Preparation method for high-dispersion superfine nanometer Mo-Cu compound powder
An ultra-fine nano, composite powder technology, applied in the field of powder metallurgy preparation, can solve the problems of complex process, high equipment requirements, long preparation period, etc., and achieve the effects of easy process, uniform structure distribution and high density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] (1) Take by weighing 16.94g sodium molybdate dihydrate, 7.70g cupric chloride dihydrate, measure 0.1L mass fraction and be the strong ammoniacal liquor of 25%, be mixed with the aqueous solution of sodium molybdate, the ammonia solution of cupric chloride, mix Add deionized water to make a 0.5L mixed solution.
[0024] (2) Divide the solution prepared in (1) into four equal portions, place them in a magnetically stirred constant temperature water bath container and heat in a 60° C. water bath for 10 minutes.
[0025] (3) The solution obtained in (2) is filtered, washed and dried.
[0026] (4) Calcining the precipitate obtained in (3) at 350° C. in air for 1 h to obtain molybdenum-copper oxide composite powder.
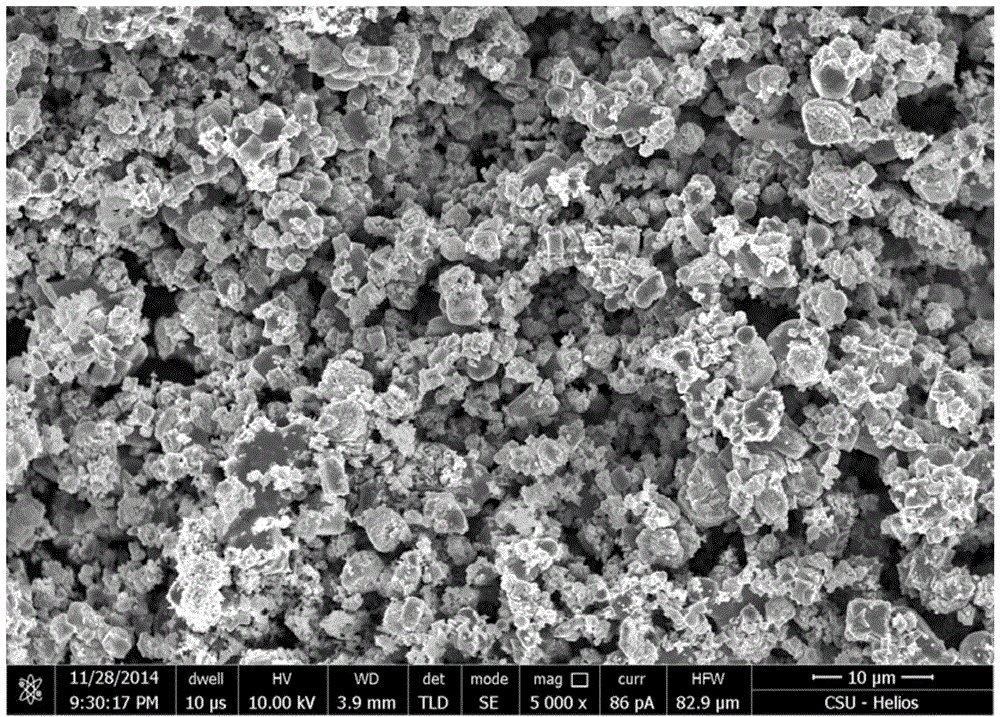
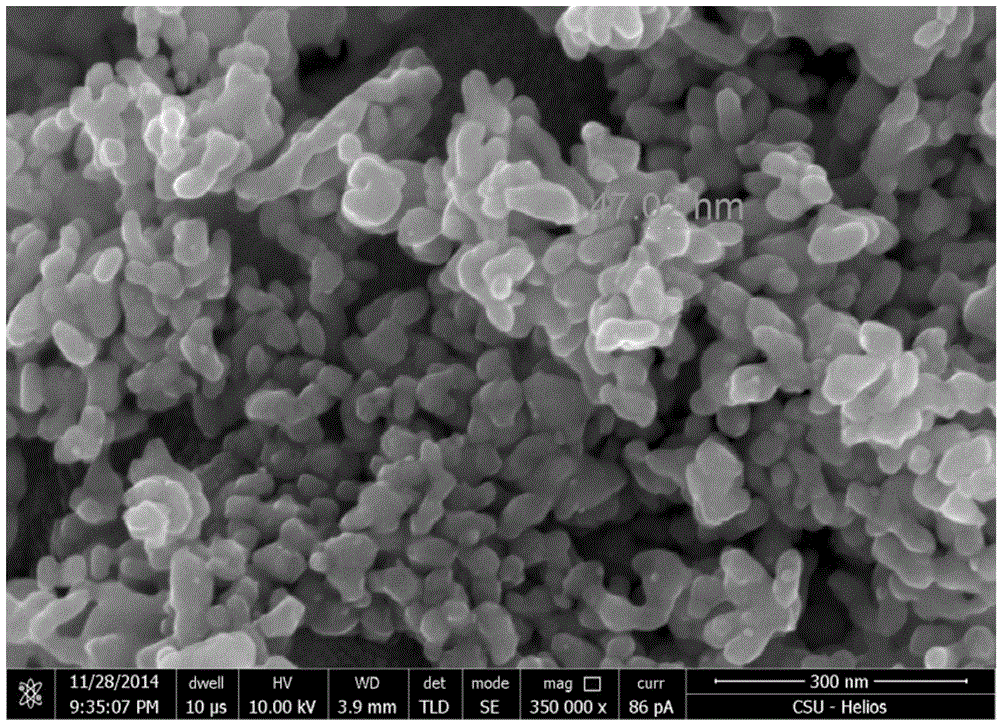
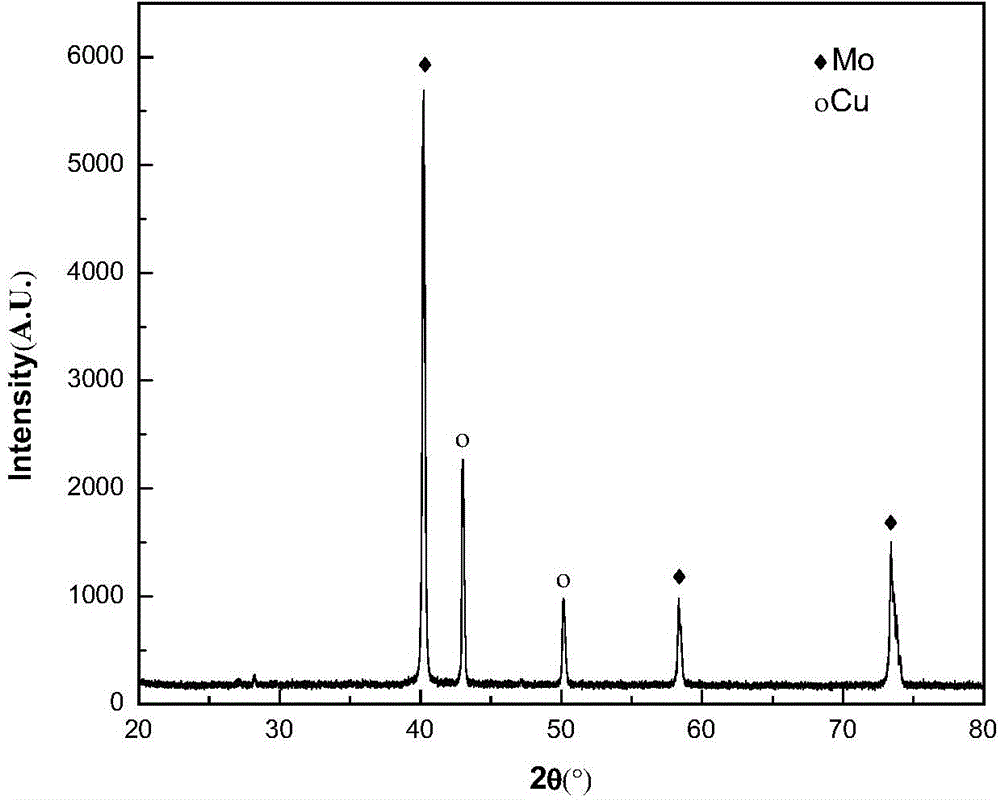
[0027] The composite powder prepared in (4) was kept in H2 at 750° C. for 2 hours to obtain 70Mo-30Cu nano-molybdenum-copper composite powder. from figure 1 It can be seen that the powder obtained in Example 1 is composed of molybdenum and copper.
[0028] D...
Embodiment 2
