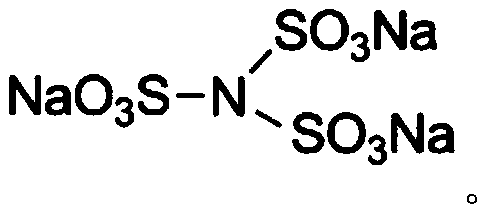
Modified sodium alginate self-developing embolization microsphere and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of sodium alginate and embolizing microspheres, which is applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of long drug loading time, uneven dispersion of the developer, influence on tumor curative effect, etc., so as to improve the drug loading capacity and drug loading rate, and prolong the drug starting time. Effective time, reducing the effect of drug side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
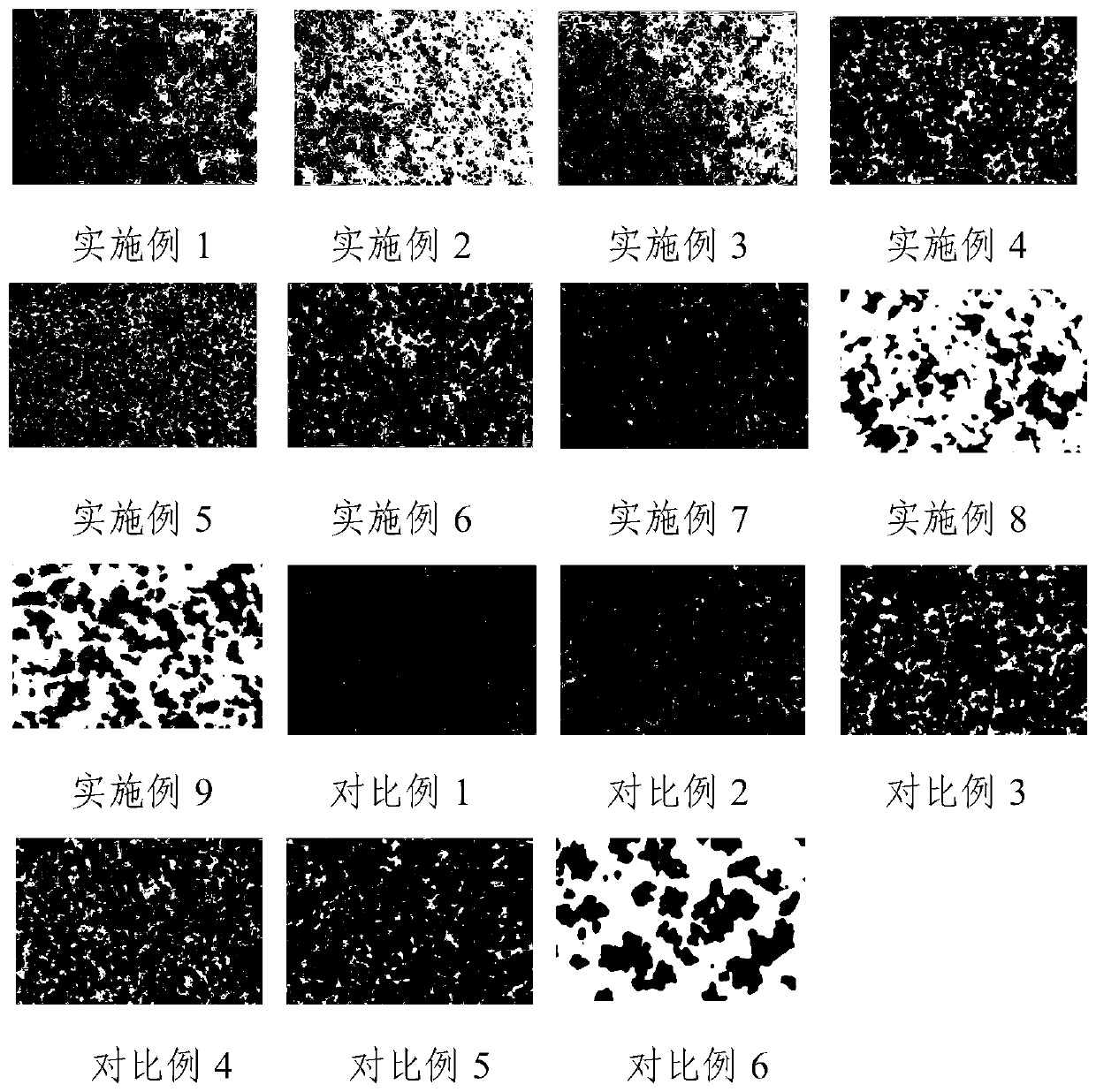
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] In this example, modified sodium alginate self-imaging embolic microspheres were prepared and further drug-loaded according to the following method:
[0049] 1. Branching modification: add sodium alginate with a viscosity of 619mpa s to the acetone solution of dibromoethane, adjust the pH of the solution to 10, pre-react for 3 hours at 55°C, add pentaerythritol, pentaerythritol and sodium alginate The molar ratio of the repeating unit was 0.3:1. Stir the reaction at 80°C for 24 hours, add excess acetone solution, filter with suction, collect the precipitate, wash and dry to obtain branched and modified sodium alginate.
