Lipase gene COLIP and lipase encoded by same
A lipase gene and coding technology, applied in the field of genetically engineered bacteria, can solve problems such as premature termination of expression, low protein expression, and impact on gene expression, and achieve the effect of reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Design and synthesis of embodiment 1 lipase gene COLIP sequence
[0029] With the aid of BioEdit software, the amino acid sequence of lipase was deduced to ensure that the active center and specific spatial structure characteristics of lipase remained unchanged, and the protease action site in lipase was eliminated to prevent its degradation. With the aid of DNA2.0 software (https: / / www.dna20.com / ), the amino acid sequence was converted into a nucleotide sequence, and a lipase gene COLIP was designed. During the design process, the following influencing factors were mainly improved: for synonymous codons of the same amino acid, the high-frequency codons of Pichia pastoris were used to replace the original low-frequency codons (among them, in the amino acid sequence of lipase, there are 21 amino acids There are synonymous codons, and the usage frequency of the synonymous codons in Pichia pastoris is shown in Table 1); the complex mRNA secondary structure is eliminated, a...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The construction of embodiment 2 Pichia pastoris recombinant genetically engineered bacteria GS115 (COLIP)
[0035] Firstly, the synthetic lipase gene COLIP was connected to pMD18-T simple vector (from Bao Biological Engineering Co., Ltd., product number: 3271). Each 10 μL ligation system contained 1 μL pMD18-T simple vector, 5 μL buffer, 2 μL lipase gene COLIP, 2 μL water, and ligated overnight at 4°C. The