Methods and compositions relating to a cardiac-specific nuclear regulatory factor
a nuclear regulatory factor and cardiac-specific technology, applied in the field of development biology and molecular biology, can solve the problems of regional contractile dysfunction, impracticality in clinical setting, loss of cardiomyocytes,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Expression Pattern of Myocardin 1 During Early Heart Development
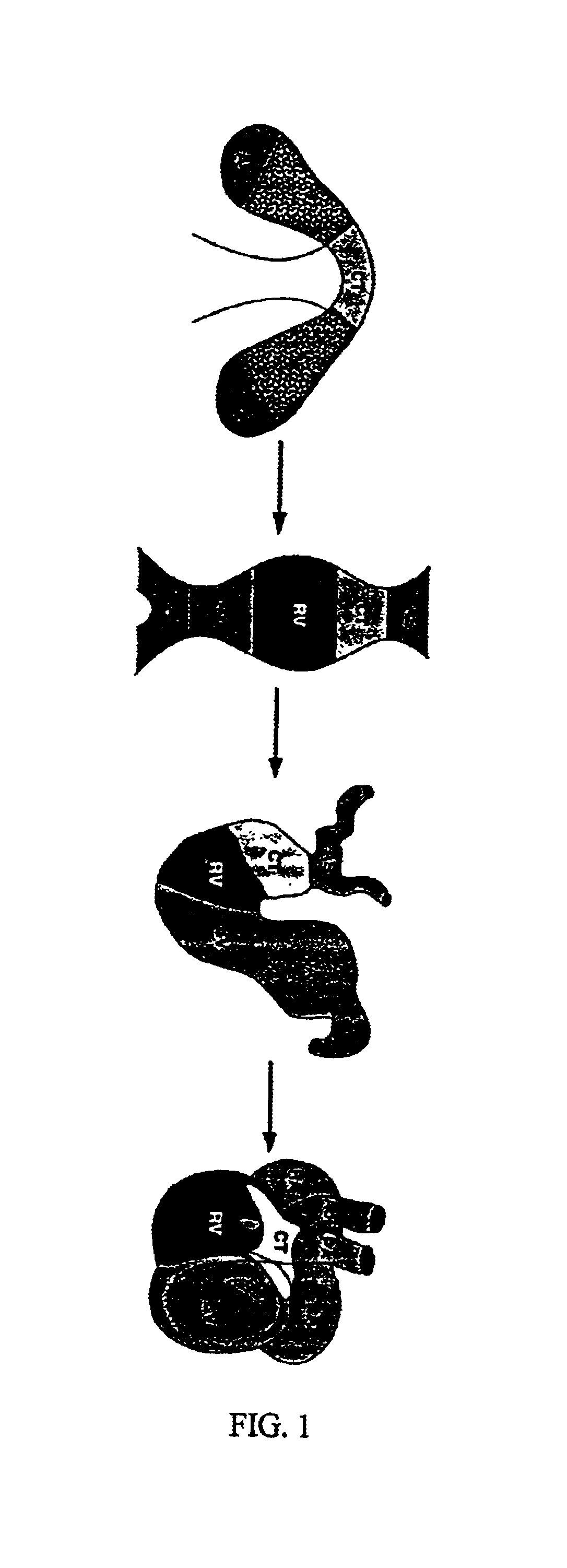
[0270]The heart is the first organ to form during mammalian development. Cardiac muscle cells originate from a region of the embryo known as the cardiac crescent and develop into a primitive heart tube along the midline of the embryo (FIG. 1). Because this is the only region of the embryo that can give rise to cardiac muscle cells, it would be expected to express a unique set of genes responsible for cardiogenesis. By identifying the genes that are uniquely expressed in this region, master control genes for heart formation can be identified. Subsequent embryonic events of looping, chamber maturation and alignment with the vascular system give rise to the mature four-chambered heart (Olson et al., 1996 and Fishman et al., 1997).
[0271]Expression of myocardin 1 was determined by whole-mount (FIG. 3A) or section (FIG. 3B and FIG. 3C) in situ hybridizations to mouse embryos at E7.75 (FIG. 3A), E8.0 (FIG. 3B), and E12.5 (FIG....
example 2
Expression Pattern of Myocardin 1 in Adult Mouse Tissues
[0275]The expression of myocardin 1 transcripts in adult mouse tissues was analyzed by Northern blot, utilizing techniques well known in the art. RNA was isolated from adult mouse heart, brain, spleen, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney and testis according to standard RNA isolation procedures, e.g., phenol / chloroform / isoamyl alcohol (RNAzol, Life Technologies, Inc.) or guanidine thiocyanate.
[0276]Briefly, fractionated RNA was transferred from an agarose gel to a membrane by upward capillary action. The transferred RNA is cross-linked to the membrane. Next, a radiolabeled probe (DNA or RNA) was hybridized to the membrane in a formamide solution. After hybridization, autoradiography was performed to detect the transcripts.
[0277]The results in FIG. 4 show that the transcripts were detected only in the heart. A RNA molecular marker illustrates the size of the transcripts.
example 3
Nuclear Localization of Myocardin 1 Protein
[0278]Cos cells were transiently transfected with an expression vector encoding myocardin 1 with a Flag-epitope tag. Transient transfection assays were performed using standard methods, such as LifofectAMINE plus (Life Technologies, Inc.), calcium phosphate or electroporation. Briefly, the cells were plated 12 hr before transfection in tissue culture dishes. They were transfected with a total of about 0.5-1.0 μg of plasmid DNA. The subcellular location of myocardin 1 protein was determined by immunostaining with anti-Flag antibody.
[0279]All myocardin 1 protein is localized to the nucleus as illustrated in FIG. 5. The inset in the lower right comer shows an enlargement of a single cell, with strong myocardin 1 staining in the nucleus, but excluded from the nucleoli.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com