Method for selectively and efficiently extracting flavones from licorice herb residues and co-producing biomethane
A technology for licorice dregs and licorice herbs is applied in the preparation of sugar derivatives, sugar derivatives, sugar derivatives, etc., and achieves the effects of increasing startup speed and gas production, simplifying separation and purification steps, and improving conversion efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
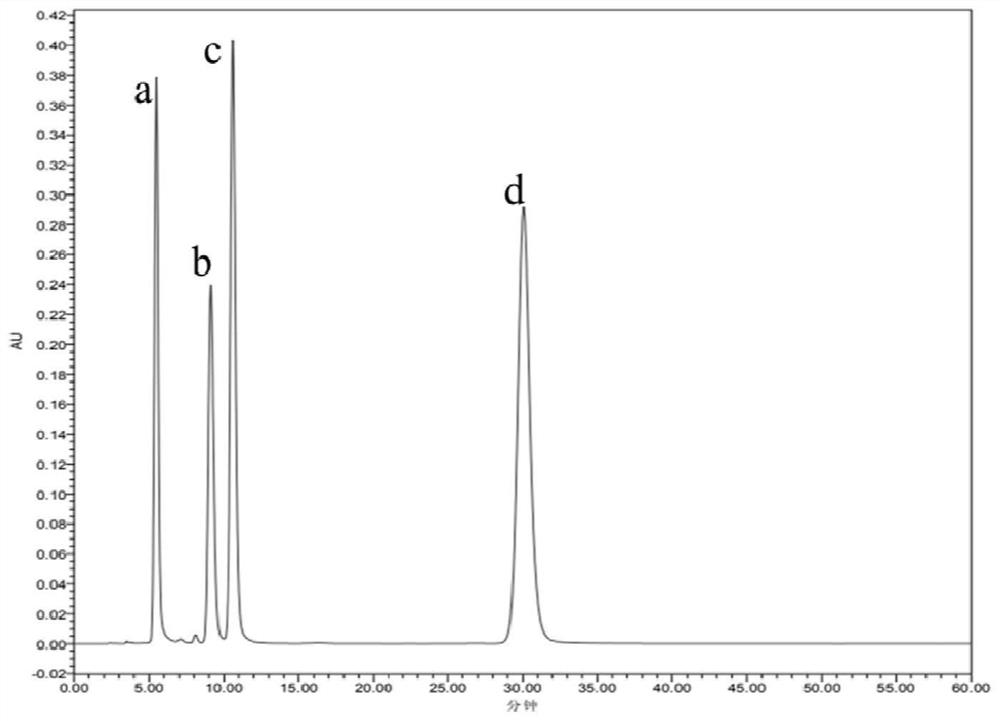
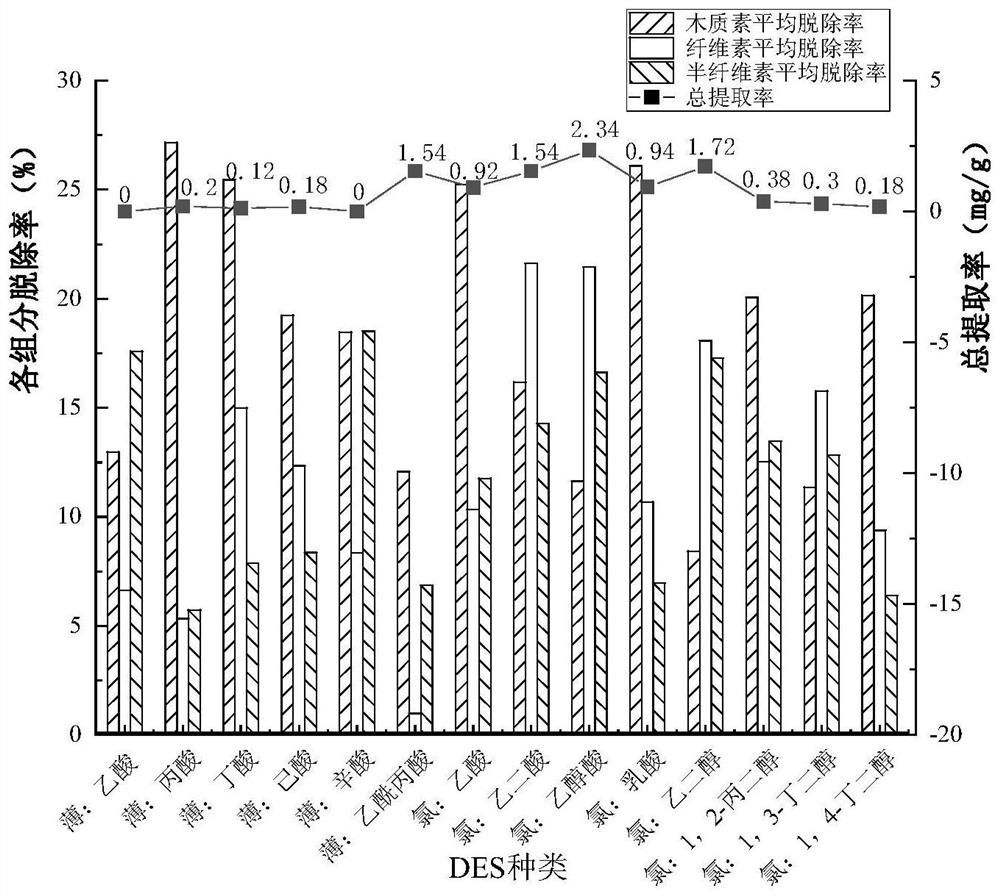
[0032] Configure the deep eutectic solvent according to the hydrogen bond acceptor and hydrogen bond donor and their molar ratio shown in Table 1 (according to Abbott et al.Chemical communications 2003, 9:70-1 method), then the solid-liquid ratio is 1:20 Add licorice residue (g / mL) (glycyrrhizae residue plus 5 times of water, boil for half an hour to obtain the residue), the extraction condition is 50°C-30min, the mixed system after extraction is separated from solid and liquid, and the extraction of total flavonoids is calculated rate and removal rate of lignin-cellulose-hemicellulose.
