Anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory porous metal stent and preparation method and application thereof
A porous metal and metal technology, applied in application, coating, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of low drug loading, inability to improve the biological effect of tissue engineering substitutes, and induce inflammation, so as to ensure long-term drug efficacy and improve Drug loading performance, effect of enhancing binding force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
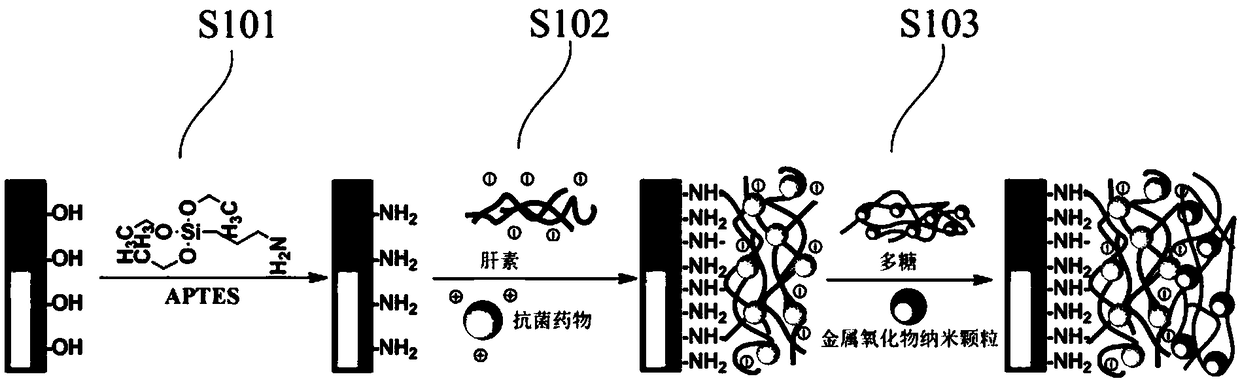
[0040] Such as figure 1 Shown, the preparation method of the antibacterial and anti-inflammatory porous metal stent of an embodiment of the present invention, comprises the following steps:
[0041] S101: Surface treatment is performed on the porous metal support.
[0042] Chemical bonds are introduced by surface treatment of porous metal scaffolds. The surface treatment method can be methods such as spray coating, spin coating, printing, dipping, sol-gel technology and the like.
[0043] In one embodiment, a silane coupling agent is used to aminate the surface of the metal stent with the nano-array structure.
[0044] Amination treatment of the surface of the porous metal support by using a silane coupling agent can successfully introduce covalent bonds on the porous metal support, which can increase the chemical reaction sites on the one hand, and increase the interaction between functional molecules and the porous metal support on the other hand. The binding force and in...
Embodiment 1
[0074] (1) Porous metal stents are prepared by anodic oxidation, wherein the electrolyte is: 10% glycerin (containing 0.5% w / v ammonium fluoride) aqueous solution, the voltage is 40-60V, and the electrolysis time is 8-12h;
[0075] (2) Soak the above-mentioned porous metal stent in 10 mM APTES solution prepared by hexane solution to complete the amination treatment on the surface of the porous metal stent;
[0076] (3) Make heparin sodium (molecular weight 200KDa) into 1 mg / mL aqueous solution, add corresponding amounts of EDC (molar ratio 1.5:1) and NHS (molar ratio 1.2:1), stir, and react at room temperature. After the reaction is complete, Separation to obtain a porous metal stent containing a heparin layer;
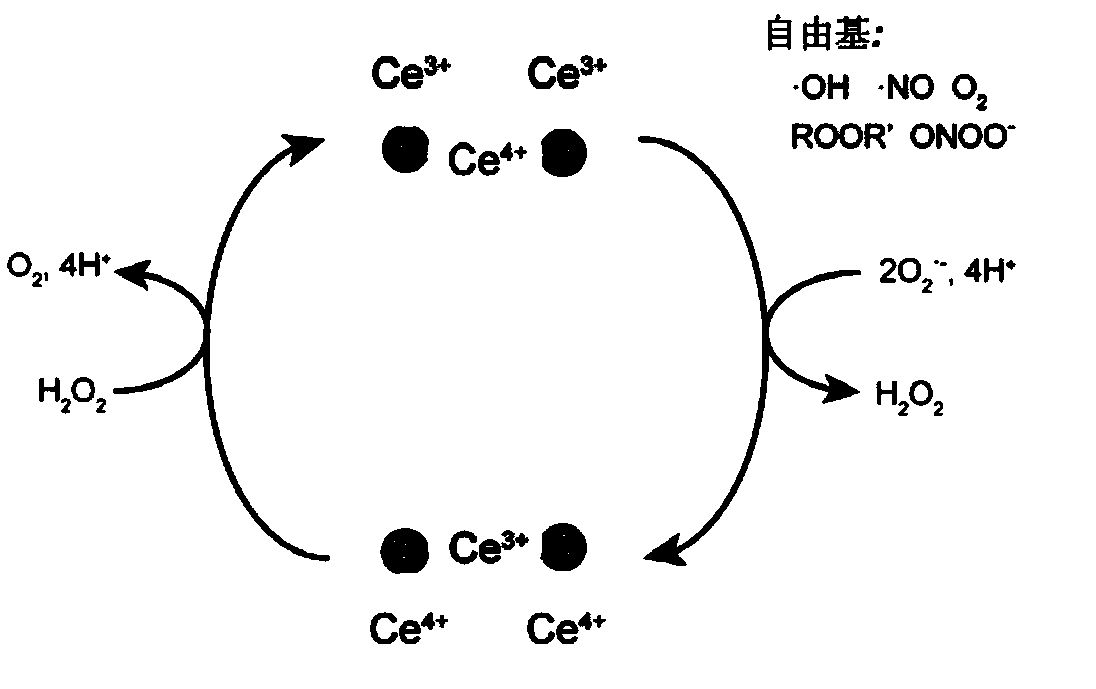
[0077] (4) 0.7M CeCl 3 ·7H 2 Add O to 5ml of 2% (w / v) low molecular weight chitosan, stir for 20min, then add 0.1mL of ammonia water (28-30%), centrifuge at 5000rpm for 10min at room temperature, collect the supernatant, and use a sliding dialysis box Carry out dia...
Embodiment 2
[0080] (1) Porous metal stents are prepared by anodic oxidation, wherein the electrolyte is: 10% glycerin (containing 0.5% w / v ammonium fluoride) aqueous solution, the voltage is 40-60V, and the electrolysis time is 8-12h;
[0081] (2) Soak the above-mentioned porous metal stent in 15 mM APTES solution prepared by hexane solution to complete the amination treatment on the surface of the porous metal stent;
[0082] (3) Make heparin sodium (molecular weight 200KDa) into 1 mg / mL aqueous solution, add corresponding amounts of EDC (molar ratio 1.5:1) and NHS (molar ratio 1.2:1), stir, and react at room temperature. After the reaction is complete, Separation to obtain a porous metal stent containing a heparin layer;
[0083] (4) 5mL polyallylamine hydrochloride (37.4mg / mL), add 15mL 10mM KMnO 4 solution, stirred for 10min, centrifuged to collect the precipitate, washed 5 times with pure water to obtain the manganese dioxide product, and 5ml of 2% (w / v) low molecular weight chitosa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com