Molybdenum disulfide nanosheet, preparation method and application thereof and method for degrading halogenated antibiotics through electrochemical reduction
A technology of molybdenum disulfide and nanosheets, applied in the fields of molybdenum sulfide, chemical instruments and methods, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of restricting wide application, high cost and scarcity of noble metal catalysts, and achieve the effect of wide application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0039] The invention provides a preparation method of molybdenum disulfide nanosheets, comprising the following steps:
[0040] a) mixing ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate, thiourea and water to obtain a mixed solution;
[0041] b) heating and reacting the mixed solution to form molybdenum disulfide nanosheets.
[0042] Regarding step a):
[0043] The present invention uses specific ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate and thiourea as reaction raw materials to synthesize molybdenum disulfide nanosheets, which can not only synthesize molybdenum disulfide, but also obtain molybdenum disulfide nanosheets with suitable size, and the distribution of catalytic active sites makes the catalytic effect reach The best, can effectively degrade halogenated antibiotics. If other raw materials are used, such as sodium molybdate as molybdenum source and cysteine as sulfur source, the degradation effect of the obtained molybdenum disulfide is very poor.
[0044] In the present invention, the mol...
Embodiment 1
[0075] 2 mmol of ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate and 28 mmol of thiourea were dispersed in 70 mL of deionized water, and ultrasonically stirred for 30 minutes to form a homogeneous solution. After that, the solution was transferred to a 100 mL autoclave and heated to 220 °C for 18 h. After cooling to room temperature, the black suspension was repeatedly filtered and washed with ethanol and water, and dried in a drying cabinet at 80°C overnight. Finally, black molybdenum disulfide catalyst powder is obtained.
