Method for loading nanometer metal phosphide on porous carbon
A technology for supporting metals and phosphides, which is applied to phosphides, phosphorus compounds, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming and energy-consuming, difficult to achieve, and slow heating rate in the reduction process, and achieve uniform size and low cost. , the effect of high monodispersity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
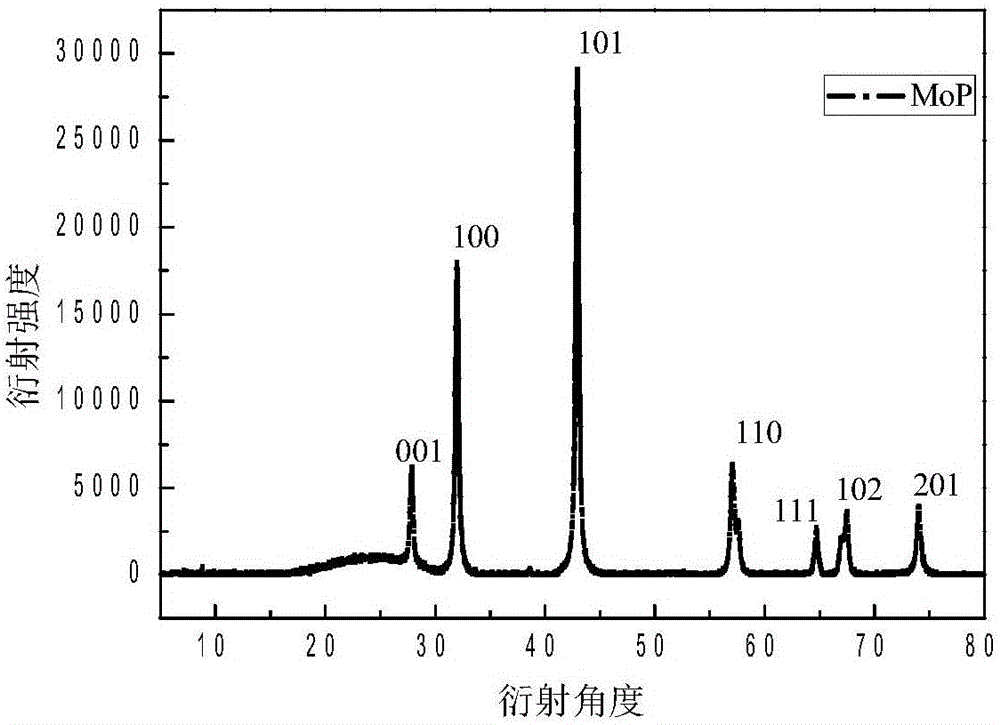
[0028] Example 1: Porous carbon loaded MoP
[0029] Synthetic raw materials: glucose, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, ammonium molybdate
[0030] (1) Weigh 1g glucose, 0.01g ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and 0.1g ammonium molybdate (H 24 Mo 7 N 6 o 24 ?4H 2 O) Put it in a 100ml beaker, then grind the medicine in the beaker with a mortar for 10 minutes, and then heat it to form a molten state;
[0031] (2) Put the molten material in (1) in a crucible tank and put it in a tube furnace, and put the sample at 800°C H 2 Calcined under the same conditions for 5 hours, a dark brown bulky solid was obtained, which was determined to be molybdenum carbide (MoP) supported on porous carbon by XRD.
Embodiment 2
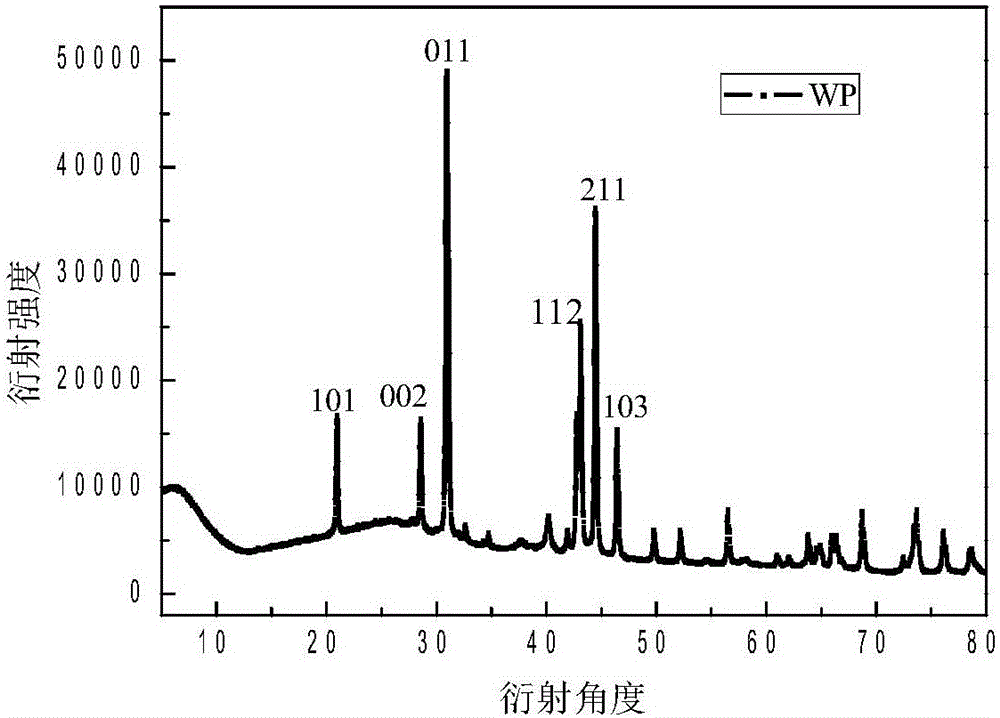
[0032] Example 2: Porous carbon loaded nano WP
[0033] Synthetic raw materials: glucose, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, ammonium tungstate
[0034] (1) Weigh 2g glucose, 0.5g ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.3g ammonium tungstate ((NH 4 )10H 2 (W 2 o 7 ) 6 ) in a 100mL beaker, heated and stirred to form a molten state;
[0035] (2) Afterwards, put the beaker into an oven at 120°C and react for 4 hours to obtain a dark brown puffy solid.
