Method for preparing p-aminodiphenylamine
A technology of p-aminodiphenylamine and nitrodiphenylamine, which is applied in the field of preparation of p-aminodiphenylamine, can solve problems such as difficult solvent recovery, long hydrogenation time, and hydrogenation of azobenzene, so as to avoid the control of moisture content, Simple operation and improved reaction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1. 50g of powdered activated carbon was pretreated, soaked in 200g of 3% nitric acid solution at 30°C for 8 hours, washed with deionized water until neutral, then soaked in 3% hydrogen peroxide solution for 4 hours, washed, and dried at 105°C for 16 hours.
[0030] Get the treated activated carbon 20g for later use. Dissolve a certain amount of palladium chloride and lanthanum nitrate in 100mL of 2% hydrochloric acid solution, pour it into a container filled with carrier activated carbon, stir for 4 hours, take it out, add 10mL of 5% formaldehyde for reduction, and use 5% sodium hydroxide The pH of the solution was adjusted to 6-8, maintained for 4 hours, taken out, washed with deionized water, and vacuum-dried at 80°C for 8 hours to obtain the finished catalyst, which was designated as Cat1.
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2. 50g of powdered activated carbon was pretreated, soaked in 200g of 3% hydrochloric acid solution at 60°C for 8 hours, washed with deionized water until neutral, soaked in 5% hydrogen peroxide solution for 4 hours, washed, and dried at 105°C for 16 hours.
[0032] Get the treated activated carbon 20g for later use. Dissolve a certain amount of palladium nitrate and cerium nitrate in 100ml of 2% nitric acid solution, pour it into a container filled with carrier activated carbon, stir for 5 hours, take it out, add 10ml of 5% hydrazine hydrate for reduction, and use 5% sodium hydroxide The pH of the solution was adjusted to 6-8, maintained for 4 hours, taken out, washed with deionized water, and vacuum-dried at 80°C for 8 hours to obtain the finished catalyst, which was designated as Cat2.
Embodiment 3-6
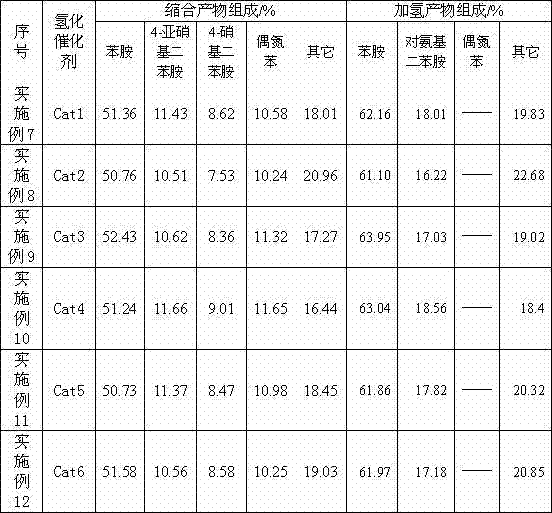
[0033] Example 3-6. The catalyst was prepared by the method of Example 1, and the contents of each component were shown in the table.
[0034] Table 1 The content of each component in the catalyst
[0035] Example catalyst palladium rare earth element 1 Cat1 5% (added in the form of palladium chloride) La (added in the form of lanthanum nitrate) 0.05% 2 Cat2 7% (added in the form of palladium nitrate) La (added in the form of lanthanum chloride) 0.70% 3 Cat3 9% (added in the form of palladium acetate) Ce (added in the form of cerium chloride) 0.18% 4 Cat4 11% (added in the form of palladium chloride) Pr (added in the form of praseodymium chloride) 0.33% 5 Cat5 13% (added in the form of palladium nitrate) Nd (added as neodymium chloride) 0.65% 6 Cat6 15% (added in the form of palladium acetate) Sm (added as samarium chloride) 0.90%
[0036] Above-mentioned embodiment 1-6 is the preparation of h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com