RNA (ribonucleic acid) polymerase based multiplex detection method for NTPs (nucleoside triphosphates) by adopting in-vitro transcription machine, kit and application
A technology of RNA polymerase and in vitro transcription, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of inability to quickly detect NTP content and correlation changes, cytotoxicity, poor sensitivity and selectivity, and difficulty in satisfying rapid multiplexing Detection and other problems, to achieve instant and rapid monitoring, high sensitivity, efficient and fast detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Example 1
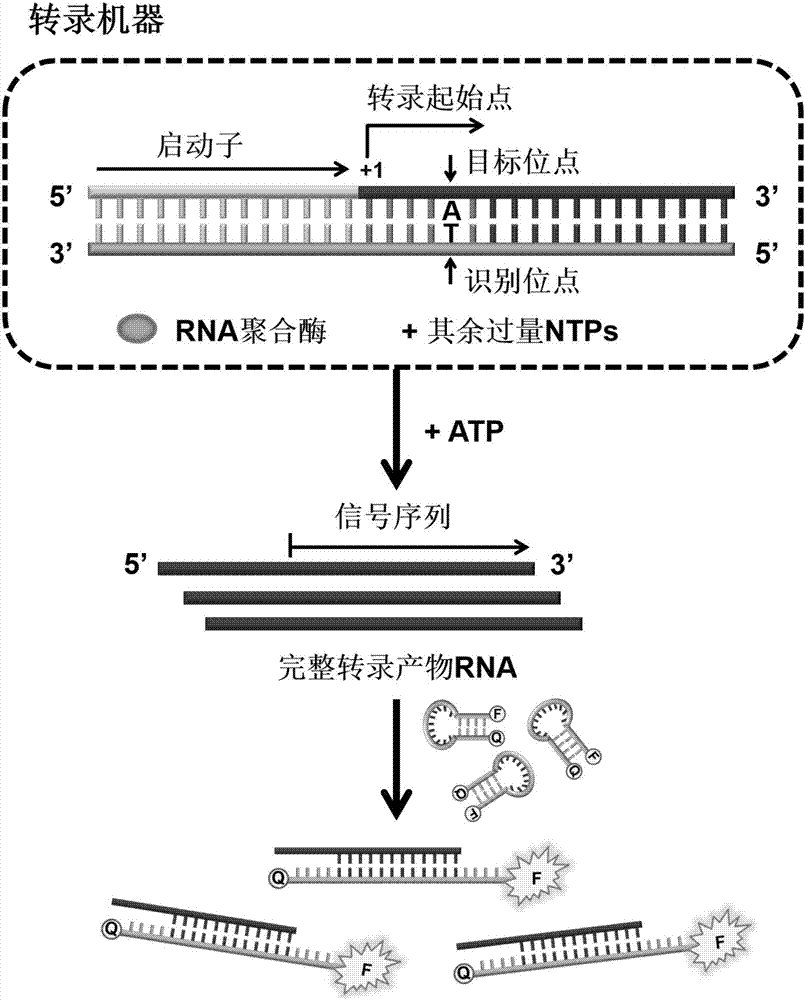
[0068] according to figure 1 Schematic diagram of the principle, using ATP as a model, in the presence of excess NTPs, when ATP is added to the in vitro transcription machine based on RNA polymerase, the transcription reaction will pass the recognition site smoothly, and the synthesis includes the ATP to be tested and the subsequent signal sequence The transcription product RNA, the signal sequence of the transcription product RNA is recognized by the ring part of the molecular beacon, so that the conformation of the molecular beacon changes and the signal of the fluorescent group is restored, thereby converting ATP into RNA in a 1:1 signal mode and fluorescent signals of molecular beacons.
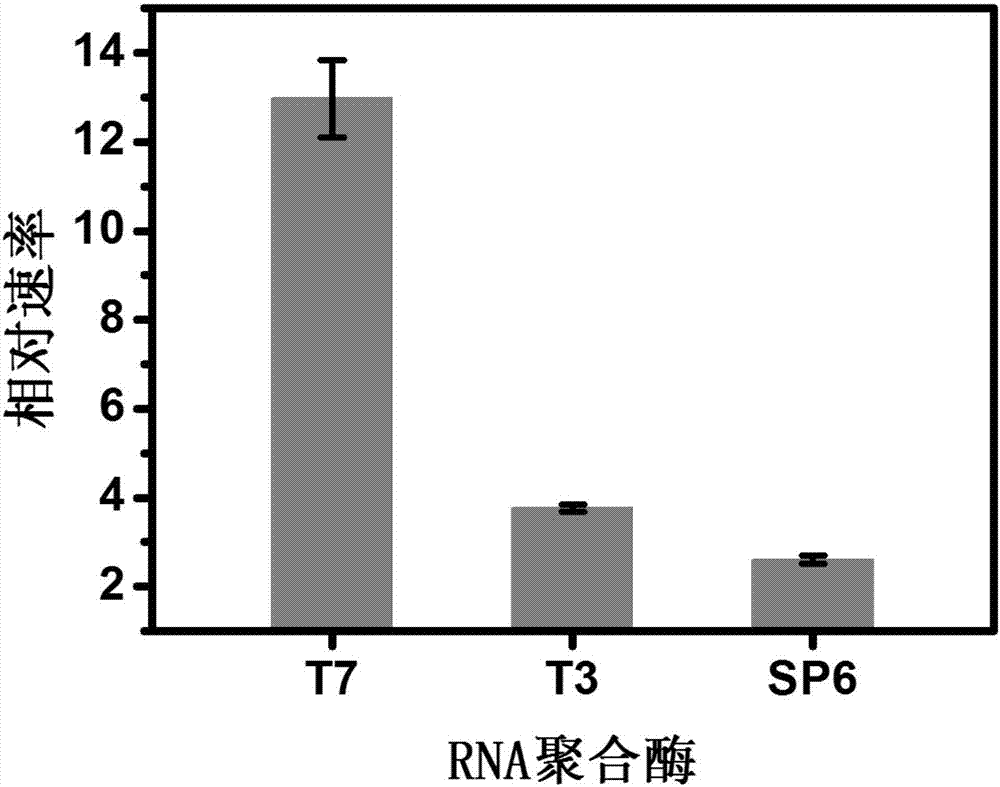
[0069] In order to compare the effects of three common commercial RNA polymerases on the performance of the in vitro transcription machine, T7 RNA polymerase, T3 RNA polymerase and SP6 RNA polymerase are selected, and the promoter regions of the template strand and the...
