Preparation and application of nano-micelle imaging agent for cervical cancer sentinel node
A sentinel lymph node and nano-micelle technology, which is applied in the preparation of in vivo experiments, drug delivery, emulsion delivery, etc., can solve the problems of low specificity of lymph node imaging agents, inability to observe in real time, dye retention, etc., to achieve Maintain colloidal stability, reduce quenching, and improve stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Example 1 Preparation of targeted peptide-modified fluorescent nanoimaging agent
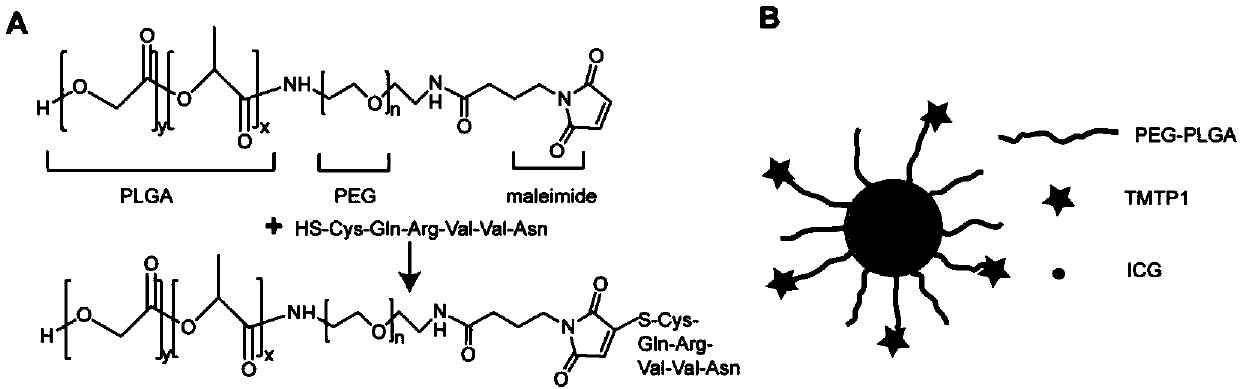
[0056] 1. Synthetic peptide TMTP1
[0057] Use peptide solid-phase synthesis technology to synthesize cyclic polypeptide c (NVVRQC) head-to-tail amide bonds to form a ring. The synthesis process is completed by Wuhan Baiyixin Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The purity of the synthesized cyclic polypeptide c (NVVRQC) is 98%. RP-HPLC and MS technique detection, its molecular weight is 699.2, and quality is 20mg.
[0058] 2. Preparation of fluorescent nanoimaging agent
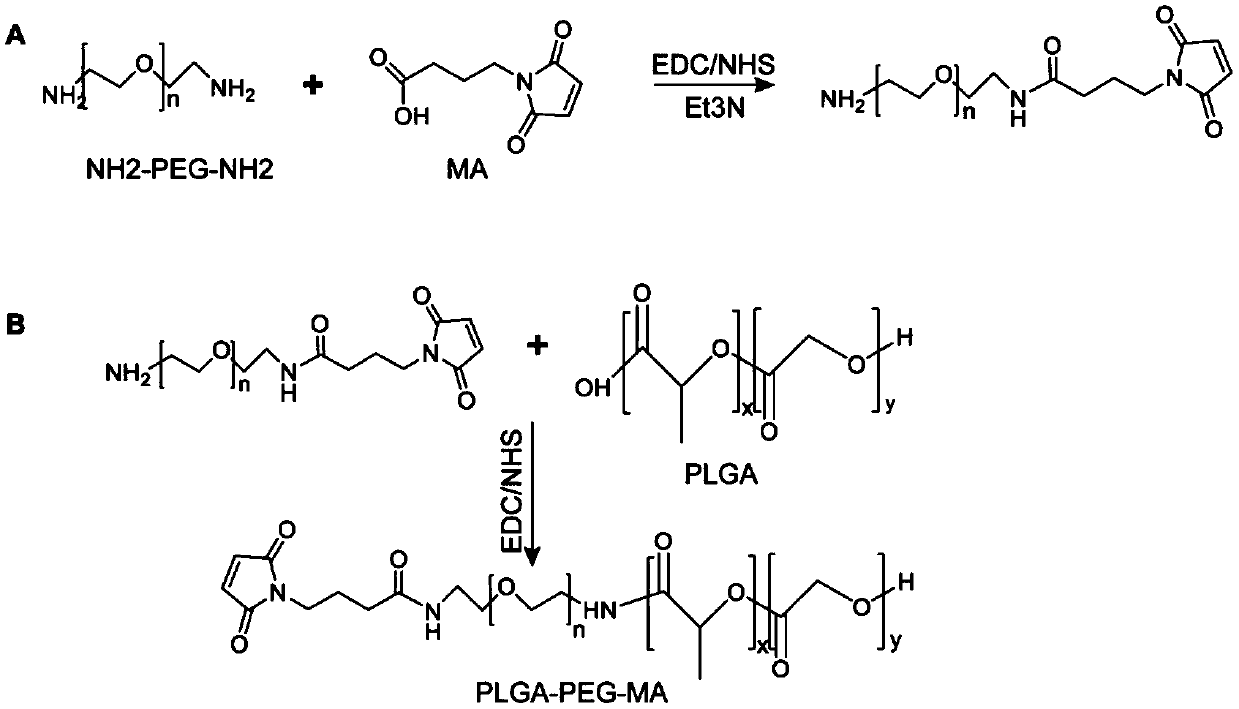
[0059] (1) Synthesis of MA-PEG-PLGA copolymer: first activate MA (maleimide butyric acid) in DCM (dichloromethane) with EDC and NHS for 5 hours, and then add polyethylene glycol diols of different molecular weights Amines (2KDa, 3KDa, 4KDa and 10KDa) were reacted with triethylamine for 48h to obtain a PEG solution with MA end groups; PLGA (50 / 50 20000) was activated in DCM with EDC and NHS for 5h to obtain the activated product of...