[0036] (3) Grind the product obtained in (2) with a mortar and put it in a crucible. The product obtained from the reaction was heated at 800°C 2 Under the condition of heat treatment for 7 hours, the porous carbon supported WP was obtained.
Embodiment 3
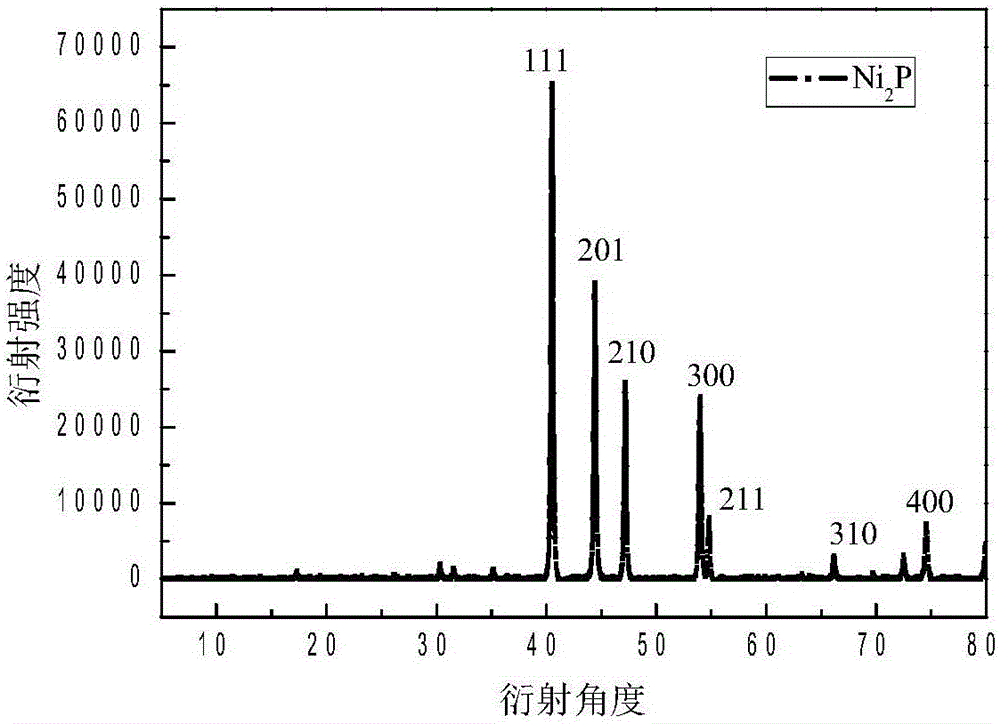
[0037] Example 3: Porous carbon loaded nano-Ni 2 P
[0038] Synthetic raw materials: sucrose, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, nickel nitrate
[0039] (1) Weigh 3g sucrose, 0.5g ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and 2.5g nickel nitrate (Ni(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2O) Put it in a 100mL beaker, then place the beaker in a heatable magnetic stirrer, raise the temperature of the magnetic stirrer to 120°C, and keep stirring for 10min until the drug in the beaker forms a molten state.
[0040] (2) Afterwards, put the molten liquid into an oven at 180°C and react for 48 hours to obtain a dark brown fluffy solid.
[0041] (3) Grind the product obtained in (2) with a mortar and put it in a crucible. The product obtained from the reaction was heated at 700°C in 5% H 2 / Ar heat treatment for 5 hours to obtain porous carbon supported Ni 2 p.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com