Embodiment 2
[0090] Example 2
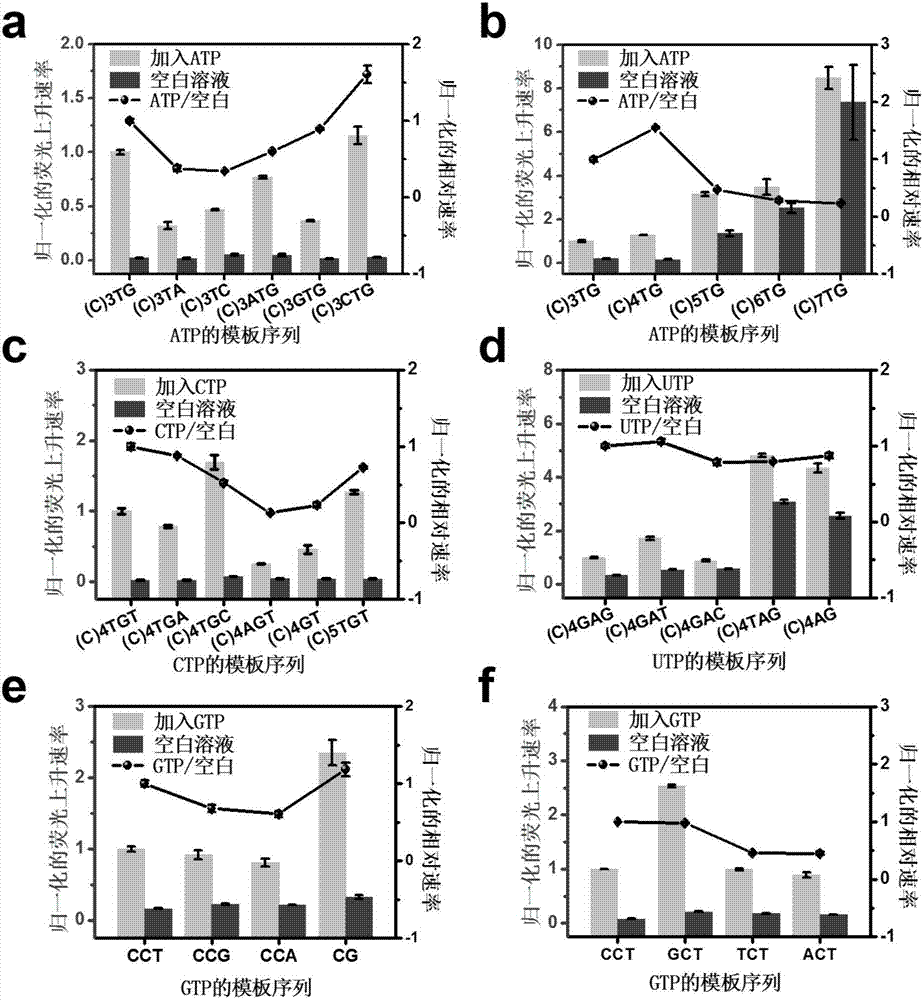
[0091] In this example, we first used ATP as the target, and when we changed the base types before and after the target site T, we found that the fluorescence rise rate of the target system and the blank system could be significantly changed, and thus the relative rate was affected. The relative rate is used as an indication of the signal window, and the larger the value, the larger the signal window and the better the performance of the transcription machine. When optimizing the sequence of the template transcription region of ATP, it is mainly divided into three steps: (1) fix the recognition site and the upstream sequence to be the same, and compare the downstream adjacent base types of the recognition site; (2) the downstream adjacent bases Set as the optimal base, change and compare the type of adjacent bases upstream and downstream of the recognition site; (3) set the upstream and downstream adjacent bases as optimal bases, and compare the number of b...
Embodiment 3
[0144] Example 3
[0145] According to the optimization results of the template sequence of the transcribed region of the above NTPs, the optimal template sequence of each NTPs was used to detect the concentration gradient of standard NTPs and draw a standard curve to obtain its linear range and detection limit.
[0146] The specific steps of detection are as follows:
[0147] Unless otherwise specified, the reaction volume is 20 μL, and the experimental conditions are 1x reaction buffer [100 μg / mL BSA, 40 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), 6 mM MgCl 2 , 2mM spermidine, 10mM DTT], the pre-hybridized template strand and coding strand (concentration ratio 1:1) dissolved in 1x reaction buffer, and the pre-annealed molecular beacon ( The final concentration is 200nM), and the remaining three non-test NTPs are added at a final concentration of 0.5mM, and an RNase inhibitor (final concentration 1U / μL) is added to avoid the degradation of the transcript RNA, and finally a certain concentration o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com