Process for polymerization preparation of macromolecular emulsion without heating
A technology of polymer emulsion and emulsion polymerization, which is applied in the field of preparation of polymer emulsion polymerization, can solve the problems of complex polymerization process, decrease of polymer molecular weight, and high equipment investment, so as to reduce process operation, improve polymerization efficiency, and ensure stable quality Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
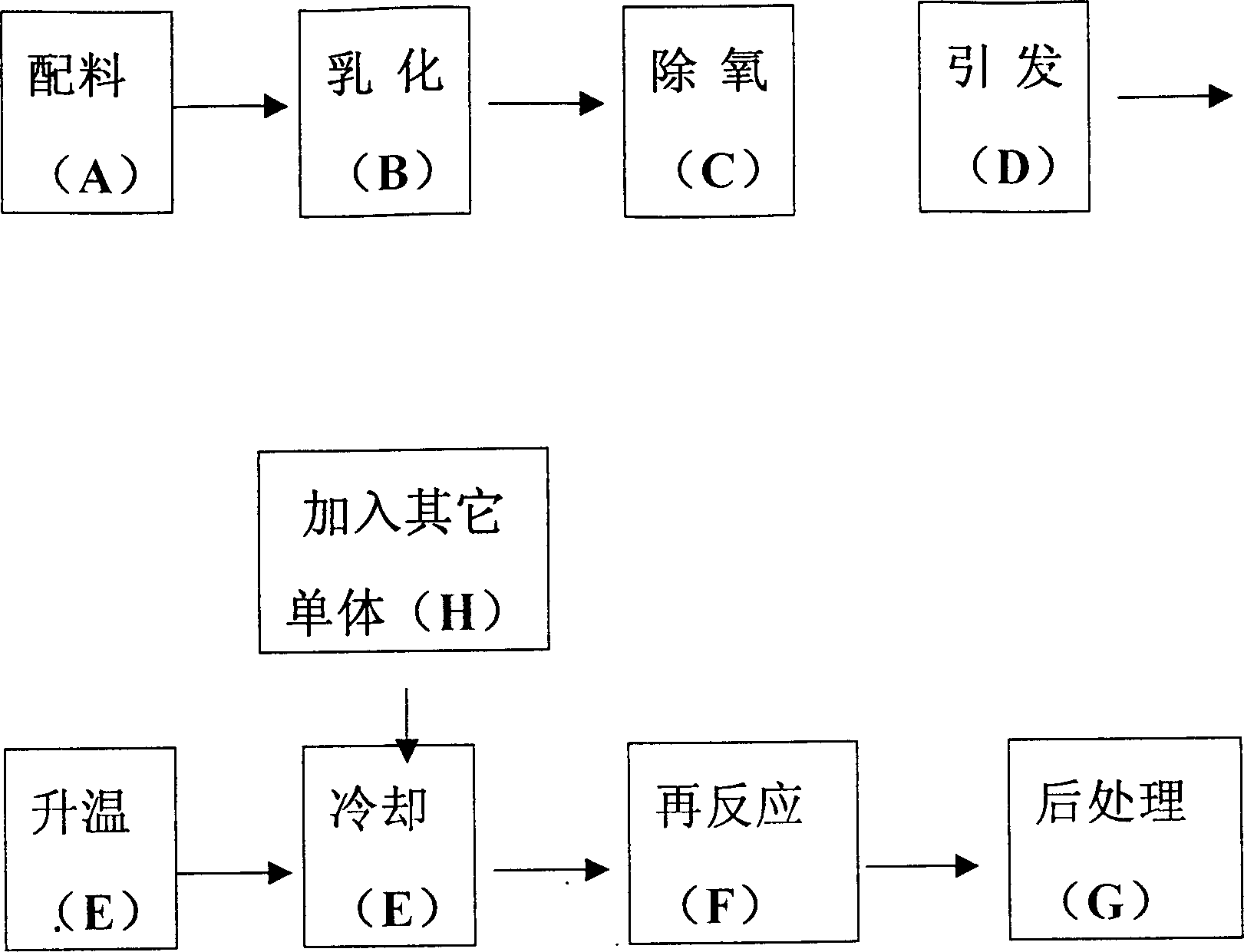
[0020] see attached figure 1 , raw material selection: methyl acrylate (MA), butyl acrylate (BA), acrylonitrile (AN), acrylic acid (AA), N,N-methylenebisacrylamide (NNMBAN), diisooctyl succinate sulfonate Sodium (AOT), Potassium Persulfate (PPS), Ascorbic Acid (LAAS), Ammonia (AW).
[0021] Process: Mix 17 parts MA, 5.5 parts BA, 5.5 parts AN, 0.9 parts AA, 0.00035 parts NNMBAN, 1.5 parts AOT, 0.25 parts AW and water. Emulsify at high speed for 15 minutes. Start stirring, and deoxygenate with nitrogen for 5 minutes. 0.13 parts of PPS were added, and at room temperature of 15°C, 0.04 parts of LAAS were added. After nine minutes, the temperature of the emulsion system reached 69°C, and cooling water was started. When the temperature reached 78°C, the temperature was stopped and the cooling was stopped. After fifteen minutes, the temperature of the emulsion system was 74°C, and the cooling was continued until the temperature of the emulsion system was 65°C. A solution of 0.04...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Raw material selection: methyl acrylate (MA), butyl acrylate (BA), 2-ethylhexyl acrylate (IOA), acrylic acid (AA), nonylphenol polyoxyethylene ammonium sulfate (PAS), N,N-sulfite Methylbisacrylamide (NNMBAN), hydrogen peroxide (POH), ascorbic acid (LAAS), ammonia water (AW).
[0025] Process: Mix 33.5 parts BA, 22.5 parts IOA, 2.5 parts AA, 2.2 parts PAS, 0.5 parts AW, 0.0018 parts NNMBAN and water. Emulsify at high speed for 25 minutes. Start stirring, and deoxygenate with nitrogen for 4 minutes. 0.085 part of POH was added, and at room temperature 25°C, 0.04 part of LAAS was added. Ten minutes later, the temperature of the emulsion system reached 65°C, and cooling water was started. When the temperature reached 78°C, the temperature stopped rising, and cooling was stopped. 0.004 part of MA was added, and 0.025 part of LAAS 10% solution was added in about 70 minutes. The reaction was completed for another 10 minutes, 0.27 part of AW was added, the temperature of the...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Raw material selection: methyl acrylate (MA), ethyl acrylate (EA), methacrylic acid (MAA), N-hydroxymethylene acrylamide (NHMAM), nonylphenol polyoxyethylene ammonium sulfate (PAS), peroxide Hydrogen (POH), Erythorbic Acid (DAAS), Ammonia (AW).
[0029] Process: Mix 16 parts EA, 11 parts MAA, 0.065 parts NHMAM, 1.4 parts PAS, 0.18 parts AW and water. Emulsify at high speed for 18 minutes. Start stirring and deoxygenate with nitrogen for 3 minutes. 0.092 parts of POH were added, and at room temperature 10°C 0.043 parts of DAAS were added. After four minutes, the temperature of the emulsion system reached 55 °C, and the cooling water was started. After the maximum temperature reached 82 °C, the cooling was stopped for ten minutes. After fifteen minutes, the temperature of the emulsion system was 70 °C, and the temperature of the emulsion system was 65 °C. parts MA, 0.042 parts of LAAS 10% solution was added over an hour or so. The reaction was completed for another 15...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com