Paenibacillus elgii D7 and application thereof to cellulose degradation
A technology of bacillus and cellulose, applied in the application of degrading cellulose, the field of new strains of cellulose degradation, can solve the problems of less research, and achieve the effects of easy cultivation, mild degradation conditions, and easy extraction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1: Screening of cellulose degrading bacteria
[0029] Tobaccowasteextract (tobaccowasteextract, referred to as TWE), domestic existing papermaking tobacco sheet production process (see Figure 14 shown), the specific preparation method is: add water to tobacco chips, tobacco powder or tobacco stems, extract at 55°C-65°C for 20min-80min, and the volume of water used is about 8 times the mass of raw materials. After solid-liquid separation, the solid part (which can be directly used as cellulose for the degradation of Paenibacillus D7) is made into a paper base after pulping, and the liquid part is sprayed or soaked on the paper base after concentration, wherein the liquid part (i.e. (extract of waste tobacco leaves) is concentrated until no liquid flows out, washed with water, and dried to obtain a concentrate.
[0030] Take 1ml of the above waste tobacco leaf extract, add water to dilute the waste tobacco leaf extract to 10 -4 、10 -5 、10 -6 , spread on th...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: Identification of cellulose-degrading bacteria
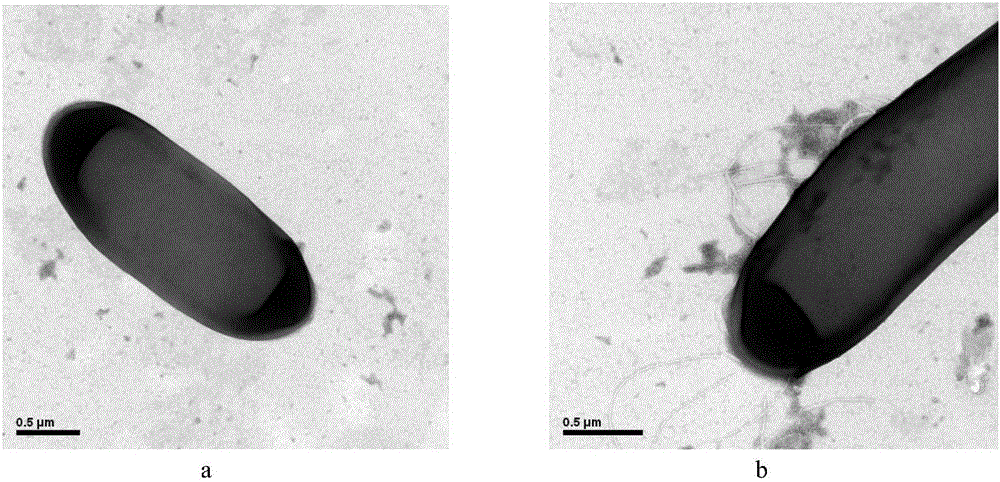
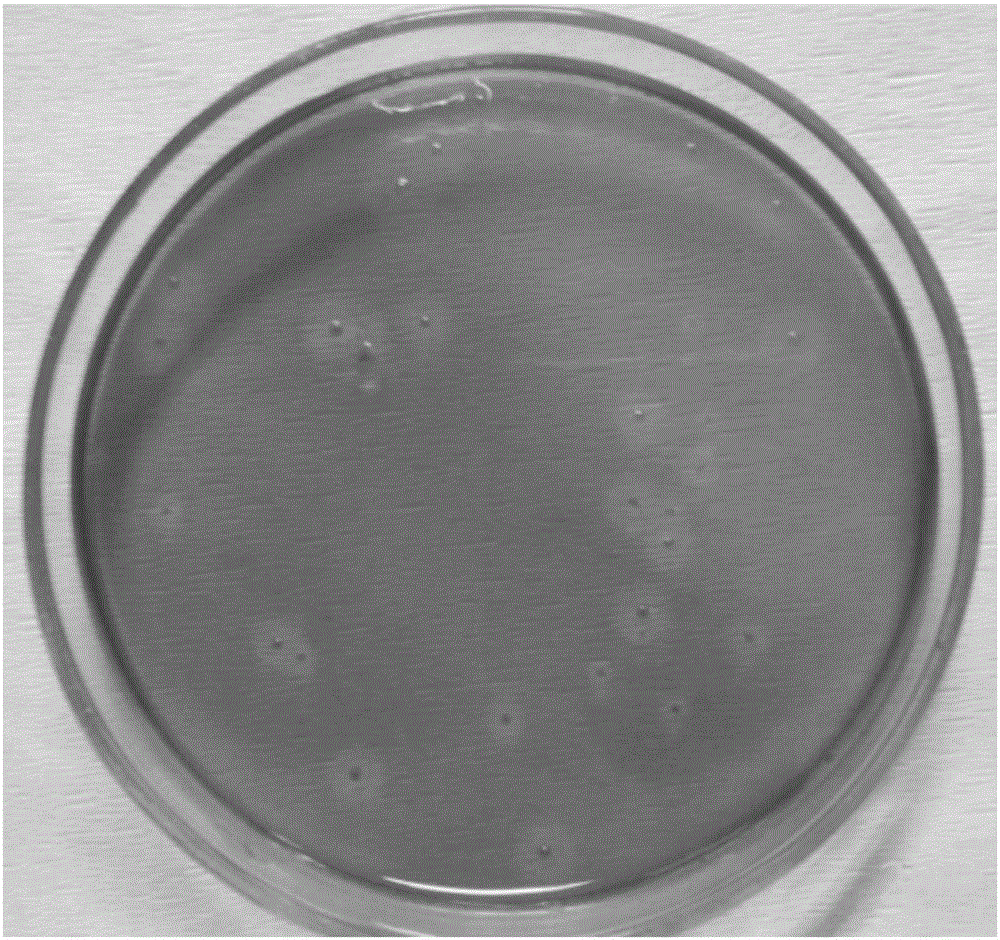
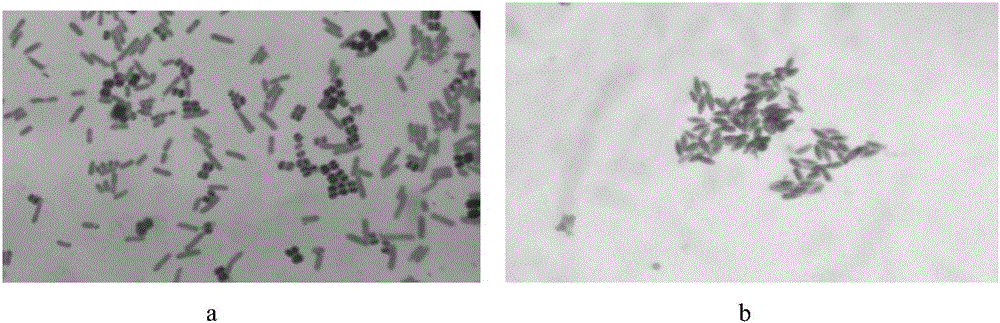
