System and method for utilizing, disposing and discharging salt-containing waste
A technology for waste and salty wastewater, applied in chemical instruments and methods, seawater treatment, natural water treatment, etc., can solve the problems of increased seawater salinity in offshore sea areas, unfavorable development of offshore aquaculture industry, and high production, utilization and disposal costs. Good environmental and economic benefits, lower disposal costs, and lower treatment costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Take waste salt from a chemical company, and detect its composition as sodium chloride 0.5-6.42%, potassium chloride 8.36%, sodium bicarbonate 7.52%, sodium carbonate 1.08%, sodium benzoate 3.84%, 2-aminopyridine 1.46%, other organic matter 2.13%, water 27.16% and traces of other impurities. In view of the high sodium chloride content of the waste salt and the presence of harmful impurities such as organic matter and carbonate, high temperature melting, water dissolution and filtration can be used to remove insoluble matter, the filtrate can be adjusted to pH 7-8 with hydrochloric acid, and inorganic salts can be added to adjust the components.
[0049] Take 100 grams of the above-mentioned waste salt and put it into a molten salt furnace, slowly heat up to 600°C, after drying and preheating, heat up to 1300°C to melt to remove organic matter and some insoluble residues, cool down, add water to dissolve, and filter to remove insoluble matter . The solution was adjusted...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Take 1000 grams of metallurgical saline wastewater, which contains 0.12% sodium chloride, 16.24% sodium sulfate, 64ppm copper, 8138ppm zinc, 62ppm chromium and a small amount of other impurities. In view of the characteristics of heavy metal harmful impurities in the saline wastewater, heavy metals can be removed by adding chemicals after adjusting the pH value.
[0060] The pH of the aqueous solution is adjusted to 8.0 under stirring, a heavy metal scavenger is added thereto, and then a polyacrylamide solution is added, and after standing still, impurities such as precipitates are filtered to obtain an impurity-removing salt solution. The solution was concentrated to dryness to obtain the inorganic salt. After testing, the inorganic salt contains 32.45% sodium, 0.56% chlorine, 66.95% sulfate, 2ppm copper, 14ppm zinc, 3ppm chromium, fluorine (ND), lead (ND), barium (ND), arsenic (ND), and a small amount of others Impurities, the above are mass percentages (calculated a...
Embodiment 3
[0064] The by-product salt washed with fly ash contains 29.94% of sodium, 9.52% of potassium, 2.02% of calcium, 58.44% of chlorine, 2ppm of copper, 9ppm of zinc, 3ppm of nickel, 2ppm of lead and a small amount of other impurities in the mixed salt. Percentage (calculated on solid matter).
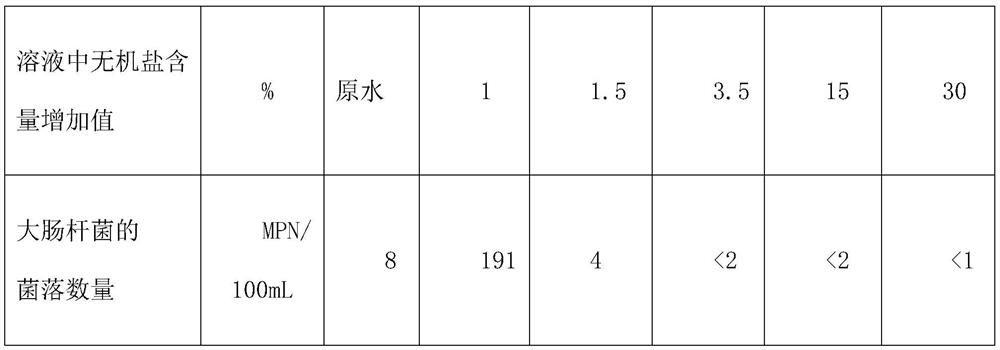
[0065] The fly ash was washed with chloride and fresh water to prepare different proportions of saline solution. After standing for 0.5-6 hours, the number of E. coli colonies in the water solution was detected. The experimental detection data are shown in the table below.
[0066]
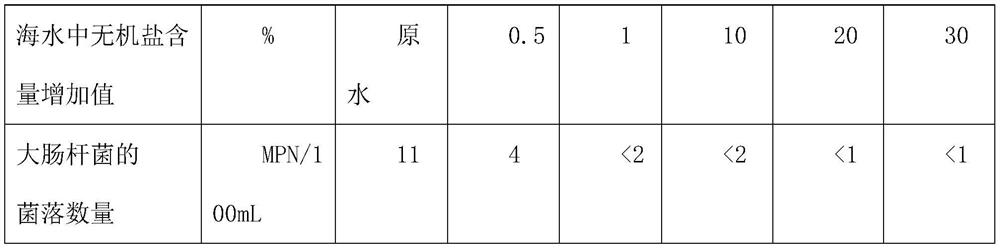
[0067] The fly ash was washed with chloride and seawater to prepare different proportions of saline solution. After standing for 0.5-6 hours, the number of E. coli colonies in the water solution was detected. The experimental detection data are shown in the table below.
[0068]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com