Kitchen waste treatment process with reclamation, harmlessness and reduction
A technology for kitchen waste and treatment process, applied in the direction of fatty acid esterification, fatty substance recovery, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of incomplete oil recovery, low oil recovery efficiency, low degree of resource utilization, etc. Easy to control conversion efficiency and complete resource utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1 Utilizes the new technology of the present invention to the processing situation of kitchen waste in a certain university canteen
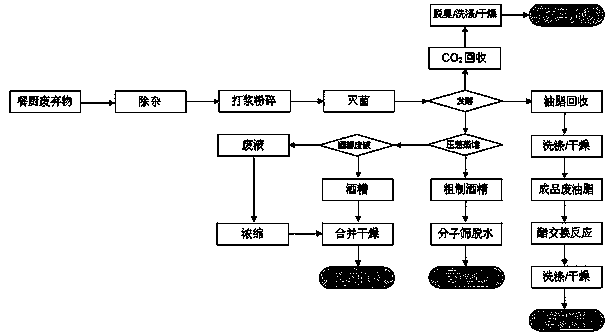
[0036] S1. Removal of impurities: Remove disposable plastic lunch boxes, chopsticks, paper cups and other debris from the kitchen waste collected in the university canteen.
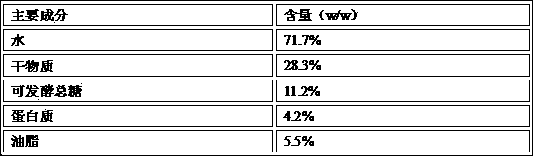
[0037]S2. Beating and pulverizing: directly beat and pulverize the above-mentioned kitchen waste after impurity removal, and then use the Kjeldahl method, Soxhlet extraction method and starch acid hydrolysis method to determine the protein, oil and Fermented total sugar (including starch) and other main components, the results are as follows:
[0038]
[0039] S3. Sterilization: The above-mentioned beaten and pulverized kitchen waste was sterilized at 121° C. for 15 minutes, and cooled for later use.
[0040] S4. Fermentation:
[0041] S41. Preparation of seed liquid: Inoculate the preserved glycerol strain of Stainphagocystis No. 1 into 2mL YPD (cont...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment 2 Utilize the new process of the present invention to the processing situation of a restaurant kitchen waste
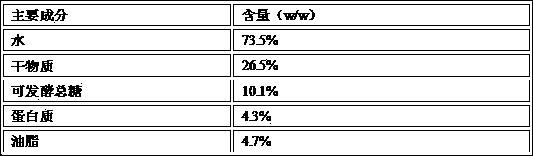
[0049] The differences between this embodiment and Example 1 are: the source of the kitchen waste in step S1 is the restaurant; the main components of the kitchen waste in S2 are different (see the table below); the sterilization temperature in S3 is 105°C, The time was 40 minutes; the cell concentration of the mature seed solution in S41 was 120 million / mL; the inoculum size in S42 was 5%, and the conditions of the pre-fermentation stage were different (temperature was 28°C, stirring speed was 300 rpm, stirring culture was 5 Hours); the main fermentation conditions in S43 are different (temperature is 28°C, stirring speed is 0 rpm, cultured for 60 hours); the transesterification reaction conditions in S6 are to add 1% (w / w) concentration to waste oil Sodium ethoxide and absolute ethanol with a molar ratio of alcohol to oil of 15:1 were reacted at 25...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Embodiment 3 Utilize the new technology of the present invention to the processing situation of certain restaurant kitchen waste
[0053] The differences between this embodiment and Example 1 are: the source of the kitchen waste in step S1 is a restaurant; the main components of the kitchen waste in S2 are different (see the table below); the sterilization temperature in S3 is 90°C, The time was 60 minutes; the cell concentration of the mature seed solution in S41 was 0.8 billion / mL; the inoculum size in S42 was 15%, and the conditions of the pre-fermentation stage were different (temperature was 32°C, stirring speed was 100 rpm, stirring culture was 3 hour); the main fermentation conditions in S43 are different (temperature is 32°C, stirring speed is 50 rpm, and culture is 36 hours); the transesterification reaction condition in S6 is to add 1.5% (w / w) concentration to the waste oil Sodium ethoxide and absolute ethanol with a molar ratio of alcohol to oil of 10:1 were ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com