Anti-Escherichia coli Bacillus alvei strain and its antiseptic application in cosmetics
A technology of bacillus and Escherichia coli, which is applied in the field of antiseptic application, to achieve the effect of guaranteeing the quality of cosmetics, wide antibacterial spectrum and strong development potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1: Determination of Bacillus strains of the present invention and their secondary metabolites to Escherichia coli antibacterial effect
[0028] 1. Experimental method
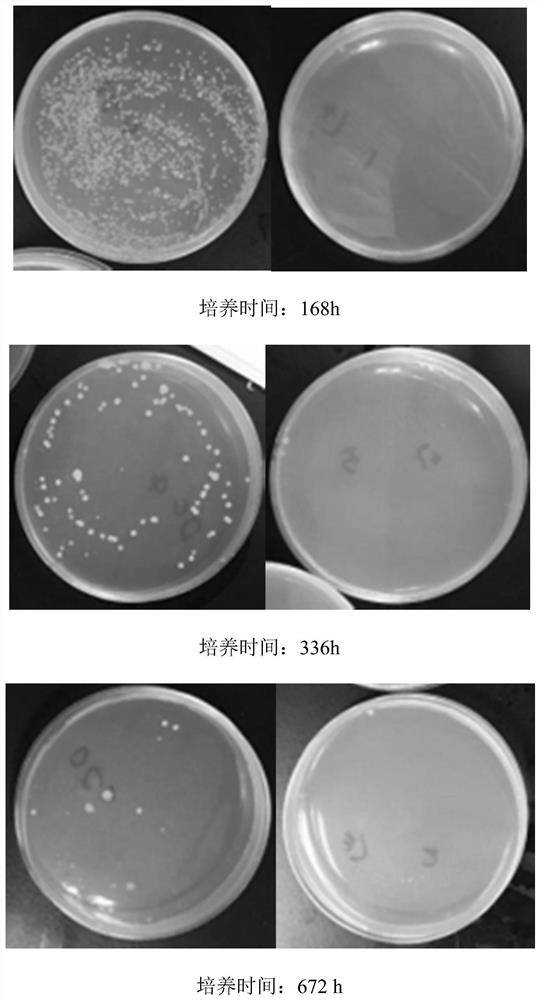
[0029] Use a disposable polyethylene culture dish, add LB medium, and cool down. The blank group was coated with Escherichia coli at an appropriate concentration, and a filter paper sheet was placed on a designated area on the medium, and sterile water was added to the filter paper sheet; the experimental group was coated with an appropriate concentration of Escherichia coli, and a filter paper sheet was placed on a designated area on the medium. A certain concentration of sterilized Bacillus thallus and its supernatant crude purification are added to the tablet.
[0030] After the inoculation was completed and the double-layer sealing film was sealed, it was cultured upside down in a 37°C incubator for one week, and the diameter of the inhibition zone of each group of cultures against Escher...
Embodiment 2
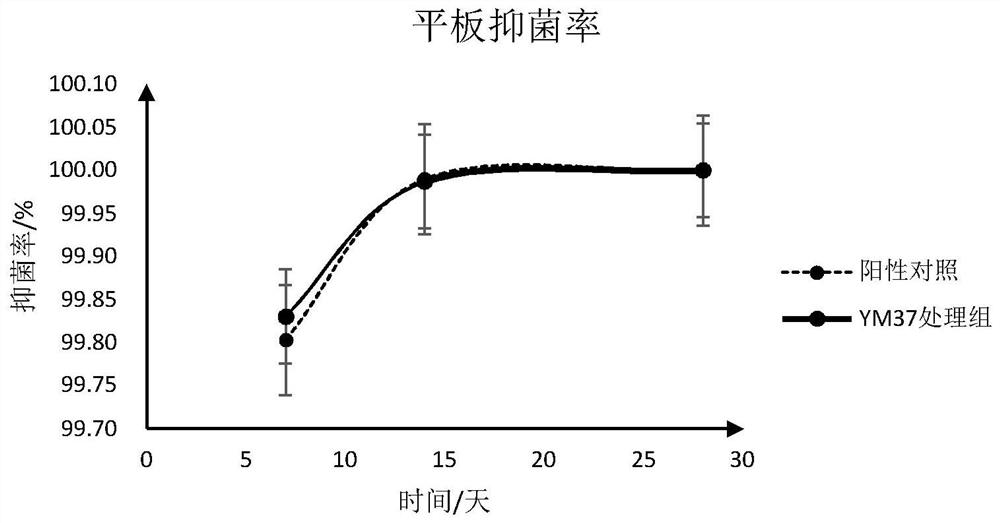
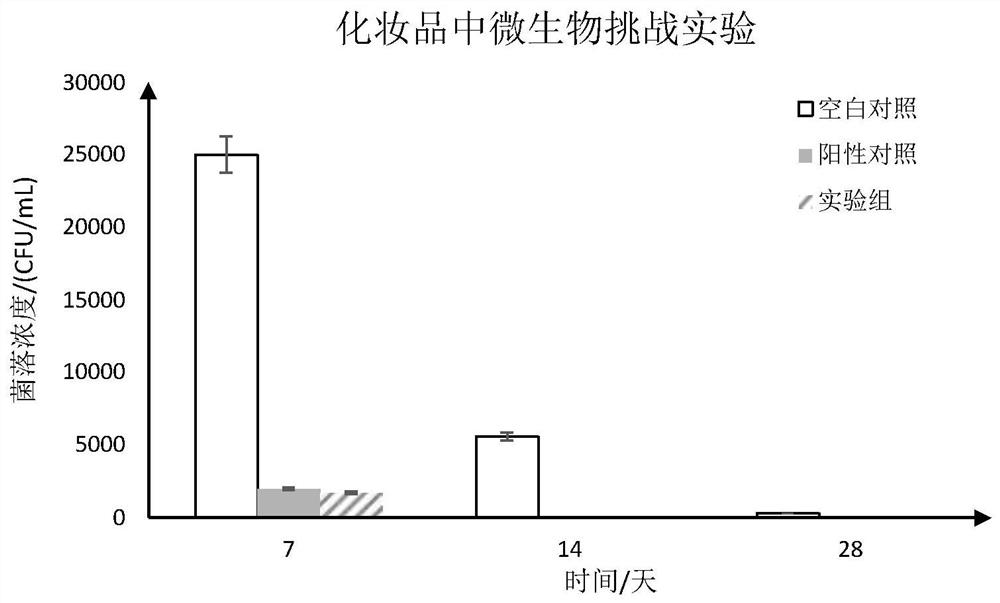
[0039] Embodiment 2: simulated cosmetics storage test
[0040] 1. Experimental materials, reagents and instruments
[0041] Experimental materials: moisturizing skin care water without preservatives (ingredients: glycerin, vitamin C, vitamin E, rose hydrosol: linalool, eugenol, rose ether), Escherichia coli, Bacillus numbered YM37, normal saline, Sterile water, centrifuge tubes, bamboo sticks, sealed bottles with blue caps, etc.