[0040] On the primary screening medium, three strains with larger transparent circles were selected and inserted into the Congo red cellulose screening medium for re-screening, and the strain with the highest enzyme activity was named D7, so the follow-up cellulase research Using D7 as the research object, the size of the transparent circle produced by D7 (see figure 1 As shown) the colony shape is round, milky white, with a moist surface, and the ratio of colony diameter to transparent ring diameter is 2:7. TEM observation results (see figure 2 shown), strain D7 was rod-shaped with flagella. Gram-negative, spore-forming (see image 3 shown). The results of the physiological and biochemical characteristics of the strain were: starch hydrolysis, nitrate reduction, contact enzyme test, cellulose hydrolysis were positive, while indole test, urea test, citrate, H 2 S test was negative.
[0041] The bacterial...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3: Growth characteristics and enzyme production of Paenibacillussp.D7
[0043] (1) Slant culture: inoculate Paenibacillus D7 into the slant culture medium, cultivate at 37° C. for 24 hours to obtain slant bacteria; the final concentration of the slant culture medium consists of: sodium chloride 10 g / L, peptone 10 g / L, Yeast extract 5g / L, agar 18g / L, solvent is water, pH is 7.0.
[0044] (2) Seed culture: inoculate the slant bacteria in step (1) into the seed medium, cultivate at 37°C for 24 hours, and obtain the seed liquid; the final concentration of the seed medium consists of: sodium chloride 10g / L, peptone 10g / L L, yeast extract 5g / L, solvent is water, pH is 7.0.
[0045] (3) Fermentation culture: inoculate the seed liquid into the fermentation medium with an inoculum volume concentration of 1%, and cultivate it at 37° C. and 180 r / min for 24 hours to obtain a fermentation liquid. Sampling was taken to determine the dry weight of the bacteria, and the stan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com