Novel phytase, encoding gene, cell and feedstuff additive including the enzyme
A phytase and gene technology, applied in the field of microbial engineering, can solve problems such as cost reduction, and achieve the effects of good stability, strong phytic acid hydrolysis ability, and good pH stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Cloning of embodiment 1 Yersinia rohdei phytase gene
[0046] Usually, by comparing the protein and nucleic acid sequences of genes in the same family, some relatively conserved sequences can be found. Therefore, similarity cloning is a very effective and simple method when obtaining other desired gene sequences of the same family.
[0047] According to the classification of phytase, it can be obtained that most of the phytase derived from bacteria belong to the histidine acid phosphatase family. Through the multiple sequence alignment program CLUSTAL W and the block analysis program BLOCKS (http: / / blocks.fhcrc.org / blocks / make_blocks.html), we found histidine Two conserved regions RHGXRXP and HD regions in acid phosphatase protein sequence. Based on these two conserved regions, we designed degenerate primers as described in to amplify part of the phytase sequence from Yersinia rochei genomic DNA.
[0048] Acquisition of Partial Phytase Gene Sequence
[0049] We de...
Embodiment 2
[0106] Example 2 Expression of phytase AppA in Pichia pastoris
[0107] Construction of expression vector
[0108] In order to obtain the coding region of the mature protein, primers (YmF and YmR) were designed and synthesized. The sequences of primers YmF and YmR with EcoRI and NotI restriction sites are listed in Table 4. The coding region of the mature protein was amplified from Y. rochei genomic DNA using primers YmF and YmR. The expression vector pPIC9 (Invitrogen, SanDiego) was ligated through EcoRI and NotI restriction sites to construct the yeast expression vector pPIC9-AppA. The ligation product was used to transform Escherichia coli competent cell JM109. Positive transformants were subjected to DNA sequencing, and transformants with correct sequence were used to prepare recombinant plasmids. Expression plasmid vector DNA was further used to transform Pichia pastoris.
[0109] Table 4: Primers for amplifying the full length of the mature protein
[0110] ...
Embodiment 3
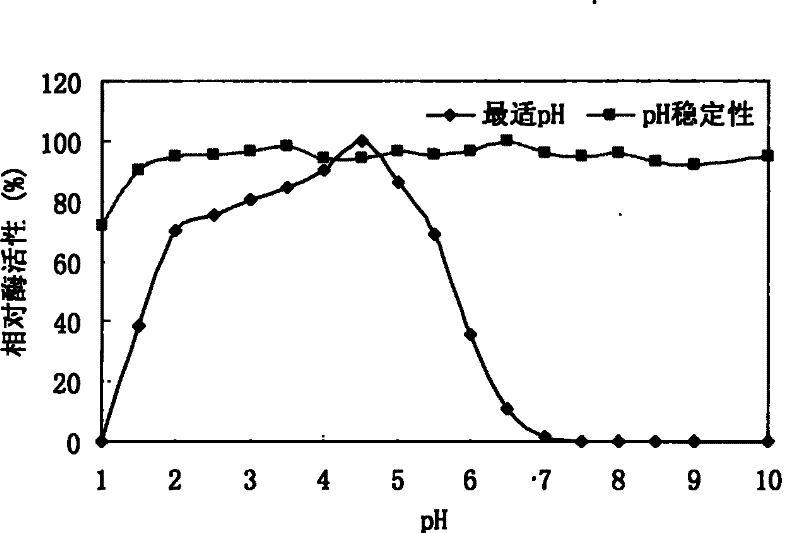
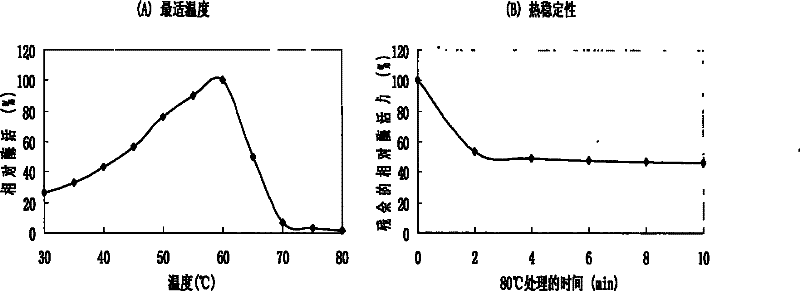
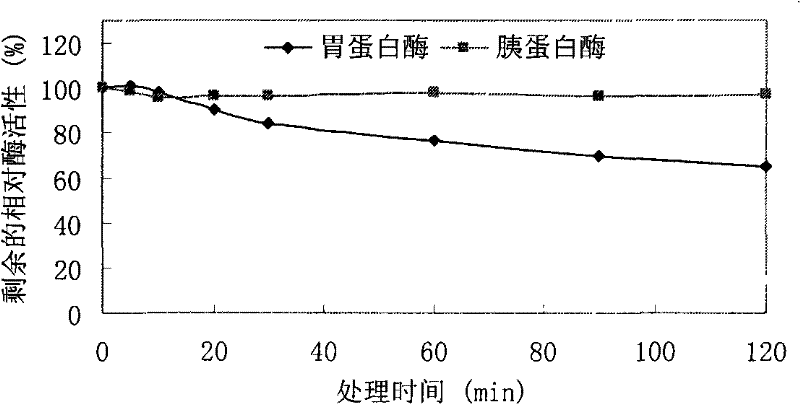
[0115] Example 3 Preparation and purification of recombinant phytase r-AppA
[0116] In order to purify the recombinant phytase r-AppA expressed by yeast, the transformants with supernatant enzyme activity of 429U / mL were cultured in shake flasks under better culture and induction conditions. After two days of induction, the phytase activity was detected by the method described in Example 4, and the enzyme activity of the supernatant reached 927 U / mL. After centrifugation at 12000g for 10 minutes, the supernatant containing phytase protein was collected and yeast cells were removed. Use a 0.22 μm filter membrane to vacuumize the supernatant to remove other impurities in the supernatant. Ammonium sulfate precipitation was performed on the treated supernatant, ammonium sulfate powder was added to the supernatant to reach 80% saturation, and stirred overnight. The precipitate was collected by centrifugation, and the precipitate was dissolved with 0.1M Tris-HCl buffer, pH 8.0. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com