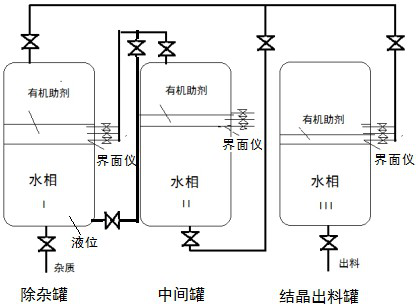
Aqueous phase refining method of long-chain dibasic acid in biological fermentation broth
A long-chain dibasic acid and bio-fermentation technology, applied in the field of refining, can solve the problems of harsh operating environment, unstable acetone, and many crystallization gradient control points, and achieve the effects of simplifying the process, avoiding solvent residues, and good selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Embodiment 1: Purify long-chain dibasic acid from biological fermentation broth according to the following steps
[0020] (1) Sterilize the ceramic membrane with 30% sodium hydroxide solution, then wash the ceramic membrane with pure water or deionized water, and maintain the pH at pH 7.0;
[0021] (2) Select dodecanedibasic acid with a concentration of 180g / L and a pH of 8.5 to terminate the fermentation broth, maintain the fermentation temperature of the terminated fermentation broth at 26°C, the stirring speed at 200 rpm, and the ventilation volume at 400m 3 / minute; the ceramic membrane filtration terminates the fermentation liquid and directly separates the solid from the liquid to obtain the fermentation clear liquid; the bacteria and alkanes are used for the sterilized follow-up fermentation liquid to continue production;
[0022] (3) The temperature of the fermented supernatant was raised to 60°C, and the pH was adjusted to pH 2.5 with sulfuric acid with a mass...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Embodiment 2: Purify long-chain dibasic acid from biological fermentation broth according to the following steps
[0026] (1) Sterilize the ceramic membrane with 32% sodium hydroxide solution, then wash the ceramic membrane with pure water or deionized water, and maintain the pH at pH 8.0;
[0027](2) Select tridecanedioic acid with a concentration of 180g / L and a pH of 8.5 to terminate the fermentation broth, maintain the fermentation temperature of the terminated fermentation broth at 30°C, the stirring speed at 350 rpm, and the ventilation rate at 700m 3 / minute; the ceramic membrane filtration terminates the fermentation liquid and directly separates the solid from the liquid to obtain the fermentation clear liquid; the bacteria and alkanes are used for the sterilized follow-up fermentation liquid to continue production;
[0028] (3) The temperature of the fermented supernatant was raised to 80°C, and the pH was adjusted to pH 3.0 with sulfuric acid with a mass fra...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Embodiment 3: Purify long-chain dibasic acid from biological fermentation broth according to the following steps
[0032] (1) Sterilize the ceramic membrane with 32% sodium hydroxide solution, then wash the ceramic membrane with pure water or deionized water, and maintain the pH at pH 9.0;
[0033] (2) Select pentadecanedibasic acid with a concentration of 180g / L and a pH of 8.5 to terminate the fermentation broth, maintain the fermentation temperature of the terminated fermentation broth at 35°C, the stirring speed at 500 rpm, and the ventilation rate at 1000m 3 / minute; the ceramic membrane filtration terminates the fermentation liquid and directly separates the solid from the liquid to obtain the fermentation clear liquid; the bacteria and alkanes are used for the sterilized follow-up fermentation liquid to continue production;
[0034] (3) The temperature of the fermented supernatant was raised to 98°C, and the pH was adjusted to pH 3.8 with 98% sulfuric acid to ac...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com