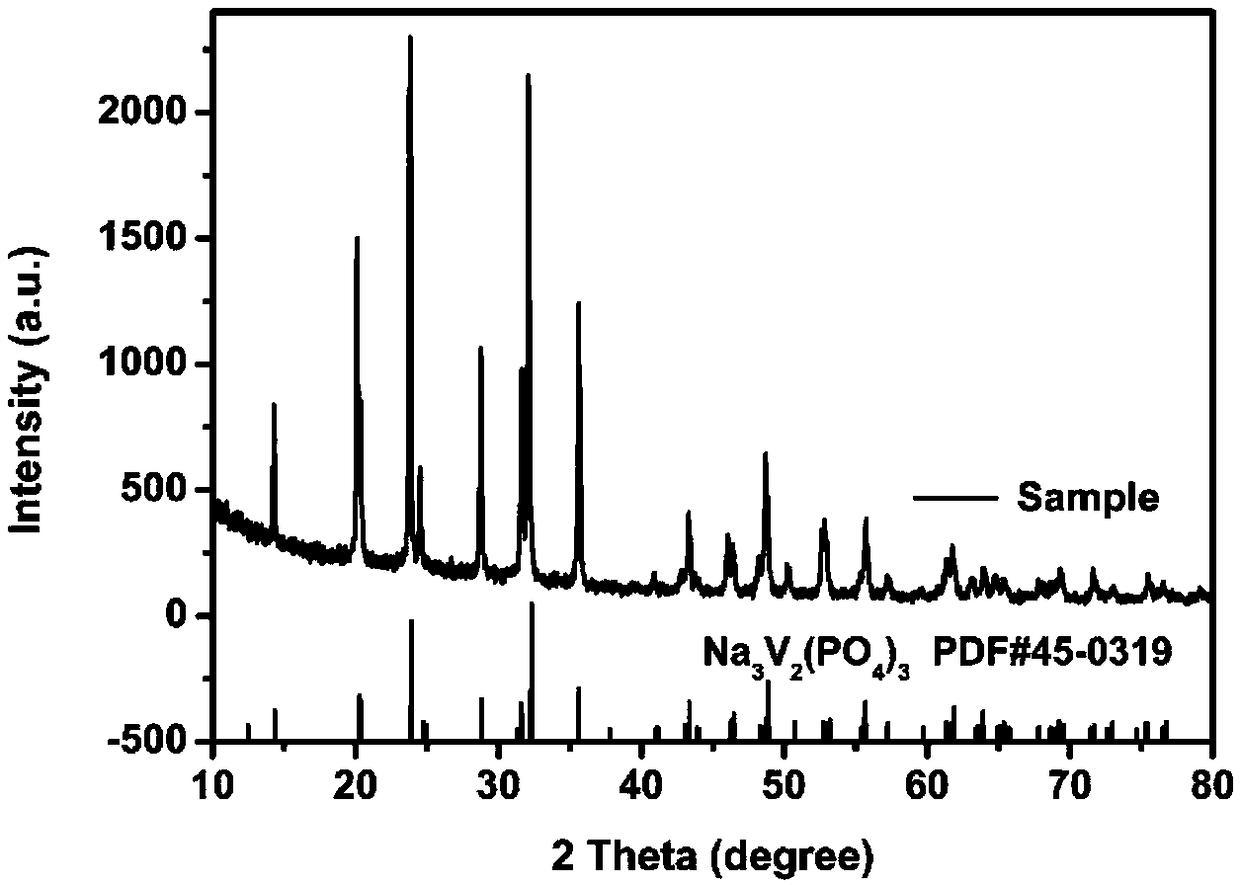
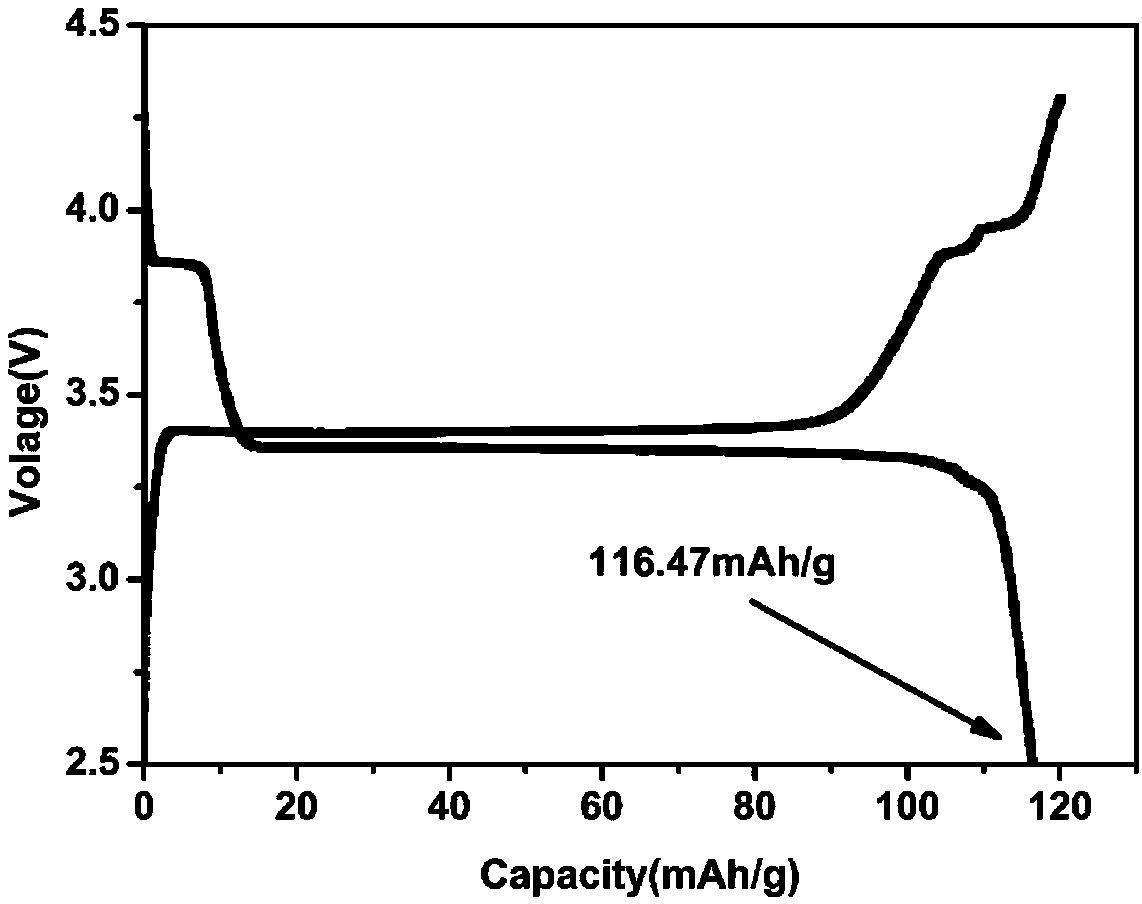
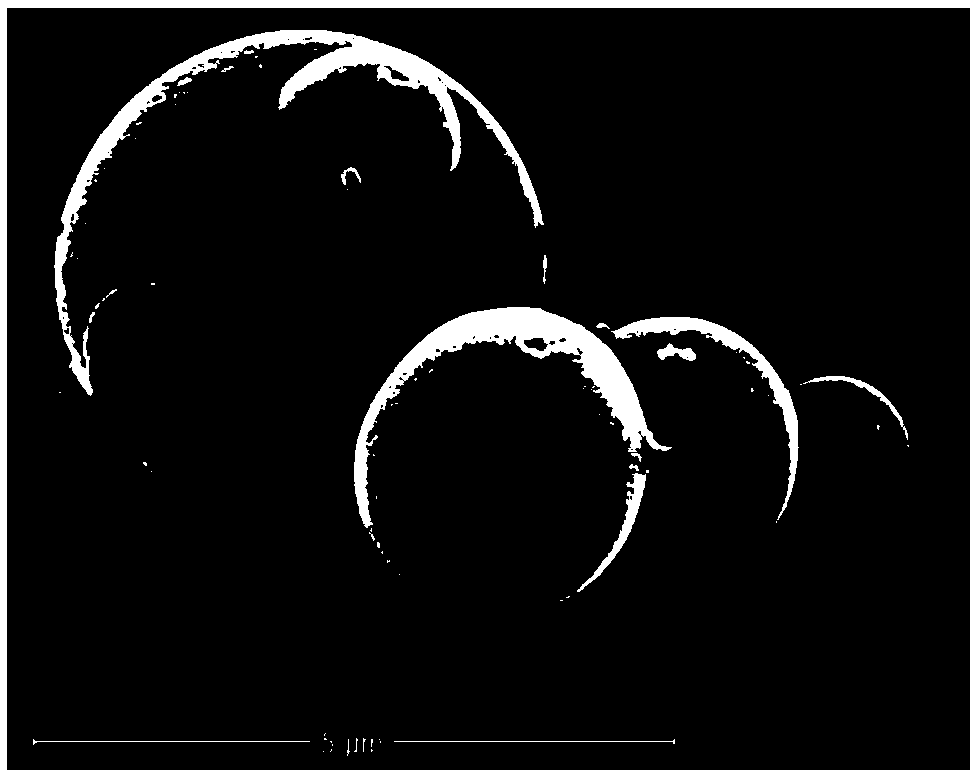Method for preparing multi-stage spherical sodium vanadium phosphate composite positive electrode material
A composite positive electrode material, sodium vanadium phosphate technology, applied in the direction of battery electrodes, electrical components, electrochemical generators, etc., can solve the problems of poor material performance, easy uneven thickness of carbon coating, cumbersome steps, etc., and reduce the production cost. Difficulty and cost, improved electrochemical performance, and the effect of complete grain development
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] A preparation method of a multi-stage spherical sodium vanadium phosphate composite positive electrode material, the specific steps are as follows:
[0034] (1) Weigh 2.941 g of trisodium citrate dihydrate and 1.5015 g of urea, dissolve them in 40 ml of deionized water, stir in a water bath at 60°C, and fully dissolve to obtain a colorless solution A;
[0035](2) Weigh 2.3398g of ammonium metavanadate, 3.4509g of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and 2.7009g of anhydrous oxalic acid and dissolve them in 40ml of deionized water, stir in a water bath at 60°C, and fully dissolve to obtain blue solution B;
