Human-derived biological tissue material and culture cell stimulation method and device
A technology for biological tissue and cell culture, applied in tissue cell/virus culture devices, biochemical equipment and methods, methods for supporting/immobilizing microorganisms, etc. Problems such as poor material compliance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
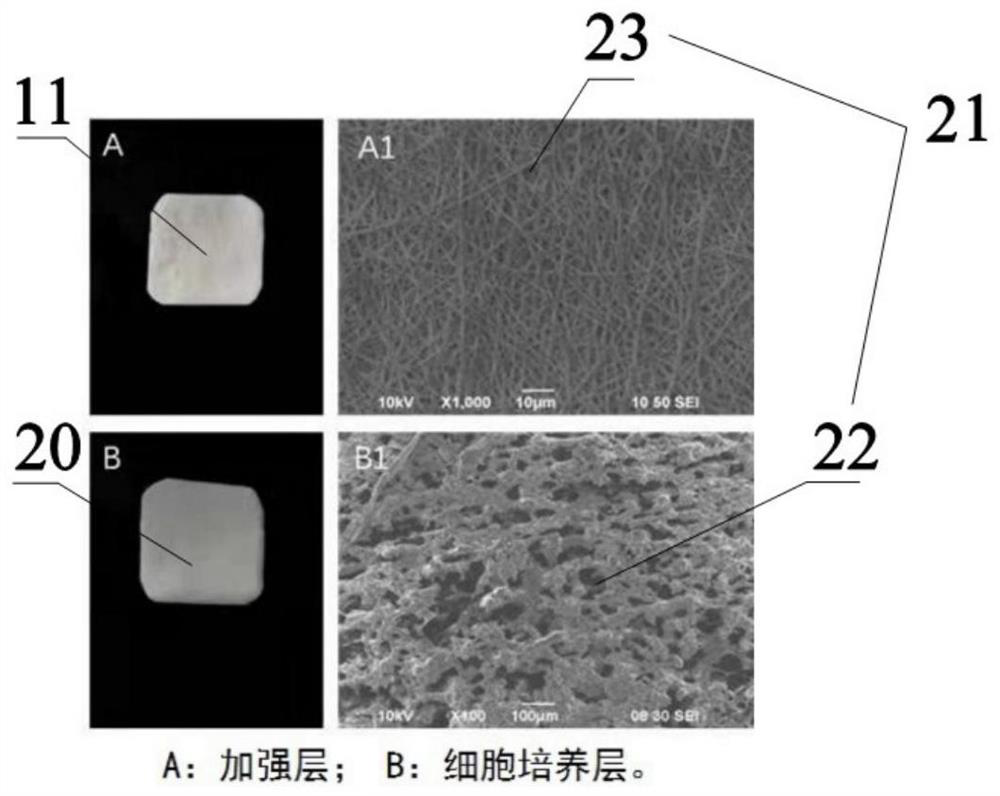
[0060] A method and device for dynamically cultivating a biocomposite esophagus of a polymer material under stimulation of mechanical properties. The materials of the dense polymer nanofiber layer (i.e. a reinforcement layer 11) and the porous support (i.e. a cell culture layer 20) include polyurethane, polytetrafluoroethylene, expanded polytetrafluoroethylene, silk protein (fibroin ), silk fibroin, polycaprolactone (PCL), polylactic acid (PLA), polyethylene terephthalate, polyglycolic acid (PGA), polylactic-polyglycolic acid (PLGA) , carboxymethyl starch, starch acetate, chitosan (Chitosan), carboxymethyl chitosan, alginic acid / alginate, carboxymethyl cellulose, gelatin, collagen (Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ), transparent At least one of hyaluronic acid (HA), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), polyacrylamide (PAM), polyacrylic acid, and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP).
[0061] Preferably: the thickness of the dense polymer nanofiber layer is 5-200 μm, the diameter of the pores is 1-20 μm, and the fiber di...
Embodiment 2
[0067] A method and equipment for dynamically cultivating an extracellular matrix polymer biocomposite patch under mechanical stimulation.
[0068] The appearance of the extracellular matrix polymer biocomposite patch prepared in this example is as follows: figure 1 Shown, its preparation method is specifically as follows:
[0069] (1) Dissolving PCL and gelatin in hexafluoroisopropanol to obtain an electrospinning stock solution, the specific parameters of which are shown in Table 1 below:
[0070] Table 1 Electrospinning solution preparation parameters
[0071]
[0072] (2) Electrospinning the above-mentioned electrospinning stock solution to obtain such figure 2 The dense polymer nanofiber layer shown; the specific parameters of electrospinning are shown in Table 2 below:
[0073] Table 2 Electrospinning parameter control
[0074]
[0075] (3) Evenly smear the prepared foaming solution on the upper surface of the dense polymer nanofiber layer prepared in step (2...
Embodiment 3
[0085] A method and device for dynamically cultivating biocomposite blood vessels of polymer materials under stimulation of mechanical properties.
[0086] (1) Dissolving PCL and gelatin in hexafluoroisopropanol to obtain an electrospinning stock solution, the specific parameters of which are shown in Table 1 below:
[0087] Table 1 Electrospinning solution preparation parameters
[0088]
[0089]
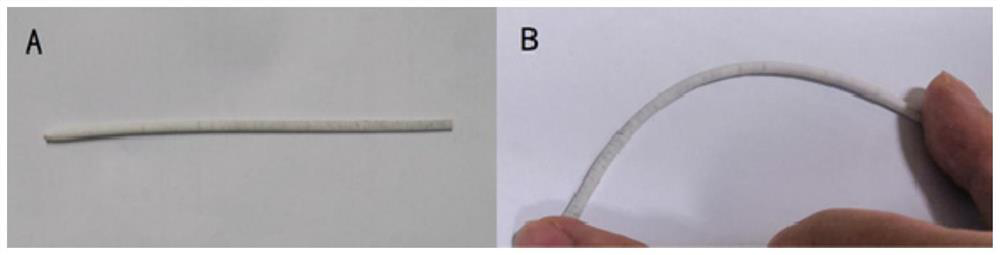
[0090] (2) Electrospinning the above-mentioned electrospinning stock solution to obtain a dense polymer nanofiber layer, such as Figure 4 , where A is the unbent state, B is the bent state, it can be seen that the tubular structure is still maintained in the bent state,
[0091] The specific parameters of electrospinning are shown in Table 3 below:
[0092] Table 3 Electrospinning parameter control
[0093]
[0094] (3) Evenly smear prepared foaming liquid (polyurethane, polytetrafluoroethylene, expanded polytetrafluoroethylene, silk protein ( fibroin ), silk fibroin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com