Biochemical compound soil heavy metal pollution fixed remediation agent and application
A biochemical and fixed restoration technology, applied in the restoration, application, soil conditioning materials and other directions of polluted soil, can solve problems such as limiting the application of heavy metal treatment in soil, and achieve a short period of treatment of heavy metal pollution, strong operability, and a preparation method. simple effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
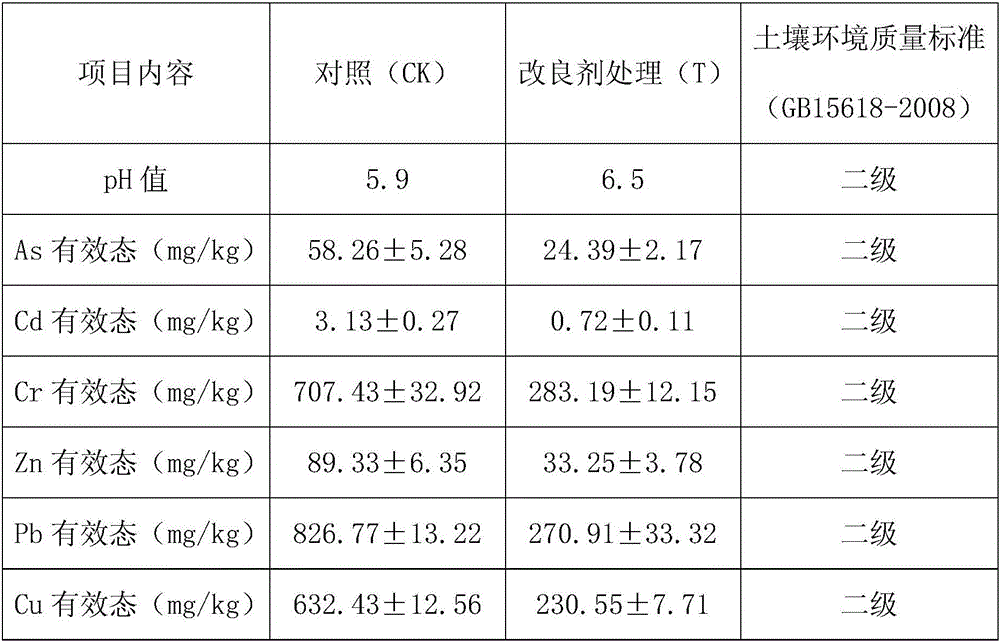
[0030] The experimental soil was taken from the 0-25cm soil layer soil of a vegetable field polluted by heavy metals in a suburb of Guangzhou City. The effective state adopts the DTPA-TEA method, and the soil As effective state is measured by 0.5ml.L-1NaHCO 3 Leaching method; the mass ratio of each raw material used to treat the soil is mercapto bentonite (montmorillonite: sepiolite=3:1, and it is formed through mercapto modification, any conventional mercapto modification technology can be used, the same below ): zeolite (120 mesh): iron powder (120 mesh): mercapto chitosan (90% food grade chitosan modified by thioglycolic acid): photosynthetic bacteria: actinomycetes: yeast: lactic acid bacteria [wherein photosynthetic The bacteria are Rhodopseudomonas palustris (strain number CICC 23812); It is an industrial strain of Enterococcus faecalis (strain preservation number: CICC 20422), purchased from the China Industrial Microorganism Culture Collection Center, and formed throu...
Embodiment 2
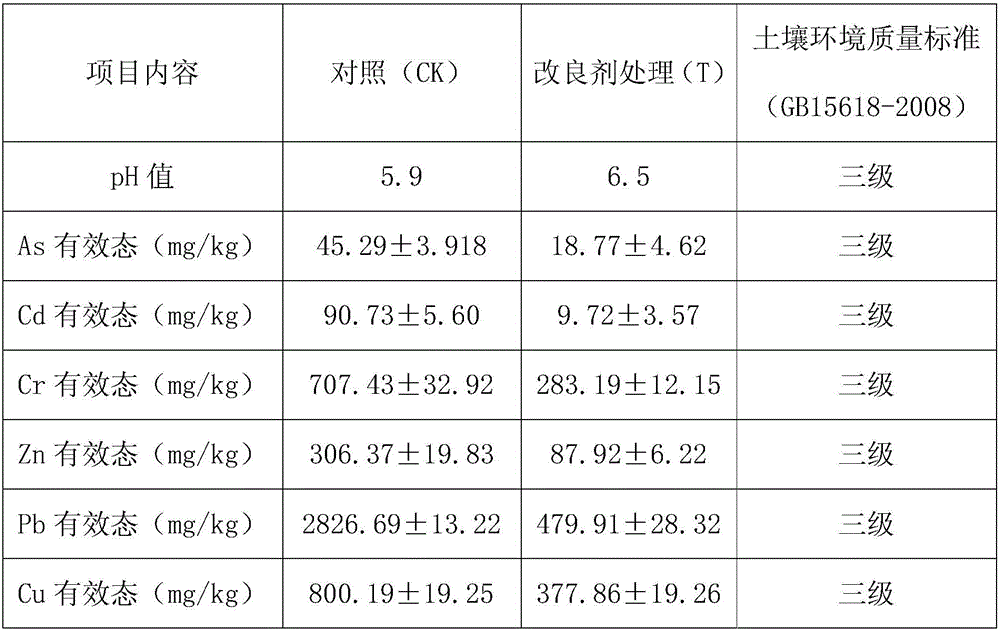