ligation mixture was transformed into Escherichia coli (from the China Center for Type Culture Collection, the collection number is CCTCCAB93006), and the recombinant plasmid pMD-COLIP containing the lipase gene COLIP was obtained after detection by PCR. The transformation system of Escherichia coli is: 10 μL of ligation system and 100 μL of Escherichia coli competent cells. The transformation process was: put the ligation mixture on ice for 15 min, then place the ligation mixture at 42°C for 80 sec; then place it on ice for 2 min; add 0.8 mL of LB liquid medium to ...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Fermentation of embodiment 3 Pichia pastoris recombinant genetically engineered bacteria GS115 (COLIP)
[0040] Seed culture: inoculate the activated recombinant Pichia pastoris genetically engineered strain GS115 (COLIP) into 50 mL (250 mL Erlenmeyer flask) seed medium YPD, and cultivate at 28° C. and 250 r / min for 20 hours. The formula of the seed medium YPD is: formula: 1% yeast extract powder, 2% peptone, 2% glucose.
[0041] Fermenter medium: glucose 40g / L, KH 2 PO 4 20g / L, CaSO 4 1g / L, (NH4) 2 SO 4 5g / L, MgSO 4 .7H 2 O10g / L, K 2 SO 4 14g / L, CuSO 4 0.002g / L, MnSO 4 .H 2 O0.003g / L, ZnCl 2 0.007g / L, FeSO 4 .7H 2 O0.007g / L, biotin 0.004g / L.
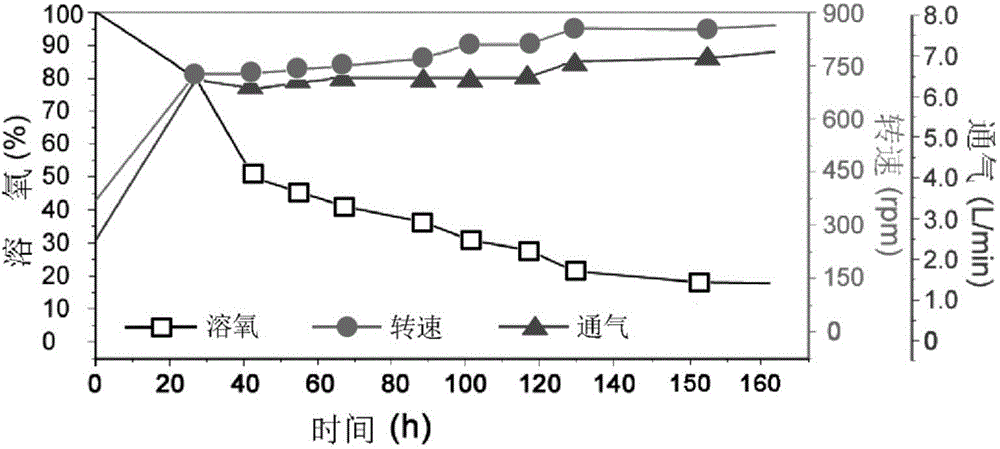
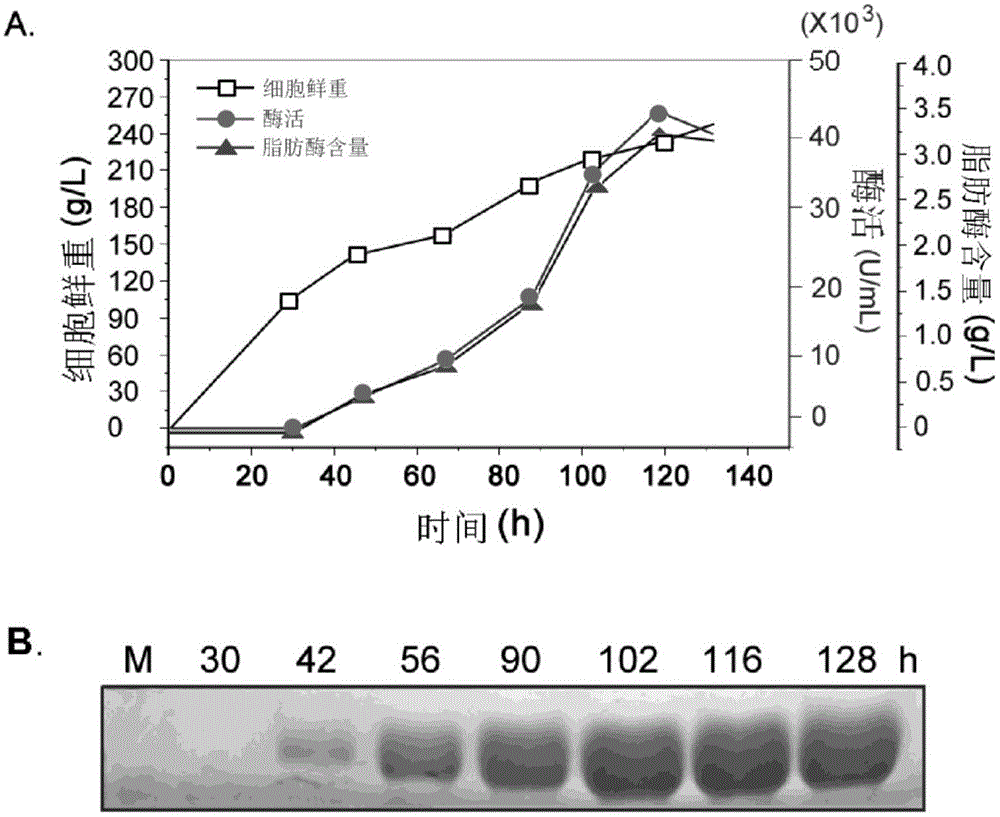
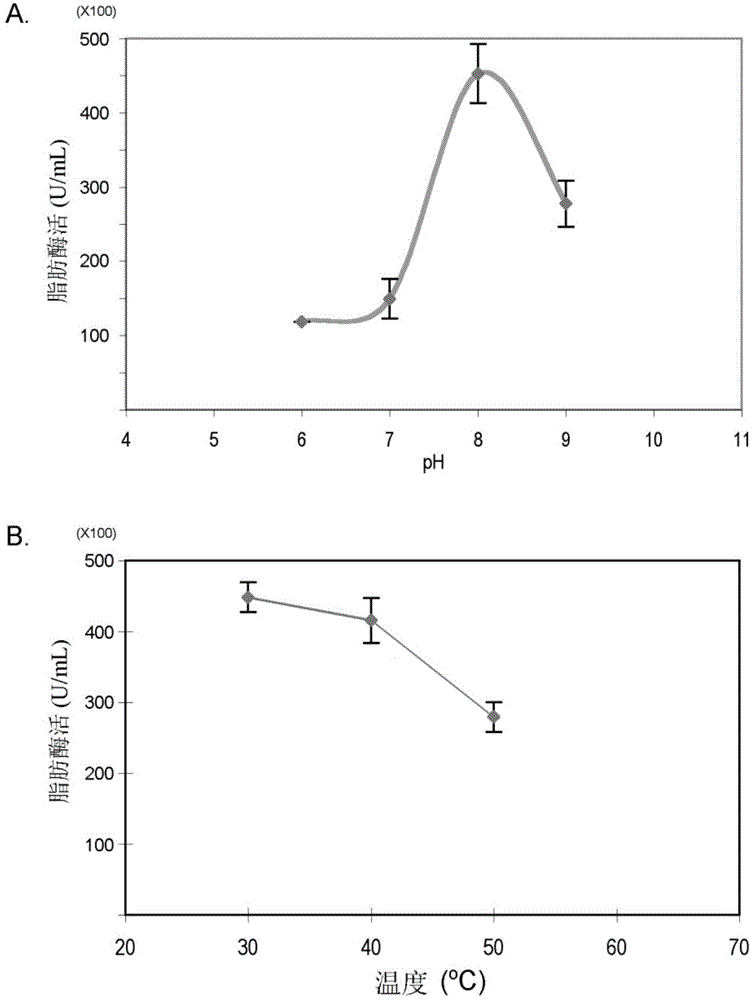
[0042] Fermentation tank fermentation: under the conditions of the fermentation tank, the above-mentioned seed liquid was inserted into a 10L fermentation tank (the volume of the fermentation medium was 8L) according to the inoculation amount of 5% (V / V), and after culturing at 28°C for 24 hours, 400mL of 20wt was ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com