A method for increasing production of low-carbon olefins and aromatics by steam cracking of coker gasoline
A technology for coking gasoline and aromatics, applied in the production of bulk chemicals, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of poor fluidity of asphaltenes, affecting production, difficult to open ring, etc., to reduce coking rate and improve selectivity, total aromatics Yield improvement effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
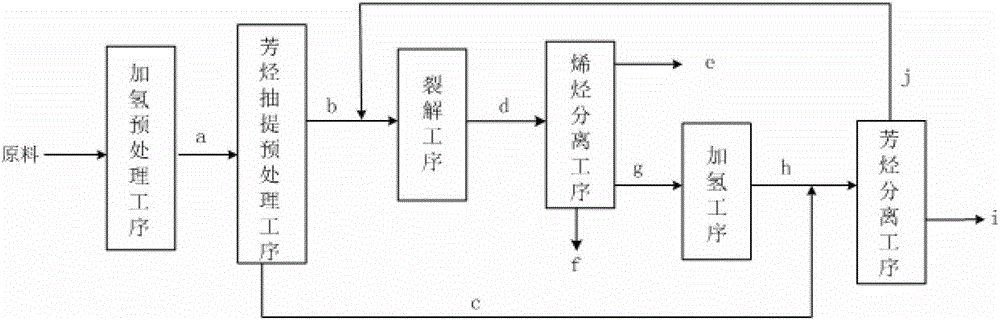
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] A kind of coker gasoline is used as the raw material, and its raw material properties are shown in Table 1. The raw material is mixed with hydrogen and sent to the hydrogenation small-scale reactor, and is contacted with the hydrogenation catalyst at an average reaction temperature of 180°C to react and remove the raw material. Impurities such as diolefins, colloidal components and metals in the oil, the catalyst is LY-9801 (Pd series catalyst, Pd content is 0.3wt%), the reaction conditions are as shown in Table 2, and the composition of the reaction effluent is shown in Table 3, and the effluent After heating, the product enters another hydrogenation small-scale reactor, and contacts with a hydrogenation catalyst at an average reaction temperature of 300°C to carry out olefin saturation, hydrodenitrogenation and hydrodesulfurization reactions. The catalyst is a supported non- Noble metal catalyst consisting of 26 wt% WO 3 / 7wt%MoO 3 / 3wt%NiO), the balance is alumina. ...
Embodiment 2
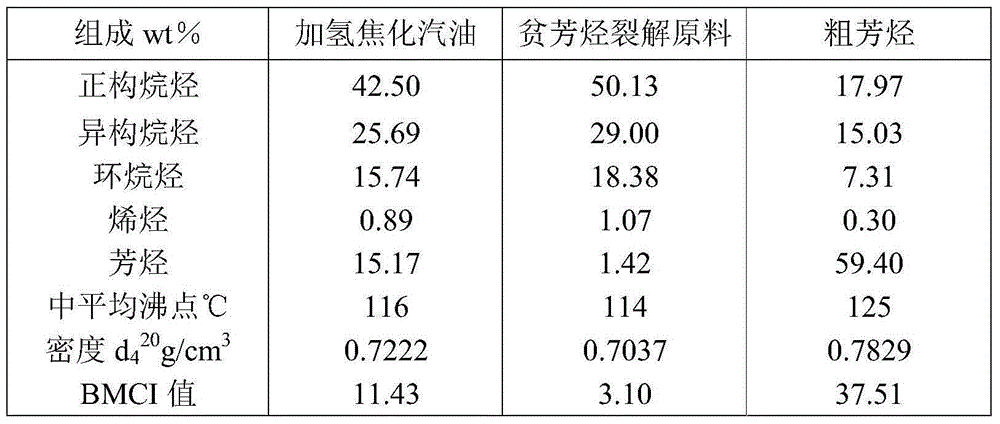
[0044] The hydrocoked gasoline raw material obtained in Example 1 was sent to the solvent extraction experimental device. Sulfolane is selected as the solvent, the solvent mass ratio is 3, the extraction tower pressure is 0.6MPa, the extraction temperature is 80°C; the recovery tower pressure is 0.035MPa, the tower top temperature is 30°C, the tower bottom temperature is 169°C, and the reflux ratio is 0.8. After separation, the aromatic-lean stream with 1.42% aromatics content and the crude aromatics stream with 59.40% aromatics content were obtained. The basic composition properties of the streams before and after extraction are shown in Table 4.
