Polyurethane material capable of dissolving plasma clot in high efficiency and preparation thereof
A polyurethane material and polyurethane technology, applied in the field of biomedical functional polymer materials, can solve the problems of limiting the grafting density of bioactive molecules, it is difficult to achieve high-density grafting, and the anticoagulation process cannot be achieved.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] (1) Polyurethane surface graft copolymerization PHEMA
[0033]Put 0.98g of potassium thiocyanate and 40mL of anhydrous acetonitrile in a 100mL reaction flask and stir to dissolve. 0.82 mL of acryloyl chloride was slowly dropped into the reaction bottle, and stirred at room temperature for 12 hours. The precipitate was removed by filtration, and the filtrate was directly used in the next reaction. Put 60 polyurethane diaphragms (thickness 0.5mm) with a diameter of about 7mm in a reaction flask containing 30mL of the above filtrate, add 0.75g of triethylamine to the reaction flask, stir and react at 65°C for 2-12 hours, and then put the polyurethane The diaphragm is taken out, washed with acetonitrile and dried to obtain a polyurethane diaphragm with carbon-carbon double bonds on the surface. Place 0.082g of azobisisobutyronitrile, 6.5g of HEMA, 40mL of methanol and 60 pieces of polyurethane diaphragms with carbon-carbon double bonds on the surface in a 50mL reaction bo...
Embodiment 2
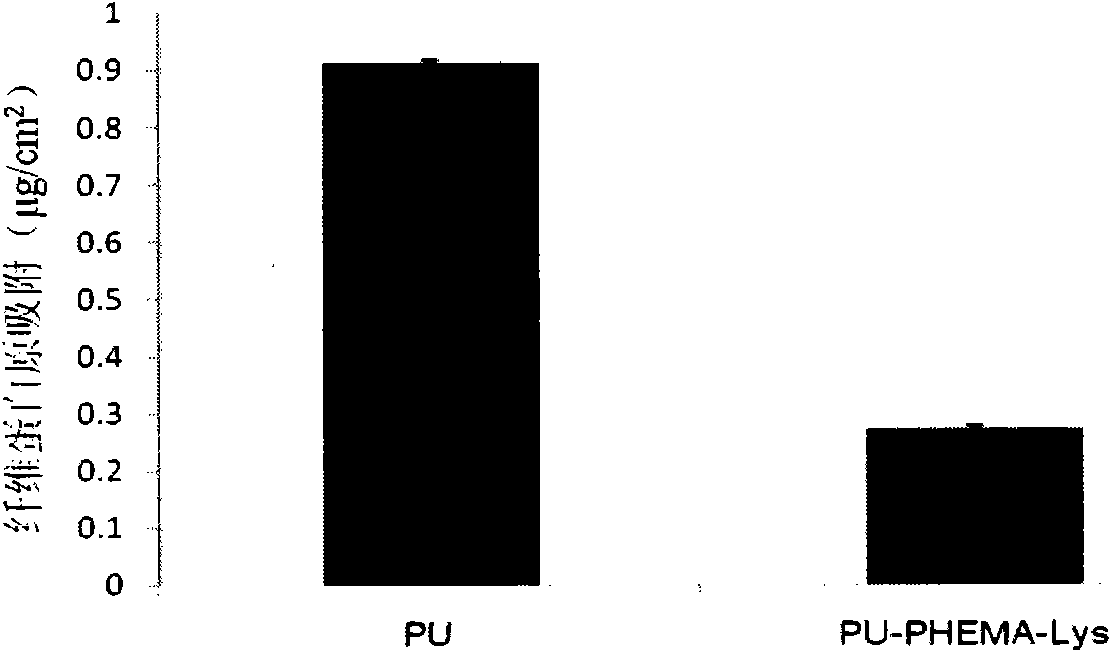
[0038] The lysine surface prepared according to the method of Example 1 was tested for the adsorption of isotope-labeled fibrinogen to reflect its ability to reject non-specific protein adsorption. isotope by the ICl method 125 I was labeled on the tyrosine residue of fibrinogen, and the labeled and unlabeled fibrinogen solutions were mixed according to the mass ratio of fibrinogen of 1:19, and the modified and unmodified polyurethane membranes were placed in a static place. In this solution for 3 hours, washed three times with PBS or TBS buffer solution with a pH of 7.4, and finally read the amount of radioactivity on the membrane through a gamma counter and converted it into the mass of protein, and finally obtained figure 1 .