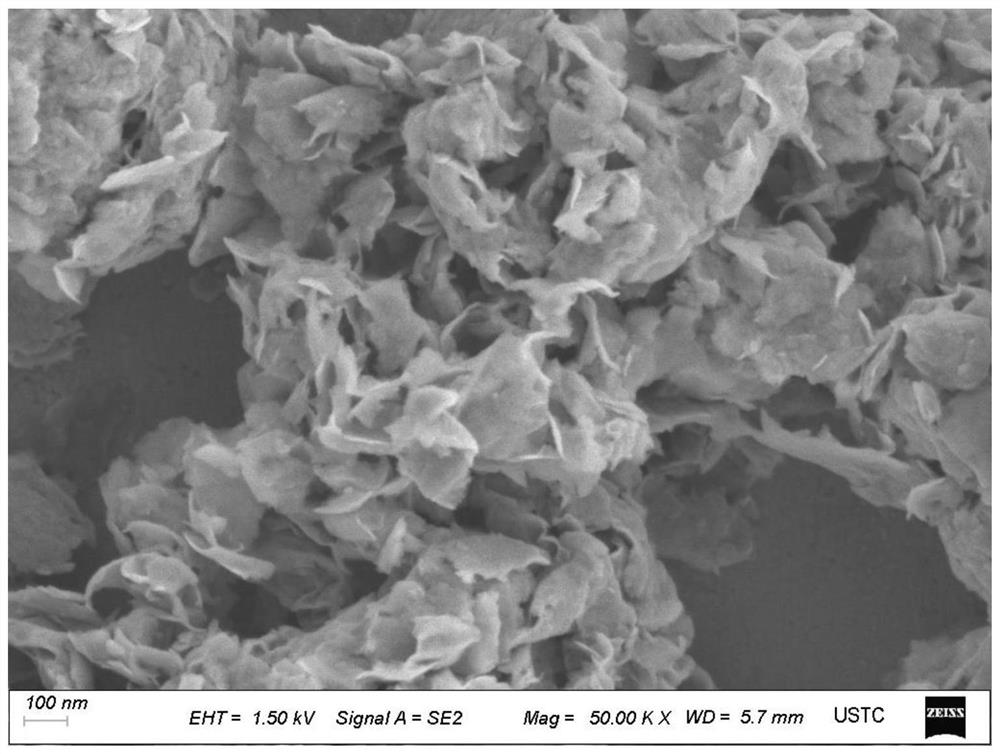
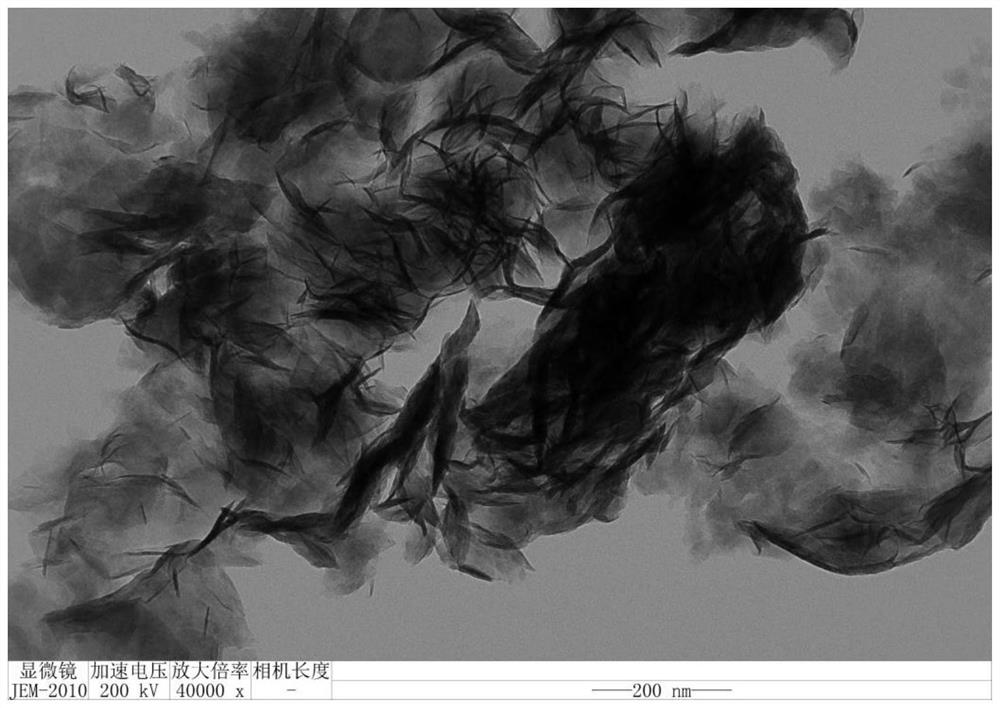
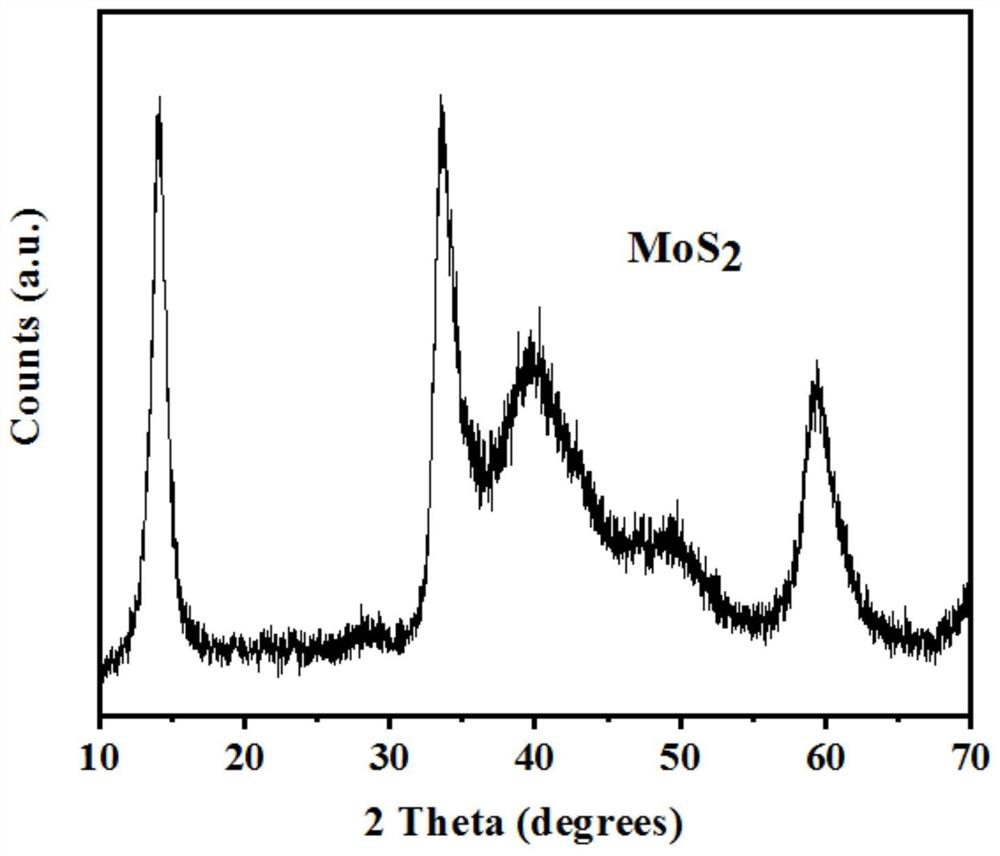
[0076] figure 1 It is the X-ray crystal diffraction pattern of the molybdenum disulfide catalyst obtained in Example 1, which proves that the obtained product is MoS 2 . figure 2 Be the scanning electron microscope image of the molybdenum disulfide catalyst obtained in Example 1, image 3 It is a transmission electron microscope image of the molybdenum disulfide catalyst obtained in Example 1, and it can be seen that the obtained molybdenum disulfide has a nano-flak...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Example 2 Catalytic degradation of florfenicol solution
[0078] S1. 10 mg of the molybdenum disulfide catalyst obtained in Example 1 was dissolved in a mixed solution containing 50 μL of Nafion solution, 450 μL of water and 500 μL of ethanol, and ultrasonically treated for 1 hour to form a homogeneous solution. Then, drop-coat the above catalyst solution to 1x3cm 2 On the carbon paper of the same size, it was dried at room temperature overnight to obtain a working electrode, which was used for later use.
[0079] S2. Use an H-type electrolytic cell as the reactor, and divide the reactor into a cathode compartment and an anode compartment with a proton exchange membrane. The volume of the electrolyte sewage is 80 mL, and the catholyte contains 0.1M Na 2 SO 4 Electrolyte solution and 20mg / L florfenicol solution, anolyte containing only 0.1M Na 2 SO 4 a. And magnetically stir the cathode chamber at a constant rate.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com