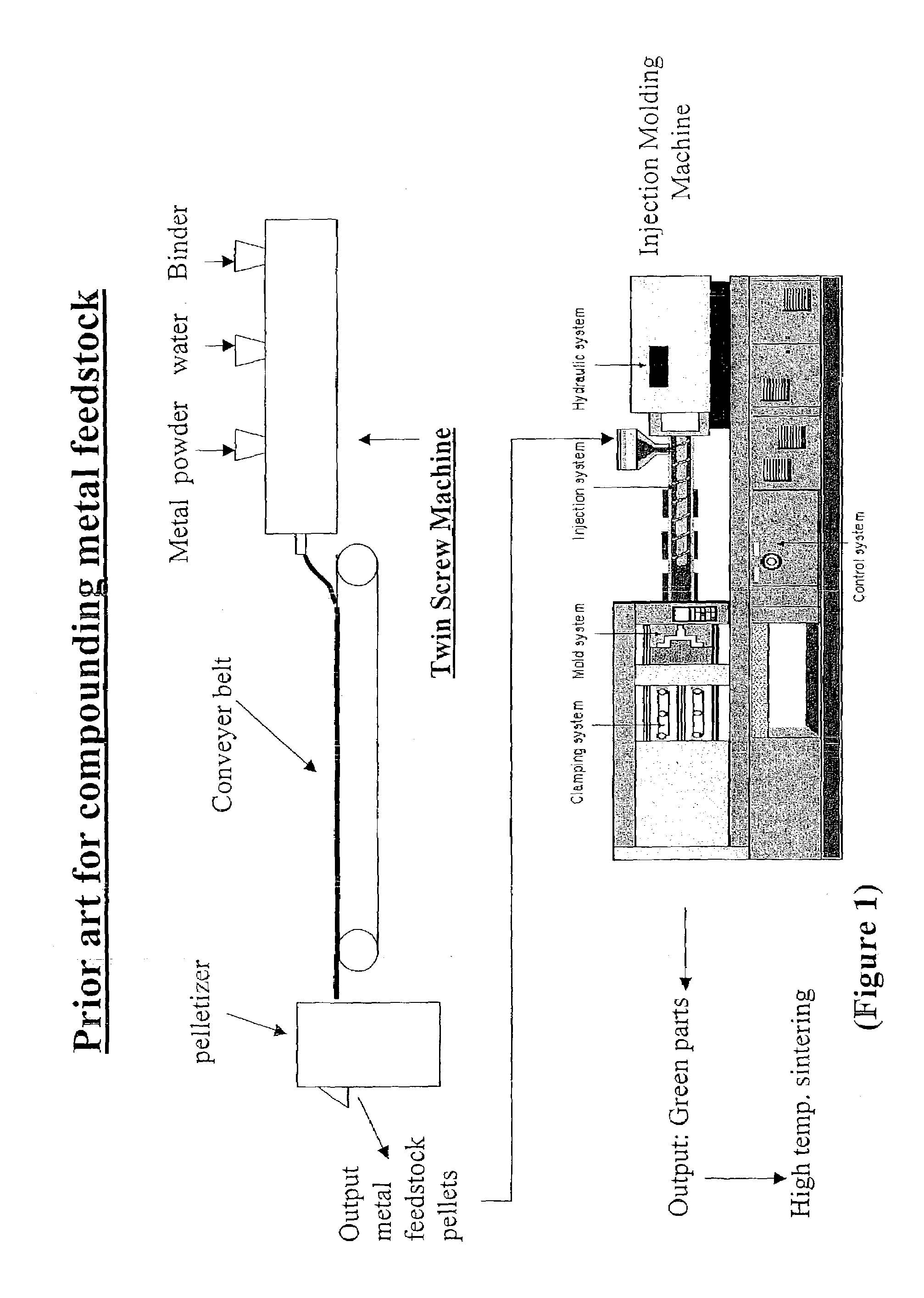
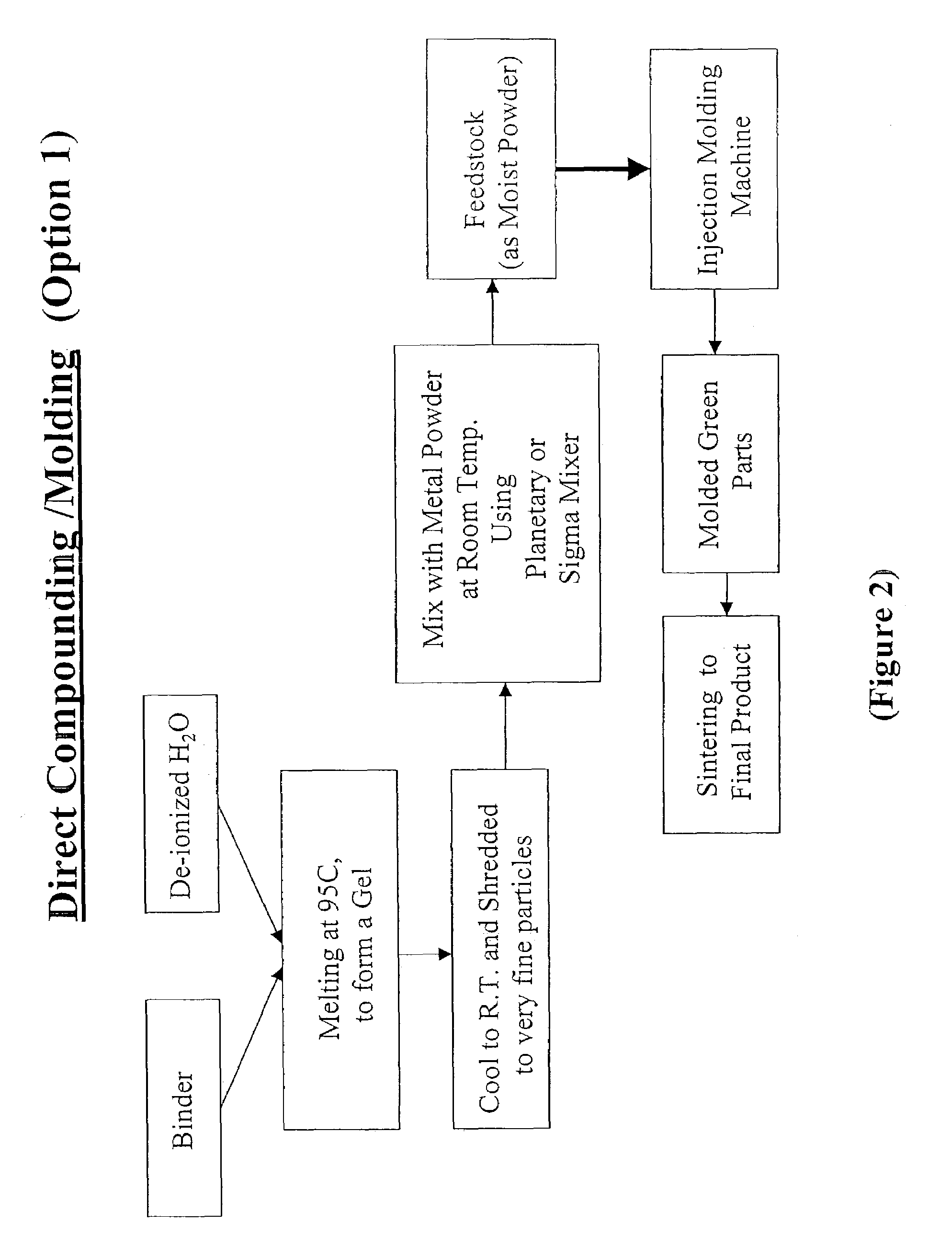
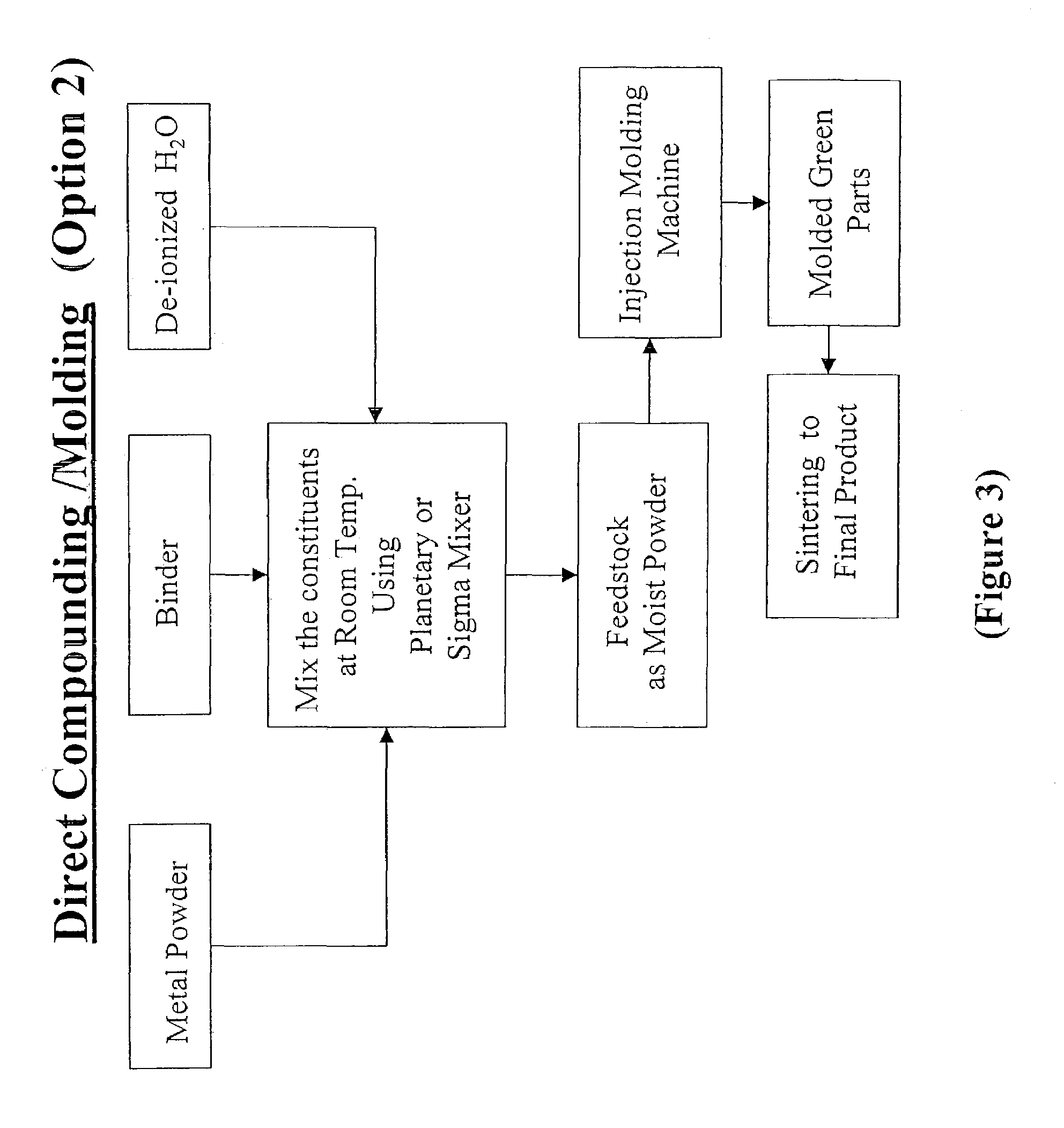
Aqueous binder formulation for metal and ceramic feedstock for injection molding and aqueous coating composition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0041]A batch of feedstock was prepared using 10 kg of 17–4 PH stainless steel powder having an average particle size of 15 micron. A total of 180 g binder with a ratio of 2.2 of colloid 710H to glucose was mixed with 1132 g of in-situ water containing 2 g of sodium tetraborate to adjust the pH of the water to about 9.4 and 1.5 g potassium chloride. Also, a mixture of 0.12 g potassium sorbate and 0.12 g sodium benzoate were added as biocides to inhibit the growth of molds and bacteria. The 180 g binder and biocides were pre-mixed with the in-situ water. This mixture was transferred into a sigma blender and mixed for 10 minutes at room temperature. Then the temperature was raised to 93–98° C. (200–208° F.). The mixing was continued for 15–25 minutes and allowed the binder to melt. The metal powder was added to the mixer in two steps. Initially 4.5 kg of the metal powder was added into the mixer and blended with the binder for 15 minutes, and then the remaining of the metal powder (2....