[0036] (3) Add solution B slowly to solution A drop by drop, and stir in a water bath at 60°C for 30 minutes to form a mixed solution;
[0037] (4) Put the mixed solution obtained in step (3) into a hydrothermal kettle, conduct a hydrothermal reaction at 160° C. for 12 hours, dry and grind to obtain a precursor powder;
[0038] (5) Under the protection of nitrogen, heat th...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A preparation method of a multi-stage spherical sodium vanadium phosphate composite positive electrode material, the specific steps are as follows:
[0045] (1) Weigh 2.941 g of trisodium citrate dihydrate and 0.75075 g of urea and dissolve them in 40 ml of deionized water, stir in a water bath at 50°C, and fully dissolve to obtain a colorless solution A;
[0046] (2) Weigh 2.3398g of ammonium metavanadate, 3.4509g of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and 2.7009g of anhydrous oxalic acid and dissolve them in 40ml of deionized water, stir in a water bath at 50°C, and fully dissolve to obtain blue solution B;
[0047] (3) Add solution B slowly to solution A drop by drop, and stir in a water bath at 50°C for 15 minutes to form a mixed solution;
[0048] (4) Put the mixed solution into a hydrothermal kettle, conduct a hydrothermal reaction at 140°C for 6 hours, dry and grind to obtain the precursor powder;
[0049] (5) Heat the precursor powder at 300°C for 4 hours under the p...
Embodiment 3
[0052] A preparation method of a multi-stage spherical sodium vanadium phosphate composite positive electrode material, the specific steps are as follows:
[0053] (1) Weigh 2.941 g of trisodium citrate dihydrate and 3.003 g of urea and dissolve them in 40 ml of deionized water, stir in a water bath at 80°C, and fully dissolve to obtain a colorless solution A;
[0054] (2) Weigh 2.3398g of ammonium metavanadate, 3.4509g of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and 2.7009g of anhydrous oxalic acid and dissolve them in 40ml of deionized water, stir in a water bath at 80°C, and fully dissolve to obtain blue solution B;
[0055] (3) Add solution B slowly to solution A drop by drop, and stir in a water bath at 80°C for 45 minutes to form a mixed solution;
[0056] (4) Put the mixed solution into a hydrothermal kettle, conduct a hydrothermal reaction at 180°C for 18 hours, dry and grind to obtain a precursor powder;
[0057] (5) Heat the precursor powder at 400°C for 6 hours under the prot...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com