[0033] (1) Take by weighing 19.36g sodium molybdate dihydrate, 5.17g cupric chloride dihydrate, measure 0.08L mass fraction and be the strong ammoniacal liquor of 28%, be mixed with the aqueous solution of sodium molybdate, the aqueous ammonia solution of cupric chloride, mix Add deionized water to make a 0.5L mixed solution.
[0034] (2) Divide the solution prepared in (1) into four equal portions, place them in a magnetically stirred constant temperature water bath container and heat in a water bath at 80° C. for 5 minutes.
[0035] (3) The solution obtained in (2) is filtered, washed and dried.
[0036] (4) Calcining the precipitate obtained in (3) at 450° C. in air for 0.5 h to obtain molybdenum-copper oxide composite powder.
[0037] (5) Heat the composite powder prepared in (4) at 600° C. for 3 h in H2 to obtain 80Mo-20Cu nanomolybdenum-copper composite powder.
Embodiment 3
[0039] (1) Take by weighing 18.88g sodium molybdate dihydrate, 10.77g cupric chloride dihydrate, measure 0.1L mass fraction and be the strong ammoniacal liquor of 26%, be mixed with the aqueous solution of sodium molybdate, the ammonia solution of cupric chloride, mix Add deionized water to make a 0.5L mixed solution.
[0040] (2) Divide the solution prepared in (1) into four equal portions, place them in a magnetically stirred constant temperature water bath container and heat in a water bath at 70° C. for 15 minutes.
[0041] (3) The solution obtained in (2) is filtered, washed and dried.
[0042] (4) Calcining the precipitate obtained in (3) at 400° C. in air for 2.5 hours to obtain molybdenum-copper oxide composite powder.
[0043] (5) Heat the composite powder prepared in (4) at 800° C. for 2 h in H2 to obtain 65Mo-35Cu nanomolybdenum-copper composite powder.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com