[0033] Table 1 Composition of different deep eutectic solvents
[0034] Numbering hydrogen bond acceptor hydrogen bond donor The molar ratio of 1 L-menthol (thin) Acetic acid 1:1 2 L-menthol (thin) propionic acid 1:1 3 L-menthol (thin) butyric acid 1:1 4 L-menthol (thin) caproic acid 1:1 5 L-menthol (thin) bitter 1:1 6 L-menth...
Embodiment 2
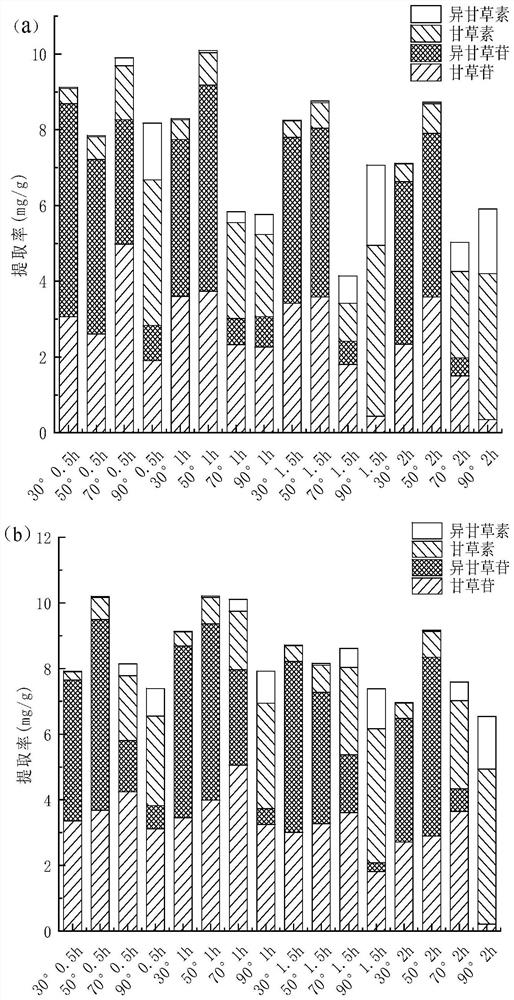
[0037] Choline chloride and glycolic acid were prepared in a molar ratio of 1:3 to obtain a deep eutectic solvent (according to Abbott et al. %, 30%, to obtain two deep eutectic solvent systems with different water contents, then add licorice dregs to the two systems according to the solid-liquid ratio of 1:15 (g / mL) The medicinal residues obtained in half an hour), the extraction conditions are 30min, 50min, 70min, 90°C for 30min, 60min, 90min, 120min, the mixed system after extraction is filtered for solid-liquid separation, and the sum of liquiritin, isoliquiritin and liquiritinin in the liquid is calculated The extraction rate of isoliquiritigenin.
[0038] The result is as image 3 As shown, the deep eutectic solvent can extract liquiritin and isoliquiritin with high selectivity at low temperature (30-50° C.), and extract liquiritin and isoliquiritigenin with high selectivity at high temperature (70-90° C.). And under the condition of low temperature (30~50℃), the short...
Embodiment 3
[0040]Choline chloride and glycolic acid are prepared in a molar ratio of 1:3 to prepare a deep eutectic solvent (according to Abbott et al. Chemical communications 2003, 9:70-1 method), and water is added to make the deep eutectic solvent have a moisture content of 20% , and then according to the solid-liquid ratio of 1:15 (g / mL), add licorice dregs (glycyrrhizae plus 5 times of water, boil for half an hour to obtain dregs), the extraction condition is 30 ° C for 30 min, and the mixed system after extraction is filtered solid-liquid separate.
[0041] It is measured that the liquid is rich in liquiritin and isoliquiritin, the extraction rate is 8.7mg / g licorice residue, the purity is 95.4%, and the solid phase residue is directly connected to the anaerobic according to the method reported in the literature (Bioresour. Ferment the strains and ferment for 30 days to obtain biomethane. Its biomethane production is increased by about 120% relative to the untreated feedstock.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com