In-situ synthesis of cadmium oxide nanometer gas-sensitive element with secondary pore structure
An in-situ synthesis, cadmium oxide technology, applied in the field of gas sensing elements, can solve the problems of in-situ synthesis of gas sensing elements, such as less research, complex preparation process, poor ether selectivity, etc. selective effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
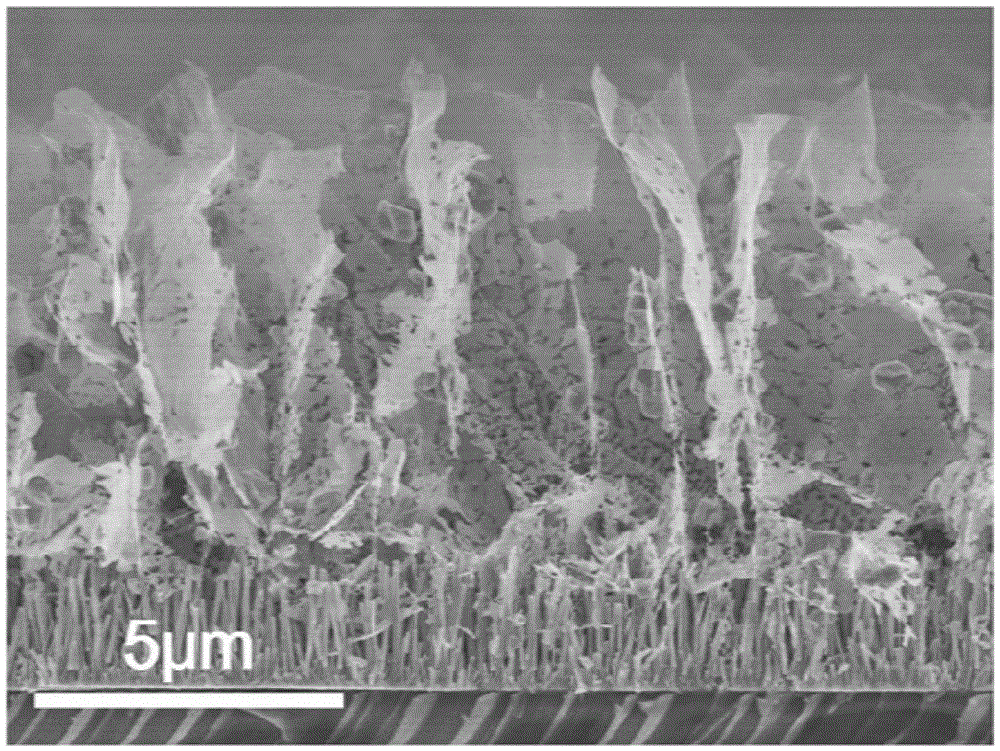
[0030] (1) Synthesis of ZnO nanorod array seed layer
[0031] ①Using ethylene glycol monomethyl ether as a solvent, prepare a mixed solution of zinc acetate at a concentration of 0.1M and ethanolamine at a concentration of 0.2M; immerse the glass slide in the above solution for 30 seconds, and then place the glass slide base in an oven Drying treatment; after repeating the above operation twice, anneal the above glass slide substrate in air at 500°C for 1 hour, so that the seed layer is in firm contact with the glass slide substrate;
[0032] ② Using deionized water as a solvent, prepare a mixed solution of 0.025M zinc nitrate and 0.025M hexamethylenetetramine;
[0033] Take 80ml of the above mixed solution in the reaction kettle, and put the above glass slide substrate into the reaction kettle filled with the mixed solution, with the side with the seed layer facing down, and the height of the mixed solution is just below the substrate;
[0034] ③Put the reaction kettle in an...
Embodiment 2
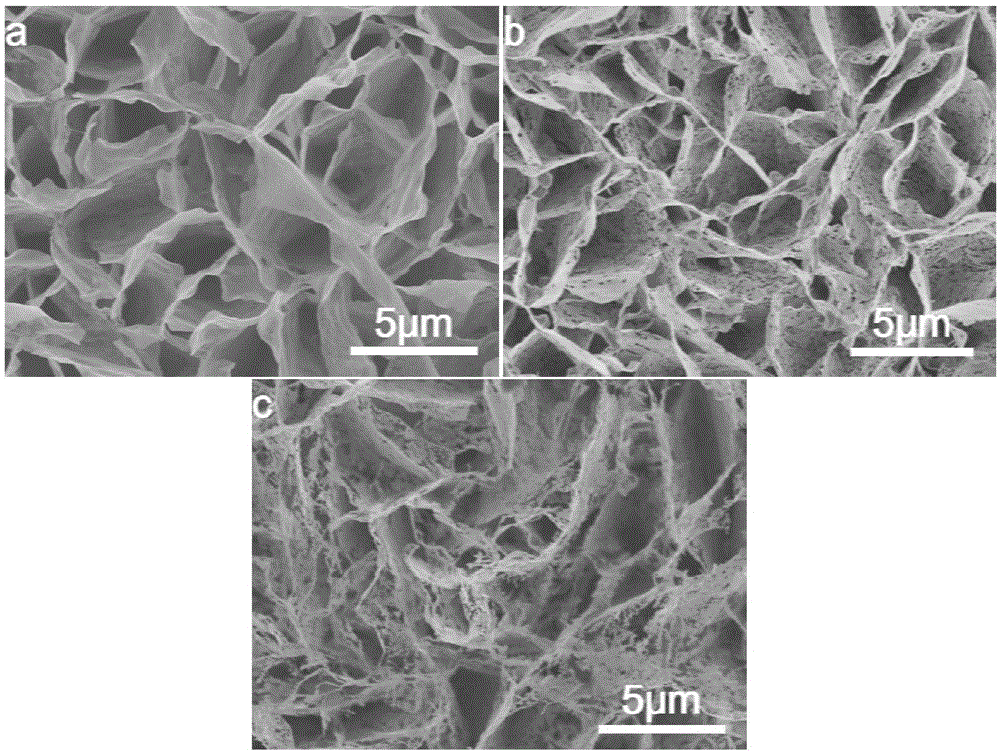
[0042] The present embodiment is similar to embodiment 1, and the difference is: the oxidation temperature of cadmium oxide in step (2) 3. is 360 ℃, by figure 2 -a It can be seen that at this working temperature, the morphology of the obtained cadmium oxide is a complete nanosheet array. At this oxidation temperature, under the same conditions, the sensitivity of the bilayer structure to ether is 36%, and the response and recovery time are 22s and 51s, respectively.
Embodiment 3
[0044] This example is similar to Example 1, except that the oxidation temperature of cadmium oxide in step (2)③ is 440°C. Depend on figure 2 -c It can be seen that at this working temperature, the morphology of the obtained cadmium oxide is spongy cadmium oxide. At this temperature, under the same conditions, the sensitivity of the bilayer structure to ether is 43%, and the response and recovery time are 44s and 57s, respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com