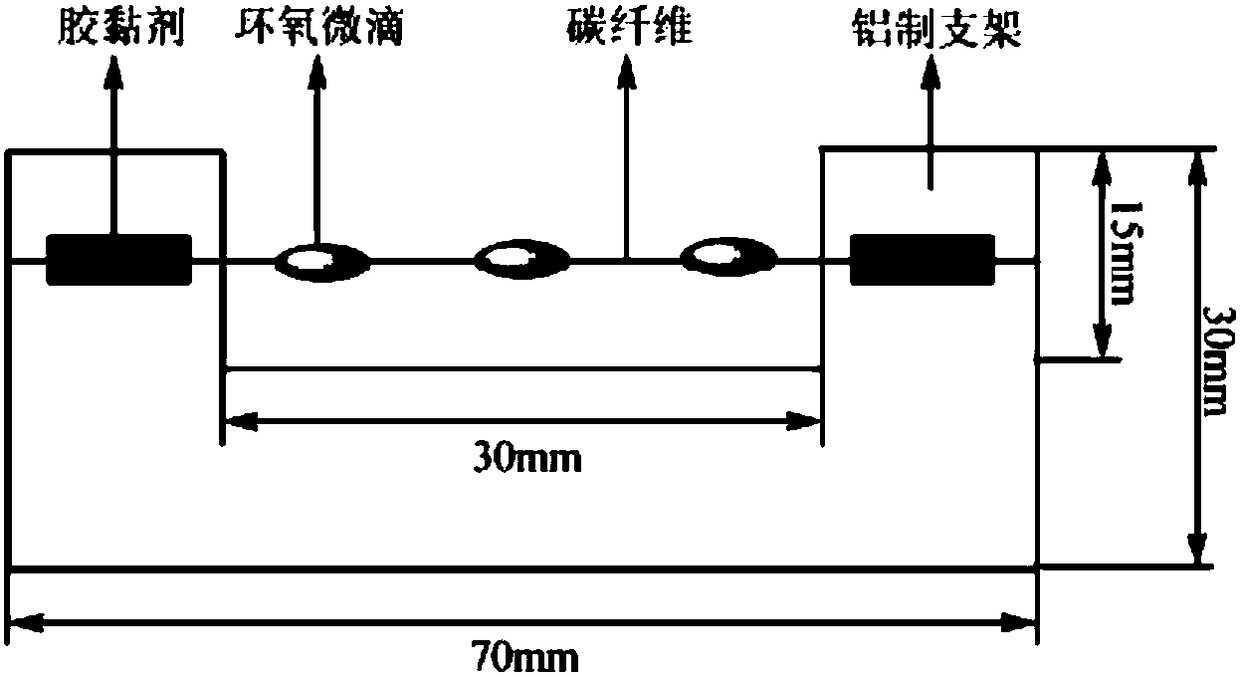
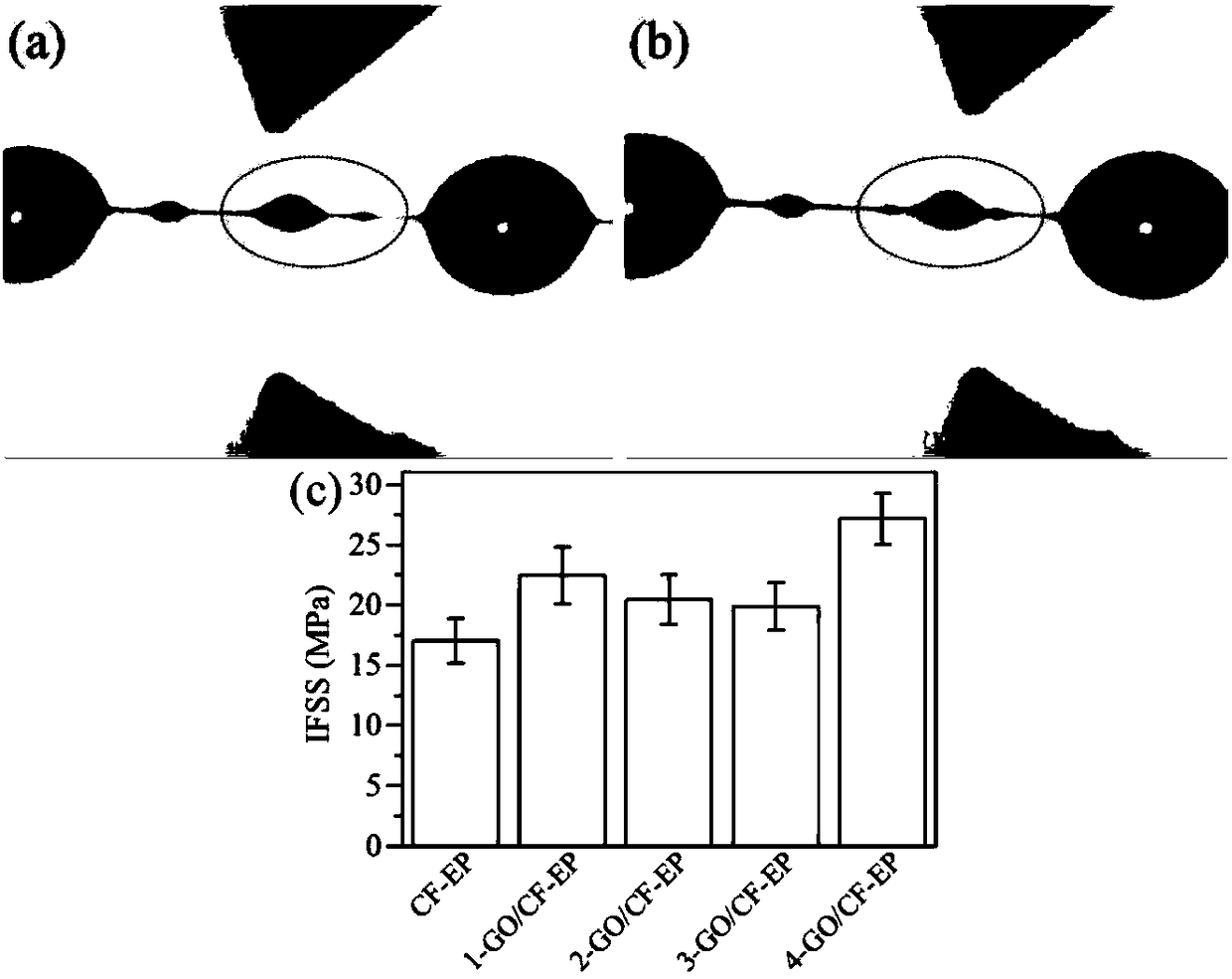
Preparation method of silane coupling agent assisted electrophoresis deposition initiated graphene oxide modified carbon fibers
A silane coupling agent, electrophoretic deposition technology, applied in the direction of carbon fiber, fiber treatment, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the contact area between carbon fiber and resin, reducing the interface performance of composite materials, and unfavorable reinforcement mechanical properties, etc., to achieve improvement Effects of interfacial shear strength, shortening modification time, increasing reactive sites and effective contact area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0038] This application provides a method for preparing graphene oxide. In an ice-water bath, graphite powder, sodium nitrate, concentrated sulfuric acid and potassium permanganate are mixed and reacted to obtain a mixture A, and the temperature of the mixture A is raised to 35±5°C for a period of time. Add water, then raise the temperature to 98±5°C and react to obtain a mixture B, dilute the mixture B with water, add hydrogen peroxide solution to react, filter, wash, and dry to obtain graphene oxide.
[0039] Further preferably, the ratio of concentrated sulfuric acid to sodium nitrate is 180:2.5, mL:g, and the mass ratio of graphite powder, sodium nitrate and potassium permanganate is 2:1:6.
[0040] Further preferably, the reaction temperature for obtaining the mixture A is 2±0.5° C., and the reaction time is 1 h.
[0041] Further preferably, the reaction time for raising the temperature to 35±5°C is 30±5 minutes, and the reaction time for raising the temperature to 98±5°C...
Embodiment 1
[0050] (l) Put the carbon fibers in an acetone solution, react at a constant temperature of 70°C for 24 hours, wash them alternately with absolute ethanol and deionized water several times, and then dry the washed carbon fibers at 80°C to constant weight. Prepare 1% aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) and 0.5% ethanol aqueous solution, hydrolyze at room temperature for 2 hours, put the dried carbon fiber into the above mixture and ultrasonically treat it at 60°C for 30 minutes, deionize After repeated washing with water and drying at 80°C, the carbon fiber pretreated by the silane coupling agent was obtained to a constant weight.
[0051] (2) Graphene oxide was added into deionized water, and ultrasonically treated for 20 minutes to obtain a graphene oxide aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.03 mg / mL, and the pH value of the deposition solution was adjusted to pH=10 with potassium hydroxide.
[0052] (3) Add the graphene oxide aqueous solution obtained in step (2) into t...