example 2
[0043]Portion of the feedstock material from example 1 was molded to make 140 parts using two cavity steel mold. The parts molded at 800 psi (5.6×103 KN / m2) injection pressure and 300 psi (2.1×103 KN / m2) pack pressure. The barrel temperature was 90° C. (194° F.) and mold temperature was 24° C. (75.2° F.). Initially, the cooling time (the time parts stay in the mold after injection cycle) was set to 15 seconds. The cooling time gradually reduced after every 25 shots. The lowest cooling time that the part could be ejected and remove from the mold cavity was about 6 seconds. The yield of this molding trial was >98%. The average part weight was 3.61±0.04 grams. A sintering experiment conducted on 30 of these parts under the following conditions to determine the final density and shrinkage.
[0044]
TemperatureHolding Time (hr.)Atmosphere 25° C.0Nitrogen450° C.3.5Nitrogen switch to hydrogen750° C.1Hydrogen1340° C. 1.0Hydrogen900° C.5 min.Hydrogen switch to nitrogen 25° C.0Nitrogen
The average...
example 3
Composite Feedstock
[0045]This example illustrates the application of the invention for preparation of aqueous stainless steel / titanium carbide feedstock material. Stainless steel 17–4 PH and titanium carbide powders having average particle size of 15 micron and 3.8 micron respectively were used in this example. 100 g of the same Colloid binder composition as example 1 was mixed with 505 g of in-situ H2O, 0.1 g potassium sorbate and 0.1 g sodium benzoate in a sigma blender. The temperature was raised to 93–98° C. (200–208° F.) which melted the binder. A mixture of 4200 grams 17–4 PH powder with 800 grams of titanium carbide powder was added to the melted binder. The mixing continued for about 50 minutes to produce homogeneous materials. The material was cooled to 32–37° C. (90–100° F.) before removing it from the sigma mixer. The material was shredded twice to produce uniform small pieces of feedstock. The moisture content of the feedstock adjusted to 8.3%. Spiral experiment conducte...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com