a complex shape. For example, a stack of the first current collector and the first active material layer has a first slit and a second slit. The first slit extends from a first edge of the stack. The second slit extends from a second edge of the stack, is the slit closest to an electrode tab, and is not parallel or vertical to the longest edge of the current collector.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
System and methods for promoting health
InactiveUS8337437B2Increased longevityQuality improvementCosmonautic condition simulationsChiropractic devicesBone densityQuality of life
Owner:LONGEVITY FITNESS
Adjustable lift support apparatus
ActiveUS7344117B2Low costSimple structureStands/trestlesKitchen equipmentEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:BENQ CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com