[0035] The experimental soil was taken from the soil 20-25cm below the surface layer polluted by heavy metals near a battery factory in Dongguan City. The effective state adopts the DTPA-TEA method, and the soil As effective state is measured by 0.5ml.L-1NaHCO 3Leaching method; the mass ratio of each raw material used to treat the soil is mercapto bentonite (montmorillonite: sepiolite=3:1, and modified by mercapto): zeolite (120 mesh): iron powder (120 mesh) : Mercapto-chitosan (90% food-grade chitosan modified by thioglycolic acid): Photosynthetic bacteria: Actinomycetes: Saccharomyces: Lactic acid bacteria [wherein the photosynthetic bacteria is Rhodopseudomonas palustris (strain number CICC 23812) ; Actinomycetes is Nocardia corals (bacterial strain number CICC 23623); Yeast is Candida tropicalis (bacterial strain preservation number: CICC 1253); Lactic acid bacteria is the industry of Enterococcus faecalis (bacterial strain preservation number: CICC 20422) Bacteria, purch...
Embodiment 3
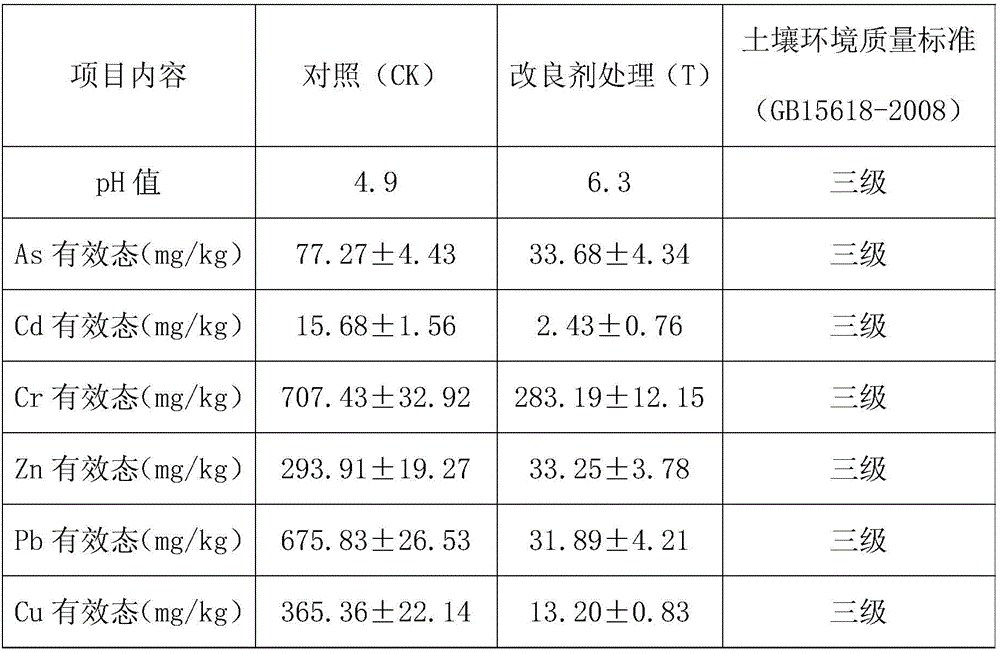
[0039] The experimental soil was taken from the soil 20-25 cm below the surface of a mining area polluted by heavy metals in a suburb of Heshan City, Guangdong Province. The effective state adopts the DTPA-TEA method, and the soil As effective state is measured by 0.5ml.L-1NaHCO 3 Leaching method; the mass ratio of each raw material used to treat the soil is mercapto bentonite (montmorillonite: sepiolite=3:1, and modified by mercapto): zeolite (120 mesh): iron powder (120 mesh) : Mercapto-chitosan (90% food-grade chitosan modified by thioglycolic acid): Photosynthetic bacteria: Actinomycetes: Saccharomyces: Lactic acid bacteria [wherein the photosynthetic bacteria is Rhodopseudomonas palustris (strain number CICC 23812) ; Actinomycetes is Nocardia corals (bacterial strain number CICC 23623); Yeast is Candida tropicalis (bacterial strain preservation number: CICC 1253); Lactic acid bacteria is the industry of Enterococcus faecalis (bacterial strain preservation number: CICC 204...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com