Hydrogenation catalyst and application thereof
A technology of catalysts and additives, applied in the field of nickel-based catalysts, can solve the problems of catalyst nickel grain growth, overheating, catalyst activity and selectivity reduction, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Get nickel nitrate trihydrate (133g), zinc nitrate hexahydrate (145g) and ammonium dimolybdate (25g), add in 2000ml water, be dissolved into solution after stirring, above-mentioned solution and sodium carbonate solution are carried out concurrent precipitation, precipitation temperature is 75-80°C, the pH value of the precipitation is controlled between 7-7.5, after the precipitation is completed, add pseudo-boehmite and age at 90°C for 3 hours, wash the precipitate until it is free of sodium ions, and then add it to the precipitate filter cake 30 g of magnesium nitrate aqueous solution (containing 5 g of magnesium nitrate), the resulting filter cake was dried at 90° C. overnight, then roasted, and then shaped after adding 5.0 g of hydrotalcite. The shaped catalyst particles are reduced in hydrogen, and the reduced catalyst is fed with nitrogen containing a small amount of oxygen as a passivating agent until there is no temperature rise in the reduction reactor. The ze...
Embodiment 2
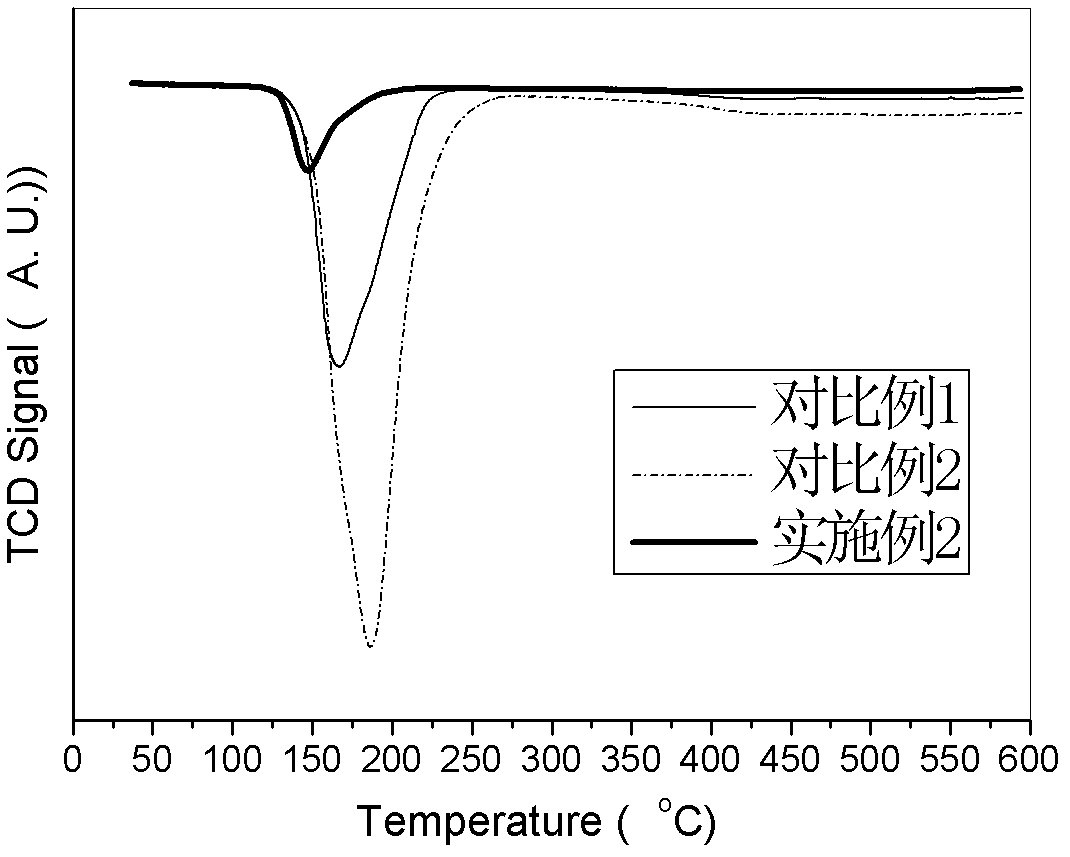
[0039] After getting nickel nitrate trihydrate (179g), zinc nitrate hexahydrate (130g) and 40% manganese nitrate aqueous solution (40g) and fully stirring, add silica sol 100g containing 15 grams of silicon dioxide and continue to stir until viscous, then add Add 5g of graphite, 10g of water and 20g of methylcellulose, continue to stir until it forms a dough, add 5g of potassium nitrate, continue to stir for 10 minutes, then dry the resulting dough at 120°C for 2 hours and bake at 400°C for 4 hours. The catalyst particles obtained by molding are reduced in hydrogen, and nitrogen containing water vapor as a passivating agent is first introduced into the reduced catalyst, followed by nitrogen containing a small amount of oxygen, and finally air, until the reduction reactor has no temperature rise . by H 2 - The percentage of zero-valent nickel in the total nickel content measured by TPR is 92%, such as figure 1 .
