A kind of preparation method of free radical grafting regenerated cellulose yarn
A technology of regenerated cellulose and free radicals, applied in plant fibers, fiber treatment, dyeing methods, etc., can solve the problems of unsalt-free and environmentally friendly dyeing of cellulose fibers, poor dye adsorption, and large amount of reagents, etc., to achieve strong reactivity , grafting rate increase, low production cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
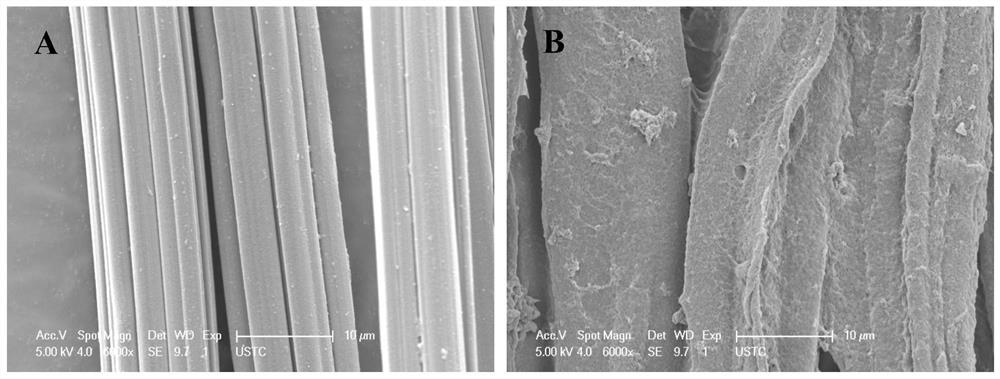
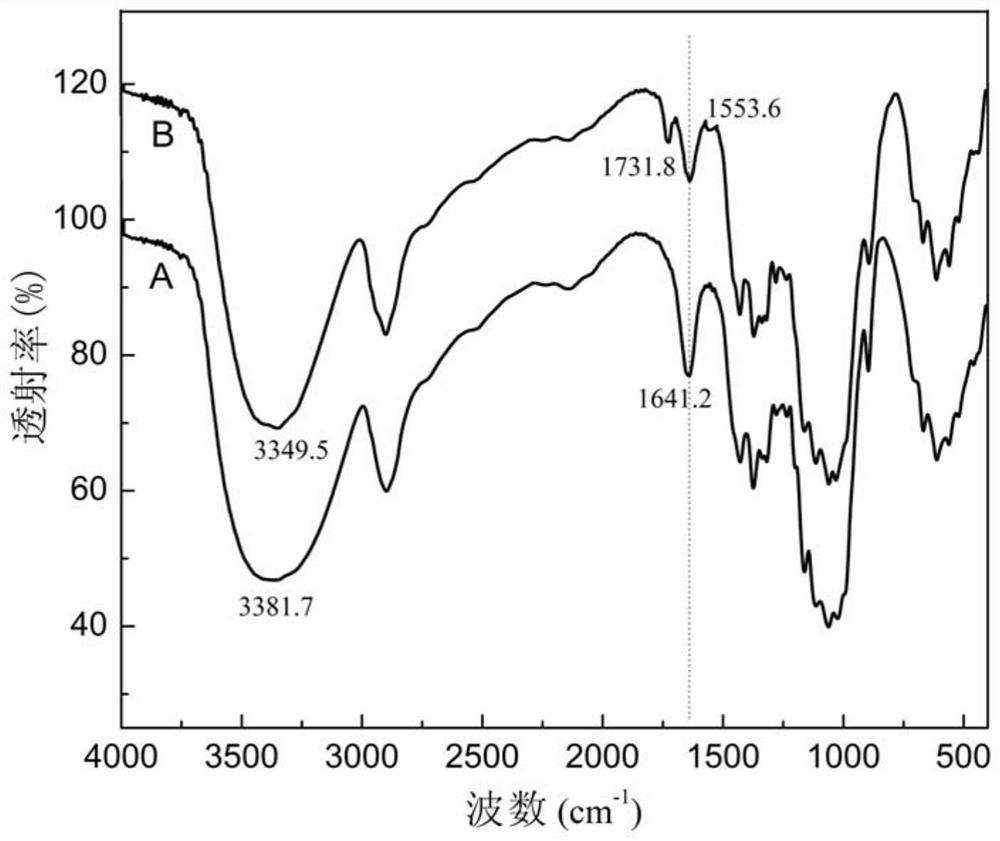
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] (1) Dissolve chitosan with a viscosity average molecular weight of 50,000 and a deacetylation degree of 93% in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride / 1-carboxymethyl-3-methyl In imidazole bisulfate (mass ratio is 9:1) binary ionic liquid, after cooling to room temperature, add acrylic acid monomer according to the mass ratio of acrylic acid and chitosan as 0.3:0.7, and then add initiator potassium persulfate to make Its mass concentration in the binary ionic liquid is 0.5%.
[0026] (2) Stir the above binary ionic liquid solution evenly for 10 minutes, then add viscose fiber yarn at a bath ratio of 1:30 under nitrogen protection (the mass ratio of acrylic acid and chitosan to viscose fiber yarn is 0.5:1), The reaction was stirred at 35 °C for 1 h. After the reaction, the viscose fiber yarn was taken out, washed with hot water for 5 times, and dried in a vacuum oven at 60°C for 2 hours to obtain acrylic acid and chitosan copolymerized modified viscose fiber yarn samples. ...
Embodiment 2
[0028] (1) Dissolve chitosan with a viscosity average molecular weight of 20,000 and a deacetylation degree of 95% in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride / 1-carboxymethyl-3-methyl Imidazolium bisulfate (mass ratio is 8:2) binary ionic liquid, after cooling to room temperature, add acrylic acid monomer according to the mass ratio of acrylic acid and chitosan as 0.5:0.5, and then add initiator potassium persulfate to make Its mass concentration in the binary ionic liquid is 1%.
[0029](2) Stir the above binary ionic liquid solution evenly for 10 minutes, then add viscose fiber yarn at a bath ratio of 1:30 under nitrogen protection (the mass ratio of acrylic acid and chitosan to viscose fiber yarn is 0.5:1), The reaction was stirred at 50 °C for 1 h. After the reaction, the viscose fiber yarn was taken out, washed with hot water for 5 times, and dried in a vacuum oven at 60°C for 3 hours to obtain acrylic acid and chitosan copolymerized modified viscose fiber yarn samples. Aft...
Embodiment 3
[0031] (1) Dissolve chitosan with a viscosity average molecular weight of 20,000 and a deacetylation degree of 95% in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride / 1-carboxymethyl-3-methyl Imidazolium bisulfate (mass ratio is 8:2) binary ionic liquid, after cooling to room temperature, add acrylic acid monomer according to the mass ratio of acrylic acid and chitosan as 0.5:0.5, and then add initiator potassium persulfate to make Its mass concentration in the binary ionic liquid is 1%.
[0032] (2) Stir the above binary ionic liquid solution evenly for 10 minutes, then add bamboo pulp fiber yarn at a bath ratio of 1:30 under nitrogen protection (the mass ratio of acrylic acid and chitosan to bamboo pulp fiber yarn is 0.5:1), The reaction was stirred at 50 °C for 1 h. After the reaction, the bamboo pulp fiber yarn was taken out, washed four times with hot water, and dried in a vacuum oven at 60°C for 3 hours to obtain acrylic acid and chitosan copolymerized modified bamboo pulp fiber ya...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of deacetylation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of grafting | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| antibacterial rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com