Recycling harmless treatment method of stainless steel pickling waste water
A technology for the harmless treatment and pickling of wastewater, which is applied in the fields of metallurgical wastewater treatment, water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc. The effect of high burial cost, small footprint and high recovery purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] The stainless steel pickling wastewater to be treated in this example was taken from a stainless steel pickling factory in Dainan, Jiangsu, and the water quality components are shown in Table 2 below.
[0046] Table 2 Water quality of stainless steel pickling wastewater in Example 1
[0047] project HNO 3 HF Fe 3+ Ni 2+ Cr 3+ f - (excluding HF) Concentration (g / L) 176.4 38.2 31.5 6.7 5.8 34.2
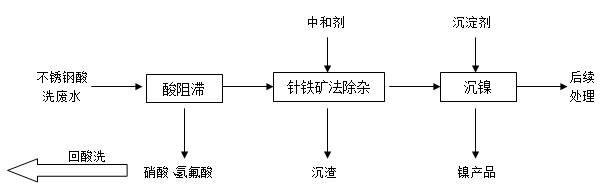
[0048] A kind of resource harmless treatment method of stainless steel pickling wastewater in this embodiment, its technological process is as follows figure 1 As shown, the stainless steel pickling wastewater is retarded by anion exchange resin, and then the goethite method is used to remove impurities, and then the neutralization precipitation method is further used to recover nickel. The specific steps are:
[0049] 1) Acid separation and recovery of nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid: pump the stainless steel pickling wastewater in ...
Embodiment 2
[0066] The water quality and basic steps of the wastewater treated in this example are the same as in Example 1, the difference is that in step (1), the acid concentration of the effluent is monitored by the conductivity, and when the conductivity suddenly rises to 40mS / cm, the liquid intake is stopped, and the obtained When the pH of the metal ion recovery solution is > 1.5, the recovery rate of metal ions drops to 75.3%. During the resin regeneration process, clean water is used to elute inorganic acids such as nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid adsorbed in the resin column from top to bottom. When the conductivity of the effluent drops to At 160mS / cm, stop regeneration; in step (2), the metal ion solution reacts in a three-necked flask at 80°C, neutralizes the acid generated by the reaction with 5% sodium carbonate and adjusts the end point pH to 5.0, and the nickel loss rate increases to 10.35%, but with the nickel recovered by washing, the total recovery rate is 99.3%, and ...
Embodiment 3
[0068] The water quality and basic steps of the waste water treated in this embodiment are the same as those in Example 1, the difference being that step (2) uses 10% sodium carbonate to adjust the end point pH to 3.5, and the loss rate of nickel is reduced to 8.5%. Nickel, the total recovery rate is 99.1%, the residual concentration of chromium rises to 85mg / L, and 28.05g of calcium chloride is added after 10 minutes of reaction (the dosage of calcium chloride is 110% of the theoretical amount of calcium required for the removal of fluoride ions ) to remove fluoride, and the concentration of fluoride ion after the reaction is 6.5mg / L. In step (4), the impurity-removing sediment was washed twice with water, and 2.01g (the weight of lime powder is 6% of the dry residue weight) of lime powder was added for stabilization. The leaching toxicity of the stabilized sediment met the requirements of GB 5085.3-2007. Requirements, for harmless sediment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com