Embodiment 3
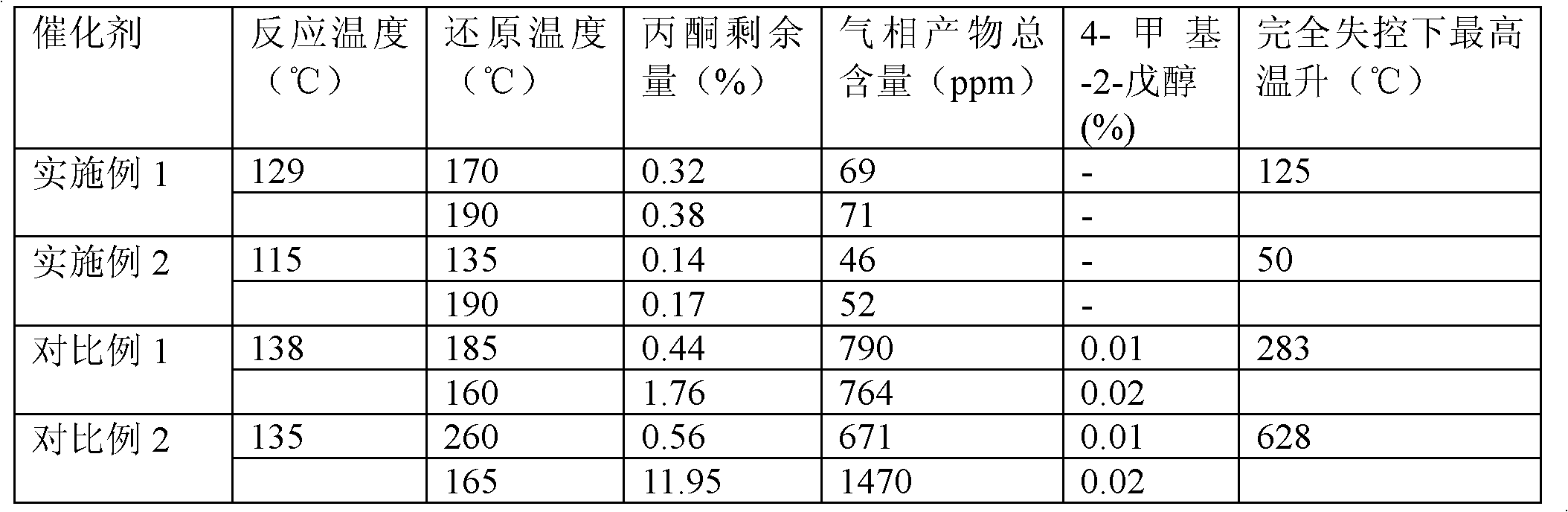
[0045] The catalysts of Examples and Comparative Examples are all applied to hydrogenation of acetone, the catalyst loading is 50ml, and the volume space velocity of acetone is 0.6h -1 , the molar ratio of oxygen to acetone is 3. The reaction results are shown in the table below:
[0046]
[0047] Calculation method of maximum temperature out of control: maximum temperature = cumulative heat release of reduction / specific heat value of catalyst X 0.9, 0.9 is assumed heat dissipation coefficient.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com