Urine preservation solution, preservation method and urine preservation tube
A technology for preserving liquid and urine, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, preservation of human or animal bodies, and containers for laboratory use, etc. problems, to achieve high sensitivity, avoid the interference of cellular genomic DNA, and avoid the effect of microbial interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
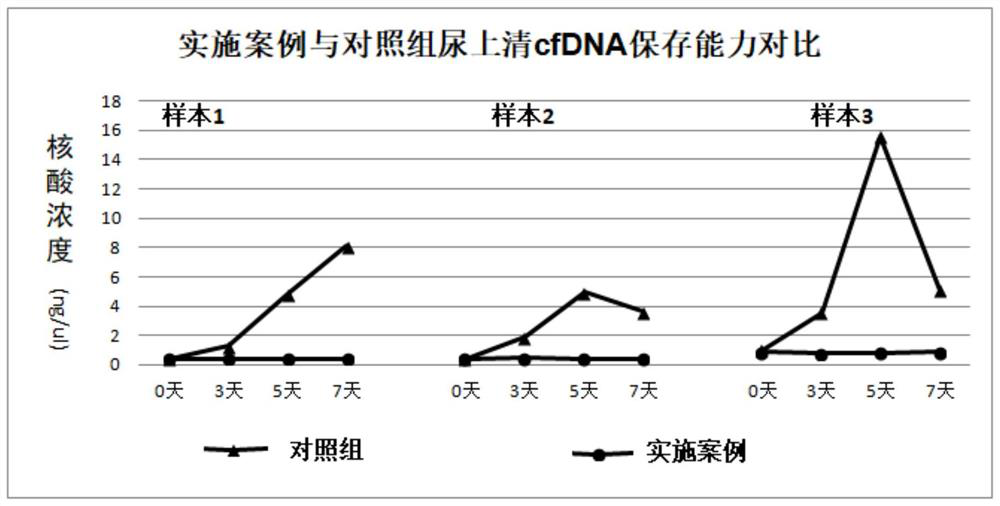
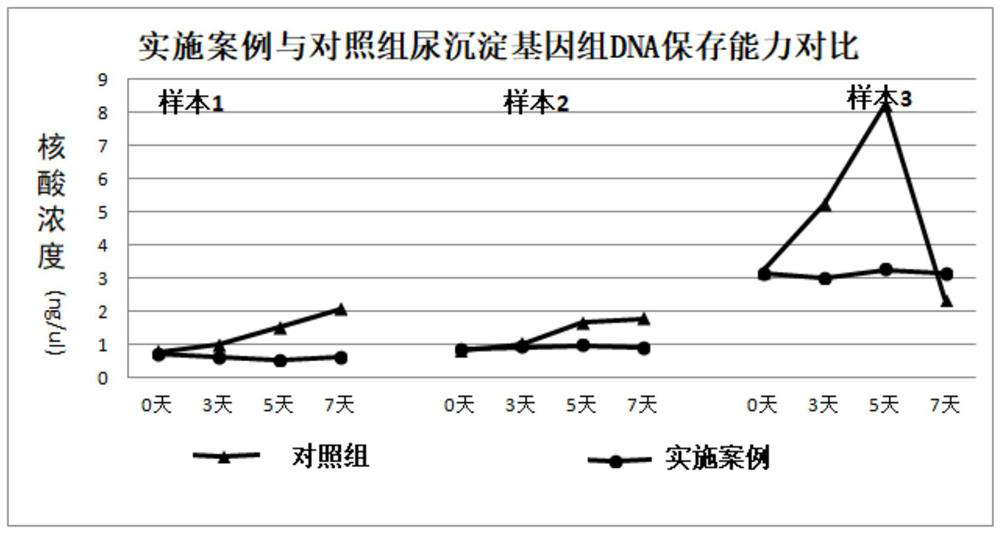
[0096] Example 1. DNA Preservation Capacity
[0097] The preparation method of the urine preservation solution of the present embodiment: use ultrapure water to prepare 0.1wt% diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC) in a fume hood, use this DEPC solution as a solvent to prepare solution 1, and solution 1 contains the following mass percent ( wt%) final concentrations of reagents: 0.5% Tween 20, 6% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), 5% glycine, 1.5% paraformaldehyde and 1.5% diazonium alkyl urea with hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH of the solution to 8. The concentration of DEPC in solution 1 was estimated to be about 0.09 wt%. Use ultrapure water to prepare solutions 2, 3, and 4. Solutions 2, 3, and 4 respectively contain the final concentration reagents in mass percent: 44% Tris-HCl, 37% citric acid, and 67% trisodium citrate to prepare solutions In 2, 3, and 4, the pH of the solution was adjusted to 8 with hydrochloric acid and / or sodium hydroxide, respec...