Embodiment 3
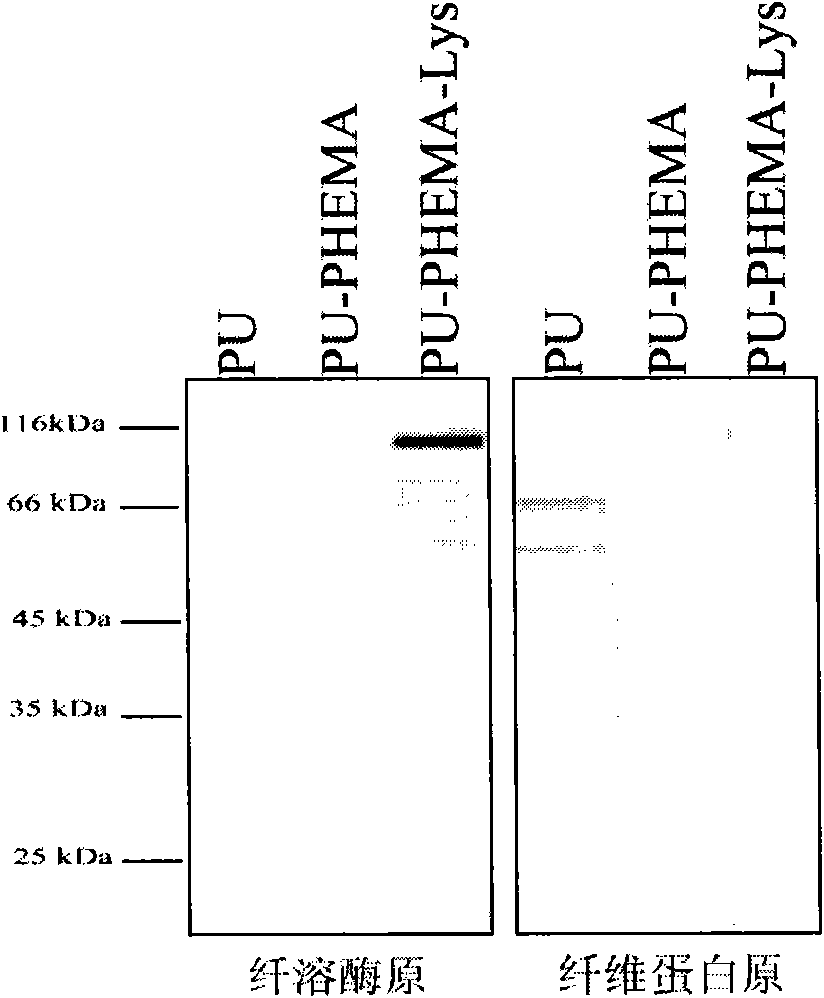
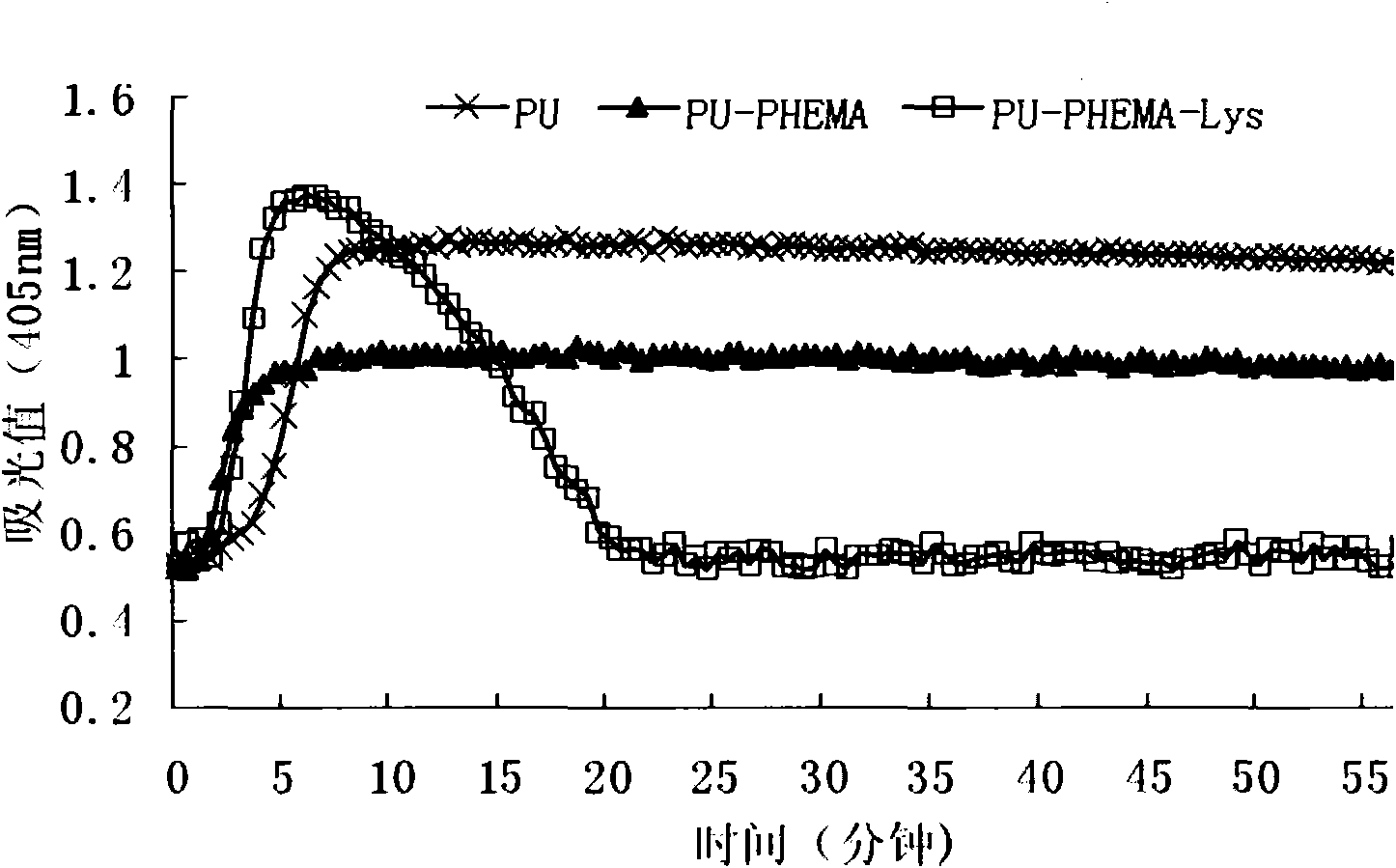
[0040] The ability of the lysine surface prepared according to the method of Example 1 to reject non-specific protein adsorption and selectively bind to plasminogen in plasma was tested by Western blot technique. First, the modified and unmodified polyurethane membranes were soaked in plasma for 3 hours, washed three times with PBS or TBS buffer solution with a pH of 7.4, and then washed with 2% (w / v) sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) solution The protein adsorbed on the surface of the membrane is eluted. Then, the protein eluate was electrophoresed on a 12% SDS-PAGE gel, and then the protein on the gel was transferred to a PVDF membrane, and the PVDF membrane was blocked with 5% skimmed milk powder, and then combined with the studied The primary antibody of the target protein and the secondary antibody labeled with alkaline phosphatase (fibrinogen and plasminogen were studied in this example), and finally by acting on the substrate 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-ind Indophosphoric acid and n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com