Nymphaea hybrida polysaccharide extract as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology for extracting perfume lotus and polysaccharides, which can be used in applications, polysaccharide/gum-containing food ingredients, pharmaceutical formulations, etc. It can solve the problems of unsatisfactory properties, polysaccharide structure breakage, denaturation, etc., and achieve pure white color, convenient operation, and stable properties Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Embodiment 1, the preparation of perfume lotus flower polysaccharide extract
[0021] Get freeze-dried perfume lotus 100g, pulverize through a grinder, and the pulverized powder is filtered through a 20-order iron sieve to obtain perfume lotus micropowder. Add 10 times the volume (1L) of water to the perfumed lotus micropowder, and extract in a water bath with mechanical stirring (400 rpm) for 4-5 hours at room temperature. The extract was initially filtered through gauze, and the filtrate was collected. The dregs were extracted twice in the same way, and the filtrates were combined three times. The filtrate was concentrated to 1 / 10 (100mL) of the original volume through a rotary evaporator again, and a volume fraction 95% ethanol solution (130mL) was added to the concentrated solution, and stirred to precipitate, when the added ethanol concentration reached 60% ( volume content), a large number of flocculent precipitates appeared. After the precipitate was filtered ...
Embodiment 2
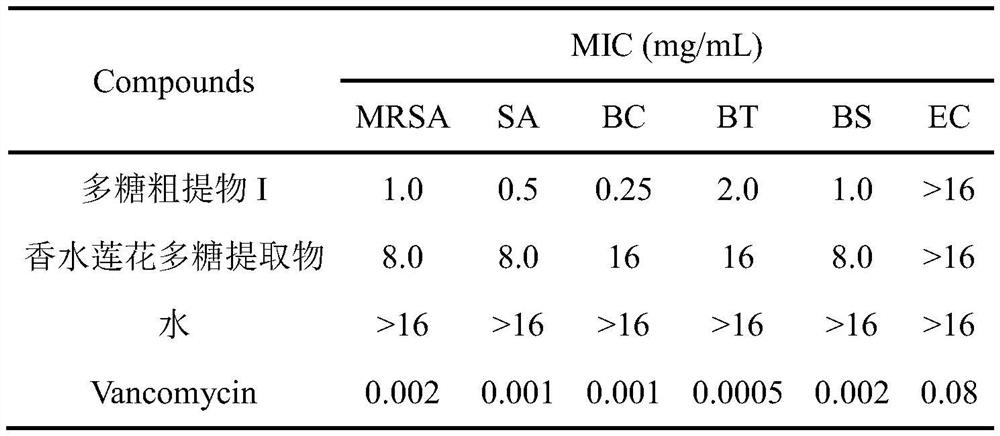
[0025] Embodiment 2: the antibacterial activity evaluation of compound
[0026] In this embodiment, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the antibacterial activity of the sample will be determined by the resazurin chromogenic method. The experimental strains were Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), Staphylococcus aureus (SA, Staphylococcus aureus), Bacillus cereus (BC, Bacillus cereus), B.subtilis (BS, Gram-positive or negative bacteria such as Bacillus subtilis), B.thuringiensis (BT, Bacillus thuringiensis) or Escherichiacoli (EC, Escherichia coli).
[0027] In the test, the 96-well plate dilution titer technique will be used to simultaneously determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of various substances. Firstly mix 7.5mL indicator solution (100μg / mL resazurin aqueous solution) with 5mL test bacteria solution (10 8 CFU / mL) Mix well, and add 100 μL of the mixed bacterial solution to all the t...
Embodiment 3
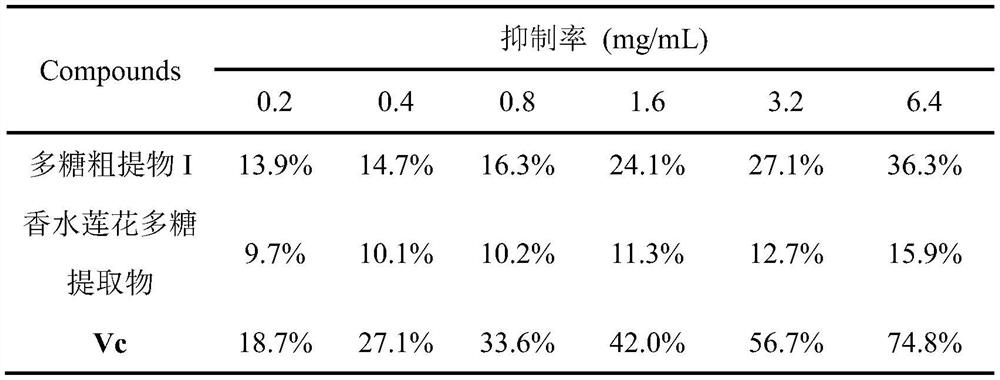
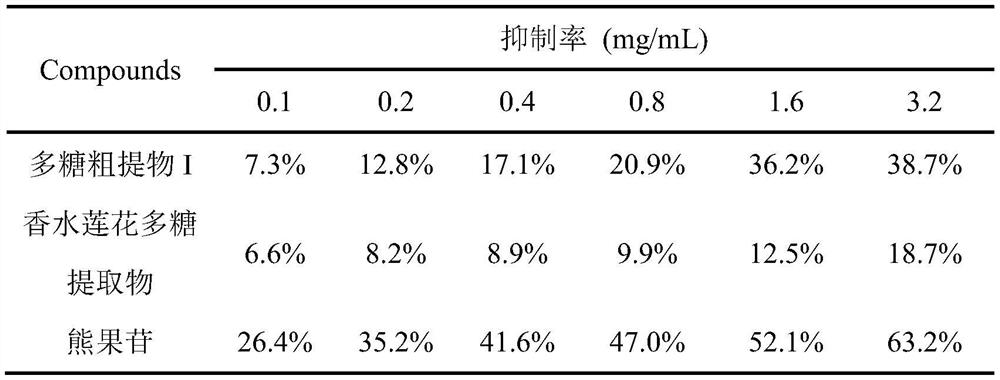
[0031] Example 3: Determination of Inhibiting Lipid Peroxidation Activity
[0032] Weigh 0.50 mL lecithin solution and add it into 1.0 mL PBS buffer solution with pH=7.0. 1.0mL of sample solutions containing different concentrations were uniformly mixed with 1.0mL of an aqueous solution containing 2.5mmol / L EDTA-Fe(II), and then added to the aforementioned PBS mixed solution of lecithin. After mixing, place it in a water bath at 37°C for 45 minutes. Then, 2.0 mL of 28% (w / v) trichloroacetic acid and 1.0 mL of 1% (w / v) thiobarbituric acid were added successively. After mixing, the mixed solution was heated in a boiling water bath at 100°C for 10 min, and the absorbance was measured at 532 nm after cooling. Use PBS buffer to adjust to zero, and replace the sample with PBS buffer to measure the absorbance A0 of the blank tube. Make 3 parallel samples for each sample, and take the average value A1. Calculate the lipid peroxidation inhibition rate according to the following for...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com