[0042] Experimental reagents: LB liquid, solid medium, Casson.
[0043] Experimental equipment: shaker, oven, ultra-clean table, etc.
[0044] 2. Experimental method
[0045] (1) Preparation of Bacillus somatic cell disruptor
[0046] Scrape a small amount of Bacillus YM37 from the plate and inoculate it into an Erlenmeyer flask containing 50 mL of liquid LB medium, and culture it overnight in a shaker at 37°C. Take 1 mL of the Bacillus suspension after overnight cultivation and add it to a conical flask filled with 50 mL of LB liquid medium, pu...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Embodiment 3: the species identification of bacillus bacterial strain described in the present invention
[0059] 1. Experimental method
[0060] According to the pClone007 Vector Kit (TSV-007) step, the total DNA of the bacterial strain of the present invention was extracted, the 16S rDNA gene of the bacteria was amplified with primers M13F-47 and M13R-48, and the amplified product was recovered for sequencing. The sequence of 16S rDNA was used to identify the species. The obtained sequence results were compared by Blast at NCBI, and the recognized standard sequence data homologous to the 16S rDNA of the strain was obtained from the genBank database, and the sequence similarity was calculated using MEGA software and Neighbor-Joining was used as the system developmental analysis.
[0061] 2. Implementation result analysis
[0062] The strain of the present invention is identified through the determination of the full sequence of 16S rDNA, and its sequence result is s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com