Embodiment 2
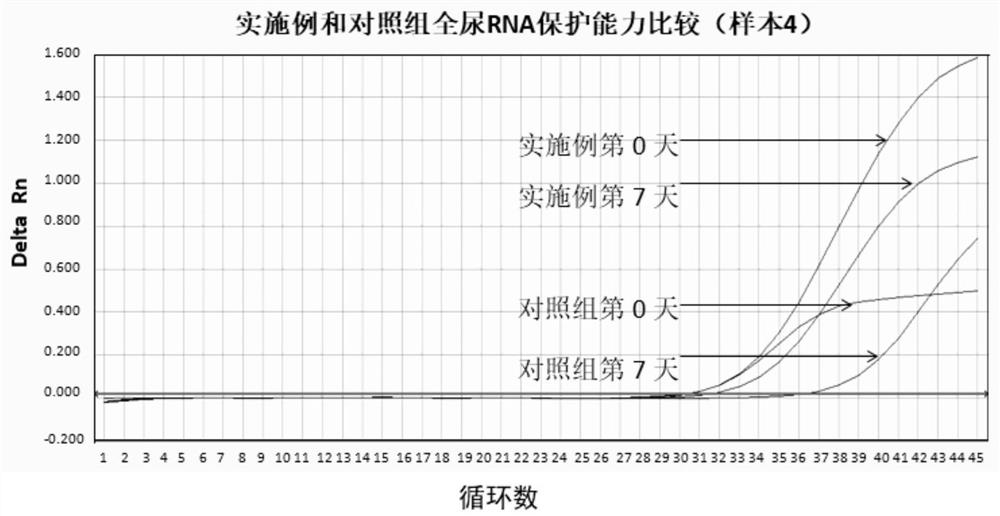
[0103] Example 2. RNA preservation ability
[0104] In this case, the morning urine of a patient with hematuria (sample 4) was used. After mixing, each sample was divided into 8 parts, and each 10 mL part was placed in a nuclease-free centrifuge tube. The implementation group randomly selected 4 tubes according to the urine and the implementation case. 1 The prepared preservation solution was mixed at a ratio of 19:1 (this operation was completed within 0.5 hours of urine separation), the control group left the remaining 4 tubes of urine untreated, the implementation group (implementation case) and the control group (control The difference is that no urine preservation solution was added to the control group, and the two groups of specimens were stored at room temperature. One tube was taken from each of the two groups at the following 4 time points for whole urine and urine sediment cell RNA extraction and RNA QPCR (real-time quantitative PCR) detection. Store at room temper...
Embodiment 3
[0108] Example 3. Ability to preserve DNA and RNA simultaneously
[0109] In this case, morning urine of patients with hematuria (sample 5 and sample 6) was used. After mixing, each sample was divided into 8 parts, and each 10 mL part was put into sterile centrifuge tubes. The preservative solution prepared in Example 1 was mixed at a ratio of 19:1 (this operation was completed within 1 hour of urine ex vivo), and the remaining 4 tubes of urine in the comparison group were stored in a urine storage tube A (contrast reagent, commodity number: CW2657) and the preservation solution of urine preservation tube A (this operation is completed within 1 hour of urine in vitro). The difference between the implementation group (the example group) and the control group is that the preservation solution is different. save. At the following 4 time points, 1 tube was taken from each of the two groups for free nucleic acid extraction from the urine supernatant. The urine was stored within 2 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com