Embodiment 2
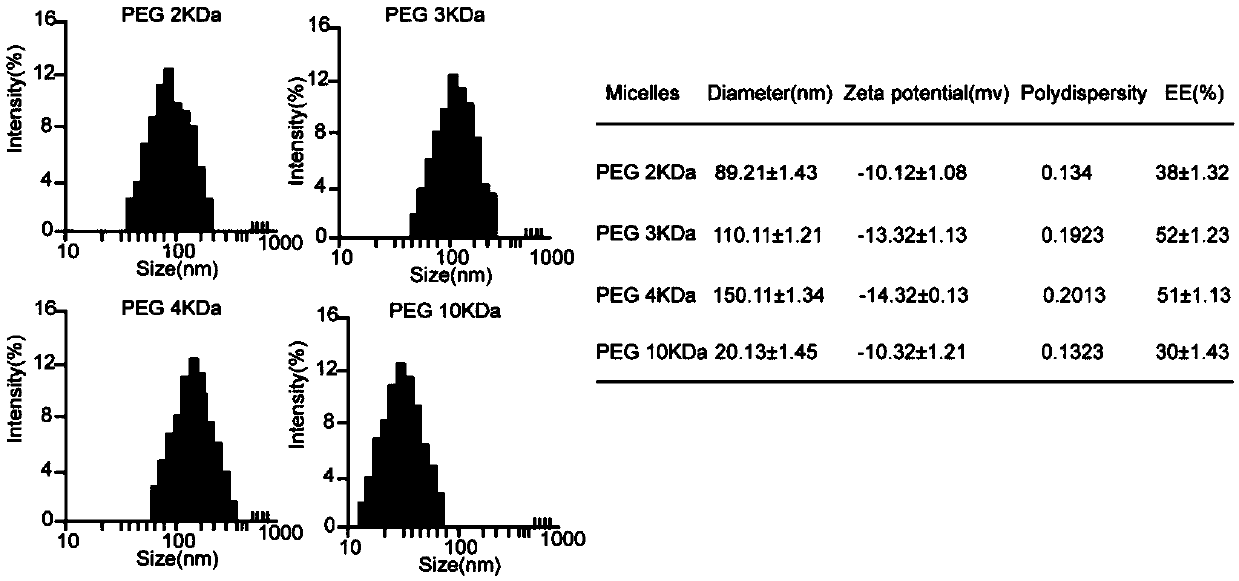
[0069] Example 2 adjusts the ratio of materials for micelles preparation and targeting peptide to improve the physicochemical properties and targeting of nanoparticles.
[0070] (1) According to the method for preparing nanoparticles in 2(2) of Example 1, "1mg cyclic TMTP1 polypeptide and the above 20mg MA-PEG-PLGA (mass ratio 1:20) are dissolved in 1ml DMF solution", we will 1mg The cyclic TMTP1 polypeptide and the above 20mg MA-PEG-PLGA (mass ratio 1:20) are adjusted to the following ratio:
[0071] A.10mgMA-PEG-PLGA+10mgPEG(5000)-PLGA(50 / 50 20000)+1mg TMTP1;
[0072] B.10mg MA-PEG-PLGA+10mgPLGA(50 / 50 20000)+1mg TMTP1;
[0073] C.15mg MA-PEG-PLGA+5mg PLGA (50 / 50 20000)+1mgTMTP1;
[0074] D.15mg MA-PEG-PLGA+5mg PEG (5000)-PLGA (50 / 50 20000)+1mg TMTP1. Wherein MA-PEG-PLGA is the copolymer synthesized by the 2 (1) method of embodiment 1, PEG (5000 )-PLGA (50 / 50 20000) is monomethoxypolyethylene glycol poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) copolymer, purchased from Jinan Daigang Biol...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Example 3 Establishment of footpad lymph node metastasis model and near-infrared fluorescence imaging
[0081] 1 Prepare tumor cells
[0082] The cervical cancer cell line HeLa was cultured in DMEM medium containing 10% serum (37°C, 5% CO2 incubator), and the luciferase gene luc expression vector was constructed through the Lentivirus system, and Hela was stably transfected with puromycin drug After 3 days of screening, hela-luc cells stably transfected with luc were obtained. Amplify hela-luc cells in a culture flask, digest with 0.25% trypsin when the cells grow to 80%, stop the digestion with complete medium, collect the cells into a 15mL centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 800rpm for 5 minutes, discard the upper After clearing, the cells were resuspended in PBS, centrifuged again, the supernatant was discarded, resuspended in PBS, and the cell density was calculated by cell counting.
[0083] 2 Establishment of tumor model
[0084] Establishment of nude mouse footpad ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com