[0045] Table 4: Logistics properties before and after extraction pretreatment
[0046]
[0047] It can be seen from Table 4 that the content of alkane in the raw material of hydrocoking gasoline increases significantly after solvent extraction, the content of aromatic hydrocarbon in the raw material of raffinate cracking drops ...
Embodiment 3
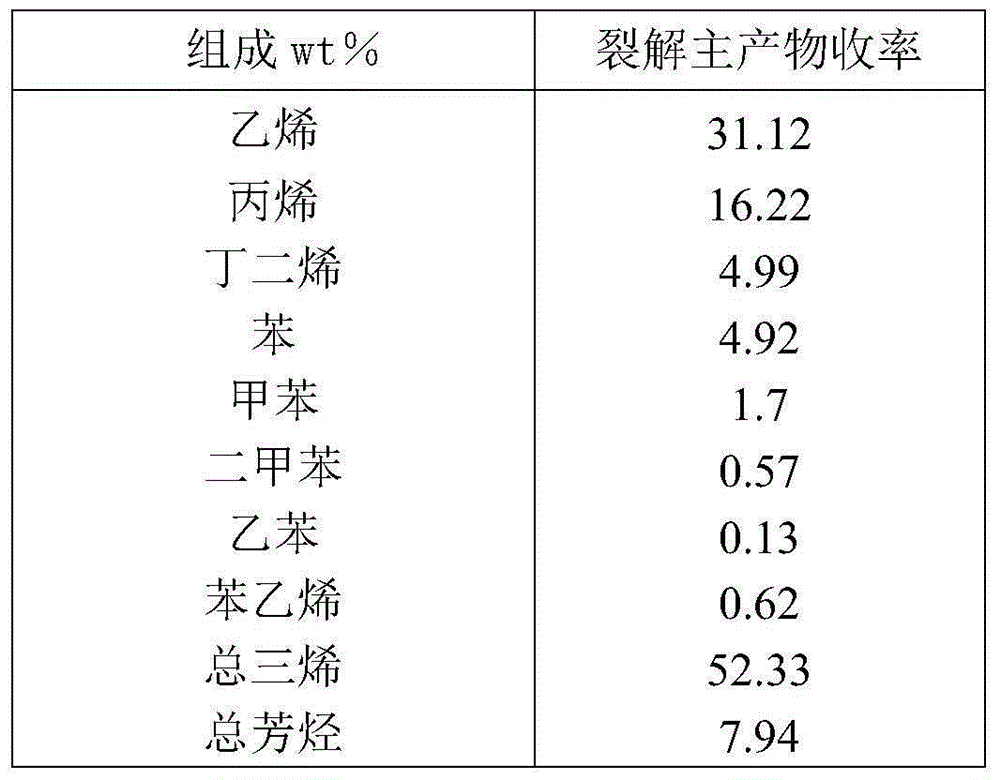
[0049] After the aromatic-poor stream obtained in Example 2 is heated to 60°C and mixed with water vapor heated to 180°C at a dilution ratio of 0.5, it is introduced into the tubular furnace hydrocarbon thermal cracking reactor. The operating temperature is 835°C, and the residence time is The cleavage reaction was carried out under the condition of 0.247s to obtain rich C 2 Alkenes, C 3 Alkenes and C 4 Products of olefins, cracked fuel oils and C 6 ~C 9 The hydrocarbon mixture of aromatic hydrocarbons, the yield of the main product of cracking is shown in Table 5; 6 ~C 9 After hydrogenation, the hydrocarbon mixture of aromatics is mixed with the crude aromatics stream to enter the aromatics separation process to obtain aromatics products such as benzene, toluene, and xylene. The total yield of aromatics is shown in Table 6.
[0050] Table 5: The cleavage yield of the main cleavage products
[0051]
[0052] Table 6: Total Aromatics Yield
[0053]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com