Embodiment 2
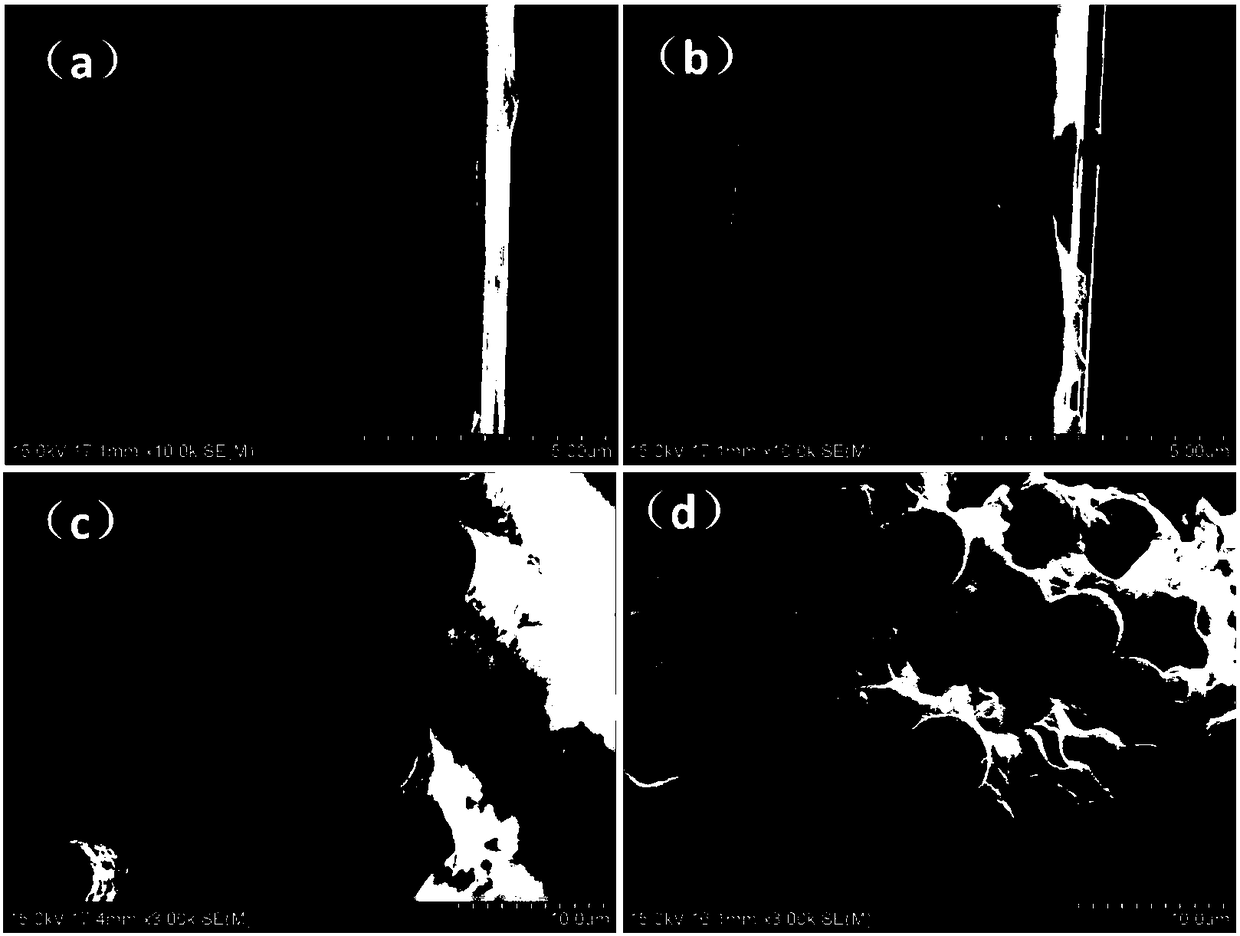
[0054] (l) Put the carbon fibers in an acetone solution, react at a constant temperature of 70°C for 24 hours, wash them alternately with absolute ethanol and deionized water several times, and then dry the washed carbon fibers at 80°C to constant weight. Prepare an aqueous solution of aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) with a mass fraction of 2% and ethanol with a mass fraction of 0.5%, hydrolyze it at room temperature for 3 hours, put the dried carbon fiber into the mixture, and treat it ultrasonically at 60°C for 40 minutes to deionize After repeated washing with water and drying at 80 °C, the carbon fiber pretreated by the silane coupling agent was obtained to a constant weight. The surface morphology of the obtained carbon fiber was as follows: figure 2 shown.
[0055] (2) Graphene oxide was added into deionized water, and ultrasonically treated for 30 minutes to obtain a graphene oxide aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.04 mg / mL, and the pH value of the depositi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com