[0050] 2. Hydrophobic modification: add oleic acid and branched modified sodium alginate to N, N-dimethylformamide, add dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and 4-dimethylaminopyridine under stirring conditions , and reacted at room temperature for 24h to obtain hydrophobically modified sodium alginate. The molar ratio of oleic acid to the above sodium alginate re...
Embodiment 2-7
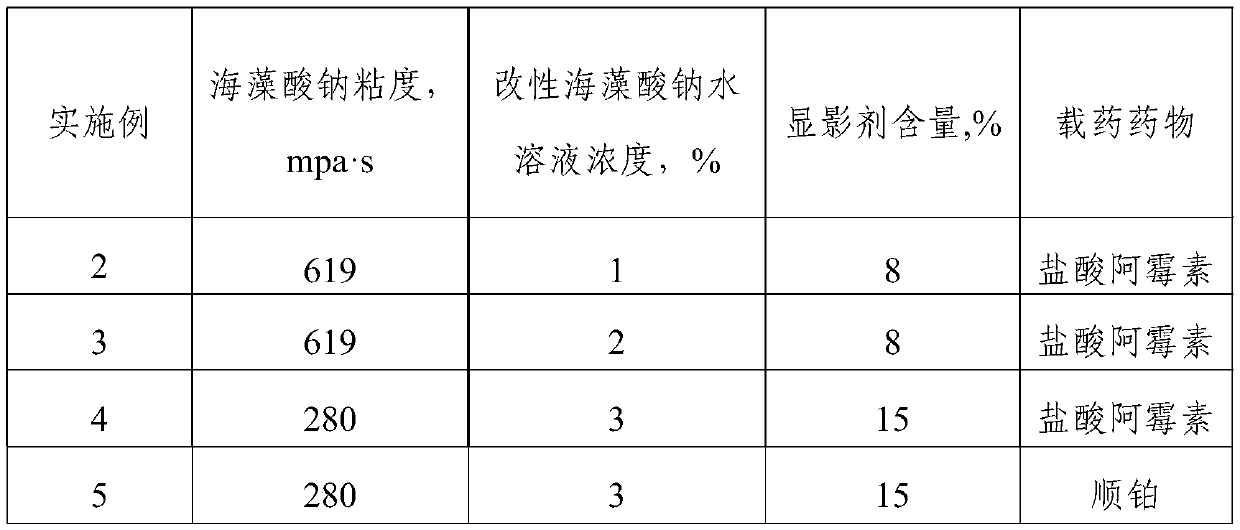
[0061] In Example 2-7, modified sodium alginate self-imaging embolic microspheres were prepared according to the method of Example 1 and further drug-loaded. The only difference lies in the raw materials and dosage during preparation, reaction conditions, developer mixing method and preparation electric field force The voltages are not exactly the same. In addition, the order of steps 2 and 3 was exchanged in Examples 6-7.
[0062] Specifically, the differences between Example 2-7 and Example 1 in the sodium alginate raw material in step 1, the concentration of the modified sodium alginate aqueous solution in step 4, the content of the developer, and the drug-loaded drug are shown in Table 1. See Table 2 for the differences between the amount of raw materials and the reaction conditions of Example 1 during chemical modification, and see Table 3 for the differences between the amount of raw materials and reaction conditions for hydrophobic modification and Example 1. See Table...
Embodiment 8
[0077] In this example, modified sodium alginate self-imaging embolic microspheres were prepared and further drug-loaded according to the following method:
[0078] 1. Branching modification: Add sodium alginate with a viscosity of 110mpa s to the acetone solution of dibromoethane, adjust the pH of the solution to 11, pre-react for 4 hours at 30°C, add glycerin, glycerin and sodium alginate The molar ratio of the repeating unit was 0.35:1, stirred and reacted at 100°C for 8 hours, added excess acetone solution, filtered with suction, collected the precipitate, washed and dried to obtain branched modified sodium alginate.
[0079] 2. Hydrophobic modification:
[0080] According to the molar ratio of 0.21:1, succinic anhydride and branched modified sodium alginate were added into dichloromethane, DMAP was added in sequence under magnetic stirring, and the temperature was raised to 35°C for 5 hours under nitrogen protection, and the filter cake was 35°C after suction filtration. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com